iExec has been gaining quite a bit of popularity and exposure recently. It is a project that is looking to build the first marketplace for cloud resources.
If you haven’t heard of them before don’t worry, many people haven’t because the team has been focused on getting results rather than pumping hype and gaining followers. They are, however, entering a very competitive landscape with a number of similar projects.
So, can iExec rise above the more established alternatives?
In this review of iExec, we will take an in-depth look into the project. We will cover some of the most important aspects including the team members, technology, potential for adoption as well as the long term prospects for the RLC token.
What is iExec?
The iExec platform is similar to Amazon S3 or Microsoft Azure, but rather than having all the servers in one centralized location, it is broken up into thousands of nodes to allow for off-chain computing for blockchain applications.
Decentralized cloud computing has been growing as blockchain startups emerge looking to take advantage of the cost effectiveness and efficiency to be had from a platform built on the blockchain.
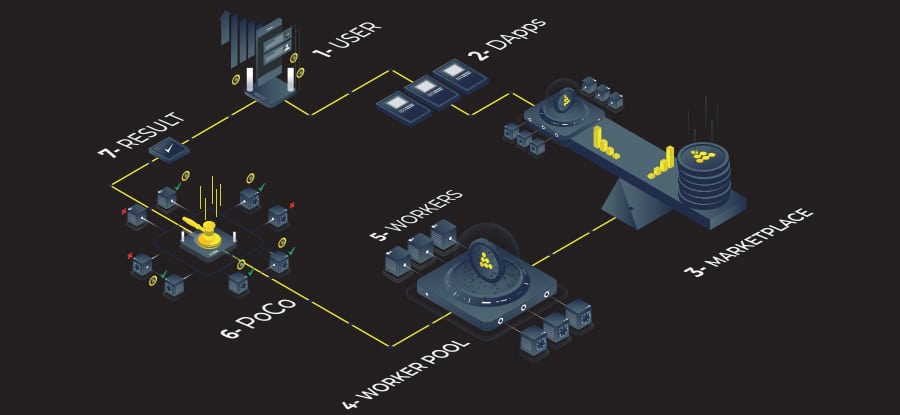 Overview of iExec. Image source: iExec One Pager
Overview of iExec. Image source: iExec One PagerOther projects with a similar focus include Siacoin, Storj, Maidsafecoin and Golem. iExec stands out from these others by focusing on using cloud services for processing power, not just for storage.
iExec is aiming at the blockchain ecosystem itself and the growing realm of decentralized applications (dApps).
Cloud Computing Today
Before looking specifically at iExec I want to take a quick look at the cloud computing industry as it exists today.
In a very short period of time cloud computing has become the industry standard for acquiring storage or processing power without spending to build out expensive IT infrastructure. For example, a company like Netflix hosts and delivers nearly all its content from Amazon’s cloud infrastructure. The same is true for many other tech companies who deliver applications and store data on servers provided by Microsoft, Google, Amazon and IBM.
There’s a very good reason that cloud computing arose. If these tech companies have tens of thousands of servers, why not outsource spare storage and processing power? And so smaller businesses gained access to otherwise expensive technology at a fraction of the cost.
iExec is looking to provide the same service, but to put it on the blockchain and decentralize it. This will make it far more secure and inexpensive when compared with traditional cloud computing options. With the cloud computing industry projected to reach $55 billion in revenue by 2026, why wouldn’t iExec want to try and access part of that industry.
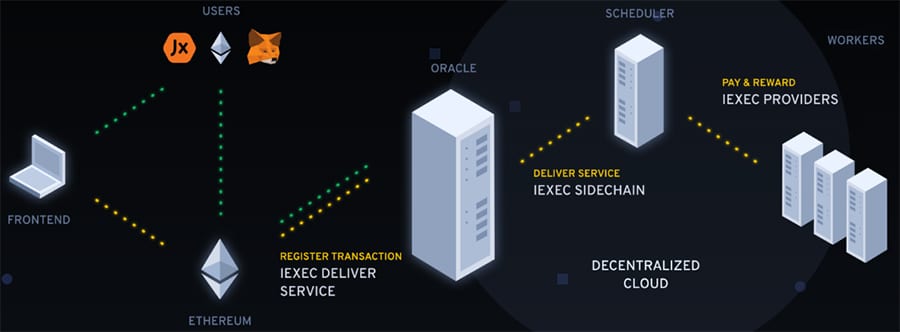 Cloud Computing architecture at iExec
Cloud Computing architecture at iExecIExec is actually going about this in a very intelligent way. They know that taking on the likes of Google, Amazon and other cloud computing giants is likely futile. So instead they are focusing on the blockchain economy by targeting decentralized applications. They want to be the logical stop for blockchain cloud computing.
This makes it easier for them to acquire customers, since the providers of dApps won’t be put off by blockchain technology. It could also be setting the stage for massive growth, since iExec is likely to grow right alongside the entire blockchain industry.
And they’re providing what will be a desperately needed service, since dApp platforms will need access to far more computing power than exists from their own networks.
As the adoption and use of smart contracts and dApps grows developers will need a way to run all the computations and instructions. Running them on the existing blockchains would cause the network to slow to a crawl, making it useless. Just look at what happened to Ethereum over the course of the CryptoKitties craze.
In essence, iExec is looking to build the infrastructure that will provide Ethereum and other dApp platforms with the computing power they need to scale as needed.
How Does iExec RLC Work?
If the platforms that host the dApps are unable to support the computing power needs, how does iExec expect to offer support for all the computing power of dApps and smart contracts? By taking them off-chain so that all the on-chain functions continue running smoothly.
To accomplish this iExec makes use of an open-sourced Desktop Grid Software called XtremWeb-HEP. This application pools all available computing resources and makes them available to the applications and platforms.
According to the whitepaper released by iExec they can make this possible on a global scale, including support for “fault-tolerance, multi-applications, multi-users, hybrid public/private infrastructure, deployment of virtual images, data management, security and accountability, and many more.”
 iExec can power a new generation of applications
iExec can power a new generation of applicationsIn essence the software makes it possible for any dApp to utilize any of the computing resources on the iExec network. This will allow developers the luxury of being able to commission processing power as large as a warehouse sized data center if necessary. This will make developing dApps more flexible and scalable, as well as being free-market driven. Developers will be able to find just the right amount of resources for whatever project they might dream up.
Not surprisingly, the matching of client needs to host availability is done using smart contracts. So, the matchmaking algorithm on the iExec platform will take network resource requests and match them with providers as appropriate. The program looks at each task and decides which computing resource is necessary to run the program. Once the match is made it moves on to the next task, and so on and so on.
To ensure that users receive the resources they request iExec utilizes a Proof-of-Contribution (PoC) consensus algorithm. This is how computational power is the protocol used by iExec for consensus over off-chain computing.
In addition to providing trust, PoCo also orchestrates the different contributions to the iExec network, ensuring payments are always fair and timely. Finally, it also includes a permission mechanism can be used to control access to applications, datasets and worker pools.
Each Piece of iExec’s Platform Puzzle
Moving beyond the technical workings of the platform, let’s have a look at the functional pieces making up the iExec platform. There are three key components; the resource marketplace, the dApp store and the data marketplace.
The Resource Marketplace: This is where providers can offer their computing resources in exchange for RLC, and where developers, individuals and other entities can shop for the resources they require to power their applications. It includes a matchmaking smart contract that ensures no provider can offer more resources than they have available.
Essentially, this allows buyers to choose from a wide variety of machines (CPU, GPU, Trusted Execution Environments), while also specifying the level of trust they see fit. Obviously, higher levels of trust in the result of a computation means a higher price.
There’s also a reputation smart contract to measure and rate the reliability of each provider. With this system more reliable providers command higher rates, but users can also choose less reliable providers to lower their costs. This helps make the marketplace completely free-market driven, with pricing decided through competition.
 Screenshot from the iExec dApp Store
Screenshot from the iExec dApp StoreThe dApp Store: Think of this as the decentralized version of the Google Play store, with all sorts of dApps built using iExec available. It’s already live, and you can go browse through and purchase apps right now if you want. And if you’re an application developer you can submit your dApp to be listed on the platform.
The Data Marketplace: In addition to having a marketplace for applications and for resources, there are plans on building a market place for data. This will be a place for data providers to sell their data to dApp developers or to anyone willing to purchase it.
This could be government data, stock market statistics, real estate data and any other type of data you might imagine. The Data Marketplace was recently released as part of the V3 update that took place in May of 2019.
The iExec Team
iExec has a strong team, with a deep background in research and cloud computing. In fact, the core team has six PhDs, and four of those have been in the cloud computing field for over a decade.
Those four are Gilles Fedak, Haiwu He, Oleg Lodygensky, and Mircea Moca. They have spent years developing Desktop Grid applications and iExec is the result of their collaborative experiences.
 Some of the iExec Senior Team Members
Some of the iExec Senior Team MembersGilles Fedak first came across Ethereum in 2016 and as a result the team was able to solve something they had been disputing since 2012 – how to create a distributed cloud computing platform based on Desktop Grid computing.
iExec Partnerships
There are a number of important partnerships and collaborations that iExec has entered into recently. These include a broad swathe of corporations in different industries. Below are a few of these recent partnerships:
- Intel: iExec and Intel have collaborated on the 5G services. For example, they have recently showcased how blockchain technology and Intel's SGX trusted execution can provide fully decentralized and autonomous solutions for smart cities.
- IBM: The IBM cloud joined iExec and an IBM worker-pool has been made available on the iExec network
- EDF: iExec has recently announced that it has partnered with EDF to optimize its cloud computing infrastructure. EDF is the largest utility provider in France.
Indeed, it is likely that there are is going to be much more collaboration with industry through their "iExec for enterprise" initiative that we discuss below.
iExec RLC Price History
The iExec ICO took place on April 19, 2017 and the team raised $12 million by selling 60 million tokens at $0.2521 each. The price of the iExec RLC remained choppy throughout the remainder of 2017, and rallied strongly along with the entire cryptocurrency market, reaching an all-time high of $4.47 on January 13, 2018.
Since then it has steadily moved lower as the cryptocurrency space endured a bear market throughout much of 2018. As of May 29, 2019 the price is $0.469, which is nearly double the ICO price. That price gives it a market capitalization just shy of $37 million and ranks it as the 141th largest coin on Coinmarketcap.com.
 Register at Binance and Buy RLC Tokens
Register at Binance and Buy RLC TokensThe majority of trading volume for iExec RLC is on the Binance Exchange, although there is a modest amount of volume on Bittrex and Upbit as well. There are a handful of other exchanges which list iExec RLC and those interested in purchasing using U.S. dollars can do so on Ethfinex.
In terms of volume, there appears to be decent levels across the exchanges as well as on different order books. This could bode well for the potential liquidity of the token should anyone want to larger orders without moving the price that dramatically.
The iExec RLC token is ERC-20 compatible, so it can be stored in any ERC-20 compatible wallet such as MyCrypto or MyEtherWallet.
iExec Development
It can sometimes be hard to get an idea of exactly how much work has been done on a project. However, one of the most effective ways to do this is by looking at the coding activity in their public repositories.
Therefore, I decided to dive into the iExec GitHub to see exactly how much code the developers were pushing. Below are the code commits for the three most active repos in their GitHub.
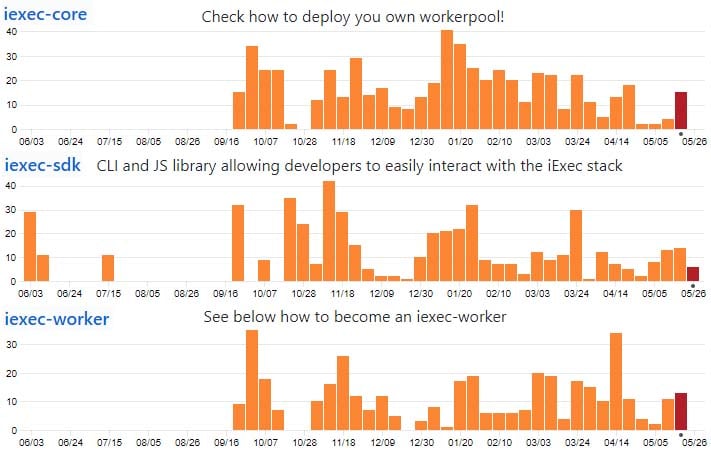 Code Commits for select repos over past 12 months
Code Commits for select repos over past 12 monthsAs you can see, there has been quite a lot of activity in these repositories. It is also worth noting that there are a total of 56 more repos in their GitHub! Many of these have similar levels of monthly activity.
This a really impressive example of the amount of hard work that the iExec team is getting done. They are pushing more code in a month than similar projects push in a year. Perhaps this is the reason that the team has been able to meet all of their roadmap objectives.
There could be good reason for all of this activity. This is because of the recent launch of V3 of the iExec protocol...
iExec V3 Update
On the 15th of May 2019, iExec released their much touted V3. This had numerous upgrades to its protocol that will make it faster, more secure and flexible.
One of the main innovations of this upgrade was the Data Wallet. This will allow data providers to list their datasets or AI models. Then, through the iExec platform, these can be used in an application powered by remote computing.
There are also a host of other technical improvements that have come about because of the upgrade. For example, the distributed computing middleware has been upgraded. Named "iExec Core", this will allow for individuals to join these public worker pools and provide their computing power.
V3 has also improved the overall efficiency of the iExec marketplace. The team has implemented a dedicated bridge which is compatible with sidechains and decentralised oracles.
Finally, iExec V3 also incorporates the "iExec for Enterprise". This can be thought of as a consulting / support service that the team is offering to corporate clients. These enterprises can then decide whether they would like to adapt the iExec technology into their own blockchains.
Conclusion
If the iExec platform works as intended and garners adoption it could begin to grow exponentially in response to growth in the use of decentralized applications. Its success goes hand in hand with the growth in blockchain adoption, and the increase in the dApp ecosystem. It’s also good to note that the iExec solution is more environmentally friendly compared with current cloud computing solutions since resources are used only as needed.
While some might say the project is overly ambitious, the team has tackled projects in the past that were just as ambitious. They were instrumental in developing the European Desktop Grid Infrastructure, a system that utilized over 200,000 nodes to complete more than 1 million tasks. That project laid the groundwork for the iExec project by demonstrating its feasibility.
It’s far too early to know if iExec can succeed, but the progress so far shows that the team is committed to making it a success. With the combination of knowledge, intelligence and experience the team has what they need to bring the iExec platform to reality, and success on this project will help support the future success of blockchain in general.



