Editor's note: The Matic Network is now known as Polygon.
The Matic Network (MATIC) is a project that’s been working on a solution to the scalability issues of the Ethereum blockchain.
Their vision is to improve scalability through proof of stake sidechains, and they believe that once scalability issues are resolved we’ll also get lower transaction fees, faster confirmations, and a number of other benefits. They are also one of the latest ICOs to be conducted on the Binance Exchange Launchpad.
Yet, how is this project different from the other scalability solutions?
In this Matic Network review I will take an in-depth look into the project and attempt to answer this. I will delve into their tech, development, roadmap and the long term potential and use cases for the MATIC token.
Matic Network Goals
In addition to solving scalability issues, the Matic Network is also focused on improving usability without losing the benefits of decentralization. They also hope to leverage the existing developer community in providing improved dApp functionality and improved user experience.
The founders of the Matic Network noticed that even though dApps are being proposed and developed in large numbers, the networks they run on are hardly prepared to support mass adoption of dApps. Plus in many cases, the user experience is quite poor, and the dApps are not designed to be approachable for the average user.
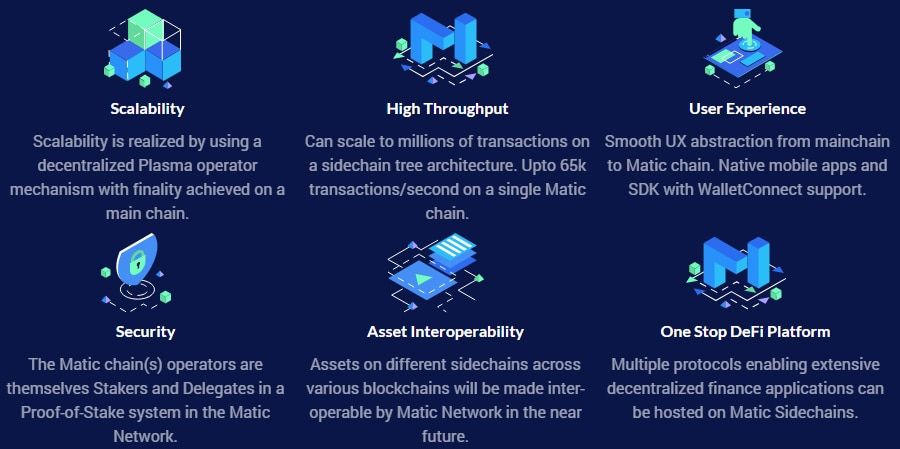 Overview of the Matic Network. Image via Matic.network
Overview of the Matic Network. Image via Matic.networkThe first blockchain chosen to highlight the potential of Matic is Ethereum. The developers began with a working implementation on the Kovan testnet. While it is an adapted version of the Plasma network, ultimately the Matic development team envisions using it as a side chain scaling solution for any blockchain.
In 2019 the team was able to first launch an alpha mainnet in June, which was the first Matic sidechain working on top of the Ethereum mainnet, which allowed developers to begin building and testing dApps. That wasn’t the end though. In September the beta mainnet went live as well. This included new features such as Heimdall, Bor and Plasma predicates.
Below is a deeper look at the problems of current blockchains and how the Matic Network plans of solving them.
Addressing Blockchain Challenges
Despite how advanced blockchain technology has become, there are still a number of problems that they face. In some cases, trying to improve one challenge could lead to potential sacrifices on other features.
The Matic Network has taken stock of all of the challenges that blockchains currently face and have attempted to address these through a number of solutions.
Scalability
Scalability can be achieved by adding additional side chains horizontally, with each side chain theoretically adding the capacity for 216216 transactions per second using the same proof-of-stake checkpoint layer. This gives the Matic Network the ability to scale to millions of transactions per second.
Size of Blockchain
Because public blockchains require each node to manage a full copy of the blocks and state of the chain, as time goes by and the blockchain grows larger, fewer nodes tend to participate, which threatens the decentralization of the blockchain.
In the case of the Matic Network, it is possible for the primary layer to store only the blocks from the last checkpoint to the most recent checkpoint. It can do this because all the prior blocks have been submitted to the main chain. This allows even mobile devices to run a node.
Slow Transactions
In most cases, blockchain transactions are slow, especially when it comes to proof-of-work blockchains. Matic uses Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to avoid this limitation, but in a special way so it is also able to maintain decentralization.
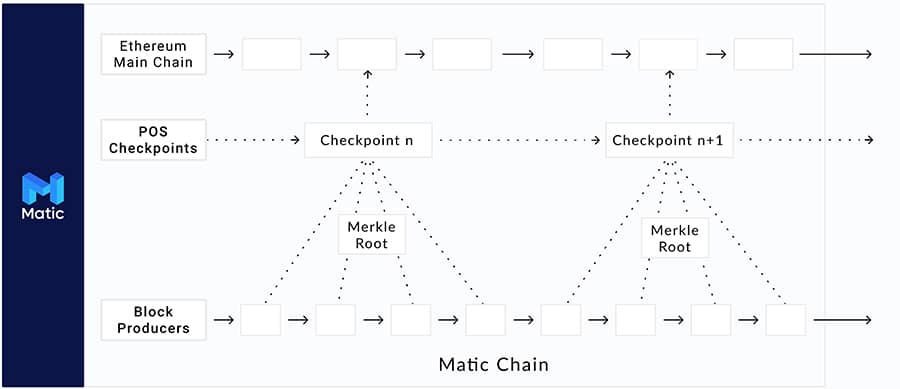 Matic Network Architecture. Image via Whitepaper
Matic Network Architecture. Image via WhitepaperIn the Matic Network consensus is done through a selection of block producers who are chosen by a set of stakers. Matic then uses proof-of-stake as a layer that validates blocks and publishes Merkle roots of the side chain blocks to the Ethereum mainchain. This allows Matic Network to keep block confirmation times under 2 seconds while also providing a high level of decentralization.
Low Transaction Throughput
In public blockchains, there is always a lag between blocks as there needs to be enough time between blocks to ensure propagation. Block sizes are also intentionally kept small to encourage rapid propagation. This limits the number of transactions per block.
Matic Network avoids this problem by producing blocks in a Block Producer layer. This allows for the rapid creation of blocks, and decentralization is ensured through the use of proof-of-stake checkpoints. This configuration theoretically allows for 216216 transactions per second on each side chain.
Multiple micropayment channels with other off-chain solutions
Solving the problem of opening multiple channels to allow for micropayments is complex, and several projects have proposed solutions. The Matic Network has solved this issue by using an Ethereum Virtual Machine, which negates the need to open payment channels for micropayments.
Instead, any valid Ethereum address is also a valid Matic address, which means any receiver doesn’t need to be in the Matic Network. They only need a Matic Wallet to retrieve the payment.
High Transaction Fees
The limited block size of most blockchains has led to variability in fees based on the pending transaction pool, and in some cases, fees have become exorbitantly high for periods of time.
Matic is able to take advantage of economies of scale by completing a large number of transactions in the Block Producer layer. This keeps costs for each individual transaction low.
Poor Usability
So far most dApp user interfaces are quite poor compared to established centralized counterparts. This needs to change. If mass adoption is to occur the dApp user experience needs to be as good as, or better than, the current centralized apps.
The Matic team is working to create mobile and web browser integrations and protocols to improve usability in a secured interaction environment for dApps.
The MATIC Wallet
The team at MATIC has been working on a wallet that aims to bridge the gap between scalability issues and the user experience of the Ethereum network. The wallet plans to make it easier for users to interact with the dApps that are deployed on Ethereum and Plasma chains.
The wallet will significantly increase transaction speed by allowing access to two different networks at the same time. Additionally, it permits connecting desktop Dapps to mobile Wallets using end-to-end encryption as simple as by scanning a QR code. This allows for user interaction with dApps without the private key leaving their device.
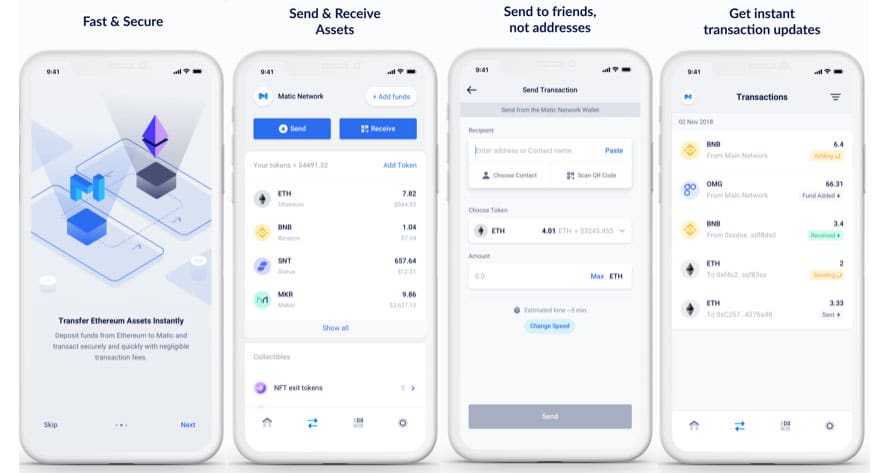 Matic Mobile Wallet UI. Image via iTunes Store
Matic Mobile Wallet UI. Image via iTunes StoreThe MATIC wallet currently remains in beta and the team is cautioning everyone not to send mainnet tokens to the wallet or they will be lost. Anyone who downloads the wallet now, there are both Android and iOS versions available, will receive MATIC test tokens.
Taking a bit of a closer look at the reviews of the wallet, they are pretty average. Users seem to be taking issue with the fact that the wallet forces either fingerprint access or Facial idea. This is a particularly sticky point especially for privacy hawks in the crypto field. It is also slightly troubling that the Matic support team has not responded to any of these questions.
Matic Dagger
Another really interesting product in the Matic suite is Dagger. This is basically infastructure which provides reliable and scalable real-time events. You can think of it as akin to an offchain solution where information needed within a dApp is fed from.
What's really neat about Dagger is how easily it can be integrated with your current dApps. Very few lines of code are required in order to get any event stream from the Ethereum blockchain. All of the integration code can be obtained from their Javascript library in their GitHub.
 Matic Dagger Unique Selling Points
Matic Dagger Unique Selling PointsDagger also helps you to engage with your users when they are offline. Essentially, you can listen for user specific events 24/7. Once these events come through you can send notifications via email or DMs to make the apps more user friendly.
Potential use cases for this? Well, you can use it to ensure the safety of your users and notify them in case their are any suspicious transactions. This could help them react almost instantaneously.
Matic Network Team
The Matic Network team remains quite small, consisting of the three co-founders, eight engineers, a head of operations and one community manager. The project has also added a pair of Operations & Marketing VPs in the past year, a VP of Finance and Operations, and several individuals whose focus is the design including a Head of Design.
Jaynti Kanani is the CEO and one co-founder of Matic. He comes from a software engineering background and was most recently a data scientist at Housing.com.
Sandeep Nailwal is the COO of Matic and a second co-founder. In addition to working as a blockchain developer he also previously held the position of CEO of Scopeweaver, and CTO (E-commerce) of Welspun Group.
 Matic Network Co-founders
Matic Network Co-foundersAnd finally, there is Anurag Arjun, who is the third co-founder of Matic and the CPO (Chief Product Officer). His background is in engineering and he has over a decade of product management experience.
The Matic Network is also partnered with several important blockchain projects, including MakerDao and Decentraland. In addition, Ari Meilich and Esteban Ordano, the CEO and CTO of Decentraland serve as advisors to the project.
Matic Marketing and Social Networks
While Matic has a good group of partners and advisors, and it is notable that they’ve been chosen to launch their ICO on the Binance Launchpad platform, they have very poor social media presence.
On Reddit, which is known as one of the top social platforms for crypto, the Matic Network has grown from just 13 readers in April 2019 to 1,600 readers in March 2020. The YouTube channel has over 1,300 subscribers, and the Twitter account has grown to 32.5k followers since in the 11 months from April 2019 when there were only 2351 followers.
Matic also has a Medium blog, which was previously updated once a month or every few weeks. It’s been updated more frequently recently, and the team has been doing a good job in keeping the community updated on developments from the project.
The largest group of followers is the project’s Telegram channel, where there are more than 30,000 members.
Taken all together, there has been huge growth in the social presence of the Matic Network in 2019, highlighting just how strongly people have gotten behind the project.
MATIC Token
The Matic Network conducted an ICO on the Binance Launchpad platform on April 24, 2019. Unlike a typical ICO where tokens are simply sold, Matic conducted their ICO as a lottery, with a total of 16,666 winning lottery tickets.
There is a total supply of MATIC of 10,000,000,000 and 19% of that, or 1,900,000,000 were made available for the ICO. That means each winning lottery ticket received 114,068.44 MATIC, which was $300 worth at the ICO price of $0.00263.
 Register on Binance to Participate in IEO
Register on Binance to Participate in IEOLottery tickets were allocated based on each users BNB balance, with the final calculation occurring at 00:00 UTC on April 24, 2019. Ticket claims for eligible users begans at 08:00 UTC on April 24, 2019 and continued for 24 hours.
Once the ticket claim period ended the winning tickets were drawn and announced at 14:00 UTC on April 25, 2019. Payments were made in BNB within 24 hours with users ensuring they had sufficient BNB in their account if they had a winning ticket.
The MATIC tokens will allow holders to become stakers and receive staking rewards once staking is implemented on the network. As network usage increases the value of MATIC tokens is expected to increase commensurately.
MATIC Price History
Following the ICO, in which MATIC tokens were priced at $0.00263, the price took off like a rocket to the moon. In less than one month, by May 21, 2019 price had reached an all-time high of $0.045017.
Of course price didn’t remain at those elevated levels, but it also didn’t sink all the way to ICO levels. In fact, price hasn’t dropped below the $0.01 level, although it did come close in October 2019.
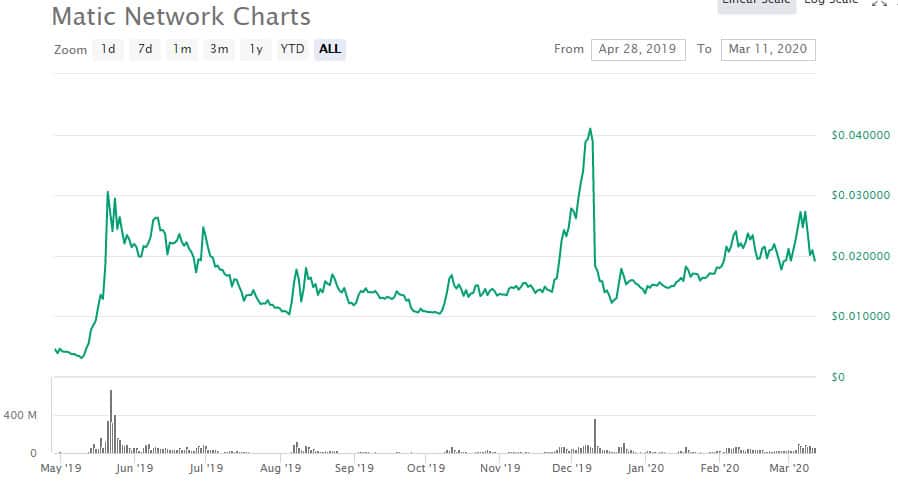 MATIC Price Performance. Image via CMC
MATIC Price Performance. Image via CMCDecember 2019 saw a huge spike that took price from $ 0.012603 to $0.042440 in the span of two weeks, however a week later price had given back all those gains. There was no fundamental reason for the rise or crash, and some have said it was all due to market manipulation.
As of February/March 2020 MATIC has been marching higher again, lifted first by news of staking going live on the testnet, and then a week later by the Indian Supreme Court lifting the ban on Bitcoin and cryptocurrency trading in India. As of March 11, 2020 the MATIC token is trading just above the $0.02 handle
Matic Network Strengths
One of the strengths of the project is the broad number of available use cases. These include decentralized exchange, identity features, credit scoring, atomic swaps, payments, and gaming networks among others.
One very interesting feature Matic has been developing is Zappier integration through Dagger. This allows developers to connect Ethereum platforms with hundreds of applications and is expected to help boost user and developer adoption.
Development
Something that I am quite interested in when looking at cryptocurrency projects and ICOs is the amount of development work that is being done. One of the best ways to assess this is through the amount of code commits they have pushed in to their public GitHub.
So, I decided to dig into the Matic Network GitHub and take a look at the code commits that have pushed. These are only the repos that they have made public and there are many more that are still being worked on. Below are the commits for the top two most active public repos.
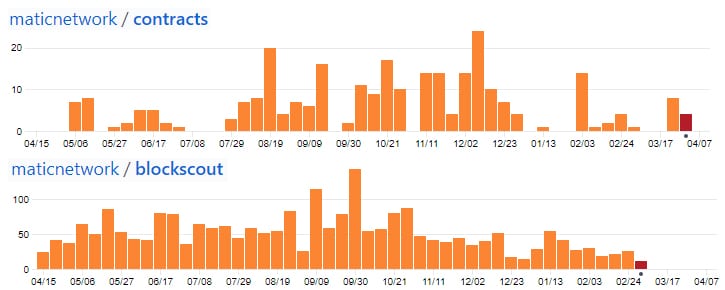 Code commits to repos in past 12 months
Code commits to repos in past 12 monthsAs you can see there has been quite a bit of activity in these repos. This is in fact more than we have seen on other projects that have completed their ICO 2 years ago. There are also a further 13 other public repos.
Moreover, it is important to point out that these are only their public commits to their main GitHub. According to this Binance Rating Report, they are working on a further 17 private repositories that have plenty more code.
All this shows that the Matic Network is indeed actively rolling out product and working on their protocol. This should be seen as another pro of the project when compared to other ICOs.
This frenetic pace of development can be considered reasonable when one is to look into their updated roadmap.
Conclusion
Matic is focused on improving the scalability of Ethereum in an adapted Plasma network. Because scalability is so important to the Ethereum network there are several competing projects aiming to do the same, but if Matic can deliver a solution first, or the best solution, they stand to become one of the top blockchain projects.
It was encouraging to see MATIC growing its community rapidly in 2019. It not only shows the ability of MATIC to market its product, but also shows the belief and support from the community. And of course the ruling of the Indian Supreme Court in March 2020 that lifted the ban on cryptocurrency trading is ultimately a positive for Indian blockchain projects like MATIC.
The mission of Matic hasn’t been proven yet, but development on the testnet, and both alpha and beta mainnet implementations seems positive. One thing the project could use is the implementation of staking. They’ve been promising this since the beginning, and actually implementing it could bring a whole new group of MATIC users and investors.



