Given the general sentiment about government actions lately and their portrayal in the media, the argument for using blockchain to enhance transparency is compelling. In a climate where trust in government is wavering, especially within the “crypto twitter” community, blockchain technology offers a promising solution.
So, where do we stand in terms of progress in this area? What are the recent breakthroughs, and who is driving them? More critically, what challenges do we face?
This article explores the applications of blockchain technology in government and aims to answer why it is an appropriate solution for enhancing government transparency. We'll delve into various applications, potential hurdles, and important factors to consider, while reviewing interesting examples of blockchain being tested in government systems. This will provide a clearer understanding of how blockchain could improve public sector operations.
The Importance of Transparency and Accountability in Government Processes
Government corruption is a global issue that undermines societal trust, economic stability and public services. The Transparency International's 2022 Corruption Perceptions Index revealed that most countries are struggling to combat corruption. The index ranks 180 countries and territories by perceived public sector corruption on a scale from 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean). The global average score has stagnated at 43 out of 100 for over a decade. Over two-thirds of countries scored below 50, and 26 countries have reached their lowest scores to date. Despite some efforts and progress, 155 countries have either made no significant headway or have worsened since 2012.
Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to enhance transparency and accountability, particularly in public procurement. Its ability to maintain immutable records is especially effective in areas where corruption is rampant. Several African countries are adopting blockchain for this very reason.
Blockchain, as a decentralised ledger, distributes entries across a network, diminishing the chances of corruption and unauthorised alterations by eliminating any single point of failure or control. Each transaction is verified and agreed upon by consensus before it is permanently added to the blockchain, ensuring the process remains open to scrutiny by all stakeholders, which increases accountability.
Essentially, blockchain creates a tamper-proof record of transactions, enhancing data security and ensuring that records are permanent. This is important for auditing and tracking government activities and spending, particularly in areas like land registries, legal documents, and licensing, where maintaining data integrity without the risk of unauthorised changes is essential.
 Image via Africa Briefing
Image via Africa BriefingApplications of Blockchain in Government
Here are a few applications of blockchain tech in the government:
Public Procurement
Public procurement is the process by which government entities purchase goods, services, and works from external suppliers, ranging from office supplies to large-scale infrastructure projects. This process is essential for public sector organisations to function effectively and deliver services. The idea is that the government is guided by principles like competitiveness, efficiency, and fairness, which help secure the best value for public money.
The process involves stages such as planning, tendering, evaluating bids, awarding contracts, and managing these contracts. Each stage is regulated by specific laws and regulations that ensure all procedures are fair and open to scrutiny. It represents a significant part of a nation’s economy and is essential for achieving cost savings and optimizing resource use, impacting government efficiency and the quality of public services. This makes the integrity and effectiveness of the process critical for good governance and maintaining public trust.
The fact that bribery significantly impacts the financial integrity of public tenders shouldn’t be too surprising, but what might be shocking is that in many cases, corruption and mismanagement can account for 8% to 25% of a tender's total value.
This corruption inflates government costs, hinders economic development, and exacerbates socio-economic disparities. Several high-profile cases illustrate these issues vividly. In 2015, the Nigeria arms procurement scandal revealed that funds intended to combat Boko Haram were misappropriated, involving government officials and private entities who diverted billions meant for arms procurement.
Similarly, South Africa faced a major scandal involving a £927 million arms deal corrupted by bribes, leading to a public uproar and a subsequent commission of inquiry. Also of note, the emergence of the term “covid-entrepreneurship” during the pandemic highlighted how emergency procurement processes were exploited for corrupt gains — a scandal in Kenya in 2020 uncovered gross overpayments for PPE (personal protective equipment), with government officials paying more than double the market value for 100,000 kits.
As mentioned, the significant vulnerability to corruption is unsurprising, given the large financial transactions and complex processes that typically require close interactions between government officials and businesses. Given our understanding of blockchain technology, it's clear that its inherent qualities can significantly curb corruption. Blockchain helps prevent malpractices such as bid tampering and unauthorised alterations by ensuring a tamper-proof record of all transactions.
 Image via Reuters
Image via ReutersProperty and Land Registry Systems
Property and land registry systems are official records managed by governments or authorised bodies that store detailed information about land and property ownership along with associated rights. These systems serve as the backbone for legal ownership validation, supporting real estate transactions, and maintaining property rights.
The primary role of these systems is to document who owns a piece of land or property, including specifics like the exact boundaries and any rights or conditions linked to it. They also keep track of any rights, restrictions, or obligations related to properties, such as easements or liens. This comprehensive registration aids in resolving disputes and facilitates transactions by ensuring that all parties have access to accurate and up-to-date information.
These registries are extremely important for real estate transactions since they provide essential information that helps prevent fraud and ensures that transactions are conducted between rightful owners. Many systems allow public access, allowing individuals and companies to confirm property details and ownership, which helps in making informed decisions.
How can blockchain help here? Traditional property and land registry systems often suffer from inefficiencies due to manual processes and the potential for human error or corruption. Blockchain technology can streamline these processes by automating and securely recording transactions, ensuring that property rights are protected without the need for prolonged verification steps. Real-world examples include Rwanda's "Irembo" platform, which utilises blockchain to digitise public services, including land registration, enhancing efficiency and minimising corruption risks.
 Image via IremboGov
Image via IremboGovVoting
The potential benefits of blockchain for voting are particularly clear. Transparency in voting holds significant importance in discussions about government transparency, as electoral processes are fundamental to democracy. Unlike other aspects of government operations — where transparency might focus on clarity in spending, policy decisions, or regulatory measures — transparency in voting digs deep into the heart of public trust.
Here, the concerns often venture into more sensitive territory, fueled by conspiracy theories and scepticism about the integrity of vote counting and electoral fairness. These concerns are less about procedural clarity and more about existential fears regarding manipulating democratic will.
Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to these electoral issues by providing a system that inherently records all transactions (or votes) in a secure manner. As mentioned, every transaction on a blockchain is timestamped and linked to the previous one, creating a chronological chain that is virtually impossible to alter without detection. This means that once a vote is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted secretly, thereby addressing common concerns about the integrity of the voting process.
Now, while blockchain won't solve all issues related to electoral mistrust — such as who has access to vote or the influence of misinformation — it can significantly enhance the mechanical transparency of the voting process itself, potentially reducing uncertainties and undermining the base for conspiracy theories around the counting and recording of votes.
Consequently, some countries have explored blockchain technology in their voting systems to some extent. One notable example is Estonia, which implemented a digital voting system in 2005. This not only increased security but also voter turnout.
The system utilises complex cryptographic techniques to ensure that votes are anonymous and tamper-proof, providing a double layer of security that is hard to achieve in traditional paper or electronic voting systems. Although Estonia's e-voting system isn't entirely based on blockchain, it incorporates blockchain-like technology for security enhancements, ensuring that votes are immutable once cast and providing a reliable audit trail.
Similarly, South Korea has also experimented with blockchain voting. In 2018, the South Korean government announced a test of a blockchain-based online voting system. As seems to be the trend, it was implemented to address public concerns about electoral integrity.
It is also worth noting that West Virginia became the first state to pilot blockchain technology in federal elections in the United States. In 2018, it allowed deployed military personnel and overseas citizens to vote via a mobile app utilising blockchain to record votes securely. This pilot explored how blockchain could simplify the voting process for citizens living abroad. However, it did face scrutiny and mixed reviews regarding security and broader applicability.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockChallenges and Considerations
Implementing blockchain in government settings requires supportive policy changes, legal adjustments, and strengthened governance frameworks for effective deployment. Additionally, civic engagement and public oversight play important roles in enhancing the effectiveness of blockchain solutions.
Furthermore, successful blockchain adoption demands strong collaboration among government agencies, industry leaders, and technology providers. This partnership is important for developing standards and solutions that address public sector needs while advancing innovation in blockchain applications. Such collaborative efforts are also key to adapting blockchain technology to the unique regulatory and operational environments of government functions.
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several technical and operational challenges, such as integrating existing systems and ensuring vendor privacy. In particular, maintaining bid anonymity while ensuring transparency and accountability poses a complex challenge. Solutions such as using hybrid blockchain systems, where hashes of bids and tender offers are recorded on a public blockchain and other functionalities are managed on a permissioned blockchain, have been suggested to mitigate some of these challenges.
Another challenge regarding on-chain voting involves potential vulnerabilities noted by experts from MIT and Harvard. These vulnerabilities include susceptibility to hacking. These experts also highlighted the risk of disruption from multiple versions, or forks, within public blockchains, which could create confusion about which version of the chain is authentic.
They also reiterate potential technical issues such as the scalability of systems to accommodate large numbers of voters and the digital divide that may prevent less tech-savvy individuals from participating in blockchain-based elections. There's also the critical concern of ensuring that voter privacy is maintained while using a technology that inherently creates a public ledger of transactions. It is important to note that this study was conducted a few years ago, and the technology has advanced significantly since then. It is likely only a matter of time before the benefits substantially outweigh the drawbacks.
Nevertheless, despite these challenges, blockchain offers a huge promise. If implemented thoughtfully, it can help conduct more secure, transparent, and inclusive elections, ultimately leading to greater democratic engagement.
Closing Thoughts
In an effort to enhance government operations and build trust between citizens and their government, blockchain seems like a no-brainer. It offers transparent, traceable, and secure recording of governmental actions, allowing for increased citizen oversight of public officials, all while reducing operational costs. Who wouldn’t want that (outside of a few Kenyan officials)?
Its ability to secure an unchangeable log of all transactions significantly reduces the possibilities for corruption and unauthorised changes. Further, the decentralised nature of blockchain means that no single entity can control or alter data, thereby upholding the integrity of government operations.
Finally, to leave things on the brightest of notes, it was just announced yesterday that El Salvador has launched its own platform that provides public access to BTC investment data via a personalised mempool.
This is what we’re talking about!
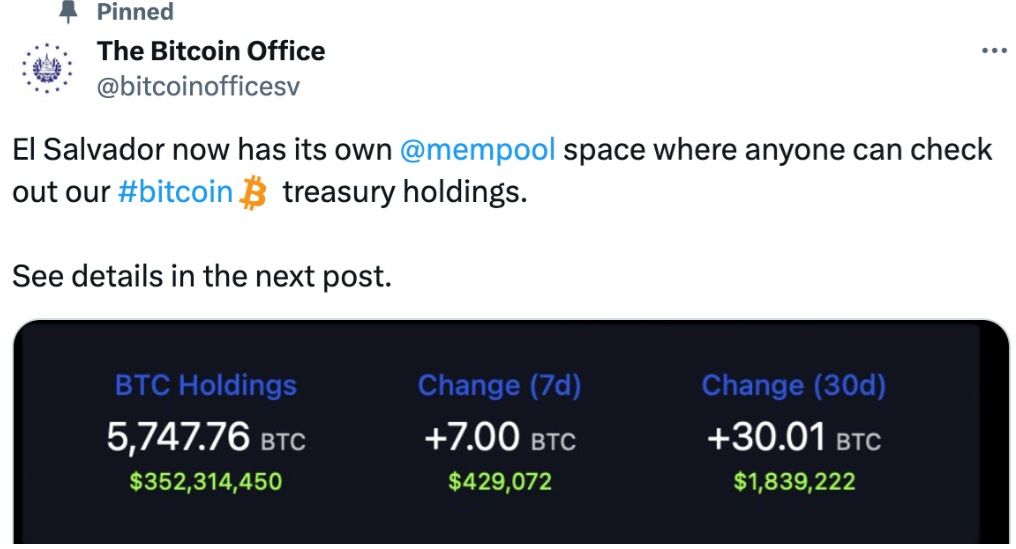 Image via X
Image via XEl Salvador's proactive approach exemplifies the core advantages of blockchain for enhancing governmental transparency — every transaction is logged and available for public viewing.
This scenario hints at a broader trend: Blockchain technology could fundamentally transform governmental operations worldwide, enhancing transparency and trust.
It really seems like we are on our way…





