Welcome to the dynamic world of Base, a new Layer 2 blockchain developed by Coinbase. Within its first year, Base has not only captured the imagination of the crypto community but has also amassed a Total Value Locked (TVL) of over $1 billion. This rapid ascent is a testament to its robust foundation and growing popularity. In this article, we delve into a curated list of the most exciting decentralized applications (Dapps) on the Base network—from groundbreaking new projects to a few established powerhouses. Join us as we explore these innovative Dapps that are setting the pace on one of the most promising platforms in the blockchain space.
Understanding Base
Base is an Ethereum layer 2 blockchain built with the Optimism OP Stack. To understand the nuances of Base, let’s learn a little more about the OP Stack, you can also check out the Base Review on the Coin Bureau. On June 6, 2023, Optimism released the Bedrock upgrade to improve the Optimism architecture for performance and compatibility with Ethereum. Key aspects of the upgrade include:
- Modularity and Simplicity: The upgrade introduced a more modular and simple architecture, making it easier for developers to interact with and build on the network.
- Ethereum Equivalence: One of the central features was achieving closer equivalence with Ethereum, improving compatibility and integration with Ethereum's tools and protocols.
- Performance Improvements: The upgrade aimed to increase the network's performance by optimizing transaction processing and reducing latency.
- Cost Reduction: It significantly lowered the gas fees and operational costs associated with transactions on the Optimism network.
Overall, the Bedrock upgrade was designed to position Optimism as a more robust, efficient, and user-friendly Layer 2 solution, enhancing its role within the Ethereum ecosystem.
The OP Stack
The Bedrock upgrade also includes the OP Stack, a suite of tools and protocols developed by the Optimism Collective to empower Optimism and to enable the building of new layer-2 chains on Ethereum. The OP Stack is similar to the Cosmos SDK in function, it is a set of blockchain layers that developers can plug-in to construct new chains seamlessly.
 The OP Stack: Image Source: Optimism Docs
The OP Stack: Image Source: Optimism DocsComponents of the OP Stack
The OP Stack is a sophisticated architecture designed by Optimism to enhance the scalability and functionality of blockchain operations, leveraging different layers and mechanisms to streamline transaction processing and state management.
- Data Availability Layer: This layer is pivotal in defining where transaction data for an OP Stack-based chain is published. It influences the security model significantly, as the availability of data directly affects a chain's ability to keep running live. The most widely used module here is the Ethereum Data Availability (DA) module.
- Sequencing Layer: This layer manages how transactions are collected and recorded onto the Data Availability modules. Initially, this is handled by a dedicated Sequencer, which under typical circumstances cannot withhold transactions beyond a certain period. Future enhancements propose more flexibility with multiple Sequencers, allowing dynamic selection and governance.
- Derivation Layer: Here, raw data from the Data Availability Layer is processed into a format usable by the Execution Layer. This includes parsing Ethereum block data, Sequencer batches, and more. A proposed Indexer module would further optimize how transactions interact with smart contracts on Ethereum.
- Execution Layer: Fundamental to the structure of state within an OP Stack system, this layer defines how state transitions occur based on inputs from the Derivation Layer. It can support various modifications of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to accommodate Layer 2 transactions and its additional tokenomics.
- Settlement Layer: This read-only mechanism establishes how external blockchains view the state of an OP Stack chain. It's crucial for processes like withdrawals, where verifying the state on a third-party chain is necessary before executing transactions. Various settlement mechanisms, including Attestation-based Fault Proof and proposed Validity Proof Settlement, offer different levels of security and trust assumptions.
- Governance Layer: This encompasses the tools and processes for managing system configuration and upgrades. Governance can be implemented through MultiSig contracts or decentralized through Governance Tokens, allowing stakeholders to vote on key decisions.
Applications and Examples
The architecture of the OP Stack can significantly enhance applications like decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, where rapid and secure transaction processing is critical. For example, a DeFi application can benefit from faster transaction sequencing and enhanced security through robust settlement mechanisms, ensuring user transactions are processed efficiently and securely.
Additionally, the flexibility in governance and state management allows for seamless upgrades and integration of new features, making it an ideal backbone for evolving blockchain-based applications that require adaptability and robust performance.
The Base layer 2 platform, developed by renowned cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase in collaboration with Optimism, leverages different layers of the OP Stack to build a robust layer 2 platform that is Ethereum equivalent, fast, secure, and interoperable with the vast Ethereum ecosystem.
Benefits of Base
Optimism’s superchain is a network of chains developed with the OP Stack that leverages the network effects of Optimism. These are Ethereum layer-2 chains that share a cross-chain communication protocol.
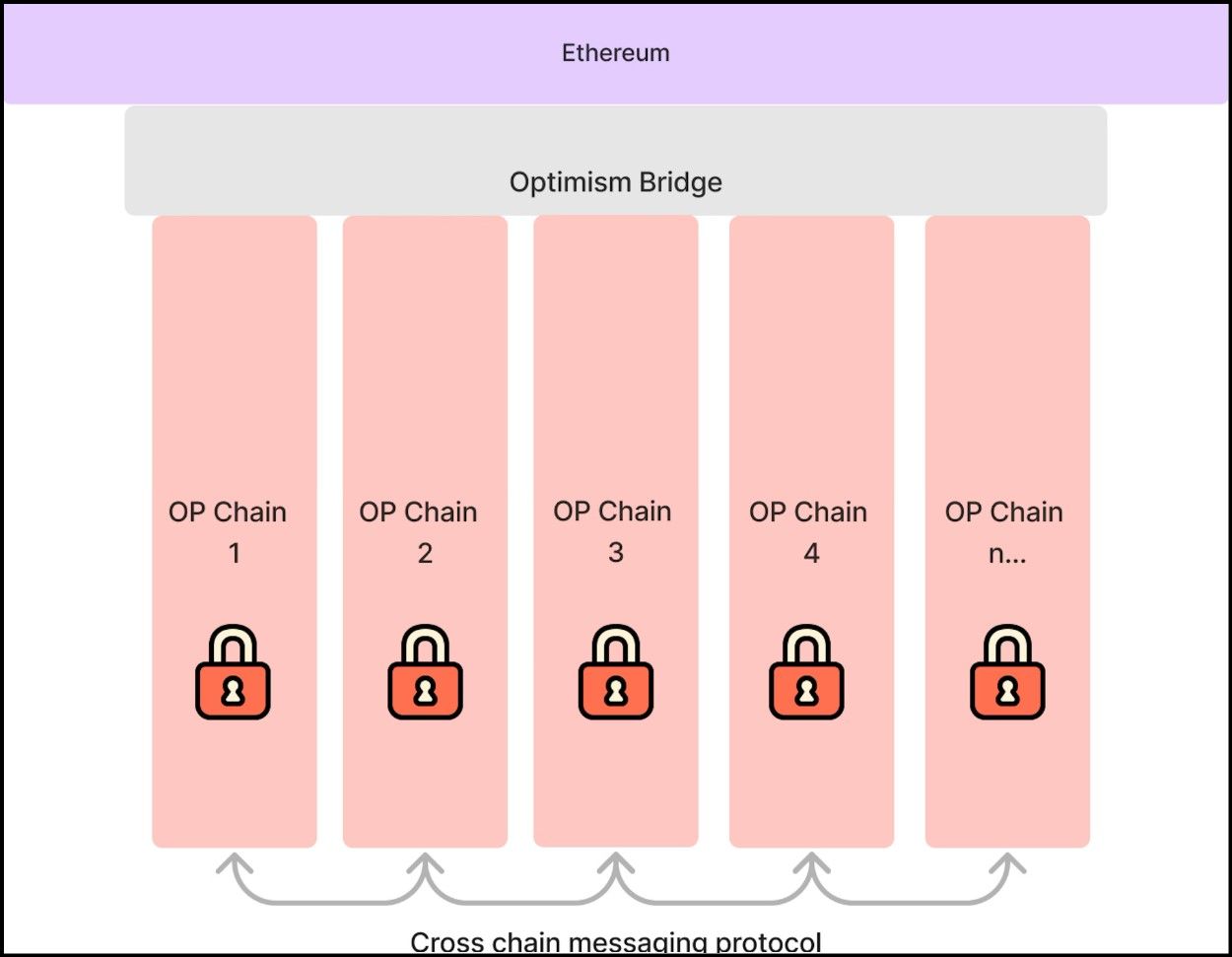 The Superchain Design | Image via Optimism Docs
The Superchain Design | Image via Optimism DocsThese chains share a communication layer that lets them seamlessly exchange information with one another, including token interoperability, cross-chain smart contract calls, and arbitrary information.
As a network of Ethereum layer-2 chains, they also inherit security from a common layer. Therefore, a Superchain is a network of OP Stack layer-2 chains; any operation on the chain can simultaneously interact with any other cross-chain operation such that they operate as a cohesive network. Optimism Superchain aims to achieve chain abstraction, where the source blockchain of any application is irrelevant because the chains communicate so efficiently with one another.
Possible benefits to the Base blockchain as a part of the Superchain include:
- Enhanced Scalability: As Optimism's Superchain is designed to handle a significantly higher throughput compared to traditional blockchain configurations, Base, built on Optimism’s technology, stands to gain from these scalability improvements. This would allow Base to support a larger volume of transactions and more complex applications, addressing one of the critical challenges in blockchain adoption—performance at scale.
- Greater Interoperability: The Superchain aims to foster enhanced interoperability between different blockchain networks. For Base, this could mean seamless integration with other chains within the Superchain ecosystem, facilitating the exchange of assets and information across different networks without the usual complexities and security concerns associated with cross-chain interactions.
- Improved Security and Decentralization: While Base benefits from Ethereum’s security through its Layer 2 nature, the Superchain vision includes further decentralization and security enhancements. These could provide additional layers of security for applications running on Base, making it a more robust platform for developers and users alike.
- Access to a Broader Ecosystem: The Superchain vision involves creating a more extensive network that includes various specialized chains. For Base, being part of this broader ecosystem means access to specialized services and features that can be integrated into its own offerings, potentially attracting a wider array of developers and users looking for specific functionalities that are optimized across different chains.
- Innovation and Flexibility: The modular and flexible nature of the Superchain allows for rapid innovation and adaptation. This environment could enable Base to quickly implement new technologies and features developed within the Superchain framework, staying at the forefront of blockchain technology advancements.
- Cost Efficiency: With the Superchain's design focusing on efficiency, Base could leverage these improvements to reduce the costs associated with transactions and smart contract executions. This is particularly advantageous for applications that require high transaction throughput with minimal fees.
Base DeFi Ecosystem
The Base ecosystem is relatively new. Having only launched in August 2023, the Base ecosystem is merely nine months old in May 2024, but hosts its fair share of new and established applications.
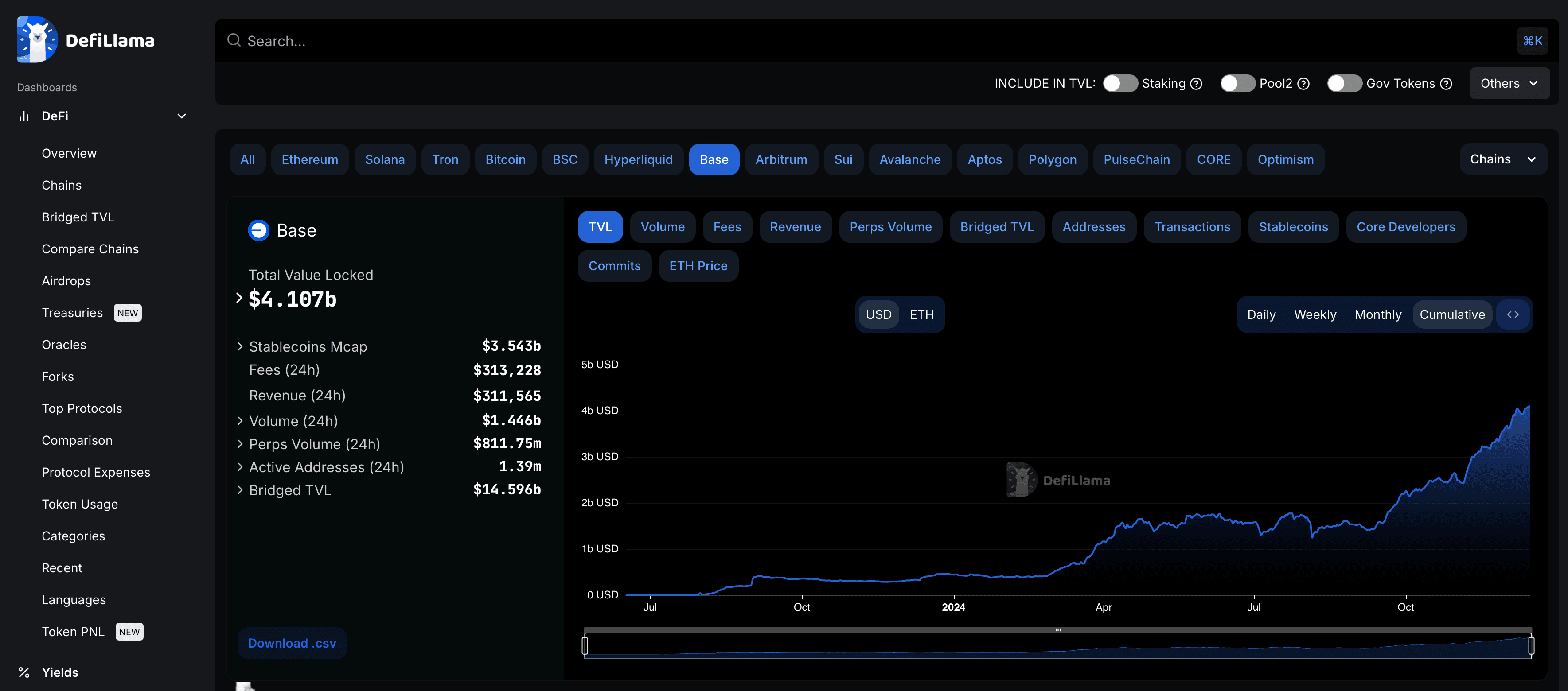 Base On-chain Stats via DeFiLlama
Base On-chain Stats via DeFiLlamaAs of December 2024, the TVL locked in Base values at about $4.1 billion. Base locked its first half a million fairly quickly, having achieved that milestone in just one month of its existence. The rise in the value locked in Base may also be attributed to the general rise in the price of digital assets following the rallies of Bitcoin in the first quarter of 2024.
Some well-known decentralized applications also live on Base include:
- Uniswap: Uniswap is one of the most prominent decentralized exchanges (DEX) based on Ethereum. It uses an automated liquidity protocol to facilitate non-custodial trading of different cryptocurrencies. By supporting Base, Uniswap can leverage lower transaction costs and higher throughput, making DeFi more accessible and efficient for a broader user base. Read our Uniswap Review to learn more.
- OpenSea: OpenSea is the largest marketplace for NFTs (non-fungible tokens), allowing users to buy, sell, and discover exclusive digital items. Integrating with Base could reduce gas fees and improve transaction speeds, enhancing user experience significantly in trading NFTs.
- Aave V3: Aave is an open-source and non-custodial liquidity protocol for earning interest on deposits and borrowing assets. Version 3 of Aave introduces more risk mitigation features, efficiency, and a more flexible architecture. On Base, Aave V3 can operate with greater scalability and lower costs, potentially increasing its adoption and usability. Read the Aave Review on the Coin Bureau.
- Compound V3: Compound is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that allows individuals to borrow or lend cryptocurrencies. The third version, often referred to as "Compound III," focuses on capital efficiency and security. Supporting Base can further enhance its scalability and lower the entry barrier for users due to reduced fees. You can learn more in our Compound Review.
- SushiSwap: Similar to Uniswap, SushiSwap is a decentralized exchange that offers additional features like yield farming. By supporting Base, SushiSwap can benefit from enhanced transaction speeds and reduced costs, improving the overall liquidity provision and trading process.
- Synthetix: Synthetix is a derivatives liquidity protocol that enables trading of synthetic assets on Ethereum. These synthetic assets mirror the value of real-world assets. Support for Base would allow Synthetix to scale its operations more effectively by taking advantage of lower transaction fees and higher throughput. Read the Synthetix review on the Coin Bureau.
- Stargate: Stargate is a fully composable liquidity transport protocol that enables instant cross-chain transfers. Integration with Base could enhance Stargate's capability to provide seamless liquidity transfers across different blockchains, improving the efficiency of cross-chain interactions.
- Balancer V2: Balancer is an automated portfolio manager and liquidity provider that allows users to create custom pools and trade tokens. Version 2 introduces improved gas efficiency and flexible pool types. Supporting Base helps Balancer V2 to reduce transaction costs and potentially attract more liquidity providers and traders.
- PancakeSwap: Initially launched on the Binance Smart Chain, PancakeSwap is a popular DEX known for its user-friendly interface and lower transaction fees. Support for Base would potentially open up PancakeSwap to a wider Ethereum-based audience, enhancing its cross-chain functionality. We have a dedicated PancakeSwap review if you want to learn more about the largest DEX on the Binance Chain.
- Synapse: Synapse is a cross-chain layer for moving assets between blockchains. Its integration with Base can improve the speed and cost-efficiency of bridging assets between Ethereum and other supported networks, enhancing user experience in multi-chain DeFi activities.
- Curve DEX: Curve is a decentralized exchange optimized for stablecoin trading due to its low slippage and fees. By integrating with Base, Curve can take advantage of the enhanced scalability and lower costs, making stablecoin exchanges even more efficient and appealing to users looking for minimal price impact trades. Learn more in our Curve Finance review.
Each of these platforms benefits from integrating with Base by leveraging its lower cost structure and higher transaction throughput capabilities, which can significantly enhance their performance and user experience in the decentralized ecosystem.
Top Base Dapps
Since we have already covered the most popular Dapps in the previous section, we will focus on some of the newer generation Dapps on the Base blockchain here. If you want Guy's take, feel free to check out his guide on how to find the next 100x on Base:
Aerodrome Finance
Aerodrome Finance wants to become the liquidity hub for the Base ecosystem. Interestingly, the economic model of Aerodrome is quite similar to that of Curve Finance, the liquidity hub of the Ethereum ecosystem.
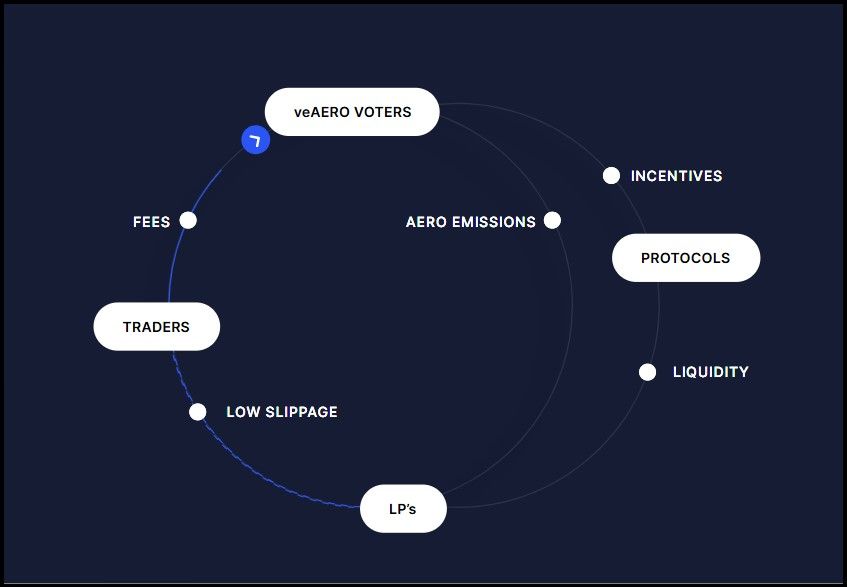 Aerodrome Protocol Design | Image via Aerodrome Docs
Aerodrome Protocol Design | Image via Aerodrome DocsIt focuses on optimizing liquidity provision efficiency and incentivizing protocol participation through governance tokens, rewards, and fee distribution. Here are some essential characteristics of Aerodrome:
- Liquidity Provision and Fee Generation: Aerodrome is designed attract liquidity to facilitate efficient token swaps, minimizing slippage. It generates fees from trading, which are distributed to the liquidity providers (LPs), providing fundamental economic incentives for liquidity provision.
- Token Emissions: Aerodrome’s use of $AERO token emissions to reward liquidity providers is quite similar to Curve’s use of $CRV tokens. In both protocols, these tokens are distributed proportionally to the amount of liquidity that users contribute to the pools. Furthermore, both protocols require liquidity to be staked in specific gauges or pools to be eligible for these emissions. This mechanism not only secures the liquidity within the protocol but also aligns the incentives of liquidity providers with the long-term health of the protocol.
- Voting and Governance: Similar to Curve, Aerodrome rewards $AERO token to pool LPs proportional to their votes. Governance requires $AERO token holders to lock their funds in a time-based contract to receive $veAERO, or vote escrowed AERO tokens. Contributors can use vote escrowed tokens for participating in Aerodrome governance. This system ensures voters with a genuine vested interest in the success of the protocol only participate in governance.
- Fee Distribution: Both Aerodrome and Curve distribute trading fees back to token holders who participate in governance. In Aerodrome, veAERO voters receive 100% of the protocol trading fees from the previous epoch as well as any additional voter incentives for the current epoch.
As of May 2024, Aerodrome manages a TVL of over $600 million, making it the most valued DeFi protocol on Base. About 45% of the chain’s total lacked value under one application.
Extra Finance
 Extra Finance Homepage
Extra Finance HomepageExtra Finance is a yield farming protocol on Base. It offers leveraged yield farming, where you can borrow additional funds from the protocol to amplify your returns from farming strategies. Extra finance offers up to 7x leverage on select deposits and allows users to customize faring strategies, including using liquid staking tokens.
Leveraged yield farming on Extra finance is particularly prominent in low-risk assets. Stable assets like stablecoins or LST tokens of established networks with a relatively manageable volatility curve tend to offer limited returns when being staked or farmed. Therefore, Extra finance lets users amplify their returns by offering leverage on such strategies while also keeping the risk under control due to the relative price stability of such assets.
EXTRA is the native ERC-20 token of Extra finance, and in typical farming protocol fashion, it is used to reward liquidity providers through token emissions. Similar to curve finance on Ethereum and Aerodrome on Base, Extra also employs a vote escrowed governance model. Anyone who wishes to contribute to protocol governance decisions must acquire EXTRA tokens and lock them in a time-bound smart contract to earn veEXTRA tokens, which measure their vote in governance decisions.
Beefy Finance
Beefy Finance is a DeFi protocol operating on over 26 chains (DeFiLlama). It is a yield farming protocol whose primary function is automated yield optimization. Beefy is a multi-chain yield optimizer that maximizes returns from yield farming by leveraging various multi-chain strategies.
 Beefy finance Homepage
Beefy finance HomepageWith support for several chains such as Ethereum, Binance Chain, Polygon, Base, Fantom, and many more, users’ funds can access opportunities across many networks, optimizing for returns, risk, volatility, transaction fees, and more. Here are some key features of Beefy:
- Multi-Chain Support: Beefy Finance supports a wide range of blockchains, including Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Ethereum, Polygon, Fantom, and several others. This broad compatibility allows users to access diverse DeFi opportunities across different networks from a single platform.
- Automated Yield Optimization: Beefy uses smart contracts known as "vaults" to automatically reinvest earned interest into the underlying liquidity pool. This compounding effect increases the efficiency of capital, potentially leading to higher yields compared to manual reinvestment.
- Diverse Investment Strategies: The protocol offers various investment strategies, each tailored to specific tokens and pools. These strategies are designed to manage risk and optimize returns by utilizing tactics such as staking, farming, and providing liquidity.
- High Efficiency: Beefy Finance optimizes gas costs and transaction timings to enhance the profitability of farming strategies. This operational efficiency is crucial on networks with high transaction fees.
- Community-Driven Governance: Beefy's governance is community-driven, with token holders able to propose and vote on changes to the protocol. This includes decisions about new strategies, adjustments to existing ones, and the overall direction of the platform.
- Security Measures: Beefy prioritizes security with regular audits conducted by respected firms in the industry. This is vital in maintaining user trust and protecting assets managed by the protocol.
The Beefy Token, $BIFI, is an ERC-20 token and native to the Beefy protocol. It serves two essential functions – protocol governance and stakeholder incentives paid through their incentive programs.
Moonwell
 Moonwell Homepage
Moonwell HomepageMoonwell is a lending and borrowing protocol operating in Base on Ethereum, as well as Moonbeam and Moonriver on Polkadot. It allows lenders to deposit their assets in single-sided liquidity pools that earn a variable interest rate. Moonwell supports the following assets:
- USDC (USD Coin)
- USDbC (USD Base Coin)
- DAI (Dai)
- ETH (Ethereum)
- cbETH (Coinbase Wrapped Staked Ethereum)
- wstETH (lido Wrapped Staked Ethereum)
- rETH (Rocket Pool Ethereum)
An interesting feature in Moonwell is “USDC Anywhere”. The feature enables cross-chain lending and borrowing USDC, allowing accessing USDC on Base from a variety of other networks. A neat aspect of this feature is that Circle’s Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP), which is USDC’s in-house cross-chain interoperability solution powers such USDC operations on Moonwell. Therefore, every unit of USDC on Moonwell is canonical, not requiring constant wrapping and un-wrapping of stablecoins by third-party synthetic token protocols and cross-chain bridges. This feature is available with the following networks:
- Base
- Ethereum
- Optimism
- Polygon
- Arbitrum
- Avalanche
The Moonwell protocol has two native tokens – WELL and MFAM. The WELL token is responsible for governance on Base and Moonbeam, while the MFAM token handles governance on the Moonriver network.
Overnight Finance
 Overnight Finance Homepage
Overnight Finance HomepageOvernight Finance is a money market protocol that deals with offering passive returns on stable assets. Stable tokens on Overnight are rebase tokens, which function differently than stablecoins.
Stablecoins and rebase tokens both aim to achieve price stability relative to a specific asset, often a fiat currency like the US dollar. However, they achieve this goal through fundamentally different mechanisms, which also influence their use cases and behavior in the market. Here’s a detailed comparison of the two:
Mechanism
- Stablecoins: Stablecoins achieve price stability by holding reserves of a certain asset (like USD, other stable assets, or cryptocurrencies) or through algorithmic mechanisms that adjust the supply based on demand. The most common type, collateralized stablecoins, maintain a 1:1 peg with their underlying asset by backing each token with a corresponding amount of that asset in reserve.
- Rebase Tokens: Rebase tokens adjust their circulating supply periodically based on changes in market prices relative to their target price. If the price is too high, the supply increases; if it's too low, the supply decreases. This adjustment is made directly in holders' wallets, proportionally increasing or decreasing the number of tokens each person holds.
Overnight lists Ethereum and USD-backed rebase tokens on its platform, which are all convertible to USDC. OVN token is a utility token that serves multiple purposes in the Overnight protocol. It is used for bribes to promote USD+ and incentivize conservative risk decisions, as well as for voting rights to establish decentralized risk monitoring and management processes.
Friend.Tech
 Friend.Tech | Image via Bsc News
Friend.Tech | Image via Bsc NewsFriend.Tech is a novel crypto-based social networking platform on Base. It aims to redefine social interactions by integrating a cryptocurrency aspect to it. Essentially, Friend.tech enables users to buy and sell "Keys" (similar to shares or social tokens) associated with other users' profiles, turning social clout into a tradable commodity.
The platform's model allows for trading of these Keys, with prices influenced by supply and demand dynamics, much like stocks in the financial market. This trading model not only facilitates a new form of social interaction but also provides a mechanism for influencers and creators to monetize their social presence directly through their fanbase.
Moreover, Friend.tech emphasizes user interaction through a mobile-only app, bypassing traditional app stores by requiring users to add their web interface directly to their mobile home screen. This approach aims to streamline user experience and increase engagement by simplifying access to the platform.
Despite its innovative approach, Friend.tech has faced scrutiny and concerns related to privacy and security. The platform requires linking a user's X account to their Ethereum wallet, which has raised alarms about potential overreach and misuse of permissions. Additionally, incidents like database leaks have sparked debates about the security measures and privacy policies of Friend.tech.
The app's success and rapid user growth reflect its appeal, particularly among crypto enthusiasts and social media influencers looking for new ways to leverage their online presence in the decentralized web space.
Parting Thoughts
As the Base network emerges under the auspices of Coinbase's vast user base, it's positioned for rapid growth in the bustling Layer 2 landscape. Leveraging the technical prowess of the Optimism stack, Base is inherently robust, offering a solid foundation for developers aiming to build and deploy decentralized applications (Dapps). This technical backbone not only enhances performance but also ensures a level of reliability that developers seek when choosing a platform for their applications.
Looking ahead, the Base ecosystem is poised to become a hotbed for innovation. With its close ties to Coinbase and the inherent capabilities of the Optimism technology, we can anticipate a surge in the release of novel and impactful Dapps. These applications will likely span across various domains, including finance, social media, and beyond, further enriching the ecosystem.
However, one cannot overlook potential challenges. The evolving Layer 2 environment, especially with advancements like proto-danksharding, has dramatically reduced transaction fees across Ethereum's Layer 2 solutions, levelling the playing field. This development could dilute Base's unique selling proposition, as reduced costs and increased efficiency become common features rather than differentiators. As such, Base must continue to innovate and possibly find new niches or enhanced services that distinguish it from other Layer 2 networks. This will be crucial for sustaining its growth and attractiveness to both developers and users in the competitive blockchain space.





