This is a comprehensive list of the best DApps in the Cosmos (ATOM) ecosystem. The Cosmos network is distinguished by its appchain-centric architecture. It enables the development of application-specific Layer-1 networks and allows interoperability between them with the Cosmos Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. Cosmos offers a unique landscape for DApps, where each application operates its own blockchain, allowing exceptional customization, customized governance, and token issuance.
In this guide, we will explore the top Cosmos DApps making waves. From decentralized exchanges leveraging the seamless interoperability of IBC, like Osmosis, to complex financial platforms that demonstrate the robust security and scalability of appchains, we cover a spectrum of applications that highlight the diversity of the Cosmos ecosystem.
Our focus will not only be on the functionalities and services these DApps provide but also on how they integrate within the broader Cosmos network to enhance user experience and interchain liquidity. Whether you are a blockchain enthusiast, a seasoned investor, or new to the world of crypto, this guide will provide you with insightful analysis and essential information on the best Cosmos DApps to watch.
Check out the Cosmos Review on the Coin Bureau if you wish to learn more about the protocol. You can also watch Guy explaining Cosmos on YouTube.
Let’s begin an analysis of the Top Cosmos decentralized applications.
Understanding Cosmos: What is ATOM?
Cosmos is an ambitious project aiming to become the "Internet of Blockchains" by creating an interoperable ecosystem of connected blockchains. It utilizes the Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerant algorithm for consensus and the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol for seamless token transfers between blockchains.
The Cosmos Network consists of the Tendermint Core, Application Blockchain Interface (ABCI), and Cosmos SDK, enabling developers to build customized blockchains with ease. The Tendermint algorithm, based on the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerant (PBFT) protocol, ensures consensus safety, prioritizes consistency, and achieves instant finality within 3 seconds.
 The Cosmos Ecosystem | (Image Source)
The Cosmos Ecosystem | (Image Source)Cosmos employs a delegated Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, where stakers and delegators participate in validating transactions and securing the network. Using the Cosmos SDK, developers can easily leverage the Tendermint Core to build application-specific blockchains that connect to the Tendermint Core with ABCI.
The ATOM token, initially sold in an ICO in 2017, serves as the governance and utility token within the Cosmos ecosystem. Plans are to expand its functionalities in the future. Cosmos 2.0 introduces new inter-chain collaboration capabilities, enhancing the value of the Cosmos Hub and strengthening its position in the blockchain landscape.
What Makes the Cosmos Ecosystem Unique?
The Cosmos DApp ecosystem is unique due to several key characteristics:
The Cosmos Hub
The Cosmos Hub is the main chain of the Cosmos ecosystem and is powered by the ATOM token. The Hub primarily acts as the facilitator of interchain security and interoperability with Cosmos Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC). It does not have an execution layer like EVM on Ethereum for processing smart contracts. Instead, its main function is to coordinate data and token transfers across connected blockchains.
Modularity
The Cosmos SDK is designed to be modular, allowing developers to easily create blockchains tailored to specific applications by using pre-built modules or creating new ones. This flexibility helps developers innovate and deploy applications that are optimized for their specific needs.
Appchains
Instead of deploying DApps on a shared platform like Ethereum, Cosmos Dapps are bespoke blockchains known as zones specifically tailored to their application. This concept of separate blockchains for every application is called appchains. The appchain approach allows the Dapp to have its own validators, governance models, and autonomy to upgrade without being constrained by a crowded main chain.
Interchain Security
One of the key innovations introduced by the Cosmos network is interchain security. This model allows new and smaller chains to use the security services provided by a more established blockchain (like the Cosmos Hub). This means that these appchains can leverage the validator set of the Cosmos Hub to secure their operations, benefiting from its established security and decentralization.
Therefore, when analyzing the Cosmos DApp ecosystem, we are not looking at a variety of DApps deployed on the Cosmos blockchain, but a network of tailor-made blockchains, all connected to the Cosmos Hub to share data, information and liquidity with one another.
Benefits and Considerations of Cosmos Appchains
Appchains, or application-specific blockchains, are a distinctive type of blockchain architecture promoted within the Cosmos ecosystem. Unlike traditional blockchains, which host a multitude of DApps on a single platform, appchains dedicate an entire blockchain to one application or use case. This approach allows developers to tailor every aspect of the blockchain — from its governance and economics to its functionality and security — specifically for the application it supports.
Benefits of Cosmos Appchains
Some benefits of Cosmos Appchains include:
- Cosmos SDK Makes Development Easy: One of the primary benefits of appchains in the Cosmos ecosystem is the ease of development provided by the Cosmos SDK. This open-source framework offers modular components that developers can use to build custom blockchains quickly. With pre-built modules for staking, governance, and more, developers can focus on unique features specific to their application rather than building basic blockchain functionality from scratch.
- Interoperability with Cosmos IBC: Thanks to the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, interoperability is a core advantage of Cosmos appchains. IBC allows different blockchains within the Cosmos ecosystem to transfer tokens and other data seamlessly, facilitating rich interchain interactions. Appchains can thus easily connect with established chains to leverage their assets and services, enhancing their capabilities and reach.
- Interchain security: Cosmos appchains can also benefit from interchain security — a feature that allows them to outsource their security needs to the Cosmos Hub or other large chains. This is particularly advantageous for smaller or newer chains that might not have the resources to attract a large number of validators. By piggybacking on the security of a larger network, appchains can ensure greater protection against attacks.
- Liquidity and ecosystem benefits within Cosmos: Deploying on Cosmos comes with inherent liquidity and ecosystem advantages. The interconnected nature of the Cosmos network means that assets can flow more freely across appchains, reducing liquidity silos and promoting a more vibrant and cooperative ecosystem. This interconnected liquidity is crucial for the success of financial applications, from exchanges to DeFi platforms.
- Benefits of deploying application-specific Layer 1 chains: Appchains provide performance optimizations, customized fee structures, and tailored governance models, which are not feasible on shared blockchains. By avoiding the crowded and sometimes costly environment of platforms like Ethereum, appchains can offer users lower fees, faster transactions, and a governance model that stakeholders of the specific application control directly.
Considerations About Cosmos Appchains
Some considerations about Cosmos Appchains are:
- Every appchain arranges its own crypto-economic security: While the autonomy of appchains offers significant advantages, it also comes with the responsibility of arranging its own crypto-economic security. Each appchain must design its own incentive mechanisms to attract and retain validators, which can be a complex and risky process, especially for less popular or newer projects.
- Benefits of interchain security may be limited to governance selected chains: The benefits of interchain security, while significant, may be contingent upon the governance decisions of the hub chain, like the Cosmos Hub. Smaller appchains might depend on the security services of a larger chain, which could potentially prioritize its own security or interests, especially under stress or in conflict scenarios.
- Other considerations: Appchains must also navigate potential security issues, as each chain’s capacity to process transactions securely is limited by its infrastructure and value staked by the validators. Moreover, the success of an appchain heavily relies on its ability to foster a strong community and a sustainable validator ecosystem, which can be challenging without substantial initial interest or investment.
Conclusion
Cosmos appchains represent a compelling paradigm in blockchain architecture, offering significant benefits in terms of customization, interoperability, and ecosystem integration. They allow developers to craft finely tuned environments that serve specific applications with high efficiency and governance alignment. However, the independence of appchains also necessitates a robust approach to security, economic incentives, and community engagement. Balancing these factors is essential for leveraging the full potential of appchains within the dynamic Cosmos ecosystem.
Best Cosmos DApps
Curating a list of the best Cosmos DApps can get tricky because Cosmos DApps do not adhere to the general definition of a decentralized application. Cosmos is not one blockchain but an ecosystem of several blockchain networks. Technically, there are no DApps running on the Cosmos Hub because the chain does not support an execution environment to run smart contracts.
So, I am tweaking the definition of a “Cosmos DApp” for the scope of this piece. Here is a list of Cosmos appchains, which are application-specific blockchains built using the Cosmos SDK and connected to the Cosmos Hub via IBC.
Osmosis
 Osmosis Homepage
Osmosis HomepageOsmosis is a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on the Cosmos network, specifically designed for creating liquidity and trading IBC-enabled tokens. It's an autonomous, interoperable ecosystem powered by its own blockchain and governed by the holders of its native token, OSMO.
What sets Osmosis apart are its advanced features like customizable liquidity pools, superfluid staking, and concentrated liquidity, enabling users to tailor their trading and liquidity strategies. Its unique mechanism allows users to vote on governance proposals directly impacting the protocol's development and parameters.
In the Cosmos ecosystem, Osmosis plays a critical role by enhancing liquidity for IBC-enabled tokens and fostering a more interconnected and efficient network. It acts as a central hub for asset exchange across the Cosmos, boosting the utility and adoption of the IBC protocol.
Regarding achievements, Osmosis has shown significant growth in its user base and volume, positioning itself as one of the top DEXs in the Cosmos ecosystem. A notable recent milestone includes the integration of additional blockchain tokens, expanding its reach and interoperability within the broader crypto market.
Celestia
 Celestia Homepage
Celestia HomepageCelestia is a modular Data Availability layer built using the Cosmos SDK and Tendermint Core. Data Availability is essential for blockchain security. It ensures that the validators participating in blockchain consensus have enough blockchain data to detect invalid transactions and also secure the network against liveness failures.
Celestia plays a vital role in the Cosmos ecosystem. It functions as the data availability layer for Cosmos zones, the appchains built using the Cosmos SDK. Cosmos chains can subscribe to Celestia’s DA layer using the TIA token, the token of the Celestia PoS network.
One of Celestia’s key innovations is Data Availability Sampling, a technique that allows light nodes to acquire the same crypto-economic guarantees as a full node, as long as at least one such full node functions honestly. Data Availability Sampling significantly reduces the costs of running nodes, as lighter devices such as smartphones with limited processing power and storage capacity can also easily participate in consensus, which can potentially lead to a more decentralized and secure network.
Sei
The Sei network is a layer-1 PoS blockchain built with the Cosmos SDK. It sits on a spectrum between general-purpose blockchains like Ethereum or Solana and application-specific blockchains like Osmosis and Axelar.
Sei is a parallelized network optimized for trading digital assets in its ecosystem. This makes it a general-purpose blockchain network specifically designed for building trading and lending specific decentralized applications. It supports CosmWasm smart contracts written in Rust programming language. Since Sei is designed for building trading-specific applications, it is incredibly fast, boasting 390ms block finalizing times with over 45 TPS.
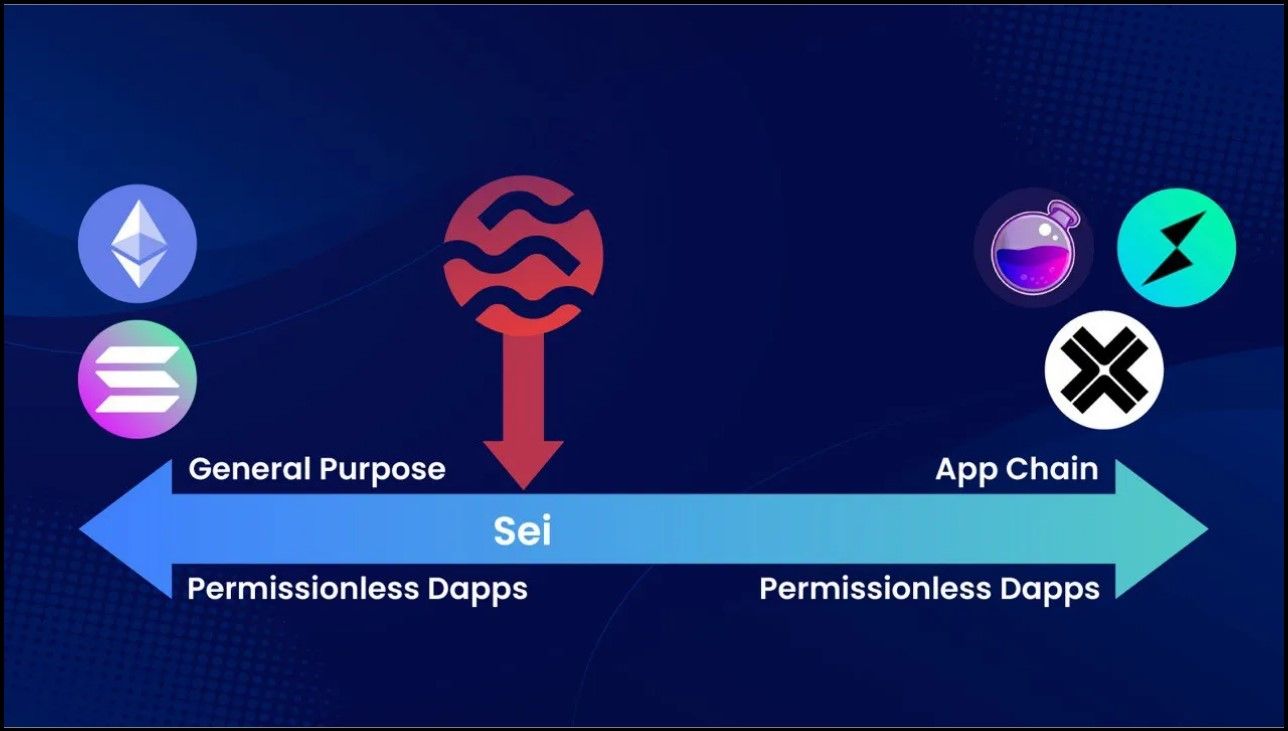 Sei is Neither General-Purpose Nor Application-Specific | Image via Medium
Sei is Neither General-Purpose Nor Application-Specific | Image via MediumIn November 2023, Sei introduced a V2 upgrade, which added support for EVM. It already had support for Rust, which meant DApps built for the Solana ecosystem could also work in Sei’s environment. Adding support for EVM is a bid to make Sei even more versatile and attract more developer attention from the most adopted execution environments like Ethereum.
Additional DeFi-centric features of Sei include:
- Native price oracle: Sei validators are required to participate as price oracles; their votes are used to calculate the price of assets at the end of every block and are penalized for non-participation and for providing bad data.
- Native order matching engine: Sei order matching engine allows individual DEXs on the blockchain to deploy their respective markets. It offers general trading features like market orders, limit orders, and stop-loss orders. Moreover, the order placement and execution can happen in the same block, which reduces slippage (other order book DEXs generally take several blocks to process orders).
- Asset agnostic order book: Instead of tokenizing positions, DEXs on Sei can track positions as a list in their smart contract state.
- Frequent batch auctioning: Sei discourages transaction frontrunning by aggregating all market orders and executing them at the same uniform clearing price.
- Transaction order bundling: Sei users can update positions on various markets in one transaction.
Akash Network
 Akash Network Homepage
Akash Network HomepageAkash Network is a compute services DePIN project. It is a decentralized solution to centralized businesses like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. For instance, Azure is a cloud computing provider comprising global servers providing computational resources to run programs on the cloud, such as websites, analytics, and networking.
Unlike Azure, Akash is a decentralized cloud computing program. Instead of centralized servers, users with personal servers, data centers, or spare computational resources participate in an on-chain compute marketplace. These providers place on-chain bids, and Tentants, who need the resources, accept the optimal offers.
Key Features of Akash Network:
- Akash Blockchain: It is a Cosmos SDK blockchain that hosts the Akash Marketplace and renders the compute services to the tenants using smart contracts. It also facilitates rudimentary processes like governance, PoS consensus, and staking.
- AKT Token: It is used for renting compute resources, staking in the network and governance.
- Economical: Akash’s decentralized compute services are significantly cheaper than traditional counterparts like Azure.
- Akash Supercloud: An upgrade addressing inefficiencies in GPU access by providing permissionless access to compute resources.
The AKT 2.0 update underscores significant architectural improvements such as an incentive distribution pool comprising AKT and some whitelisted tokens, subsidizing compute providers, and creating a public goods fund for the welfare of the ecosystem. Learn more about Akash Network in our dedicated Akash review.
Axelar
 Axelar Protocol Homepage
Axelar Protocol HomepageThe Axelar network, founded in 2020, harnesses Cosmos technologies to offer broad interoperability with Ethereum and other blockchain networks. Unlike typical interoperability solutions focusing only on asset transfers, Axelar delivers full-stack interoperability. This encompasses not just bridging assets but also enabling complex cross-chain functions like executing smart contracts and running decentralized applications seamlessly across different networks.
Axelar is distinctive in its approach to addressing the fragmentation in liquidity, services, and users across disparate blockchain ecosystems. It achieves this through a robust architecture that includes a decentralized network built on Cosmos SDK technologies, gateway smart contracts for connectivity, and a comprehensive SDK for developers. This setup is enhanced by the Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM), which introduces permissionless overlay programmability, allowing developers to deploy smart contracts and build advanced cross-chain functionalities.
In the Cosmos ecosystem, Axelar is crucial for its role in scaling cross-chain communications, connecting over 55 networks with plans for hundreds more. This scaling is driven by innovations like the AVM and the strategic enhancement of economic structures and network efficiencies.
Axelar’s significant milestones include launching its mainnet in May 2022 and introducing General Message Passing (GMP), which facilitates the transfer of diverse payloads and logic across chains, enhancing usability and composability. With its advanced cross-chain capabilities, Axelar not only bridges networks but also pioneers new forms of blockchain interoperability, mirroring the role of overlay networks in traditional internet architecture. This positions Axelar as a pivotal player in the ongoing evolution of the blockchain ecosystem.
Penumbra
 Penumbra Homepage
Penumbra HomepagePenumbra is a Cosmos SDK chain and a private decentralized exchange. It operates a shielded pool for private transfers, staking, and swapping of Cosmos tokens. The platform uses cryptographic encryption to conduct pool-to-pool shielded swaps. All transactions in Penumbra are private and untraceable.
Penumbra functions as a private layer for the entire Cosmos ecosystem. It can shield any Cosmos IBC transaction from one Cosmos zone to another, making it the shielded pool for the entire Cosmos ecosystem.
Stride
 Stride Homepage
Stride HomepageStride is a liquid staking protocol for the Cosmos ecosystem tokens. Since Cosmos ecosystem applications are actually separate layer 1 application-specific chains, each deploys a PoS mechanism to secure their respective chains. With Stride, users can comfortably liquid stake a variety of Cosmos tokens within a single platform.
Stride supports liquid staking for the Cosmos Hub token (stATOM), Osmosis (stOSMO), Celestia (stTIA), dYdX (stDYDX), Injective (stINJ), Stargaze (stSTARS), Evmos (stEVMOS), Terra (stLUNA), Umee (stUMEE), Juno (stJUNO), Comdex (stCMDX) and Sommelier (stSOMM), making Stride the liquid staking hub of the Cosmos eosystem.
Stide is performing well in the liquid staking arena. It is managing a TVL of $133.4 million in April 2024, with the TVL growing steadily since early 2024. Users who liquid stake on stride start accruing rewards instantly and can unstake their funds at any time.
Kava
Kava is a Cosmos SDK-enabled layer-1 blockchain designed to facilitate composability between EVM and Cosmos SDK environments. Central to the Kava ecosystem is its co-chain architecture that lets developers choose between Ethereum and Cosmos SDK environments for their decentralized applications.
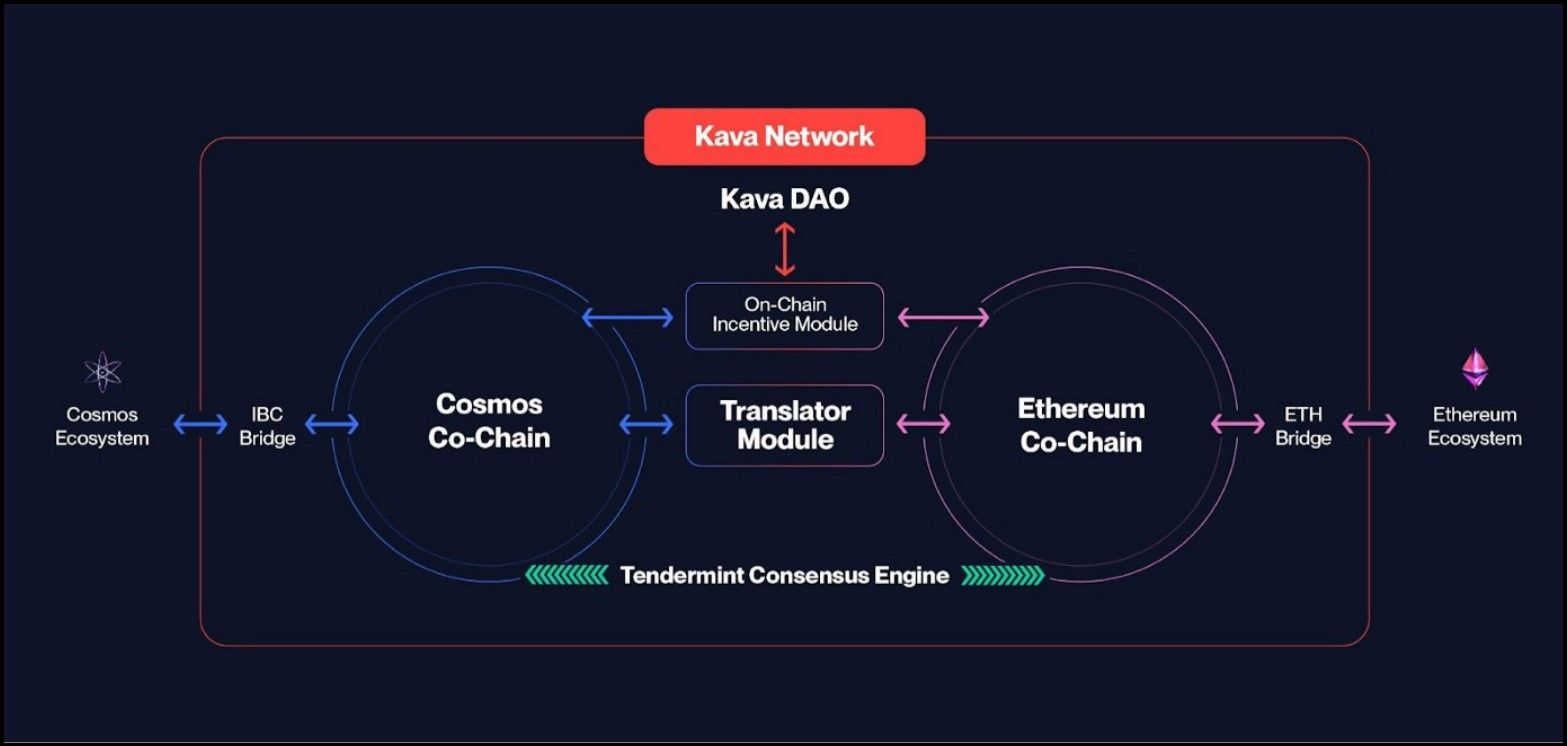 Kava Architecture | Image via Kava Docs
Kava Architecture | Image via Kava DocsThe Kava network comprises two chains: The Cosmos Co-Chain and the Ethereum Co-Chain. The Ethereum Co-Chain is EVM compatible, therefore Ethereum-DApps can easily deploy in the Kava ecosystem and enables Solidity developers to leverage the Kava network’s interoperability, composability and scalability.
The Cosmos Co-Chain is built with Cosmos SDK and functions as the bridge between Dapps in the Ethereum Co-Chain and the Cosmos ecosystem, comprising Cosmos zones and the Hub. With the Translator Module, the two blockchain environments can communicate with each other effectively and function as a cohesive network.
One of the key benefits of Kava is that Ethereum Dapps, which are technically smart contracts running on the Ethereum virtual Machine, can operate on the Kava network and leverage the ecosystem benefits of Cosmos without the developer requiring additional technical knowledge about developing in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Where to Buy ATOM
You can Buy ATOM on Binance, Bybit, Coinbase, Kraken, and every other major cryptocurrency exchange. If you are unsure about which exchange to use, refer to our article on the best cryptocurrency exchanges to make the choice.
There are several decentralized options to buy ATOM tokens as well. Osmosis, Helix, slingshot Finance, PancakeSwap and among many decentralized exchanges where you can trade ATOM. You can also check out our top picks for the best decentralized exchanges.
Best ATOM Wallets
ATOM is among the top cryptocurrencies today, so there are plenty of options available to hold ATOM, catering to different security and accessibility preferences.
Ledger Nano S Plus is a great hardware option available which also offers easy portfolio management with the Ledger Live app. Keplr and Cosmostation are among the most popular online wallets for storing ATOM and other Cosmos SDK tokens.
Check out a dedicated analysis of the Best Cosmos Wallets on the Coin Bureau to learn more.
Top Cosmos DApps: Conclusion
In this exploration of the Best Cosmos DApps (or Appchains), I learned that Cosmos’s goal of enabling developers the freedom to design customized execution environments is successfully playing out in the diversity of Cosmos ecosystem applications.
This list consists of DEX-optimized L1 chains, liquid staking layers, interoperability protocols, bridges, private DEXs and much more. A significant contributor to the diverse types of appchains in the Cosmos ecosystem is its SDK, that gives the developers the autonomy and the liberty to innovate. With the ATOM 2.0 upgrade, these appchains may potentially leverage some security of the Cosmos Hub via interchain security, which makes Cosmos more secure and appealing to mainstream users.





