AI and blockchain are growing fast. AI understands large amounts of data. Blockchain keeps that data transparent and trustworthy. Together, they are changing how industries manage and share information.
The market numbers show the momentum. Gartner predicts that blockchain will create about $176 billion in value this year and could pass $3 trillion by 2030.
The real story in 2025 and 2026 is how quickly the two are coming together. AI needs clean and verifiable data. Blockchain needs better tools for analysis, risk, and automation. Their goals now match. This is why we see growth in finance, supply chains, healthcare, and digital identity.
An AI and blockchain stack is no longer future talk. It is becoming the foundation for new financial products and Web3 systems.
For a beginner's guide to blockchain, take a look at our guide here.
Why Blockchain and AI Need Each Other
AI can be great at decision-making and automation, but it lacks transparency. Yes, you can get the desired outcome, but what led to it sometimes remains a mystery. Blockchain provides the opposite. It reveals everything, but it does not adapt quickly. Once you combine them, you get transparency plus intelligence, and that is when things start to click.
How Each Tech Solves the Other’s Limitations
AI’s biggest issue is that it hides its internal logic. Big models take in data and spit out answers, but it's tough to understand why the model made a certain call. That hurts trust. When you bring blockchain into the picture, you can store the steps the AI took. You can check its inputs, the model version it used, and even how the decision evolved. This helps users trust what AI is doing.
On the flip side, blockchain struggles with flexibility. Smart contracts run fixed rules. Networks slow down during busy times. Validators waste energy on repetitive processes. AI steps in as the optimizer. It can predict traffic on a network, adjust resources, and catch validators acting strangely. Now the blockchain becomes faster and more efficient.
So when you put the two together, blockchain covers AI’s trust gap. AI covers blockchain’s speed and adaptability gap. It becomes a real partnership.
Where the Technologies Converge Naturally
Let's see where they come together on their own. Integrity of data is a major concern. AI thrives on clean, honest data, and blockchain protects this data from tampering.
Fraud detection is another area. AI can spot suspicious behavior, while blockchain gives investigators a clean audit trail. Smart contracts become more flexible when AI feeds them real-time insights. Smart contract automation also benefits from this mix. AI can provide signals or predictions, and the contract can act when certain conditions are met.
Decision-making becomes more decentralized when AI helps evaluate choices. Even privacy improves when zero-knowledge and secure computing come into play. Furthermore, privacy and access control hold the system together. Zero-knowledge tools and secure multi-party methods make it possible to use information without revealing it. This allows AI to work with the data it needs while keeping sensitive details protected.
Five Primary Synergies Between Blockchain and AI
Now let’s dive into the practical part. This section will take a deeper look into five primary synergies between Blockchain and AI, using real examples. This section will demonstrate how these two technologies work in parallel in the real world and why they have become major players in the tech world.
Synergy #1 — Trustworthy, Verifiable AI
One of the biggest questions people ask about AI is simple: “Can we trust it?” Blockchain helps answer that by recording the AI decision process. If the model took in certain data, transformed it, and produced an output, you can check every step.
Healthcare and pharmaceuticals are two examples of industries that rely on this. People want to be certain that the drugs or analyses made by AI are ethical and accurate. This is where blockchain comes in. It ensures that the process was not tampered with, and it helps in catching bias. And in case the data was incomplete or incorrect, the audit trail makes it easier to fix.
So, this combination gives us AI that is not just powerful, but also accountable.
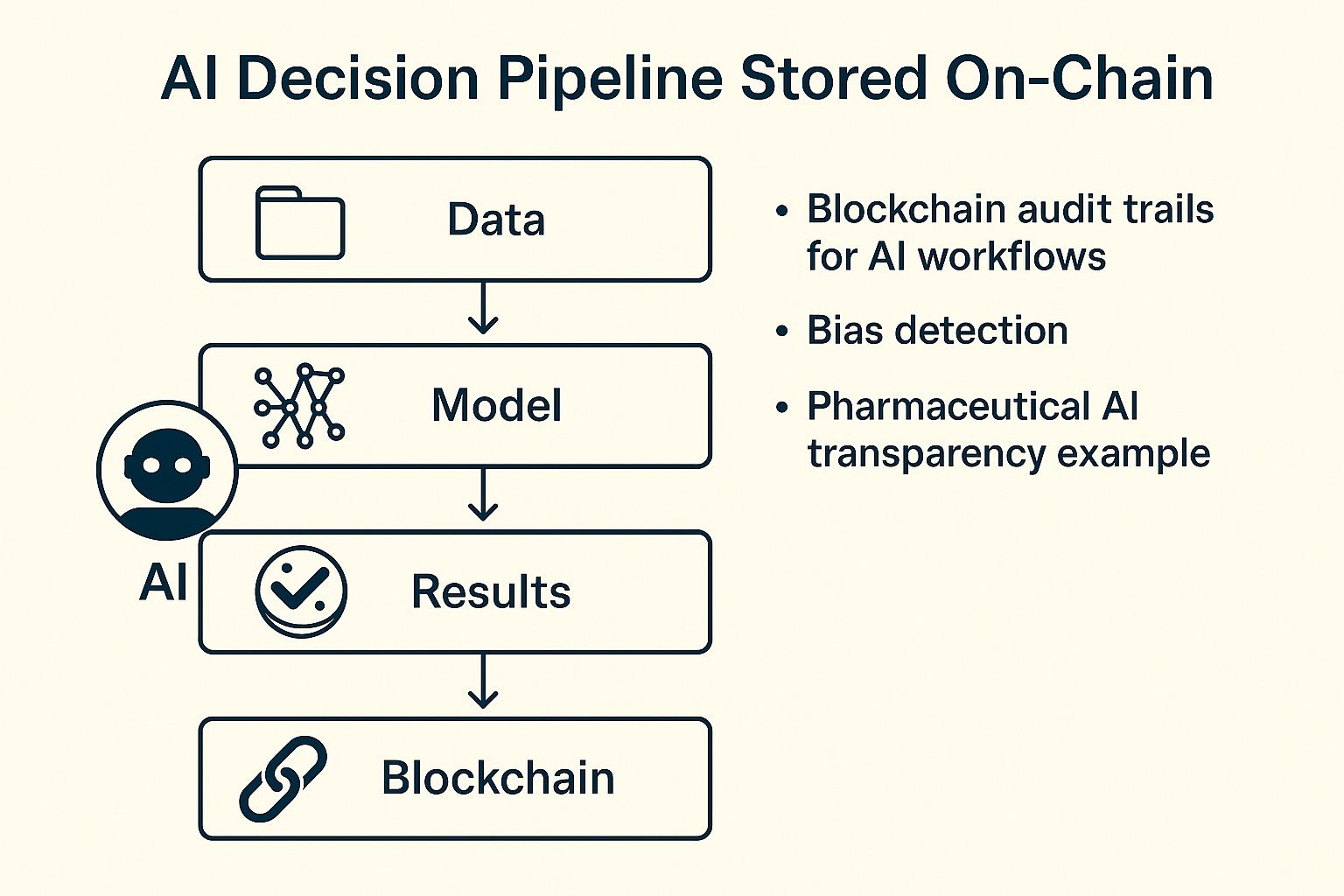 AI Decision Pipeline Stored On-Chain
AI Decision Pipeline Stored On-ChainSynergy #2 — Faster, Smarter Blockchains
AI-enhanced consensus is one of the biggest quiet upgrades happening behind the scenes. Instead of every validator following rigid rules, AI models can help them choose the most efficient way to reach agreement, reducing wasted steps and smoothing out the path to finality.
Blockchains also get congested at predictable moments — token launches, market volatility, large NFT drops. AI can spot these patterns early. It watches network flow in real-time, forecasts incoming spikes, and helps the protocol rebalance before gas fees explode.
On the security side, AI vulnerability scanners are becoming standard. They comb through smart contracts line by line, flag risky logic, compare patterns to past exploits, and catch issues humans typically overlook.
And the numbers are real. Early research shows that AI-driven optimization can cut PoS validator energy use by 15%–25%, which is a meaningful efficiency gain at scale.
Synergy #3 — Superior Security
Blockchain gives security its foundation by locking data in a format that can’t be quietly changed. AI builds on top of that. It tracks behavior across wallets, contracts, and networks, and it flags anything that doesn’t fit the usual pattern.
A big advantage here is adversarial attack prevention. AI models can spot spoofed activity, coordinated bot behavior, or attempts to exploit a protocol long before the attack reaches critical stages. Instead of reacting after the fact, systems can adjust in real time.
There’s also AI-powered threat scoring. Every action, such as a withdrawal, a contract call, or a wallet interaction, can be automatically ranked by risk. That gives exchanges, DeFi apps, and validators an early warning layer that works around the clock.
Identity gets a major upgrade, too. AI can handle the biometric checks, things like face or voice recognition, with a level of accuracy that keeps improving. Blockchain then locks that identity data into a decentralized record that can’t be quietly altered. Put together, you get a digital ID system that makes impersonation much harder and doesn’t depend on one company controlling all the sensitive information.
Decentralized AI Training
Big tech usually dominates AI because it controls the data, the compute, and the training pipelines. Decentralized training challenges that structure entirely. Federated learning lets models train across thousands of devices without exposing private information. Each update is then verified on-chain, so nobody can slip in poisoned data or manipulated gradients.
Secure multi-party computation adds another layer by letting different groups work on the same model without having to expose their data to each other. And that leads to the bigger point: once training is spread out across many participants, the system doesn’t need to lean on a few tech giants with giant server farms. Anyone can take part, and no single company ends up controlling the entire process.
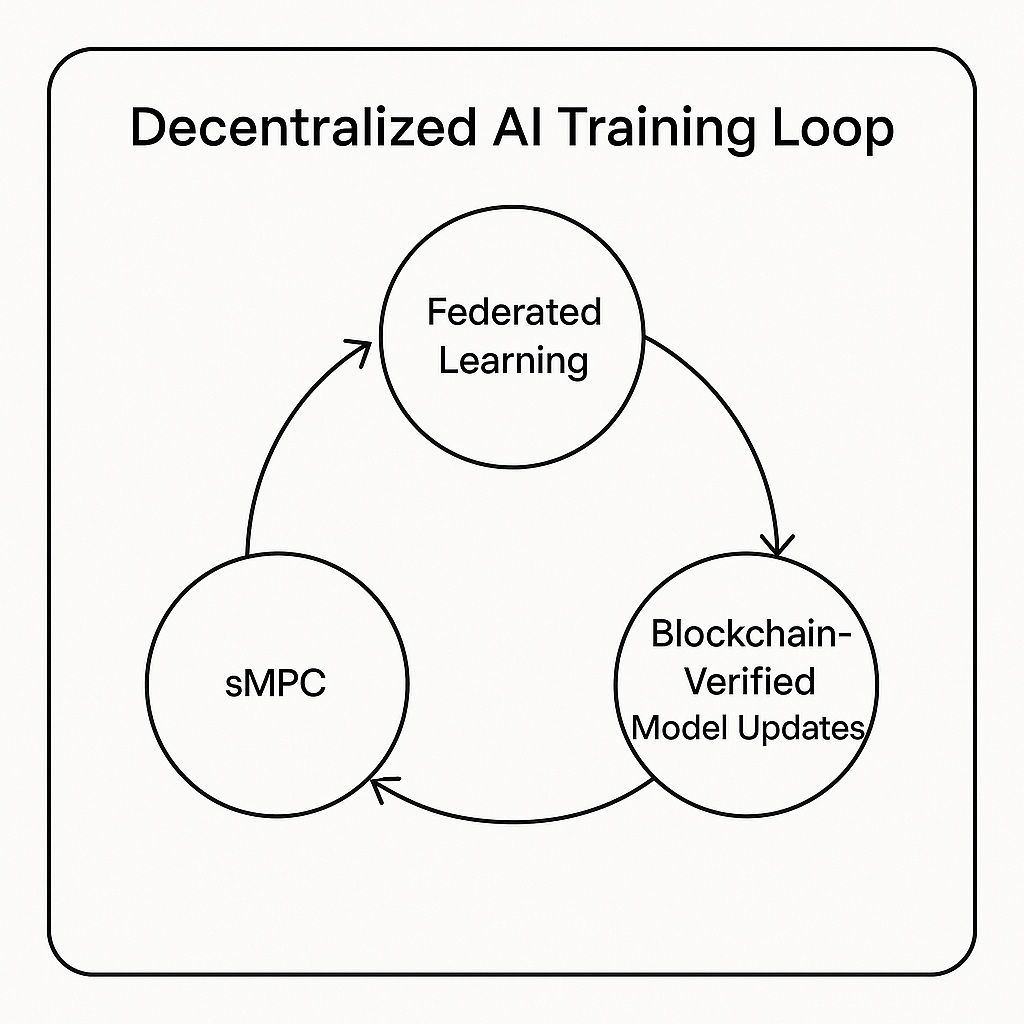 Decentralized AI Training Loop
Decentralized AI Training LoopSynergy #5 — Intelligent Smart Contracts
Smart contracts get a lot smarter when you plug AI into them. Instead of running on fixed rules, they can use dynamic logic, such as changing terms, thresholds, or actions based on the data they receive. Machine-learning models can stream signals to them in real-time, giving the contract a sense of what’s happening right now instead of only reacting to past events.
You can see how this works in something like insurance. An insurance policy could shift premiums on the fly when the risk goes up or down, or even pause coverage if the system predicts something is about to break. The same approach can carry over to supply chains, lending markets, or even energy networks.
And as the tech improves, these contracts will take over more of the routine back-and-forth on their own. We are moving toward a world where agreements don’t just execute, they negotiate, update, and manage themselves with far less human involvement.
AI Agents and Blockchain Economics
AI agents are arguably the most transformative developments emerging today. These autonomous programs carry out tasks independently, interact with the world, and execute actions continuously. Blockchain provides the infrastructure that makes this autonomy possible.
Agents expand what digital systems can do without human involvement. They coordinate services, negotiate prices, manage data, and adapt to changing conditions. Blockchain ensures these agents can hold funds, verify identities, and execute secure transactions.
To get a better understanding, read our guide on AI agents.
What AI Agents Are and Why Blockchain Enables Them
AI agents function like digital workers. They can make choices, interpret data, and carry out tasks on their own. The problem is that traditional systems weren’t built for autonomous software. An AI agent can’t open a bank account, hold money, or pass a KYC check, which means it can’t participate in the economy directly.
Blockchain fills that gap. It gives agents decentralized wallets, cryptographic identities, and the ability to pay for services or receive payments without needing a bank or a central authority to vouch for them. It becomes the trust layer that lets these agents operate in the real world.
Analysts estimate that the AI-agent economy could reach about $50 billion by 2030, with growth coming from logistics, finance, IoT networks, and a wide range of digital services. As these systems develop, blockchain provides the trust layer that lets agents operate safely, verify their identities, and take part in economic activity on their own.
Real-World Examples
We’re already seeing early versions of agent ecosystems running in the real world. Bosch and Fetch.ai are building networks where sensors can sell their data on their own, setting prices and completing transactions without human help. Deutsche Telekom is experimenting with agent-based systems that let network services coordinate and manage themselves. And projects like OLAS and Autonolas provide the underlying frameworks for autonomous agents to run on-chain services, handle governance tasks, or manage everyday operational workflows.
Together, these examples show that AI agents have progressed from a research idea to something that’s now entering actual production use.
How AI Agents Will Reshape Web3
AI agents are poised to transform how Web3 operates. They will drive machine-to-machine commerce, allowing digital entities to buy and sell services. IoT devices may negotiate access to capacity or power. Autonomous DAOs may rely on agents for governance and execution rather than human intervention.
Micro-payments will be a fundamental part of this transformation. Chains such as BSV, Lightning, and Solana can process a high volume of low-cost transactions. This allows agents to transact at rapid speeds, manage resources, and interact across global systems without friction.
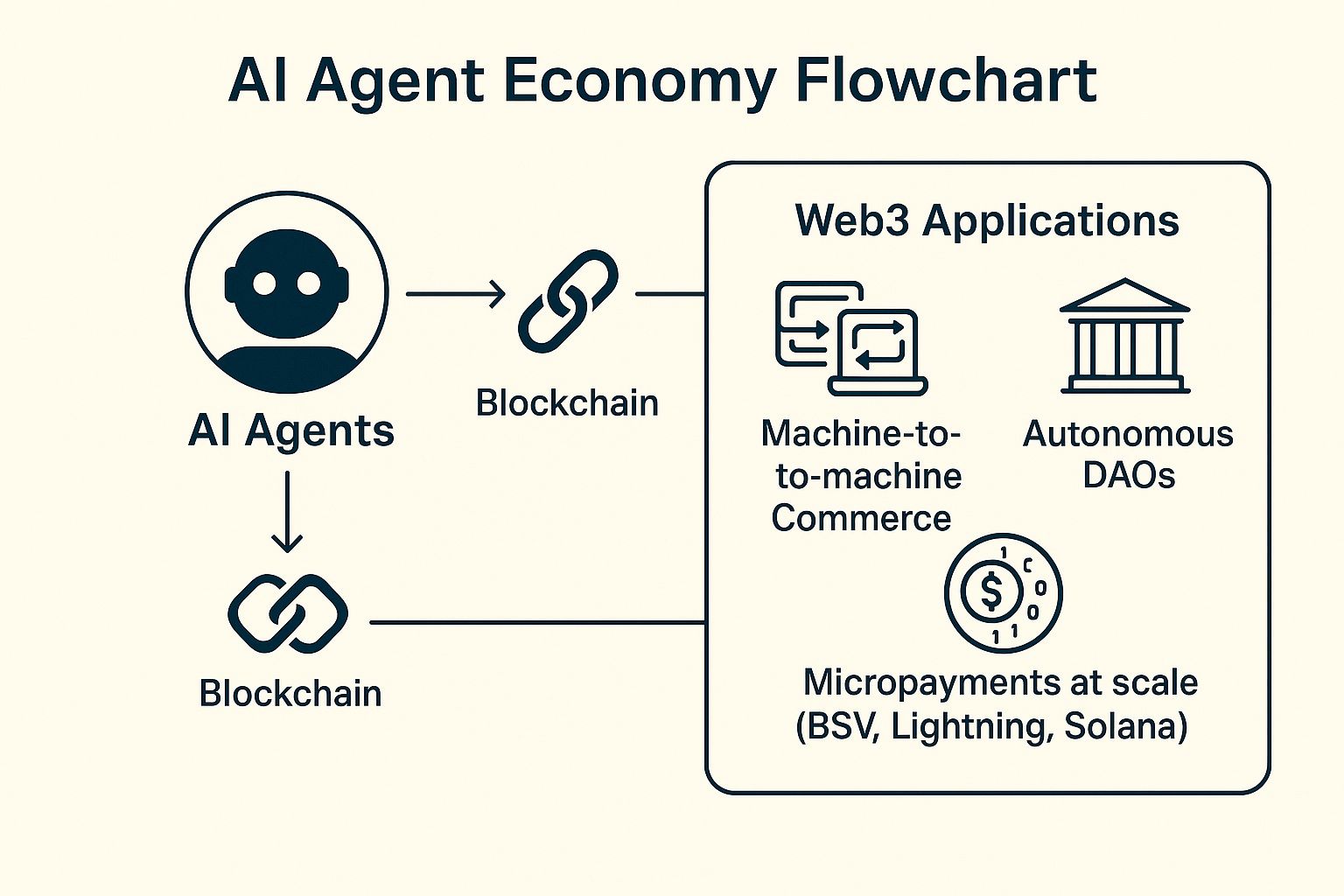 AI Agent Economy Flowchart
AI Agent Economy FlowchartReal-World Applications Across Industries
AI and blockchain convergence is not theoretical. A number of industries are already employing the two technologies in tandem, leading to results. These early deployments show how combined systems can solve problems that traditional setups struggle with.
Healthcare
Healthcare depends on clean, reliable data. If records are off, AI tools can make the wrong call. Blockchain helps lock the data into a format that can’t be quietly changed, which makes AI diagnostics safer to run.
BurstIQ is one example. It shows how this works in practice. Their system uses blockchain to keep medical records stable and trustworthy so AI can analyze them without second-guessing the source. This also works for clinical trials. Putting the data on-chain makes it more difficult to tamper with, and the audit history helps with HIPAA standards. With the inputs verified, the AI can concentrate on the actual findings.
Finance
Banks and fintech companies use AI for fraud checks, scoring customers, and reviewing documents. Blockchain adds a layer of certainty by showing whether the underlying data is authentic.
Some lenders now move loan approvals from days to minutes because AI handles the assessment while blockchain proves the paperwork hasn’t been altered. The same setup helps with AML: AI flags suspicious behavior, and the on-chain logs give investigators a clean trail to follow.
Supply Chain
Tracking goods is easier when both AI and blockchain are involved. AI can estimate demand, warn teams about delays, and notice patterns that might indicate counterfeit goods. Blockchain keeps the records solid, and the AI works with that foundation. The blockchain layer keeps the records reliable, while AI brings the intelligence on top.
Gaming + Digital Rights
Rights management is one of the clearest examples of this synergy. Microsoft Xbox and EY built a royalty system that cut processing times from 45 days to around four minutes by shifting settlement data onto blockchain. AI helps verify digital assets, detect fraud, and flag suspicious activity, while the blockchain layer confirms ownership and payouts.
IP + Patents
Patent systems also benefit from the AI-blockchain combo. For instance, companies like IBM and IPwe have implemented a distributed ledger system, like blockchain, to maintain patent records, allowing easy verification. AI then flags potential overlaps by identifying similar inventions, while highlighting promising licensing opportunities at the same time. In addition, smart contracts are used to automate several routine tasks, cutting the amount of manual work in the end.
Decentralized AI Ecosystems (Platforms + Tutorials)
Let’s move on to decentralized AI ecosystems. These are basically networks where AI and blockchain work together, but without everything running through one big central system.
Instead, the work is spread out — the data, the computing power, the services. Different people and machines handle different pieces. It makes the whole thing a lot more flexible. And honestly, a lot more fair. Because of that setup, AI and blockchain can actually fit together pretty naturally. No forcing it. No weird workarounds.
The aim here is pretty straightforward: open up AI so more people can build with it, keep the data clean and honest, and make sure privacy isn’t an afterthought.
 Decentralized AI Ecosystems Are Built Around Open Access To Data, Compute Power, and Shared Services
Decentralized AI Ecosystems Are Built Around Open Access To Data, Compute Power, and Shared ServicesKey Blockchain-AI Platforms
A number of projects are now creating tools designed for AI, and each one tackles a different need in the overall system.
SingularityNET operates a marketplace where developers can offer and use AI services without relying on a central platform. Fetch.ai supplies the framework for autonomous agents that can search, negotiate, and act on their own. Ocean Protocol focuses on data exchange, giving organizations a safe way to share datasets so AI models can train on information that’s been verified. Akash Network and io.net supply decentralized GPU power, giving AI developers access to compute without depending on major cloud providers. Hyperledger combined with IBM Watson serves enterprise users who need permissioned networks and AI tools inside a controlled environment. BSV with Teranode targets extremely high throughput, supporting workloads that involve large AI datasets and massive event streams.
| Platform | Cost/Tx | Speed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSV | <$0.0001 | 1M+ TPS | Massive AI datasets |
| Ethereum L2s | $0.01–0.10 | 4k TPS | Smart contract AI |
| Hyperledger | Free (self-host) | 3.5k TPS | Enterprise |
| Solana | ~$0.00025 | 65k TPS | Agents + automation |
Tutorials
Let's go through these tutorials one by one.
Tutorial #1: How to verify data on Ocean Protocol
Begin by browsing data listings on the Ocean Protocol marketplace. Select a dataset to view its associated Data NFT. The Data NFT stores information about ownership, licensing, and access. Review lock time details to understand whether access is temporary or permanent. Examine licensing rules to ensure the dataset can be used in your workflow.
Tutorial #2: How to check liquidity lock on DEXTools
Search for a token pair on DEXTools. Open the pair and examine the liquidity lock badge. This badge shows whether liquidity is locked and for how long. Review the wallet address controlling the lock and assess whether the duration aligns with best practices. Short lock times may indicate a higher risk.
Tutorial #3: How to inspect on-chain governance using Hyperledger Explorer
Connect Hyperledger Explorer to your blockchain network. View chaincodes to understand deployed smart contracts. Inspect transaction histories to analyse how governance decisions were executed. This offers insight into proposal outcomes, voting patterns, and participant actions.
DAOs Powered by AI
AI makes it easier for DAOs to go through proposals by pulling out what matters, showing what could happen, and pointing out any trouble spots. It can also take care of the basic follow-up work once a vote passes.
A clear example is investment DAOs, which use agent forecasts to guide their decisions. These agents scan market conditions, suggest allocation changes, and flag moves that look risky. The DAO can then act on those insights or let certain tasks run on autopilot. It leads to a steadier governance flow and limits how often humans need to intervene.
Decentralized Data Marketplaces
People and organisations can earn from their data through decentralized marketplaces and still retain ownership. AI accesses the data through privacy-preserving processes that keep sensitive information out of view. Payments can be handled through small, automatic transactions, making it easy to charge for a single dataset or even a single query. Smart contracts take care of splitting and distributing the money fairly, which creates a more balanced data economy for both contributors and developers.
Technical Architecture and Implementation
Building blockchain AI systems isn’t as simple as just combining two technologies. You have to know how the on-chain and off-chain parts communicate with each other.
Hybrid setups are the norm. Some pieces stay on-chain for security, others off-chain for speed and privacy. The key is balance — fast, safe, and private all at once.
Get it right, and you get apps that actually work well without shortcuts.
Most of the demanding AI work takes place off the blockchain, where the hardware can process it quickly. The blockchain is then used to store the pieces that need to be trusted and recorded. This simple division helps the entire system run smoothly without losing the benefits of either side.
Scalability
AI models require far more power than a blockchain can provide on its own. To solve this, many projects rely on Layer 2 networks. These systems move the heavy processing away from the chain while still keeping important results anchored on it. This keeps everything fast without sacrificing transparency.
A common setup is to run the model on regular hardware and store the final output on the chain. It stops bottlenecks but still lets developers track everything that went on.
Privacy and Security
Privacy becomes important as soon as AI touches anything sensitive. There are practical ways to protect that information while still getting useful work done. Zero-knowledge tools can confirm that the output is valid without revealing the data behind it. Secure multi-party methods let different groups work together without sharing their raw files. Basic encryption covers the rest of the journey. Together, these techniques help teams nurse data and keep users confident in the system.
Interoperability
AI systems often rely on information from different networks. This makes communication between chains increasingly important. Connectors and bridges help move information where it needs to go, and enterprise links allow older systems to join the workflow. When everything clicks together, developers can create apps that run across different networks, without being stuck on just one blockchain.
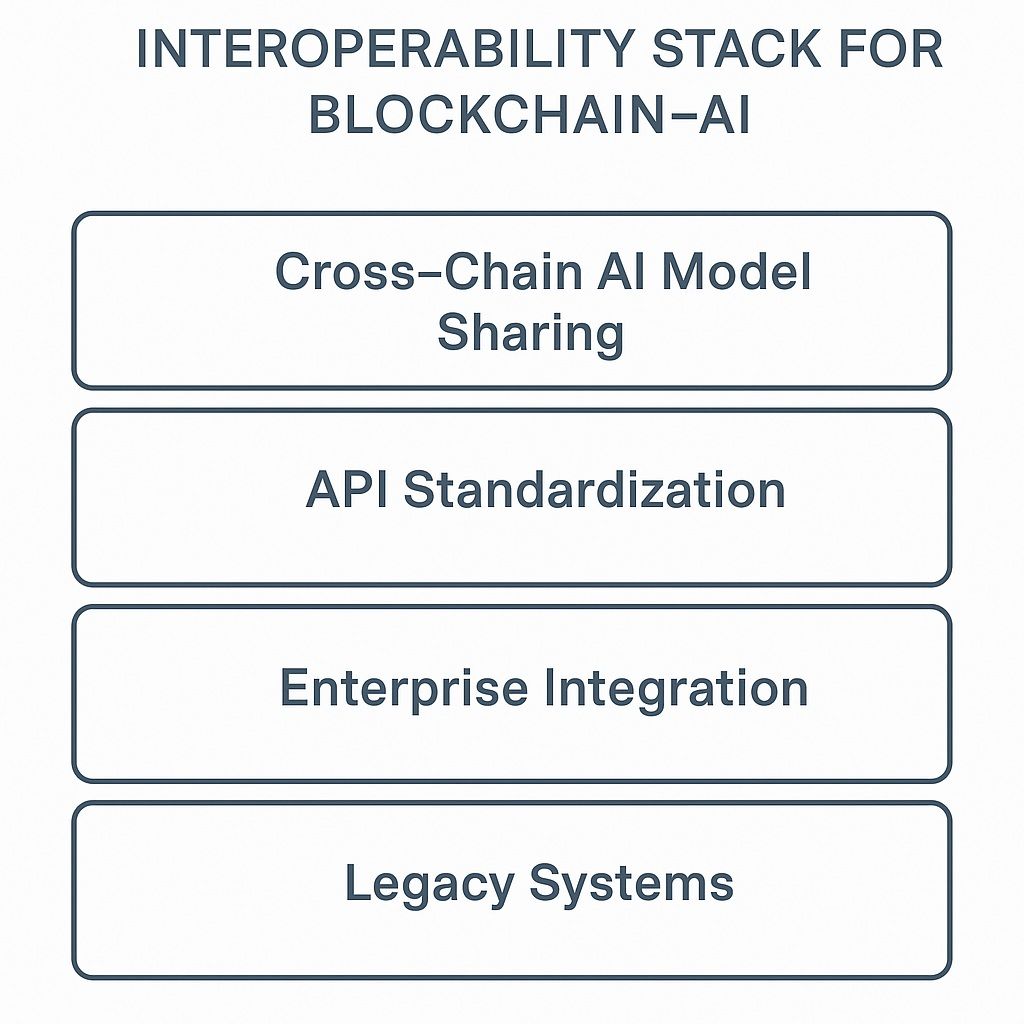 Interoperability Stack For Blockchain-AI
Interoperability Stack For Blockchain-AIChallenges and Barriers
Combining blockchain and AI sounds great in theory, but it’s not without its challenges. Some are technical. Others arise from how organisations operate or how rules are written. Recognizing these limits early leads to more realistic and informed planning.
Technical Challenges
Blockchains are not here to store large amounts of data or process heavy workloads. AI systems often need both. Slow access speeds and network delays can make real-time AI work difficult on a blockchain. Training models also depends on GPU hardware, and shortages can drive up costs. Layer 2 networks, shared compute markets, and more efficient models help ease these issues, but they do not obliterate them.
The primary task is to use each layer for what it does best. You want the trust of the chain without sacrificing performance.
Skills Gap
It is not common to find people who are experienced in both AI and blockchain at a level where they can merge the two effectively. Each field has its own learning curve. Building a system that uses both requires knowledge of distributed systems, contracts, data pipelines, security practices, and machine learning. Many organisations eventually discover that training and hiring become as important as the technology itself.
Regulation and Ethics
When it comes to regulation and ethics, authorities across the globe are actively looking into the use of personal data by automated systems. These new rules are formulated to ensure the fairness of systems and make them easier to understand. Blockchain can play a role in this regard by making data use more visible. However, oversight remains an essential element. Teams need to monitor for bias, explain their models, and protect private information.
Market Maturity
Most organisations adopt new technology slowly. Systems that blend AI with blockchain can be expensive to set up and maintain, so many teams wait until they see clear results. We are beginning to see more real-world examples that show the benefits, but broad adoption will build up gradually.
Implementation Roadmap (With Tools + KPIs)
A clear roadmap takes a team from just an idea to a functioning blockchain AI system. Every stage lets you plan carefully and move forward steadily.
Setting the right KPIs from the start keeps the project focused. The usual targets? Lower costs, faster processing, better accuracy, and less manual effort.
Phase 1 — Strategy
First, choose a use case that makes a real impact and has solid data to work with. Score it simply to see if it’s realistic. Check the difficulty, cost, data quality, and expected benefits. Figure out who’s in charge and who will use it. Set KPIs that match your goals, and note any early risks — like privacy rules or other must-dos.
Phase 2 — Architecture
For this, simply choose a blockchain that matches what you are trying to achieve. It could be a public network, a Layer 2 platform, or an enterprise system. Pick the AI models you intend to use and work out the level of compute they will require. Plan how data will move through the system and identify the points where privacy controls must be applied.. This is also the time to address compliance, access rules, and basic governance. Tools such as Hyperledger frameworks, IPFS, or data catalogues can support these tasks. This phase creates the foundation that everything else depends on.
Phase 3 — Development
Build the data pipelines, train or adjust the model, and connect it to the blockchain through the appropriate contracts or agent tools. HuggingFace, Hardhat, Hyperledger Fabric, and Ocean Protocol libraries are commonly used during this stage. The testing stage should cover accuracy, privacy, system security and on-chain behaviour. Regular checkpoints help confirm that the project still aligns with the KPIs defined in the strategy phase.
Phase 4 — Pilot and Iterate
Next, run a pilot with a small group of users or a limited dataset. Make sure to monitor the system's behavior and compare the results with your KPIs. Gather feedback from both technical staff and operational teams. Note any slow points, workflow issues, or areas where the model struggles. Use what you learn to adjust the design, improve governance, and prepare the organisation for a wider rollout. This is also the stage where training and readiness work normally begin.
Phase 5 — Scale
Once the pilot delivers steady results, expand the system to more users and larger datasets. Add new features as needed and formalise the processes that will support long-term use. Introduce business models that can sustain compute, storage, and maintenance costs. Ongoing improvements are essential. Regular checks, audits, and updates help the system remain consistent with your goals and with regulatory expectations.
Decentralized GPU Networks and AI Compute Markets
Decentralized GPU markets are emerging as a critical solution to AI’s rising compute demands. These networks provide cost effective access to GPUs that would otherwise be controlled by large cloud providers.
Why GPUs are the new oil
Training modern models is expensive. Stable Diffusion XL, for example, costs around $514 per week to train on AWS. Costs climb quickly as models grow larger. Decentralized GPU markets reduce these expenses and widen access to powerful hardware.
Cost Comparison
| Provider | GPU Cost/hour | Weekly Model Training Cost |
|---|---|---|
| AWS EC2 | ~$3.00 | ~$514 |
| Akash Network | ~$0.50 | ~$84 |
| io.net | ~$0.39 | ~$65 |
Why this matters
Lower compute costs democratize AI development and reduce dependency on large cloud platforms. They also support agent ecosystems, decentralized AI applications, and new research models. As computing becomes more accessible, innovation expands across more teams and regions.
Future of Blockchain-AI Convergence
As blockchain and AI evolve, their convergence will influence how digital systems operate in the decade ahead. Understanding the early trends helps teams prepare for changes in data, applications, and trust models.
Emerging Trends
Several early signals point to where the space is heading. Work on quantum-resistant cryptography aims to secure systems against future threats. Decentralized AI networks are gaining traction as a way to share compute and models without relying on a single provider. Agent economies are starting to form as autonomous services interact and trade on their own. On-chain provenance tools will help confirm the source of AI models and datasets. If you take a step back, it’s clear where this is headed. Data, computing, and AI will work together across networks — faster, safer, and more openly than ever.
Industry Impact
Power will move away from centralized technology providers as decentralized systems become more capable. Tokenized AI services and distributed data markets will create new economic models. Organizations will unlock efficiencies through automation, transparency, and intelligent decision-making.
Preparing for What’s Next
Teams that want to stay ahead can’t just focus on one thing. They need a mix of skills, the right tools, and some clear rules for what’s okay and what’s not.
Innovation sandboxes are great for this — a place to tinker, test, and experiment without breaking anything.
The teams that start early get the real advantage. They’re not just reacting when things converge — they’re riding the wave, ready for whatever comes next.




