Nothing can be as interesting as the prospect of a "risk free" trade.
Is there even such as thing? Can a trader really make a return without accepting a certain level of risk from their position? Doesn't this go against the notion of risk vs. return?
These are some of the many questions that a trader will ask themselves when someone mentions a risk-free trading opportunity.
Yet, there are a number of traders who are doing just that. They are making risk free returns by engaging in cryptocurrency arbitrage.
In this post, we will take you through everything you need to know about the process and how you can make the most of crypto market arbitrage.
What is CryptoCurrency Arbitrage?
Cryptocurrency arbitrage is merely an extension of arbitrage in more traditional markets and environments. It is the notion that a profit can be made by merely buying and selling the same assets in different markets in order to take advantage of the price difference.
Given that the trader is merely buying and selling the asset simultaneously, there should be no market risk. This is why they are usually considered a risk-free trade and why they are generally quite hard to find in traditional financial markets.
In fact, they are thought so hard to find that there is even a theory that option pricing is based on what is called "no arbitrage pricing" which asserts that arbitrage opportunities should not exist.
 No arbitrage pricing method explained
No arbitrage pricing method explainedWith cryptocurrency arbitrage though, the case is different.
This is because of the relatively new and underdeveloped state of the cryptocurrency markets. There are still market inefficiencies and barriers that make arbitrage opportunities possible.
As more traders and developers start getting involved in the market they are likely to take these opportunities with open hands. As more traders get involved and they start to take advantage of the arbitrage, the potential profits will diminish.
Now is an ideal time to get involved in crypto arbitrage if you still want to be able to earn decent returns.
Crypto Arbitrage Examples
There are a number of different arbitrage opportunities that exist in the cryptocurrency markets. Some of these exist across exchanges, others within an exchange and some a mispricing between a derivative price and that of the underlying physical product.
Simple Arbitrage
This is merely an arbitrage where you will buy one asset on one exchange and you will sell it in another at exactly the same time. If there is a mispricing in the price of the token then you will bag the spread the moment that you do this.
For example, assume that Ripple XRP is trading for 0.58 on Binance and is trading for 0.56 on Bitstamp. There now exists an immediate opportunity for arbitrage by buying the coin at 0.56 and then selling it at 0.58.
Fiat Triangular Arbitrage
The concept of triangular arbitrage is most commonly associated with price differences in forex markets. It involves an arbitrage where three different currencies are used. The mispricing exists between the relative prices of the forex pairs.
This can also exist in a large way in cryptocurrency assets that are priced in other currencies. For example, the Kimchi premium is a well-known market phenomenon that exists between the price of Bitcoin in USD on a US exchange, vs. the USD equivalent price of Bitcoin in South Korean Won that is listed on a South Korean exchange.
That seems like a mouthful, let's take a look at an example.
Assume that a trader was to buy the Bitcoin in USD on Coinbase Pro, send it to a South Korean exchange and then sell the coins for KRW. The Korean Won they get, when converted to USD, will get the trader a nice profit. Here is a graphical example with pricing at time of publishing.
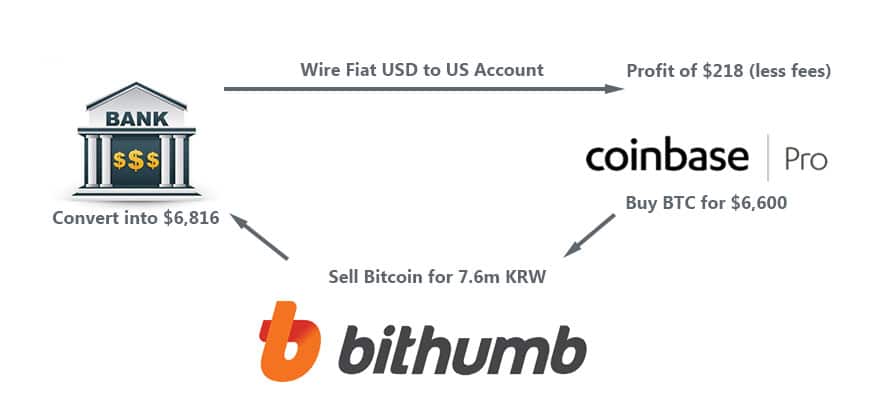 Triangular Fiat arbitrage opportunity (excluding Fees)
Triangular Fiat arbitrage opportunity (excluding Fees)In fact, the Kimchi premium has been so high in the past that CoinMarketCap even removed the Korean exchange pricing from their aggregate charts given the distortion that it had. There were occasions that the Kimchi premium even approached 30%.
The mispricing happens on a number of different exchanges that are servicing local markets. For example, if you take a look at the below image you will see the price of Bitcoin in USD on Kraken is $6,680.
 Price of Bitcoin in USD on Kraken
Price of Bitcoin in USD on KrakenHowever, if we take a look at the price of Bitcoin in South African Rands on Luno, converted into USD, we have the following price.
 Price of Bitcoin in ZAR on Luno in South Africa
Price of Bitcoin in ZAR on Luno in South AfricaSo, what this shows is that there is a profit to be made by buying Bitcoin on Kraken, sending the Bitcoin to Luno, cashing out the Bitcoin into ZAR and then buying USD with that ZAR.
Sound simple?
Well, there are a number of things that you have to consider such as fees, exchange controls and free movement of capital. We will touch on that briefly later on.
Crypto Triangular Arbitrage
While Fiat triangular arbitrage is the most profitable, there also exists the opportunity to make a triangular arb profit on the mispricing between three pairs of different coins. This mispricing can even occur on the same exchange.
Let us take a look at an example of what I am talking about. Below is the mispricing that we have between the pricing of Ethereum, Litecoin and Bitcoin on a single exchange.
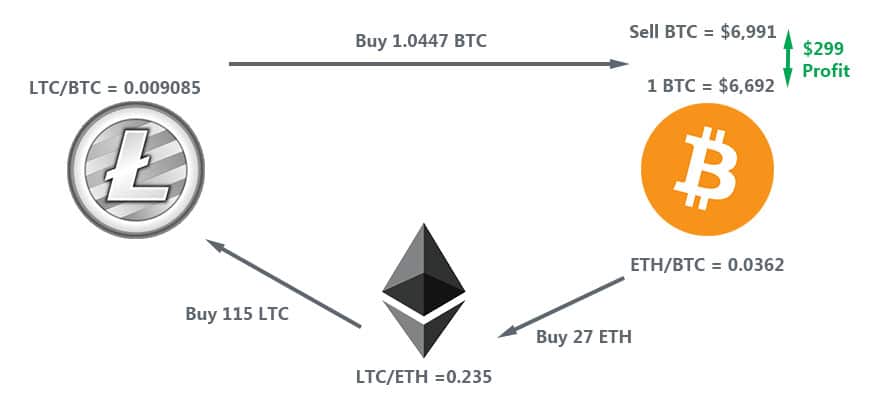 Example of a Cryptocurrency arbitrage opportuniy (Excluding fees)
Example of a Cryptocurrency arbitrage opportuniy (Excluding fees)In this case, there is an arbitrage between the BTC price of ETH and the ETH price of LTC. The trader is able to make this triangular crypto arbitrage and increase the size of his Bitcoin pie.
This mispricing is quite unlikely to happen now but it is well known that there was a great deal of it in the 2017 bull run. In fact, a developer even designed a trading bot that would take advantage of the mispricings the moment that they happened.
Convergence Arbitrage
This is another discipline that is borrowed from trading the traditional financial markets. It is the notion that there is an asset that is overvalued on a certain exchange but undervalued on the other.
The hope of the trader in this situation is that the law of no arbitrage implies that the price of the assets is likely to converge at some point in the future. You will buy the coin where it is undervalued on the exchange and you will short sell it on the other exchange where it is overvalued.
Hence, in order for you to complete a convergence crypto reverse arbitrage, you should have access to an exchange that will allow you to short sell the crypto asset.
Let us take a look at a practical example.
Assume that the price of Litecoin is currently sitting at $61 on HTX. However, the price of Litecoin on Poloniex is $64. Clearly, there is an arbitrage opportunity here.
You will then short sell LTC on Poloniex as it is overvalued and you will buy LTC on HTX. As the price corrects, you will bag the profit margin of $3.
Cash-and-Carry-Arbitrage
This is an arbitrage strategy that tries to take advantage of mispricing between assets in the futures and the physical markets. It is something that is now open to Bitcoin given that futures contracts were launched last year.
The strategy is essentially a market neutral strategy that involves taking a long position in the physical markets and then a short position in the futures market with the hope that you can make a profit on a certain mispricing.
It is called "Cash and Carry" as it involves carrying the asset until the expiry of the Futures contract. On expiry of the futures contract, you will settle the futures position with your long position in the asset. The hope is that on the delivery of the asset, you can make a profit by delivering the asset and pocketing the difference (minus any carrying costs).
In well developed markets such as the S&P 500 or in the fiat currency markets, the opportunity for futures arbitrage is much less pronounced. However, with the introduction of Bitcoin futures on the CME and CBOE last year, the attractiveness opens up many more opportunities.
For example, let us take a look at an example of a potential arbitrage opportunity. Currently, the future price of Bitcoin on the CBOE for delivery on the 14th of November is $6,800. The price of Bitcoin on the spot market at Binance for example is $6,686.
So clearly, there is an arbitrage opportunity here. This is actually relatively mild when compared to the differences that one could have observed back in December of last year when futures for delivery only a few weeks ahead were 10-20% higher than spot prices.
In more technical speak, the Forward Curve for Bitcoin is upward facing. You will then take advantage of this by buying Bitcoin and holding it to the expiration of the contract. Below is a helpful image.
 Trading differences in Futures markets and Spot markets
Trading differences in Futures markets and Spot marketsOf course, in traditional financial markets there could be other costs that are associated with it that could reduce your gains. These are what are called "carrying costs". However, when holding a digital asset, there are no real carrying costs to be concerned about. All one need do is store those in their wallets and wait until expiration.
Causes of Crypto Mispricing
There are a number of factors that can drive the mispricing in cryptocurrency markets. Asset mispricing will occur in markets that are less developed and hence less effecient than traditional markets.
In traditional financial markets, there are high frequency trading hedge funds that take up tiny opportunities in a relatively short period of time and ensure that these markets are kept efficient.
These still do not exist to the same extent in cryptocurrency markets. This is why triangular arbitrage even on a single exchange can exist between simple pairs.
In the case of a Fiat triangular arbitrage such as the Kimchi premium, it comes down to the imbalances in Supply / Demand in the country in question as well as the relative difficulty of moving Fiat currency between the different countries. Some countries have exchange control in place that makes it hard to simply wire out large quantities of money.
In the case of the Bitcoin futures arbitrage, the fact that they are cash settled is no doubt a large factor in why there is a mispricing. According to Aaron Brown of AQR Capital Management, the lack of physical settlement is what drives the divergence. He stated that
The wide arb spread is a big issue. It’s an illiquidity, it has to go away.
What are the Risks?
While an arbitrage is meant to be a "risk free" trade and a way to make a profit, there are still a few risks that you have to consider when embarking on a cryptocurrency arbitrage trading strategy.
Order Slippage
Slippage is a term that is used in financial markets to refer to the difference between the price that was expected for the trade versus the price that you actually got. This is indeed quite a problem in cryptocurrency markets and can deplete your expected arbitrage profits.
Moreover, slippage is positively correlated to the size of an order. The larger order that you are placing to take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity, the larger the slippage is likely to be.
 Order slippage example in Forex markets. Image Source: thefxview
Order slippage example in Forex markets. Image Source: thefxviewAll of your calculations could have been based on the mispricing at the current time, however if the price that you actually got for the asset was more or less then it will decrease the actual profit.
Volatility Reductions
In the case of crypto arbitrage, volatility is actually your friend. When there is more volatility in the pricing of these assets, then there is more scope for a mispricing to exist.
However, when markets are stable then there are less opportunities for severe mispricings to exist. Any severe mispricing is easily spotted in times of calm markets and traders will quickly take advantage of it.
This is indeed quite evident as most of the mispricing between triangular arbitrage and futures arbitrage occurred in the market rallies of late 2017.
Low Liquidity
This is another risk that is often quite prevalent in the cryptocurrency markets.
Often cryptocurrency arbitrage opportunities only exist because the markets are so illiquid to actually do anything about it. You will often observe this for some Altcoins that have the low market caps.
No large institutional trading firm or high frequency trading firm is going to try and take advantage of a mispricing for a coin that only has $50k of 24-hour volume. It will be incredibly hard for them to enter and exit the position.
This is also perhaps why cryptocurrency arbitrage can be such a good strategy for a smaller retail trader. The lower levels of liquidity mean they can trade without the competition from these advanced trading algorithms.
Conclusion
Arbitrage is no doubt one of the most interesting cryptocurrency trading opportunities that exists on the market today.
The notion of being able to make a profit from a mispricing with no market risk is too good to pass up. Of course, there are other risks but these are easily manageable.
It is also one of those strategies that is still only open to retail traders. The large institutions have entered the markets yet and whittled away the mispricings that exist.
So, while the markets are still in these relatively new stages of their development, make hay while the sun is shining.



