If you're interested in crypto, you’ve probably heard about Layer 1s and Layer 2s (L2). They're the buzzwords that have been making waves in the world of cryptocurrency. Well, in short, there's more than just Layer 1s like Bitcoin and Ethereum. There's also the world of Layer-2 blockchains and they're the cool new kids on the block.
Now, you might be wondering, "What is a Layer-2 blockchain?" Well, don't worry; it's not as complicated as it sounds. Imagine the main blockchain, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, as the bustling city centre, with everyone conducting their business, making transactions and settling contracts. It's like the heart of the blockchain universe, but here's the catch: it can get a little crowded and slow, just like a city during rush hour.

That's where the Layer-2 comes into play, offering a breath of fresh air in the crypto world. Think of Layer-2 as a sleek, high-speed subway system that runs beneath the bustling streets of the city. It's designed to alleviate congestion, reduce transaction fees in this case, and make everything run smoother and faster.
But how does it work? At its core, Layer-2 technology is all about taking some of the workload off the main blockchain's shoulders. Instead of the main Layer 1 processing every little transaction on the main chain, Layer-2 solutions take up the strain and create a secondary layer where most of the action happens. This layer can handle a vast number of transactions quickly and cheaply, thanks to innovative technologies like sidechains, state channels and rollups.
 Examples of the Vast ETH Layer 2 Ecosystem, Image via Reddit
Examples of the Vast ETH Layer 2 Ecosystem, Image via RedditYou've probably heard about how Layer-2 blockchains are like the turbo boosters of the crypto world. Well, they're not just here to make transactions faster and cheaper; they're also the secret sauce for solving one of blockchain's biggest challenges: scalability.
Imagine the main blockchain as a cosy neighbourhood coffee shop. It's got a certain charm, but as more people flock in for their morning brew, it starts getting packed and service slows down. Transactions on the main blockchain can feel a bit like waiting in a never-ending line for that cup of coffee. That's where Layer-2s come in.
Layer-2 solutions essentially divert most of the transaction traffic away from the congested coffee shop and into a hyper-efficient drive-thru. It's like ordering your coffee and being out the door in seconds, all while the coffee shop isn't overwhelmed. This means that transactions on Layer-2 networks are not only lightning-fast but also cost a fraction of what they would on the main chain.
One of the coolest things about Layer-2s is their ability to scale. It's like adding extra lanes to a highway during peak traffic hours. As more people use Layer-2 solutions, the network can expand to accommodate them without clogging up the main blockchain. This scalability is a game-changer for blockchain's practicality and real-world usability.
 Image via Bitcoinke
Image via BitcoinkeSo, why should you care about Layer-2 blockchains? Well, for starters, they're making cryptocurrencies more accessible and user-friendly. With faster transaction times and lower fees, they're turning blockchain technology from a niche interest into a practical tool for everyday use.
In this guide, we're going to delve deeper into the world of Layer-2 blockchains. We'll explore their benefits, different types and showcase some big L2s that are changing the game. Whether you're a crypto enthusiast or just curious about this evolving technology, join us to uncover the fascinating world of Layer-2 blockchains. It's a ride worth taking in the ever-evolving landscape of digital finance.
How Do Layer-2s Work?
A Layer-2 blockchain is a scaling solution designed to improve the performance and scalability of a base layer blockchain, such as Ethereum, by processing transactions and smart contracts off-chain or in a more efficient manner. Layer-2 solutions aim to address the limitations of the base layer blockchain, which may include slow transaction processing times and high fees, especially during times of network congestion.
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the world of finance by offering a decentralized, secure and transparent system for transferring value. However, the limitations of the first layer (Layer 1) blockchains have become apparent over time. Slow block times, confirmation delays and congestion-induced high transaction costs have hindered the seamless functionality of these networks.
To understand how Layer 2s work, we need to understand the different blockchain layers, how they interact with each other and how they complement each other. If we imagine the blockchain layers as the layers of a pyramid, with each Layer built on top of the next, we can start by looking at Layer 1 as the foundation of the pyramid.
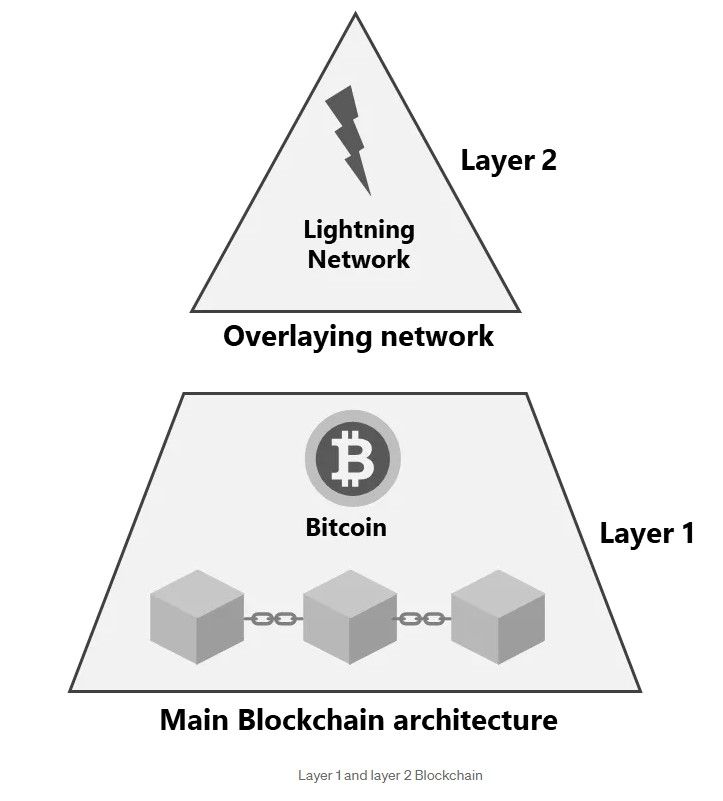 An Explanation of How L1s and L2s Work. Image via Medium
An Explanation of How L1s and L2s Work. Image via MediumThe Foundation: Layer 1
Layer 1 serves as the bedrock of any blockchain network and it forms the fundamental layer upon which all other blockchain innovations are built. Notable examples of Layer 1 blockchains include blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, Avalanche, and plenty more. These pioneering networks operate on the core principles of decentralization and security, which are the cornerstones of blockchain technology.
Decentralization is a key attribute of decentralized Layer 1 blockchains. It means that no single entity or authority has control over the network. Instead, transactions are validated and recorded by a distributed network of nodes, each acting as an independent verifier. This decentralized nature ensures the network's resilience against censorship and single points of failure, making it highly secure and trustless.
Another critical aspect of Layer 1 blockchains is their ability to maintain a complete history of all transactions. This transaction history, referred to as the blockchain ledger, is an immutable and transparent record of every transaction ever executed on the network. It allows anyone to trace the origin and destination of funds, providing a high level of transparency and security.
 Image via Binanceacademy
Image via BinanceacademyHowever, the secure and decentralized infrastructure of Layer 1 blockchains comes at a cost. The most notable trade-offs are slow block times and high transaction fees, particularly during periods of network congestion.
Slow block times refer to the intervals between the creation of new blocks on the blockchain. This means that users have to wait for these durations to see their transactions fully confirmed, which can be impractical for certain uses like instant payments.
Additionally, high transaction fees can be a barrier to entry for some users. When the demand for blockchain space exceeds its capacity, fees will spike. This happens often during periods of high activity such as NFT mints, meme coin hype or ordinal inscription frenzy. Users are forced to pay higher fees during these periods to have their transactions prioritized by miners or validators. This congestion-induced fee increase can make transactions prohibitively expensive for everyday users.
 A Look at a Few of Ethereum's Layer 2s. Image via Pixelplex
A Look at a Few of Ethereum's Layer 2s. Image via PixelplexFor more information on Layer 1 blockchains, check out our educational article What is a Layer 1 Blockchain Protocol?
Layer 2: A Solution for Scalability and Efficiency
As we move up the imaginary pyramid, we approach the 2nd layer, or ‘Layer 2’. Layer 2 solutions are designed to enhance the scalability and efficiency of Layer 1 blockchains. They work by moving some transactions off the main blockchain, thus reducing congestion and speeding up transaction processing. One of the most notable Layer 2 solutions for Ethereum is the Ethereum Layer 2 or EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine).
How Do Layer 2 Solutions Work?
There are many different Layer 2 scaling solutions being developed and implemented but the two biggest ones are Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups:
Optimistic Rollups are a Layer 2 scaling solution that takes an optimistic approach to transaction validation. Here's how they work:
- Batching Transactions: In an Optimistic Rollup, multiple transactions are grouped or "rolled up" into a single bundle, forming a rollup chain.
- Optimistic Validation: Transactions within this rollup are considered valid by default, assuming that all participants act honestly. This optimistic assumption greatly reduces the computational load on the Layer 1 Ethereum blockchain.
- Dispute Resolution: If a dispute arises due to fraudulent or invalid transactions, anyone can challenge the transaction's validity.
- Execution on Layer 1: If a dispute occurs, the Layer 1 blockchain is used to validate the disputed transactions. This is where the actual execution and validation take place, ensuring the correctness of the disputed transaction.
- Finality: Once the disputes are resolved and transactions are confirmed as valid, the results are added to the Layer 1 blockchain, and the state of the rollup is updated.
Optimistic Rollups offer scalability by minimizing the need for immediate Layer 1 verification, which can be a bottleneck. They are well-suited for use cases where the risk of fraudulent transactions is low.
Zero-Knowledge Rollups, or zk-Rollups, are another Layer 2 scaling solution. They work differently:
- Batching Transactions: Similar to Optimistic Rollups, zk-Rollups batch multiple transactions into a single rollup.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Instead of relying on Layer 1 verification, zk-Rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to demonstrate the validity of transactions within the rollup. These proofs cryptographically confirm that the transactions are valid without revealing the details of the transactions themselves.
- Layer 1 for Final State: Unlike Optimistic Rollups, zk-Rollups don't need Layer 1 for transaction validation. Layer 1 is only required to store the final state of the rollup, which consumes significantly less computational resources compared to verifying each transaction.
- Scalability: Zk-Rollups provide even greater scalability because they offload the verification work entirely to Layer 2, reducing congestion and costs on the Layer 1 blockchain.
Both Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups are promising solutions for Ethereum's scalability problem. They offer faster transaction processing and reduced fees, but they come with different trade-offs in terms of security and implementation complexity, making them suitable for different use cases within the Ethereum ecosystem.
That’s Ethereum covered, but what about Bitcoin?
Lightning Network: Bitcoin's Layer 2
For Bitcoin, the Lightning Network serves as its Layer 2 solution. It enables faster and cheaper transactions by creating off-chain payment channels. Users can open channels, transact off-chain and then settle the final balances on the Bitcoin blockchain. The Lightning Network is ideal for microtransactions and day-to-day spending, offering near-instant confirmations and minimal fees. The Lightning Network is designed to address some of the limitations and challenges associated with Bitcoin's Layer 1 and does so in the following ways:
- Scalability: Bitcoin's Layer 1 operates on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which means that every transaction must be validated by miners and added to the blockchain. This process can be slow and expensive, especially during periods of high network congestion. The Lightning Network solves this problem by allowing users to create off-chain payment channels.
- Off-Chain Payment Channels: Lightning Network channels are like private, off-chain tunnels between users. When two parties want to transact frequently, they can open a payment channel by creating a multi-signature wallet on the Bitcoin blockchain. This wallet acts as a funding source for the channel. Transactions within this channel are off-chain, meaning they don't need to be recorded on the main blockchain.
- Fast and Cheap Transactions: Since transactions occur off-chain within a payment channel, they are incredibly fast and incur minimal fees. This makes the Lightning Network ideal for microtransactions and day-to-day spending. Users can send and receive small amounts of Bitcoin instantly and without paying hefty transaction fees, which might be impractical on the main Bitcoin blockchain.
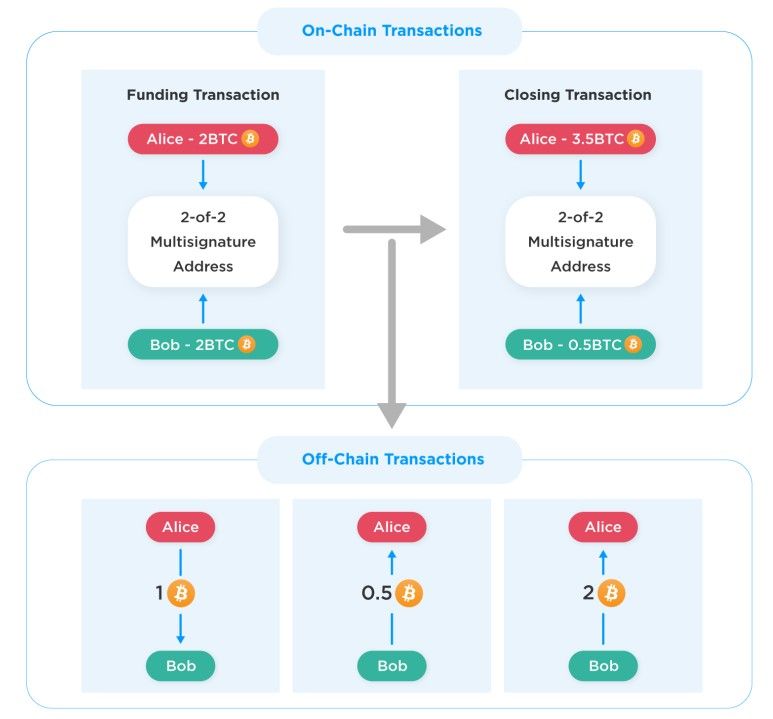 On and Off-Chain Lightning Transactions, Image via Crypto.com
On and Off-Chain Lightning Transactions, Image via Crypto.com- Security: The Lightning Network maintains security through smart contracts and cryptographic techniques. The funds in a channel can only be moved by mutual consent, and if any party attempts to close the channel improperly, they risk losing their funds. This incentivizes honest behaviour.
- Routing: Lightning nodes act as intermediaries for routing payments across the network. When a user wants to send Bitcoin to someone else, the network can automatically find a path of connected Lightning nodes to facilitate the payment. This routing capability enables the network to scale and connect users effectively.
- Privacy: Lightning Network transactions offer a degree of privacy since they are not publicly recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain. However, it's important to note that the level of privacy may vary depending on how users set up and use their Lightning channels.
- Mainnet Settlement: While Lightning Network transactions occur off-chain, the final balances are periodically settled on the Bitcoin mainnet. This settlement process ensures that the channel participants' final balances are accurately reflected in the Bitcoin blockchain.
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin that offers faster, cheaper and more scalable transactions by creating off-chain payment channels. It's particularly well-suited for use cases like microtransactions and everyday spending, providing near-instant confirmations and minimal fees while maintaining the security and trustless nature of the Bitcoin network.
Why Were Layer 2s Created?
Layer-2 solutions emerged as a response to the pressing scalability challenges that plagued prominent blockchains, notably Ethereum. These decentralized networks, initially envisioned as platforms for secure and efficient transactions and smart contracts, faced a critical bottleneck as their popularity skyrocketed.
With a growing number of users and an ever-expanding array of decentralized applications (DApps) vying for limited processing capacity, congestion within these blockchains became a persistent headache. This congestion not only hampered transaction speeds but also led to exorbitant gas fees, rendering many activities on the network economically unfeasible for the average user.
For example, in 2021, when NFT mints were full of hype and speculation was rampant, the average Ethereum transaction reached a record $23.43. These levels of transactional costs might not be a big deal for a whale who is trying to push through transactions worth hundreds of thousands or millions of dollars, but to the average individual, these transaction costs essentially made Ethereum unusable.
This problem is not exclusive to Ethereum. Bitcoin has also suffered from blockchain congestion and high transaction fees. After the Taproot upgrade, some Bitcoin users realized that inscriptions and NFTs could be created, bought and sold on Bitcoin Layer 1. As a consequence, fees spiked dramatically from Ordinal inscriptions and BRC-20 tokens.
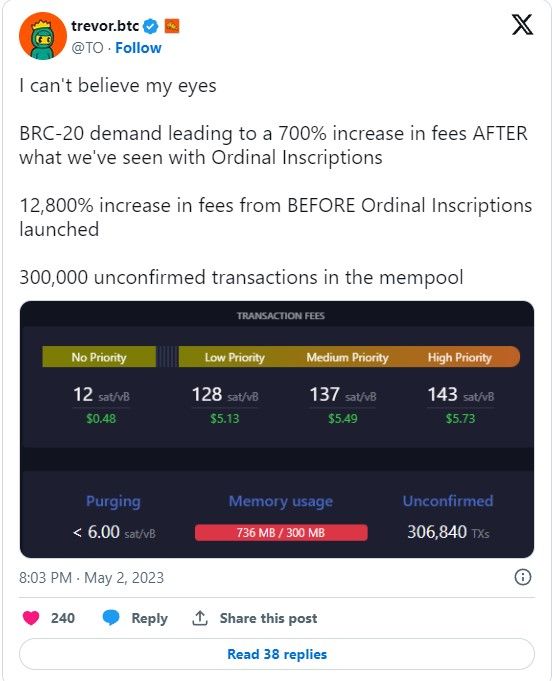 Network Congestion Can Lead to Higher Transaction Fees. Image via Twitter
Network Congestion Can Lead to Higher Transaction Fees. Image via TwitterIn essence, the surge in demand for blockchain technology and its applications exposed a fundamental limitation: the inability of these platforms to handle the escalating volume of transactions efficiently.
Enter Layer-2 solutions, which were conceptualized and developed as a remedy to these scalability woes. These solutions offer a secondary layer built on top of the primary blockchain, allowing for a significant boost in transaction throughput and overall network performance. By diverting a substantial portion of transactions away from the main blockchain and onto the Layer-2, they effectively alleviate congestion and mitigate the associated high fees, making blockchain technology more accessible and cost-effective for a broader range of users and use cases.
As the demand for blockchain-based services continues to grow, these innovative solutions play a pivotal role in ensuring that these networks can handle increased traffic and offer a seamless, cost-effective experience for users and developers alike.
Why Are Layer 2s Important?
Layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged as a crucial component in the blockchain ecosystem for several compelling reasons. In an era where the promise of blockchain technology lies in its ability to revolutionize everyday transactions and applications, the importance of Layer 2 solutions becomes evident.
One of the most pressing issues they address is the dire need for faster and more cost-effective transactions. Layer 1 blockchains, despite their inherent security and decentralization, have often struggled with scalability issues. This inadequacy can lead to impractical wait times, such as 20 minutes for a simple cup of coffee payment confirmation. It's clear that attracting real users and gaining mass adoption of blockchain technology would be an impossible feat if such delays persist. Layer 2 solutions step in to bridge this gap, offering the speed and efficiency necessary for seamless, real-world applications.
One of the key areas where Layer 2 solutions prove their significance is in the realm of decentralized applications (DApps). Particularly in the emergence of GameFi (gaming on blockchain). Gaming DApps rely heavily on microtransactions, often involving small in-game purchases or rewards.
Layer 1 blockchains struggle to handle the sheer volume of these microtransactions efficiently. Implementing these on a Layer 1 blockchain would not only be cumbersome but could also lead to exorbitant transaction fees. Layer 2 solutions offer a lifeline to the burgeoning GameFi industry and help emerging SoFi (Social Finance) DApps, such as friend.tech or Post.tech, by providing the quick and cost-effective transactions required to create immersive and economically viable gaming/social experiences on the blockchain.
 Image via Friend.tech
Image via Friend.techFurthermore, the existence of Layer 2 scaling solutions is paramount in preserving the core tenets of blockchain technology: decentralization and security. Unfortunately, the only way to achieve faster and cheaper transactions on a Layer 1 blockchain currently is to compromise on decentralization and security in some manner.
This is typically because fast and cheap Layer 1 blockchains rely on more powerful hardware to run validators. Powerful hardware isn’t affordable to large sections of the Earth's population and thus the concern is the powerful hardware would only be running in localised more wealthy countries. This leads to centralisation.
There is an argument to be had that the hardware will develop quickly over time and become cheaper, but these are debates for another time.
These trade-offs are not only undesirable but they also undermine the fundamental principles of the blockchain. Layer 2 solutions, by offloading some of the transaction processing from the base layer, allow the underlying Layer 1 blockchain to maintain its integrity while improving its efficiency. This duality ensures that base Layer 1 blockchains can continue to do what they do best — remain secure, permissionless and decentralized, and thus prevent compromising their core principles.
In a rapidly evolving blockchain landscape, Layer 2 solutions serve as a bridge between the promise of blockchain technology and its practical implementation, unlocking new possibilities for innovation and adoption.
 Image via CNN
Image via CNNFrom a Bitcoin perspective, Layer 2 Scaling Solutions are Vital for Bitcoin's practical use. You see, at its core, Bitcoin is envisioned as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that can be used for everyday transactions.
However, the inherent limitations of its Layer 1 blockchain, including slower confirmation times and fluctuating transaction fees, have often hindered its practicality for microtransactions and daily use. This is where Layer 2 scaling solutions like the Lightning Network step in. They are designed to provide rapid and cost-effective transaction processing, ensuring that Bitcoin becomes a viable and efficient means of conducting everyday payments. This improved usability is crucial for Bitcoin's broader adoption and its transformation from a store of value to a practical medium of exchange.
The Lightning Network, in particular, excels at addressing the critical issues of transaction speed and cost efficiency. By enabling off-chain transactions, it allows users to conduct an almost unlimited number of transactions instantaneously and at negligible fees. This paradigm shift in transaction processing not only makes Bitcoin competitive with traditional payment systems but also opens the door to innovative use cases that rely on fast and inexpensive transactions. Whether it's micropayments for content consumption, remittances or even machine-to-machine transactions in the Internet of Things (IoT), Layer 2 solutions empower Bitcoin to function seamlessly in a wide array of real-world scenarios.
Bitcoin's strength lies in its trustless and censorship-resistant nature, underpinned by a decentralized network of nodes. Traditional approaches to scaling often compromise these principles, but Layer 2 solutions do not. The Lightning Network, for instance, relies on the security of the Bitcoin blockchain, ensuring that users can transact with confidence while preserving the network's decentralized nature. This keeps Bitcoin true to its original vision and ensures its resistance to external control or manipulation.
Layer 2 scaling solutions are indispensable in the blockchain space as they address critical issues related to speed, cost-efficiency and scalability. They facilitate blockchain technology adoption in real-world applications and support the growth of emerging sectors like GameFi and SoFi. Furthermore, they offer a means to enhance blockchain performance without sacrificing decentralization and security. In the context of Bitcoin, Layer 2 scaling solutions, such as the Lightning Network, are essential for making Bitcoin a practical medium of exchange for everyday transactions by providing rapid and cost-effective transaction processing.
What Are The Big Layer 2s?
There are two blockchains that have progressed to using Layer 2s to address scalability and those are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known blockchain, has faced scalability challenges due to its limited transaction processing capacity. As the network grew, it became clear that the original design could not handle a high volume of transactions efficiently. To address this issue, developers and the Bitcoin community have explored various Layer 2 solutions:
- Lightning Network: The Lightning Network is the most prominent Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin. It's a second-layer protocol that enables off-chain, peer-to-peer transactions.
- Sidechains: Bitcoin has also experimented with sidechains like RSK (Rootstock) and Liquid. These sidechains allow developers to build applications and smart contracts while pegging the value of their tokens to Bitcoin. This reduces the load on the main Bitcoin blockchain and enhances its scalability.
 Image via Cryptorank
Image via CryptorankAlthough sidechains do exist on Bitcoin, they haven’t garnered a significant level of adoption compared to the Lightning Network, which stands out as an exceptional Layer 2 scaling solution for Bitcoin. Lightning network offers the following features:
- Decentralized Network Growth: The Lightning Network has exhibited remarkable growth with over 15,000 active nodes and more than 50,000 open payment channels. This extensive network of nodes allows users to transact with peers across the globe, promoting decentralization in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
- Significant Network Capacity: The Lightning Network has demonstrated its ability to accommodate substantial transaction volume. With a total network capacity exceeding 2,000 BTC, it provides the infrastructure needed to process a high volume of transactions efficiently.
- Negligible Transaction Fees: One of the standout features of the Lightning Network is its ability to drastically reduce transaction fees. Users often enjoy transaction costs that are lower than a single satoshi, making microtransactions and everyday payments not only feasible but highly cost-effective.
- Mainnet Integration: The Lightning Network operates on the Bitcoin mainnet, meaning users can transact with real Bitcoin through this Layer 2 solution. This seamless integration with Bitcoin's primary network ensures that users can experience the benefits of enhanced scalability and low fees while dealing with genuine cryptocurrency.
- Testnet for Development: In addition to its mainnet presence, the Lightning Network includes a testnet for development and experimentation. This environment is invaluable for developers and enthusiasts to test new features and innovations before deploying them on the mainnet.
- Security and Speed: The Lightning Network is built on a robust security model that leverages Bitcoin's security features. Transactions are lightning-fast, often settling in seconds, providing a seamless experience for users.
- Interoperability: The Lightning Network is designed to be interoperable with various wallets and services. This flexibility allows for easy integration into existing Bitcoin infrastructure.
From Ethereum’s perspective, the largest L2 is Arbitrum, which is an optimistic rollup. Currently, Arbitrum has the largest TVL of $5.75 billion, a market share among the ETH L2’s of 54.60% and a weekly trading volume of $1.185 billion at the time of writing.
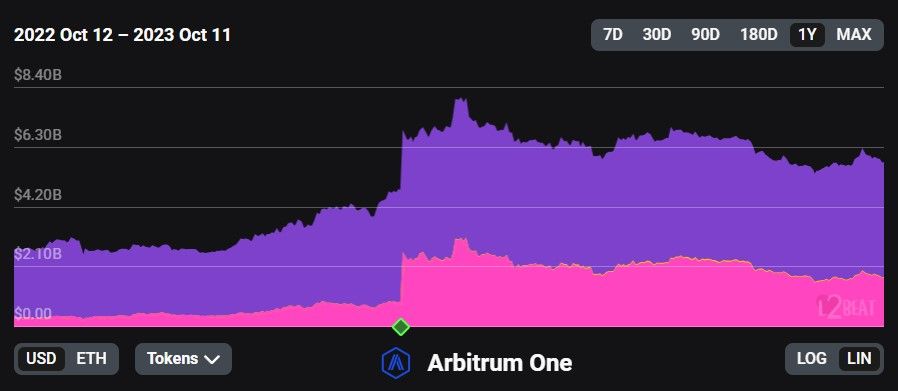 Arbitrum's TVL Over The Last Year. Image via L2Beat
Arbitrum's TVL Over The Last Year. Image via L2BeatArbitrum introduces a concept known as "Optimistic Rollup." At its core, Arbitrum Rollup functions as a sub-module within Ethereum, offering the benefits of blockchain technology without bogging down the Ethereum mainnet. The key feature of this solution is its "innocent until proven guilty" approach to transactions. Initially, transactions on Arbitrum are optimistically assumed to be valid. However, if a dispute arises, it can be resolved on the Ethereum mainnet. This process ensures Ethereum's security is inherited while drastically reducing transaction costs.
One of Arbitrum's strengths is its seamless compatibility with Ethereum. Users can employ their favourite Ethereum wallets, and developers can build and deploy smart contracts using familiar Ethereum libraries and tooling. This high level of compatibility is a result of Arbitrum using a fork of Geth, one of the most widely used Ethereum implementations, with specific modifications to make it a trustless Layer 2 solution.
Moreover, Arbitrum's latest version, Stylus, takes Ethereum compatibility even further by allowing developers to write high-performance smart contracts in languages like Rust and C++. Stylus is currently on public Testnet and opens up exciting possibilities for developers.
 Arbitrum is the Largest Ethereum L2 Solution. Image via Arbitrum
Arbitrum is the Largest Ethereum L2 Solution. Image via ArbitrumArbitrum's versatility extends to the introduction of AnyTrust chains. While Rollup chains maintain the highest standards of decentralization and trustlessness, AnyTrust chains offer a different trade-off. These chains don't have the same decentralization guarantees but provide lower fees. In AnyTrust chains, data is managed off-chain, and in case of a challenge, they revert to "rollup mode." This approach, while not as trustless, significantly reduces user costs and may suit applications with different security requirements.
Arbitrum takes the concept of scalability further by allowing multiple chains to run in parallel. Currently, on the Ethereum mainnet, two Arbitrum chains exist: Arbitrum One, a Rollup chain, and Nova, an AnyTrust chain. This variety ensures that users and developers can choose the most suitable chain for their specific security and cost considerations.
 AnyTrust in One of the Two Arbitrum Chains on Ethereum. Image via Arbitrum
AnyTrust in One of the Two Arbitrum Chains on Ethereum. Image via ArbitrumArbitrum represents a significant leap forward in addressing Ethereum's scalability challenges. By providing a cost-effective and Ethereum-compatible solution, it caters to a wide range of users and developers. Its unique approach to security, openness to validators and seamless integration with Ethereum make it a promising addition to the blockchain landscape.
Be sure to check out our Ethereum Layer 2 article where we compare and contrast leading Layer 2s: Arbitrum, Optimism, Base and zkSync

Conclusion
Layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged as indispensable tools in the blockchain ecosystem. They effectively address critical issues such as slow and expensive transactions on Layer 1 blockchains, which can hinder the practical use and widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
Layer 2 solutions not only offer speed and cost-efficiency but also play a crucial role in preserving the core principles of decentralization and security, which are fundamental to blockchain's appeal.
Whether you're interested in blockchain gaming or simply wish to use cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions like buying a coffee, Layer 2 solutions provide the necessary bridge between blockchain's potential and real-world applications. They facilitate innovation and growth while maintaining the integrity of the technology.
Specifically, within the realm of Bitcoin, solutions like the Lightning Network empower the cryptocurrency to serve as an efficient and practical medium of exchange, aligning with its original vision as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. This usability is essential for Bitcoin's broader adoption while safeguarding its trustless and censorship-resistant nature.
In essence, Layer 2 scaling solutions are the linchpin that ensures blockchain technology can meet the demands of the modern world, balancing efficiency with the principles that make blockchain truly revolutionary.





