Privacy coins exist for a simple reason: most blockchains leak more financial information than people realise. On Bitcoin and Ethereum, anyone can see amounts, addresses, timing, and in Ethereum’s case, app activity too. That makes verification easy, but it also makes profiling cheap.
Privacy coins flip that default. They aim to limit what outsiders can learn from the ledger itself, whether that is who paid whom, how much moved, or how transactions link together over time. Some do this with privacy enforced on every transaction. Others make it optional, which changes the real-world outcome.
This guide breaks down what privacy coins are, how they work, where they actually help, and where the trade-offs show up: exchange access, wallet friction, liquidity, and regulation.
Our Top Picks By Reader Type
- Maximum default privacy: Monero (XMR) — privacy is always on, with no modes to toggle or workflows to remember. Best for users who want consistent, protocol-level confidentiality.
- Optional disclosure / auditability: Zcash (ZEC) — shielded transactions when you need privacy, transparent ones when disclosure or compatibility matters.
- Private smart contracts: Secret Network (SCRT) or Oasis Network (ROSE) — designed for keeping application-level data private, not just simple payments.
- MimbleWimble minimalism: Grin (GRIN) or Beam (BEAM) — strong on-chain privacy with reduced data leakage, but higher UX and liquidity friction.
- Beginner-friendly option: Dash (DASH) — familiar wallets, fast confirmations, and opt-in privacy tools for users easing into privacy concepts.
Safety Notes
What Are Privacy Coins?
Privacy coins are cryptocurrencies designed to hide transaction details that most blockchains expose by default.
On networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum, anyone can see transaction amounts, sender addresses, recipient addresses and timing. That openness makes verification easy, but it also makes surveillance cheap. Privacy coins change this by limiting what observers can learn, even if they can see the blockchain.
Not all privacy coins take the same approach, and those differences matter in practice.
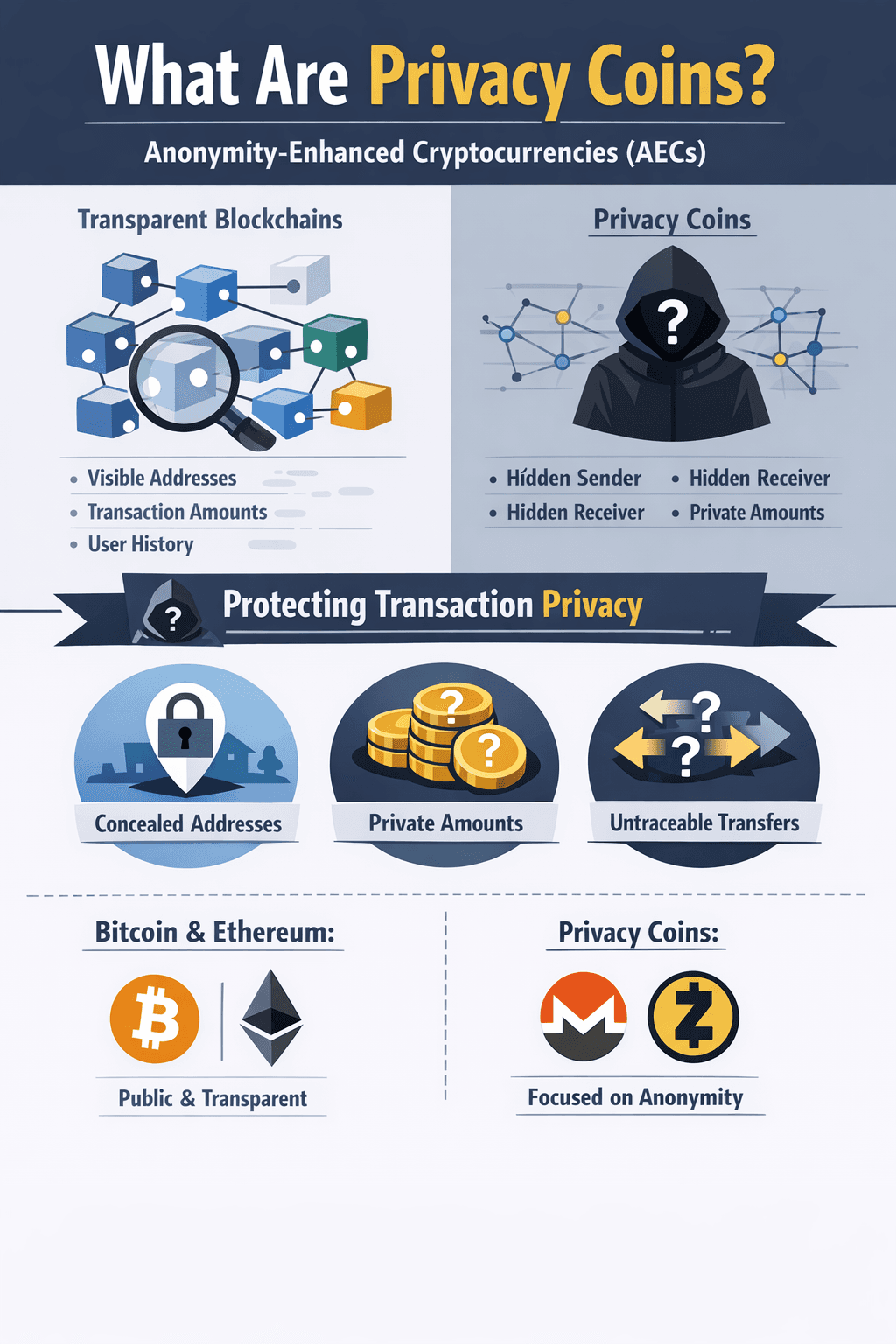 Privacy Coins, as The Name Suggests, Enhance Transaction Privacy
Privacy Coins, as The Name Suggests, Enhance Transaction PrivacyPrivacy Coin Basics (AECs Explained)
Privacy coins are often called anonymity-enhanced cryptocurrencies (AECs), a term used in regulatory and research contexts for blockchains that reduce transaction traceability.
Their goal is simple: hide who sends a transaction, who receives it, and how much value moves. Some privacy coins enforce this by default. Others make privacy optional.
On transparent blockchains, transactions are permanent. Analytics firms build profiles using address reuse, transaction graphs, exchange data, and metadata like timing and fees. Chainalysis describes this openly in its overview of blockchain tracing techniques, and these tools are not limited to law enforcement.
Privacy coins help reduce exposure by limiting what can be observed, and can push back by making it harder for these tools to see anything.
Privacy vs Anonymity
Privacy means controlling what information is revealed. Anonymity means outsiders cannot reliably link transactions to identities or trace flows between users.
Bitcoin illustrates the limits of transparent systems. Transactions and addresses are public, and once an address is linked to you, your entire history becomes traceable. A freelancer paid repeatedly to the same Bitcoin address exposes income, timing, and balances once that address connects to an exchange or invoice. This data cannot be hidden later.
Academic research, such as An Analysis of Anonymity in the Bitcoin System, shows how address reuse and clustering heuristics reveal user behavior.
Take Monero, for example. It enforces privacy by default, which means every transaction hides the sender, receiver, and amount. According to the Monero project’s own documentation on transaction privacy, this uniform behavior strengthens privacy because all users blend into the same anonymity set.
For example, two Monero payments made at the same time are indistinguishable on-chain, whether they are salaries, donations, or personal transfers. Observers cannot link participants or values.
Zcash, meanwhile, sits in the middle. It uses zero-knowledge proofs to enable private transactions, but it does not force users to use them. Funds can move between transparent and shielded addresses.
For example, if funds move from a transparent address into a shielded address, observers can still infer relationships based on timing and amounts when few users use shielding.
Zcash’s own documentation on shielded addresses explains this split design and why private usage is optional rather than default.
Why Bitcoin and Ethereum Fall Short on Privacy
Bitcoin and Ethereum were designed so that anyone can verify transactions without trusting a central party. To do this, both rely on transparent public ledgers where sender addresses, recipient addresses, amounts, and timestamps are visible to anyone.
This creates structural privacy weaknesses. Bitcoin’s own documentation warns that address reuse makes it easier to link transactions and identify users over time, which is why its official privacy guidance recommends generating a new address for each payment.
KYC onramps compound the problem. Regulated exchanges link verified identities to withdrawal addresses, a requirement reinforced by the Financial Action Task Force’s virtual asset guidance.
Ethereum expands its exposure further. Its developer documentation confirms that all transactions and state changes, including smart contract interactions and DeFi activity, are permanently public.
Even careful users leak information through metadata. A peer-reviewed survey, Privacy on Bitcoin Transactions: A Systematic Literature Review, shows how transaction graphs and timing patterns reveal behavior on transparent blockchains.
Privacy coins take a different approach by limiting what is published on-chain in the first place.
Privacy Coins Comparison Table
Before diving into individual coins, it helps to see how they compare side by side.
| Coin | Privacy (Default/Optional) | Mechanism | Amount privacy | Address privacy | Consensus | Typical speed + fees (range) | Wallet maturity | Exchange availability | Dev activity (how measured) | Governance model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monero (XMR) | Default | Ring signatures, stealth addresses, RingCT | Yes | Yes | PoW | ~2 min blocks. Fees are dynamic per byte and wallets can query estimates via get_fee_estimate. | Beginner-friendly to Advanced | Medium (region-dependent) | High, based on releases and commits in the official monero-project report | Rough social consensus with funded research and dev work |
| Zcash (ZEC) | Optional | zk-SNARKs (shielded pool), transparent option | Yes (shielded) | Yes (shielded) | PoW | 75 sec blocks. Default fee set to 0.00001 ZEC (1000 zatoshis) in the conventional fee spec. | Advanced (shielded UX varies by wallet) | Medium to Low (region-dependent) | High, based on official ZIPs and code in zcash/zcash | Foundation and ecosystem governance plus network upgrades via ZIP process |
| Dash (DASH) | Optional | CoinJoin-style mixing (PrivateSend) | Partial (mixing, not protocol-wide CT) | Partial | PoW with masternodes | ~2.5 min blocks. Default minimum relay fee in Dash Core is 0.00001 DASH per kB (actual paid fee depends on size and mempool). | Beginner-friendly | High to Medium (region-dependent) | Medium, based on releases and commits in dashpay/dash | On-chain treasury and masternode voting |
| Secret Network (SCRT) | Optional by app, private by design for Secret Contracts | Encrypted smart contracts, confidential compute (TEE-based) | Yes (in private app flows) | Yes (in private app flows) | PoS | ~6 sec blocks. Docs give a worked example: avg tx ~100,000 gas with 0.05uSCRT gas price, about 0.005 SCRT. | Medium (learning curve) | Medium (region-dependent) | Medium to High, based on releases/commits in scrtlabs/SecretNetwork | On-chain governance |
| Oasis Network (ROSE, Sapphire/Emerald) | Optional, depends on ParaTime | Confidential ParaTimes (Sapphire), EVM ParaTime (Emerald) | Yes (Sapphire-style flows) | Yes (Sapphire-style flows) | PoS | Emerald expected block time 6 seconds. Example consensus tx shows a fee like 0.0002779 ROSE at gas price 0.0000001 ROSE per gas. | Medium | Medium (region-dependent) | Medium to High, based on core repo activity in oasisprotocol/oasis-core | On-chain governance and foundation-led ecosystem |
| Firo (FIRO) | Optional privacy features | Lelantus Spark, Dandelion++ (network layer) | Yes (privacy tx types) | Yes (privacy tx types) | PoW | Block timing and fees vary by tx type. Official docs emphasize privacy tooling (Lelantus Spark, Dandelion++) on the project site here. | Medium | Low to Medium (region-dependent) | Medium, based on repo updates in firoorg/firo | Community governance with formal funding proposals |
| Grin (GRIN) | Default (protocol style) | MimbleWimble | Yes | Yes (no addresses) | PoW | Fees are weight-based. Default base fee is 500,000 nanogrin per weight unit. A plain “1 in, 2 out, 1 kernel” tx has weight 46, so minimum fee is ~23,000,000 nanogrin (about 0.023 GRIN, based on the RFC’s constants). | Advanced (interactive sends, UX quirks) | Low | Medium, based on core activity in mimblewimble/grin | Community governance via RFC process |
| Beam (BEAM) | Optional privacy modes | MimbleWimble with wallet features | Yes | Yes | PoW | Official wallet docs list minimum fees: regular tx 0.001 BEAM, and offline or max privacy flows can be around 0.011 BEAM depending on type. | Beginner-friendly to Medium | Low to Medium (region-dependent) | Medium, based on repo activity in BeamMW/beam | More structured, org-led development |
Which One Should I Choose?
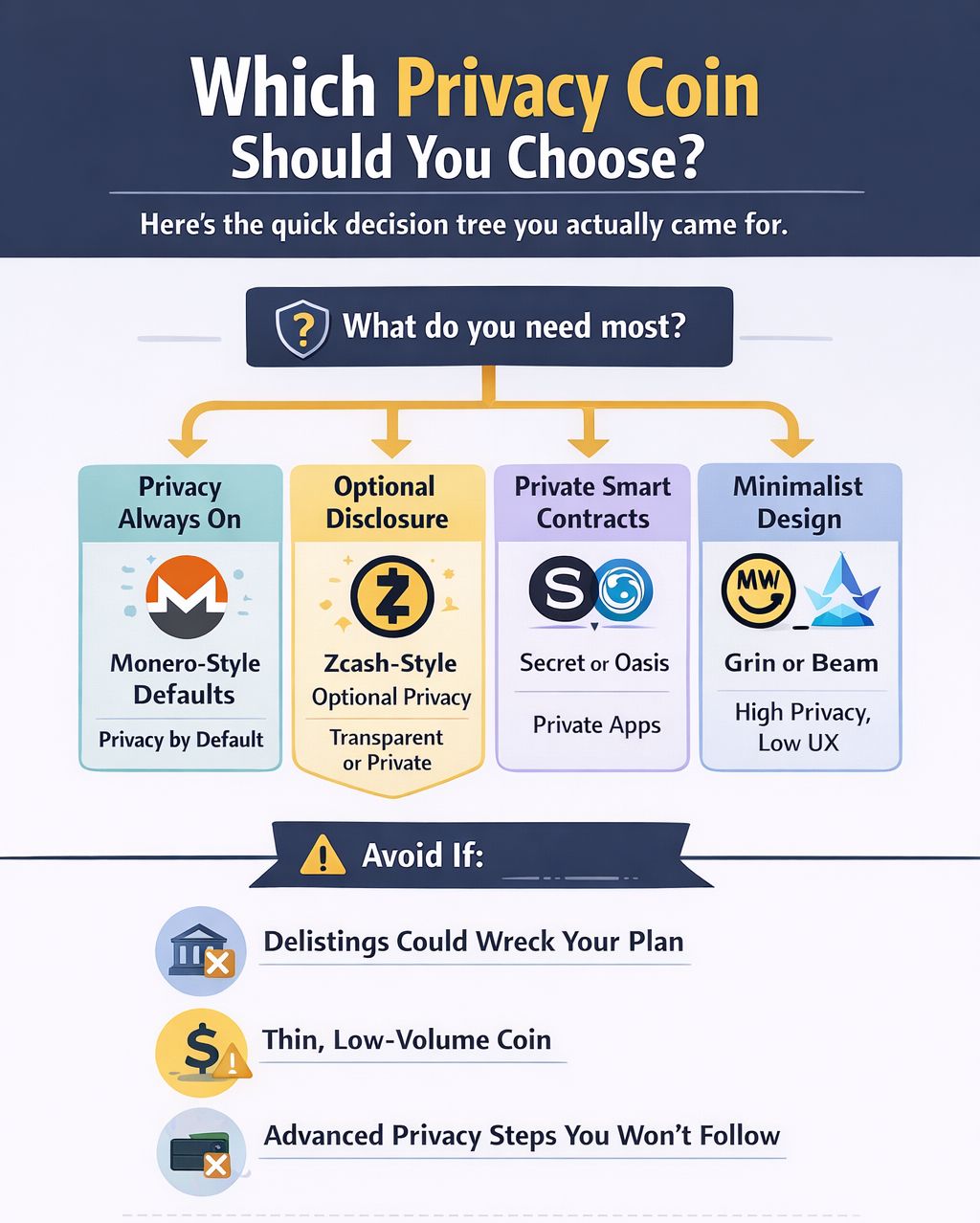 This Decision Tree Will Help You Choose The Right Privacy Coin
This Decision Tree Will Help You Choose The Right Privacy CoinHere’s the quick decision tree you actually came for.
- If you want privacy always on
Pick Monero-style defaults. You do not have to “remember” to enable privacy, and that matters. - If you need optional disclosure or auditability
Pick Zcash-style optional privacy. You can run transparent when you need it, and shielded when you do not. - If you want private smart contracts
Pick Secret or Oasis. This is less about hiding a simple payment and more about keeping app-level activity private. - If you want MimbleWimble minimalism
Pick Grin or Beam. You get strong on-chain privacy properties, but you also accept UX friction and thinner liquidity in many places.
Avoid if (the stuff people learn the hard way)
These are the deal-breakers people only notice after they’ve already bought.
- Avoid privacy coins if delistings would wreck your plan
If you rely on centralized exchanges for access, you need to accept that privacy coins face higher compliance pressure. The FATF’s requirements around virtual assets and service providers shape how exchanges treat privacy-heavy assets, and that pressure is spelled out in its official virtual assets guidance. - Avoid thin, low-volume coins if you care about usability
Low liquidity means higher slippage, fewer fiat ramps, and more friction when you want to move size. It also tends to reduce real-world privacy because fewer users means smaller anonymity sets. - Avoid advanced privacy workflows if you will not follow them consistently
Optional privacy features only help if you use them correctly every time. Wallet mistakes, address misuse, or switching between modes can undo the protections you think you have.
How We Ranked These Coins (Methodology)
We ranked coins using a practical scoring model that blends market reality, privacy design and usability.
Ranking criteria
- Market cap + liquidity: Bigger networks and deeper order books rank higher.
- Privacy model: Default-private systems score higher than optional privacy.
- Dev activity: Consistent shipping and maintenance.
- Real-world usability: Wallet UX, friction, and how reliably privacy works in normal use.
- Exchange + wallet support: Breadth of listings and whether wallets/exchanges support the privacy mode end-to-end.
- Regulatory resilience: How vulnerable the coin is to delistings and restricted on/off-ramps.
Default vs optional privacy scoring
- Default privacy: Highest score (privacy is always on, fewer user mistakes, larger anonymity sets).
- Optional privacy: Lower score unless private mode is widely used and supported across major wallets/exchanges.
Dev activity evaluation
We looked at GitHub commits + releases and (where relevant) official research/upgrade updates to confirm ongoing development.
Data sources used
- CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap for market cap, liquidity and max supply.
- Official docs + official GitHub repos for privacy mechanics and implementation details.
Coin Profiles (Our Top Picks)
Each profile below follows the same structure so you can compare privacy coins without mental gymnastics. No marketing fluff. Just how they work, what they’re good at, and where the friction shows up.
1. Monero (XMR) | Privacy-by-default that doesn’t ask permission
What it is: Monero is built for private payments where sender, receiver, and amount are obscured by default. It prioritizes everyday transfer privacy over optional features you have to “turn on.”
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Monero has no hard cap and uses tail emission (fixed block reward after main emission) per Monero FAQ.
- Typical fee range: Monero fees are dynamic and depend on transaction weight and network conditions.
- How privacy works: Monero combines one-time addresses (recipient privacy) with ring signatures and RingCT (amount privacy). RingCT is mandatory and hides amounts at the protocol level per RingCT entry. It also uses RandomX to keep mining more CPU-friendly per RandomX entry.
Best for
- Private peer-to-peer payments
- Situations where “optional privacy” is basically “usually unused”.
Trade-offs
- Some exchanges restrict or delist XMR in specific regions
- Heavier transaction data than transparent chains (privacy has a cost)
- Wallet UX can feel “different” if you’re used to account-style chains
- Privacy does not automatically hide your network metadata if you use leaky setups (VPN/Tor choices matter, but we’re not doing evasion coaching here)
Where to buy (regions vary)
- KuCoin
- Kraken
- WhiteBIT
- HTX
- MEXC
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use regulated alternatives that still list it where legal, or consider privacy tools that fit your jurisdiction. Avoid anything that sounds like “bypass” services.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Monero GUI
- Popular: Cake Wallet, Feather
- Hardware: Ledger Nano S Plus and Nano X, Trezor Model T, Safe 3 and Safe 5
Official resources
- Website: getmonero.org
- GitHub: github.com/monero-project
- Explorer directory: monero.fail
Network metadata note: On-chain privacy doesn’t automatically hide network metadata. Use non-leaky setups, but we’re not doing evasion coaching here.
2. Zcash (ZEC) | Powerful privacy tech, but you have to actually use it
What it is: Zcash supports shielded transactions using zero-knowledge proofs, designed to let you prove a transaction is valid without revealing sensitive details. The catch is simple: privacy depends on whether you transact shielded.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Max supply capped at 21 million ZEC.
- Typical fee: 0.000001 ZEC per 1000 bytes (default relay/mining fee rate, ZIP-0313).
- How privacy works: Shielded transfers use zk-SNARKs to keep sender, receiver, and amount off-chain. Protocol changes and specifications are tracked through Zcash ZIPs and official documentation. Shielded support varies by wallet and platform.
Best for
- Users who want privacy with the option to disclose or audit later
- Workflows where shielded transfers are supported end-to-end
- Scenarios requiring “prove validity without revealing everything” semantics
Trade-offs
- If shielded addresses aren’t used, transactions behave like a transparent chain
- Shielded UX can be inconsistent across wallets and exchanges
- Some regions and exchanges restrict privacy-focused assets
Where to buy (regions vary)
- Binance
- KuCoin
- Pionex
- Coinbase
- MEXC
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use a regulated venue that still lists it legally, or consider other privacy models that match your access constraints.
Wallets that support it
- Zashi: Shielded-first mobile wallet
- Ywallet: Privacy-oriented wallet with shielded support
- Trezor Model T: Hardware wallet (support varies by workflow)
Official resources
- Website: z.cash
- Support & Docs: z.cash/support
- ZIPs (specs): zips.z.cash
- GitHub: github.com/zcash
Network metadata note: On-chain privacy does not automatically hide network metadata. Shielded transfers protect transaction details, not how traffic reaches the network.
3. Dash (DASH) | Fast payments with CoinJoin-style privacy tooling
What it is: Dash is a payments-focused chain known for fast confirmations and built-in mixing tools. Its privacy feature is based on non-custodial CoinJoin rather than protocol-level “hide everything by default.”
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at approximately 18.92 million DASH.
- Typical fee: ~0.00001 DASH per kilobyte (minimum relay fee), as defined in Dash Core network parameters.
- How privacy works: Dash uses CoinJoin (formerly PrivateSend), allowing users to mix funds with others in a non-custodial way. Official documentation covers CoinJoin and InstantSend usage and limits.
Best for
- Faster, everyday payment experiences
- Users who want built-in mixing without switching chains
- People who are realistic about what CoinJoin can and can’t do
Trade-offs
- CoinJoin does not provide protocol-level hidden sender, receiver, and amount
- Privacy depends on correct usage and the size of the mixing set
- Exchange support varies by region and compliance posture
Where to buy (regions vary)
- Binance
- KuCoin
- Pionex
- MEXC
- Coinbase
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Look for regulated venues that still list it legally, or consider privacy-by-default coins if confidentiality is your primary goal.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Dash Core Wallet
- Popular: Dash Electrum and mobile wallets listed in Dash documentation
- Hardware: Ledger Nano S Plus, Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T
Official resources
- Website: dash.org
- Docs: docs.dash.org
- GitHub: github.com/dashpay
- Explorer: explorer.dash.org
Network metadata note: CoinJoin improves on-chain transaction privacy but does not conceal network-level metadata or guarantee anonymity if used improperly.
4. Secret Network (SCRT) | Encrypted smart contracts on a Cosmos-style chain
What it is: Secret Network focuses on private computation: smart contracts that can keep inputs and outputs private when designed that way. It’s less “private payments coin” and more “privacy-enabled apps.”
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: No max supply.
- Typical fee example: Docs show an example transaction cost of around ~0.005 SCRT (validator settings can affect fees).
- How privacy works: “Secret contracts” encrypt state so observers can’t trivially read sensitive contract data. Fee and gas behavior is documented in the official Fees and Gas documentation.
Best for
- Using privacy-preserving DeFi apps where supported
- Private smart contract interactions
- Builders who want a privacy-first execution environment
Trade-offs
- Privacy depends on the app and contract patterns, not just the chain brand
- Ecosystem access can fluctuate with listings and regional rules
- Validator fee settings can change (fees are not fixed constants)
Where to buy (regions vary)
- KuCoin
- Kraken
- Binance
- Bybit
- MEXC
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal venues where listed, or stick to non-privacy coins plus privacy tools if access is your main constraint.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Secret Wallet (as referenced in Secret documentation)
- Popular: Keplr (with Secret enabled), plus other Cosmos wallets that explicitly support SCRT privacy features
- Hardware: Ledger (via supported Cosmos wallet integrations, feature-dependent)
Official resources
- Website: scrt.network
- Docs: docs.scrt.network
- GitHub: github.com/scrtlabs
Network metadata note: Private contract state can reduce what’s visible on-chain, but it does not automatically hide network-level metadata or how requests reach validators.
5. Oasis Network (ROSE) | Confidential compute and privacy-enabled apps
What it is: Oasis is built around the idea of confidential computation, where certain environments can keep data private while still enabling on-chain interactions. Think “privacy-enabled apps” more than “private cash.”
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at 10 billion ROSE.
- Typical fee: Gas-based. Consensus transfers require ~1000 gas units, with fees calculated as gas × gas price per the Oasis consensus transaction specification.
- How privacy works: Oasis uses a runtime (ParaTime) model. Some ParaTimes focus on confidentiality, meaning privacy depends on the runtime and application, not the base token alone.
Best for
- Apps that require privacy-preserving computation
- Data-sensitive workflows where confidentiality is explicit
- Privacy-enabled DeFi where available
Trade-offs
- Privacy is not universal across all Oasis activity
- Understanding which runtime is in use adds UX complexity
- Exchange availability varies by region and compliance posture
Where to buy (regions vary)
- KuCoin
- Binance
- WhiteBIT
- Pionex
- Coinbase
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Stick to legal venues where listed, or consider other privacy smart contract ecosystems depending on your use case.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Oasis Wallet (web)
- Popular: Trust Wallet, MetaMask (for EVM ParaTimes where applicable), and ecosystem-recommended wallets
- Hardware: Ledger (via Oasis-supported integrations)
Official resources
- Website: oasis.net
- Docs: docs.oasis.io
- GitHub: github.com/oasisprotocol
- Explorer: explorer.oasis.io
Network metadata note: Confidential runtimes can reduce what’s visible on-chain, but they do not automatically hide network-level metadata or how transactions reach validators.
6. Decred (DCR) | Governance-heavy chain with privacy tooling (not privacy-by-default)
What it is: Decred is best known for its on-chain governance system and hybrid consensus model. Privacy is available through tooling and integrations, but it is not the same thing as a chain where all transfers are private by default.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at 21 million DCR.
- Typical fee: Variable and usage-dependent. Fees are not privacy-specific and depend on transaction structure and network conditions.
- How privacy works: Decred does not enforce universal transaction privacy. Privacy options exist through specific transaction types and tools, meaning outcomes depend on how you transact and which integrations you use.
Best for
- Users who value governance and disciplined protocol upgrades
- People who want privacy options without adopting a privacy-only identity
- Long-term holders who want a chain with formal on-chain decision-making
Trade-offs
- Not a privacy-by-default payments chain
- Privacy UX depends on tools, wallets, and integrations
- Smaller privacy set compared to chains where all activity is private
Where to buy (regions vary)
- Binance
- Pionex
- MEXC
- BYDFi
- CoinW
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use regulated venues where listed, or choose privacy coins whose primary function is private transfer.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Decrediton (Decred Wallet)
- Hardware: Ledger Nano S Plus, Ledger Nano X
Official resources
- Website: decred.org
- Docs: docs.decred.org
- GitHub: github.com/decred
- Explorer: explorer.dcrdata.org
Network metadata note: Decred’s privacy tooling can reduce on-chain traceability in certain cases, but it does not provide a universal, protocol-level privacy guarantee.
7. Firo (FIRO) | Privacy-focused transfers with modern cryptographic designs
What it is: Firo is a privacy coin designed to make private value transfers more practical and user-friendly than older, mixing-only approaches. Its privacy model has evolved over time through multiple protocol upgrades.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at approximately 21.4 million FIRO.
- Typical fee: Varies by transaction type and network policy.
- How privacy works: Firo uses specialized cryptographic constructions designed for private value transfer, rather than simple transaction mixing. Privacy behavior depends on the transaction type used.
Best for
- Private value transfers when supported end-to-end
- Users who want privacy without an always-on default model
- People who care about protocol evolution and ongoing upgrades
Trade-offs
- Exchange support can be uneven depending on region
- Not all wallets and exchanges support every privacy transaction type
- Lower liquidity and smaller anonymity sets in some markets
Where to buy (regions vary)
- MEXC
- CoinEx
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal listings where available, or consider other privacy coins with stronger exchange coverage.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Firo Wallet
- Popular: Atomic Wallet, Guarda Wallet
- Hardware: Ledger, Trezor, Tangem
Official resources
- Website: firo.org
- GitHub: github.com/firoorg
- Explorer: explorer.firo.org
Network metadata note: Firo’s privacy features focus on hiding transaction details, but they do not automatically conceal network-level metadata or guarantee anonymity across unsupported platforms.
8. Grin (GRIN) | MimbleWimble minimalism with real UX friction
What it is: Grin is a privacy-focused chain built on MimbleWimble, aiming for lightweight, scalable privacy. It is intentionally minimal and comes with a more hands-on user experience than most mainstream chains.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Infinite supply by design.
- Typical fee: 500,000 nanogrin (0.0005 GRIN) base fee, defined as the default relay fee in Grin RFC-0017.
- How privacy works: MimbleWimble uses cut-through and confidential transactions to hide amounts and reduce on-chain data. This changes how transactions are constructed and exchanged, making workflows less “plug and play.”
Best for
- Users who specifically want a MimbleWimble-native chain
- People comfortable with manual, interactive wallet workflows
- Lightweight privacy transfers where UX trade-offs are acceptable
Trade-offs
- User experience is the biggest barrier for most users
- Smaller ecosystem and fewer mainstream integrations
- Exchange availability can be thin and region-dependent
Where to buy (regions vary)
- Gate
- HitBTC
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Stick to legal venues where listed, or consider privacy coins with broader exchange support.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Grin++
- Popular: Community wallets such as Niffler
- Hardware: None (no major hardware wallet supports GRIN natively)
Official resources
- Website: grin.mw
- Docs: docs.grin.mw
- GitHub: github.com/mimblewimble
- Explorer: grinexplorer.net
Network metadata note: MimbleWimble hides transaction amounts and prunes history, but it does not automatically conceal network-level metadata or eliminate interaction-based leaks.
9. Beam (BEAM) | MimbleWimble plus an “ecosystem” approach
What it is: Beam is a MimbleWimble-based privacy chain that emphasizes productization: wallets, assets, and ecosystem tooling. It aims to make privacy tech usable without living in a terminal.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at approximately 58.47 billion BEAM.
- Typical fee: 0.001 BEAM for standard transactions and 0.011 BEAM for offline transactions, as listed in Beam wallet documentation.
- How privacy works: Built on MimbleWimble with confidential transfers by design. Beam also supports “Confidential Assets,” enabling private assets within the Beam ecosystem.
Best for
- MimbleWimble privacy with more user-facing tooling
- Users who want private-by-default behavior with product polish
- Exploring confidential assets on a privacy-native chain
Trade-offs
- Token and ticker confusion across platforms (verify what you’re buying)
- Smaller ecosystem than top-layer chains
- Exchange support varies by region
Where to buy (regions vary)
- MEXC
- Gate
- CoinEx
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal listings where available, or consider other privacy-by-default chains depending on your needs.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Beam Wallet
- Popular: MetaMask, Phantom, Rabby (via supported integrations where applicable)
- Hardware: Ledger, Trezor
Official resources
- Website: beam.mw
- Docs: docs.beam.mw
- GitHub: github.com/BeamMW
- Explorer: explorer.beam.mw
Network metadata note: MimbleWimble hides transaction amounts and reduces on-chain data, but it does not automatically conceal network-level metadata or eliminate interaction-based leaks.
10. Beldex (BDX) | Privacy ecosystem messaging, VPN, and token utility (higher scrutiny category)
What it is: Beldex is a privacy-focused ecosystem that bundles a native token with privacy-oriented applications and services. It positions itself around private usage across multiple surfaces, not just on-chain transfers.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Infinite max supply.
- Typical fee: Protocol-defined and variable; no fixed numeric fee is publicly specified.
- How privacy works: Beldex positions its chain and ecosystem around privacy primitives and privacy-focused applications. Actual privacy guarantees depend on the specific app, wallet defaults, and current chain rules.
Best for
- Users who want a privacy “suite” rather than a standalone coin
- People who value integrated privacy apps within a single ecosystem
- Transfers where confidentiality tooling and branding are priorities
Trade-offs
- Higher regulatory scrutiny risk category
- Exchange availability can be unstable across regions
- Requires verifying what is live versus what remains roadmap messaging
- Smaller global liquidity than top-tier assets in many markets
Where to buy (regions vary)
- KuCoin
- CoinEx
- MEXC
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal venues where listed. If low-regret access is a priority, consider chains with optional privacy tools rather than privacy-first branding.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Beldex Wallet
- Hardware: Tangem
Official resources
- Website: beldex.io
- Whitepaper: beldex.io/whitepaper.pdf
Network metadata note: Ecosystem-level privacy tools can reduce visible activity within specific apps, but they do not automatically eliminate network-level metadata or regulatory exposure.
11. MobileCoin (MOB) | Mobile-first private payments with Fog services
What it is: MobileCoin is designed for fast, private payments on resource-constrained devices. It combines privacy-preserving transfers with a supporting service layer intended to help lightweight clients operate efficiently.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply is not consistently published across sources.
- Typical fee: Selected automatically by the wallet based on network conditions; not a fixed, hard-coded value per MobileCoin API documentation.
- How privacy works: MobileCoin uses privacy mechanisms described in its official technical materials and relies on Fog services as a supporting component for lightweight clients. Design details are documented in the MobileCoin whitepaper and Fog threat model.
Best for
- Mobile-oriented payments where lightweight syncing matters
- Users who want privacy tightly coupled to a payment UX
- People who value a documented threat model for supporting services
Trade-offs
- Ecosystem and exchange coverage can be limited
- Supporting service assumptions matter (understand Fog’s model)
- Liquidity and availability vary widely by region
Where to buy (regions vary)
- Gate
- CoinEx
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal venues where listed, or choose a privacy coin with broader global access.
Wallets that support it
- Official: MobileCoin desktop wallet
- Popular: Atomic Wallet, MetaMask
- Hardware: Ledger
Official resources
- Website: mobilecoin.com
- GitHub: github.com/mobilecoinfoundation/mobilecoin
- Whitepaper (PDF): MobileCoin whitepaper
Network metadata note: MobileCoin’s design reduces on-chain visibility for transaction details, but supporting services introduce assumptions that users should understand when evaluating privacy guarantees.
12. Horizen (ZEN) | ZK infrastructure and sidechain framework, not “private cash” anymore
What it is: Horizen today is better framed as a broader platform and ZK-enabled infrastructure story than a simple privacy coin. If your mental model is “shielded payments coin,” update it.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at 21 million ZEN.
- Typical fee: Policy-based and node-defined, with no single fixed fee published.
- How privacy works: Horizen uses zk-SNARK verifiable certificates within its sidechain framework, with implementation details described in official repositories. A practical starting point is the official client repository README (HorizenOfficial/zen). Also relevant context: Horizen’s own materials have discussed changes to private transaction capability over time.
Best for
- People who want ZK-heavy infrastructure narratives
- Users exploring sidechain frameworks and ZK certificates
- Those who want a platform story more than private cash
Trade-offs
- Not a straightforward private payments coin in practice
- Product complexity can be high (multiple layers)
- Narrative can be confusing if you’re coming from classic privacy coins
Where to buy (regions vary)
- KuCoin
- Binance
- Bybit
- OKX
- MEXC
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal listings where available, or pick a privacy model that matches your actual goal (payments vs compute vs tooling).
Wallets that support it
- Official: Sphere by Horizen
- Popular: Atomic Wallet, Guarda Wallet
- Hardware: Ledger Nano S Plus, Ledger Nano X, Tangem
Official resources
- Website: horizen.io
- GitHub: github.com/HorizenOfficial/zen
- Whitepaper (PDF): Horizen 2.0 whitepaper
Network metadata note: Horizen’s ZK components can reduce what’s revealed within specific systems, but privacy outcomes depend on the product layer and do not automatically hide network-level metadata.
13. Aleph Zero (AZERO) | Privacy narrative anchored in ZK identity and selective disclosure
What it is: Aleph Zero is a proof-of-stake chain that frames privacy through zero-knowledge constructs and selective disclosure, particularly around identity and credentials. It is not a Monero-style private payments coin.
Quick Stats (snapshot)
- Supply notes: Maximum supply capped at approximately 520 million AZERO.
- Typical fee: Weight- and resource-based (Substrate model), calculated per transaction complexity rather than a fixed fee.
- How privacy works: Aleph Zero documents ZK-ID and registrar mechanics in official documentation, framing privacy around identity, credentials, and selective disclosure. Broader context is discussed in Aleph Zero’s materials on ZK’s role in enhancing privacy.
Best for
- Selective disclosure and credential-style privacy narratives
- Builders exploring ZK-based identity and registrar flows
- Users who want privacy features without a privacy-only chain identity
Trade-offs
- Privacy is not always-on across all activity
- Trust assumptions can shift toward registrars or issuers
- Small-cap asset risk and region-dependent availability
Where to buy (regions vary)
- MEXC
- BingX
- KuCoin
- CoinEx
- WhiteBIT
Check the CoinGecko page for the most up-to-date information on listings.
Use legal venues where listed, or treat AZERO as technology exposure rather than a required privacy rail.
Wallets that support it
- Official: Aleph Zero Wallet
- Popular: Atomic Wallet
- Hardware: Ledger (feature-dependent), OneKey, Tangem
Official resources
- Website: alephzero.org
- Docs: docs.alephzero.org
Network metadata note: ZK-based identity and credential systems can reduce what is disclosed in specific interactions, but they do not automatically hide network-level metadata or eliminate trust assumptions around issuers.
Other Notable Privacy Coins
Pirate Chain (ARRR): Privacy-by-default branding with a strong “shielded only” angle, but exchange availability can be the whole story in practice.
Verge (XVG): A historical privacy narrative that leans heavily on network-layer routing claims. Treat it as a case study in “privacy claims vs privacy guarantees."
Bytecoin: Important as an early CryptoNote lineage mention, but real-world relevance today is a separate question. If you include it, frame it as history, not a top pick.
Threshold Network (T): More “privacy infrastructure” than classic privacy coin. It fits the long-tail query set but shouldn’t be framed as a Monero/Zcash peer.
Litecoin MWEB: A mainstream-chain privacy feature worth mentioning, but it’s feature-scoped and depends on actual usage patterns and wallet/exchange support.
How Privacy Coins Work (Core Concepts and Advanced Techniques)
Privacy coins don’t rely on a single feature. They layer multiple protections together. Some obscure who is paying, others hide the recipient, others conceal the amount, and some even reduce network-level tracking. Privacy isn’t a switch you turn on. It’s a stack of defenses working together.
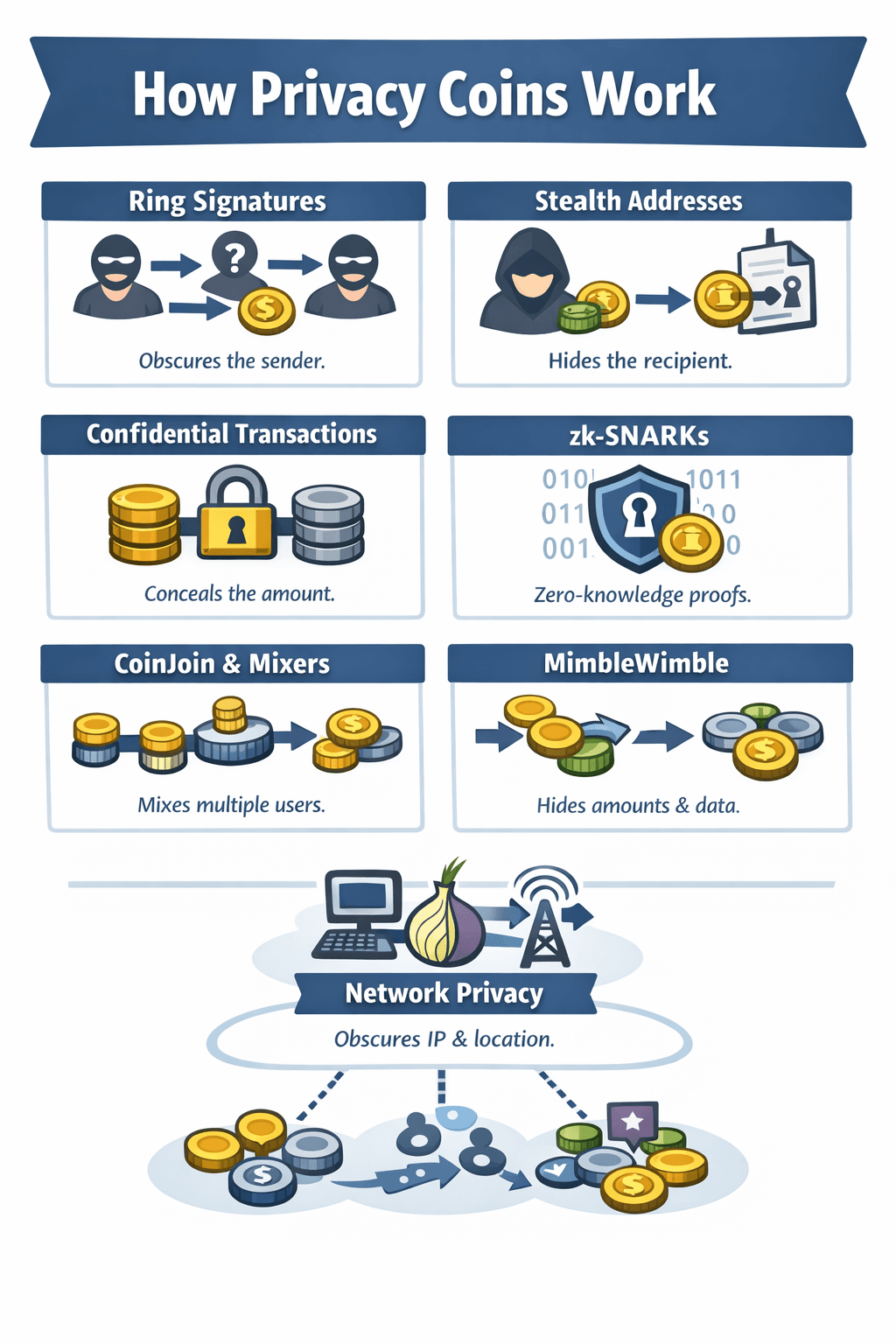 The Underlying Workings Of Privacy Coins
The Underlying Workings Of Privacy CoinsRing Signatures (Monero-style sender ambiguity)
Ring signatures obscure the sender.
When funds are spent, the real input is mixed with decoys from the blockchain. Observers can see that one input is valid, but cannot tell which one it is. Tracing becomes probabilistic rather than certain. The key idea is uncertainty. You don’t prove ownership of a specific output. You prove membership in a group of possible outputs.
Stealth Addresses (Recipient privacy)
Stealth addresses protect the receiver.
Each payment generates a unique, one-time destination derived from the recipient’s public keys. Only the recipient can detect and spend those funds. This prevents address reuse and makes it impossible for outsiders to scan the blockchain and reconstruct balances or transaction histories.
Confidential Transactions and RingCT (Amount privacy)
Confidential Transactions hide transaction amounts.
The blockchain verifies that inputs equal outputs without revealing values. RingCT combines this with ring signatures, so sender, receiver, and amount are all hidden together. To keep transactions efficient, Monero later adopted Bulletproofs, which significantly reduced proof size and fees while preserving privacy.
zk-SNARKs and Modern Zero-Knowledge Proofs (Zcash-style)
Zero-knowledge proofs take a different approach.
Instead of using decoys, zk-SNARKs allow transactions to be verified without revealing any transaction data at all. Sender, receiver, and amount exist only inside the proof. Zcash supports both transparent and shielded transactions. The limitation is adoption. If most users stay outside the shielded pool, anonymity sets shrink despite strong cryptography.
CoinJoin and Mixers (Dash/Bitcoin tools comparison later)
CoinJoin-style systems rely on user coordination.
Multiple users combine inputs and outputs into a single transaction, making flows harder to trace. Dash’s PrivateSend works this way, requiring users to opt in and often repeat mixing rounds. Privacy here depends on participation, timing, and resistance to analysis, making it weaker than systems where privacy is mandatory.
MimbleWimble (Grin and Beam)
MimbleWimble rethinks transactions entirely.
There are no traditional addresses, amounts are hidden by default, and much historical data can be safely removed. This reduces both blockchain bloat and information leakage. The trade-off is usability. Interactive transactions and unfamiliar workflows can feel awkward, even though the privacy guarantees are protocol-level.
Network-Layer Privacy (Often ignored, very valuable)
On-chain privacy doesn’t stop network surveillance.
Even if transaction data is hidden, IP-level metadata can still leak origin information. Protocols like Dandelion++ reduce this risk by obscuring transaction origin before wider broadcast. This doesn’t make users invisible, but it raises the cost of tracking and strengthens overall privacy when combined with on-chain protections.
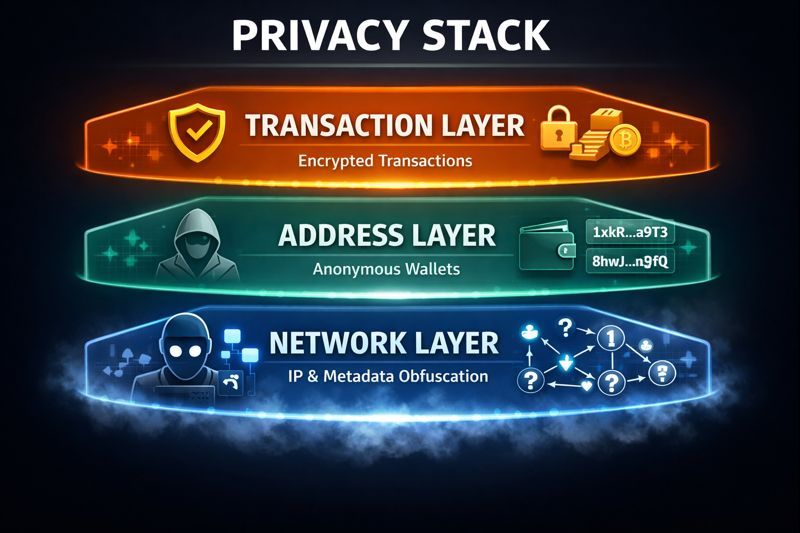 On-Chain Privacy Doesn’t Stop Network Surveillance
On-Chain Privacy Doesn’t Stop Network SurveillanceWhy Use Privacy Coins? Benefits With Real Examples
Privacy coins solve problems that transparent blockchains create by default. These problems are not theoretical. They show up in personal finances, business operations, and real-world safety concerns. Below, we follow the outline exactly and keep the framing practical and neutral.
Personal Financial Privacy
On public blockchains, financial activity becomes a permanent record. Once a wallet is linked to your identity, your income, savings, and spending patterns are visible to anyone.
For freelancers, this directly affects freelancer income confidentiality. If a client can see past payments or wallet balances, it weakens negotiating power and exposes earnings that would normally stay private.
Wallet transparency also enables doxx-by-wallet. If a payment or donation address is ever tied to your real identity, your entire transaction history becomes searchable, increasing the risk of harassment, extortion, or social engineering.
Visible balances also attract targeted scams based on holdings. Scammers actively look for wallets that appear valuable and tailor phishing or impersonation attempts around known asset levels.
Privacy coins reduce these risks by preventing casual balance checks and transaction history scraping.
Business Use
Businesses face a different but equally serious problem with transparent ledgers.
Public blockchains can expose supplier and payroll confidentiality. Payment timing, amounts, and counterparties can reveal salary structures, vendor relationships, or treasury activity that would normally remain internal. Central banks and financial regulators have acknowledged this issue. The Bank for International Settlements discusses how excessive transaction transparency can expose sensitive commercial relationships in its analysis of privacy and confidentiality in digital payments.
This transparency also allows competitors to map revenue flows. By tracking on-chain inflows and outflows, rivals can infer sales volume, cash-flow pressure, or seasonal dependence without direct access to the business.
Privacy coins allow businesses to pay suppliers, run payroll, and manage treasuries without broadcasting sensitive operational data. This isn’t about hiding wrongdoing. It’s about preserving the baseline confidentiality businesses already expect in traditional finance.
Fungibility and “Tainted Coins”
Fungibility means every unit of money should be interchangeable.
On transparent blockchains, transaction history follows coins indefinitely. That makes it possible to label coins as “clean” or “tainted” based on past activity, even when the current holder had no involvement.
This risk is widely acknowledged. The Financial Action Task Force explicitly recognizes that transaction history affects how virtual assets are treated under AML frameworks.
Privacy coins restore fungibility by hiding transaction history at the protocol level. If history cannot be selectively inspected, coins remain interchangeable, a core requirement for any asset expected to function as money rather than a reputation-scored token.
Restrictive Environments and Humanitarian Context
In some regions, financial surveillance is not abstract. Capital controls, account freezes, and restricted access to banking services are documented realities. The International Monetary Fund outlines how capital controls affect individuals and businesses in its overview of capital flow management measures.
In these environments, privacy tools are sometimes used defensively. The goal is personal safety and access, not evasion coaching. That distinction matters.
This context applies to:
- People living under strict capital controls
- Journalists and civil society actors
- Individuals moving funds for basic personal security
Privacy coins are not a solution to every problem, but they can reduce exposure where financial transparency creates personal risk.
Protection from Blockchain Analysis
Blockchain analysis works even without names.
Analysts cluster addresses, track transaction timing, and model behavior to infer relationships and activity. Transparent ledgers leak usable data even when users avoid obvious mistakes.
Public institutions openly acknowledge this capability. The Internal Revenue Service describes how blockchain analysis supports investigations in its virtual currency guidance.
Privacy coins limit what can be inferred from on-chain data alone. They don’t make users invisible, but they significantly raise the cost of large-scale tracking. That is why privacy-by-design systems exist alongside transparent chains, rather than relying solely on add-on tools.
Privacy Coins vs Privacy Tools
Privacy coins aren’t the only way users try to protect transaction privacy. Many rely on tools layered on top of transparent blockchains instead. The real difference comes down to trust, usability, and how many things can go wrong in practice.
Built-In Privacy vs External Tools
Built-in privacy is enforced by the protocol itself. Every transaction follows the same rules by default, without opt-ins, manual configuration, or reliance on third parties.
External tools shift that burden onto the user. You must choose the tool, use it correctly every time, and trust that it works as intended. Each extra step increases the risk of misconfiguration, user error, or dependency on intermediaries.
This distinction is reflected in how institutions discuss privacy-by-design systems versus add-on protections. The European Central Bank has noted that privacy outcomes depend more on system architecture than on perfect user behavior.
In short, native privacy reduces user error. External tools increase it.
Bitcoin Privacy Tools (CoinJoin etc.)
On Bitcoin, privacy tools typically rely on CoinJoin-style coordination.
Tools like Wasabi and JoinMarket combine multiple users’ inputs and outputs into a single transaction to increase ambiguity. However, all transactions still remain publicly visible on Bitcoin’s ledger.
CoinJoin improves privacy compared to basic address reuse, but it has limits. Anonymity depends on participant size and consistency, while timing and amount analysis can still reduce uncertainty. These tools help, but they don’t change Bitcoin’s underlying transparency.
Ethereum Mixing and Tornado Cash (case study)
Ethereum mixers use smart contracts to break the link between deposits and withdrawals. Funds enter a public pool and later exit to a new address, obscuring direct connections.
The Tornado Cash case highlighted the regulatory risk of this model. The Office of Foreign Assets Control demonstrated how quickly open, non-custodial infrastructure can become legally restricted.
This raised two issues: legal uncertainty around smart-contract privacy tools and compliance risk for users interacting with sanctioned contracts.
Why Native Privacy Can Be Stronger (and where it isn’t)
Native privacy systems enforce uniform behavior. When everyone follows the same privacy rules by default, anonymity sets grow naturally and individual mistakes matter less.
The trade-offs are real. Privacy coins face higher delisting risk, more complex wallets, and weaker exchange access in some regions.
Global regulators acknowledge this balance. The Financial Stability Board found “significant gaps and inconsistencies” in the implementation of crypto and stablecoin recommendations.
The choice isn’t binary. Native privacy offers stronger, consistent guarantees. External tools offer flexibility but depend on correct use and legal tolerance.
What makes sense depends on jurisdiction, risk appetite, and how much friction a user is willing to accept.
How to Buy Privacy Coins
Buying a privacy coin isn’t complicated, but there are a few realities you should understand upfront. Availability varies by region. KYC is common. And self-custody matters more here than with most other assets. We’ll keep this practical and beginner-safe.
 Step-By-Step Flow of the Privacy Coin Buying Process
Step-By-Step Flow of the Privacy Coin Buying ProcessStep-by-Step: Buying Your First Privacy Coin
Step 1: Choose an Exchange (Region Matters)
Privacy coin listings vary by country. Before signing up, confirm the exchange supports the coin in your region. Listings can change due to regulations. Most major exchanges publish region-specific availability in their support documentation. For example, Kraken explains asset availability and regional restrictions in its official supported assets overview.
 Image Via Kraken
Image Via KrakenStep 2: Completed KYC
Most regulated exchanges require identity verification. This means the exchange knows who you are at the point of purchase.
That’s expected. It also means privacy does not start at the exchange. Privacy starts after withdrawal. Regulators themselves describe exchanges as regulated gateways, including the Financial Action Task Force.
 Most Regulated Exchanges Require Identity Verification. Image Via Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
Most Regulated Exchanges Require Identity Verification. Image Via Financial Action Task Force (FATF)Step 3: Deposit Funds
Exchanges usually support:
- Bank transfers (lowest fees, slower)
- Card payments (instant, higher fees)
- Crypto deposits (if you already hold crypto)
Fees and settlement times vary by method. Exchanges like Coinbase document this clearly in their funding guides.
 There Are Multiple Deposit Methods. Image Via Coinbase
There Are Multiple Deposit Methods. Image Via CoinbaseStep 4: Place an order
Navigate to the trading page for your chosen coin, such as Monero or Zcash.
- Market order: Buys instantly at the current price
- Limit order: Sets a price and waits
Market orders are simpler for beginners. Limit orders offer more control if you’re patient.
 Market Orders are Simpler for Beginners. Image Via Binance
Market Orders are Simpler for Beginners. Image Via BinanceStep 5: Withdrawal to wallet
Leaving privacy coins on an exchange undermines their purpose. Exchanges can freeze accounts, restrict withdrawals, or delist assets. Withdrawing to your own wallet gives you control of your keys and allows the protocol’s privacy features to function as intended.
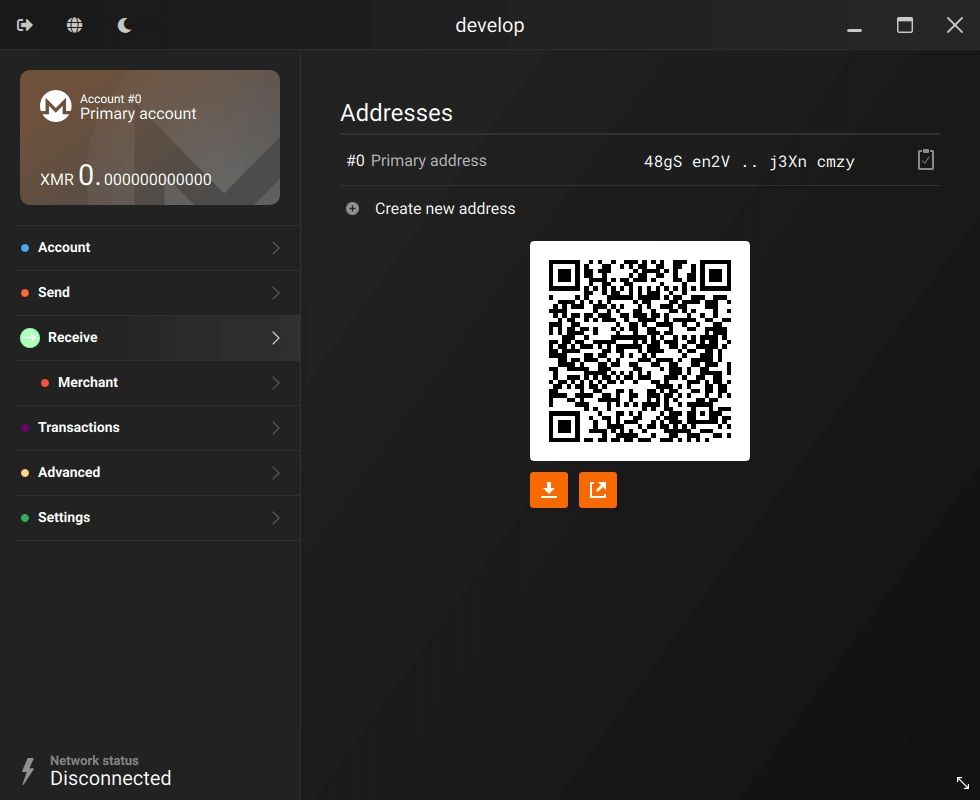 Withdrawing to Your Own Wallet Gives You Control of Your Keys. Image Via getmonero.org
Withdrawing to Your Own Wallet Gives You Control of Your Keys. Image Via getmonero.orgIf Your Exchange Doesn’t List Privacy Coins
Privacy coin delistings are usually driven by compliance costs, not technical issues. Different countries apply different interpretations of AML and travel rule requirements. Regulators have acknowledged these pressures.
If your local exchange doesn’t list a privacy coin, your options depend on what is legal where you live:
- Other regulated exchanges that still list the asset
- Peer-to-peer marketplaces, where permitted
- On-chain swaps where supported by the protocol
The key point is legality. This guide does not recommend bypassing regional restrictions.
First Transaction Walkthrough (Beginner-safe)
Receiving address basics (per coin)
Some privacy coins generate a new receiving address for every transaction. Others reuse a public address but create one-time destinations under the hood.
Wallet software handles this for you. Always use the “receive” function inside the wallet instead of copying old addresses from the transaction history.
Confirmations and time expectations
Transactions are not instant finality. Each network has its own confirmation rules. Some wallets show “pending,” “confirmed,” and “locked” states before funds are spendable.
These states are explained in official wallet guides, such as Zcash’s description of transaction confirmations.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Sending coins on the wrong network
- Forgetting memo or tag fields when required
- Closing a wallet before a transaction fully syncs
- Assuming “sent” means “confirmed”
Most lost-funds stories come down to simple process errors, not protocol failure.
Legal Status and Regulation
Privacy coins sit at the intersection of financial innovation and compliance pressure. Ownership is usually legal. Trading access is where the friction shows up. Below is a clear, date-aware snapshot without hype or fear-mongering.
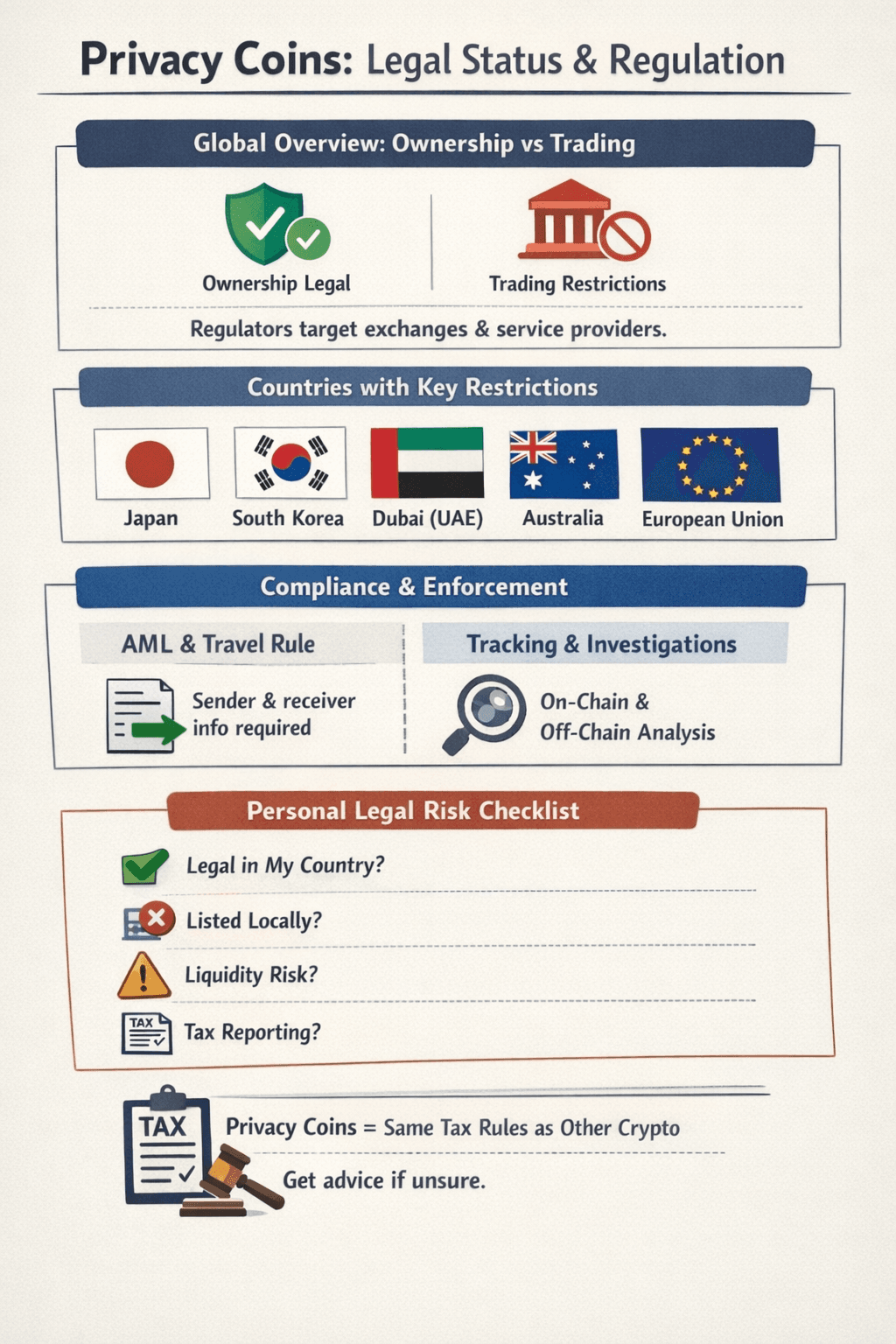 One Pager on Privacy Coins' Legal Status and Regulation
One Pager on Privacy Coins' Legal Status and RegulationGlobal Overview (ownership vs trading availability)
Most regulators do not attempt to ban cryptographic protocols. Instead, they regulate access points such as exchanges, custodians and brokers.
International policy bodies have been clear that compliance responsibilities sit with service providers. As a result, privacy coins are more likely to be delisted or restricted than outlawed outright.
Countries and Regions With Notable Restrictions
Japan
Japan’s Financial Services Agency has historically pushed exchanges to delist privacy coins due to AML monitoring concerns. The FSA outlines its regulatory approach to crypto-asset exchanges in its Virtual Currency Exchange Service Provider framework.
South Korea
South Korea applies strict AML and travel rule enforcement at the exchange level. The Financial Services Commission has made clear that exchanges must support transaction monitoring, which has contributed to privacy coin delistings. This position is outlined in the FSC’s official crypto-asset policy materials.
UAE (Dubai)
The UAE allows crypto activity under licensing regimes, but privacy-focused assets face higher scrutiny. Dubai’s Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority explains its expectations for exchange compliance and asset listings in its official regulatory framework.
Australia
Australia has not banned privacy coins, but exchanges must comply with strict AML reporting. AUSTRAC explains how digital currency exchanges are regulated under Australia’s AML laws in its guidance on digital currency exchange registration.
United States
The U.S. does not ban privacy coins at the protocol level. Regulatory pressure shows up through enforcement, exchange policies, and reporting obligations. Federal agencies focus on intermediaries rather than outlawing specific code.
European Union
The EU’s direction of travel is clearer. The Markets in Crypto-Assets framework increases compliance requirements for service providers, which affects how exchanges handle privacy-focused assets. The European Commission summarizes this framework in its overview of MiCA regulation.
AML, Travel Rule, and Compliance Pressure
The FATF Travel Rule requires exchanges and custodians to collect and transmit sender and receiver information for qualifying transfers. This rule applies globally through national implementation. The FATF describes how this affects crypto markets in its guidance on AML/CFT measures for virtual assets.
Because privacy coins limit transaction visibility, exchanges must rely on internal controls or restrict access entirely. This compliance burden explains why delisting often aligns with regulatory deadlines rather than technical changes.
Enforcement and “Can They Trace It?”
Claims that privacy coins are either fully anonymous or fully traceable are misleading.
Law enforcement agencies acknowledge that on-chain analysis has limits when transaction data is hidden by design. At the same time, investigations often rely on off-chain data such as exchange records and operational errors.
The U.S. Internal Revenue Service describes this multi-pronged approach in its public materials on virtual currency investigations. Privacy coins reduce what can be learned from blockchain data alone. They do not eliminate all investigative methods.
Personal Legal Risk Checklist
Before using privacy coins, ask yourself:
- Are privacy coins legal to own in my country?
- Do local exchanges list them, or would I need alternatives?
- Am I prepared for delisting risk or reduced liquidity?
- Do I understand my tax reporting obligations?
Privacy does not remove tax responsibilities. Most authorities treat privacy coins the same as other crypto assets for reporting purposes. When regulations are unclear, professional advice is safer than assumptions.
Privacy Coins as Investments
Privacy coins are not just tools. People also treat them as speculative assets. That matters because the investment case looks very different from the usage case.
This section keeps those two ideas separate.
 This Infographic Explains Whether You Should Treat Privacy Coins As Investments
This Infographic Explains Whether You Should Treat Privacy Coins As InvestmentsInvestment Thesis
The long-term demand case for privacy coins rests on one core trend: financial surveillance is increasing, not decreasing.
Regulators, analytics firms, and platforms continue to expand transaction monitoring. At the same time, data breaches and identity theft remain persistent problems. Public institutions acknowledge this tension. The Bank for International Settlements has discussed how digital financial systems must balance transparency with confidentiality in its work on privacy and data protection in digital finance.
Privacy coins sit on the other side of that trade-off. Their value proposition strengthens when users feel exposed on transparent chains.
The counterweight is clear. Privacy coins face heavier regulatory pressure, more delistings, and narrower fiat onramps than most other crypto assets. That caps adoption and liquidity, regardless of technical merit.
Risk Framework
Privacy coins carry several distinct risks. Ignoring any one of them leads to poor outcomes.
| Risk Category | Score | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Risk | 5/5 | Privacy coins face the highest delisting and access risk. Exchange availability can change quickly based on jurisdiction, regardless of protocol quality. |
| Liquidity Risk | 4/5 | Fewer listings and thinner order books increase slippage and volatility, especially during market stress or regulatory news. |
| Tech Risk | 3/5 | Privacy protocols rely on advanced cryptography and complex implementations. While many are well-studied, bugs are harder to detect and audit. |
| Adoption Risk | 4/5 | Strong privacy does not guarantee usage. Wallet UX, education gaps, and operational friction limit real-world adoption. |
| Narrative Risk | 4/5 | Media cycles, enforcement actions, or political statements can move prices sharply, independent of fundamentals or network health. |
Volatility and Correlation With Bitcoin
Privacy coins usually track Bitcoin during broad market moves, but they diverge during regulatory events. Historical price behavior shows that delisting announcements and policy signals often create outsized moves compared to Bitcoin itself. This pattern reflects thinner order books and concentrated liquidity.
Public market analysis from central banks and regulators consistently notes that crypto assets with lower liquidity amplify volatility during shocks, a point discussed in the European Central Bank’s analysis of crypto-asset market dynamics.
Portfolio Positioning
From a portfolio perspective, privacy coins behave more like high-risk satellites than core holdings.
They tend to work best as:
- Small, conviction-based allocations
- Diversifiers tied to regulatory and privacy narratives
- Long-term asymmetric bets rather than short-term trades
Position sizing and rebalancing matter more here than with large-cap assets. Liquidity can disappear quickly. Planning for that reality is part of the investment case, not an afterthought.
Challenges and Criticisms
Privacy coins address real problems, but they come with trade-offs that are often overlooked in bullish narratives. This section deals with the main criticisms directly, without moral panic or marketing spin.
 The Challenges and Criticisim Privacy Coins Have Faced
The Challenges and Criticisim Privacy Coins Have FacedIllicit Activity Association (and why that framing is incomplete)
Privacy coins are often framed as tools for criminal activity. That framing is incomplete.
Cash, encrypted messaging, and private bank accounts are all used for both legitimate and illegitimate purposes. Privacy alone does not imply intent. Regulators themselves acknowledge this distinction. The Financial Action Task Force notes that most financial crime still relies on traditional systems, not privacy-focused crypto assets, in its analysis of money laundering risk and methods.
At the same time, privacy coins do reduce on-chain visibility. That reality attracts scrutiny. The mistake is treating privacy as evidence rather than as a design choice with legitimate uses.
Delistings and Liquidity Constraints
Delistings are the most practical risk privacy coin users face. When an exchange removes a coin, liquidity drops fast, fiat on-ramps disappear, and price discovery weakens. These decisions are driven by compliance obligations, not technology.
Recent concrete examples:
- Binance
In January 2024, Binance announced the delisting of Monero, Zcash, and Dash for users in the European Economic Area, citing compliance requirements. - OKX
In January 2024, OKX removed Monero and several other privacy coins as part of a broader compliance update. - Kraken
Kraken delisted Monero for UK users in November 2021, then relisted it in February 2022 after regulatory clarification.
Technical Trade-offs
Strong privacy is expensive.
Privacy-focused transactions are typically larger, slower to verify, and more complex to implement than transparent ones. Wallet software must manage scanning, key derivation, and proof verification correctly. These trade-offs are acknowledged by protocol designers themselves.
Privacy reduces information leakage. It increases computational and UX overhead.
Adoption Barriers
Adoption remains uneven.
Merchant support for privacy coins is limited. Fiat onramps are fewer. Many users find privacy wallets intimidating compared to mainstream apps. Central banks studying digital payments consistently highlight usability and access as major adoption constraints. The Bank for International Settlements addresses these barriers in its work on retail digital payments and user adoption.
Without better tooling and education, privacy features stay underused even when they are available.
Notable Incidents and Public Perception
Public perception has been shaped by a handful of high-profile events.
Enforcement actions, sanctions, and government statements tend to blur distinctions between protocols, tools, and users. These moments matter because narratives move faster than technical explanations. The U.S. Treasury’s sanctions-related communications around privacy tools illustrate how quickly sentiment can shift when policy enters the conversation, as outlined in Treasury statements on digital asset enforcement.
Privacy coins are judged not only by what they do, but by how they are discussed. That gap between reality and perception remains one of their biggest challenges.
Recent Developments (2024–2025)
Exchange and Policy Moves
Dec 29, 2023 → Jan 5, 2024: OKX scheduled delistings for several privacy-coin spot pairs, including XMR, ZEC, DASH, and ZEN.
What it means for you: if your main onramp is a single exchange, access can disappear fast, and you may be forced into withdrawals on someone else’s timeline. See OKX’s official notice: OKX spot-pair delisting schedule.
Feb 5, 2024 → Feb 20, 2024: Binance announced it would delist Monero (XMR) spot pairs on Feb. 20, 2024.
What it means for you: the biggest practical risk for privacy coins is not the tech, it’s exchange access and liquidity fragmentation. Official announcement: Binance delisting notice (includes XMR).
2024–2025 theme: The “privacy coin squeeze” largely plays out at the exchange layer. You can still self-custody and transact on-chain, but the on/off-ramps get narrower, more region-dependent and more volatile.
Protocol Upgrades Worth Knowing
Monero (research + scalability direction)
In 2024, Monero’s community funding backed work toward Full-Chain Membership Proofs, a research direction aimed at improving how Monero proves membership/decoy properties without bloating usability. Official update: Full-Chain Membership Proofs development (Monero blog).
Why it matters: Monero keeps pushing on “strong privacy, less friction,” but progress comes via research-heavy steps, not flashy marketing launches.
Zcash (governance + upgrade track)
Zcash continued formalizing its upgrade path, including NU6-era changes and the follow-on NU6.1 governance/funding model work. Official overview: Zcash NU6.1 upgrade page.
Why it matters: With Zcash, it’s not just privacy tech; it’s also how the project funds and coordinates future upgrades.
Oasis (confidential compute iteration)
Oasis published regular engineering updates through 2024, reflecting ongoing changes to its stack and developer tooling around confidential compute. Official examples: May 2024 engineering update and October 2024 engineering update.
Why it matters: Privacy-smart-contract chains live or die on developer experience and runtime stability, and these updates show active iteration rather than “set it and forget it.”
How to Choose the Right Privacy Coin
There is no single “best” privacy coin. The right choice depends on what you actually want to do, how much friction you can tolerate, and how exposed you are to regulatory or liquidity risk. Use the filters below to narrow the field instead of chasing rankings.
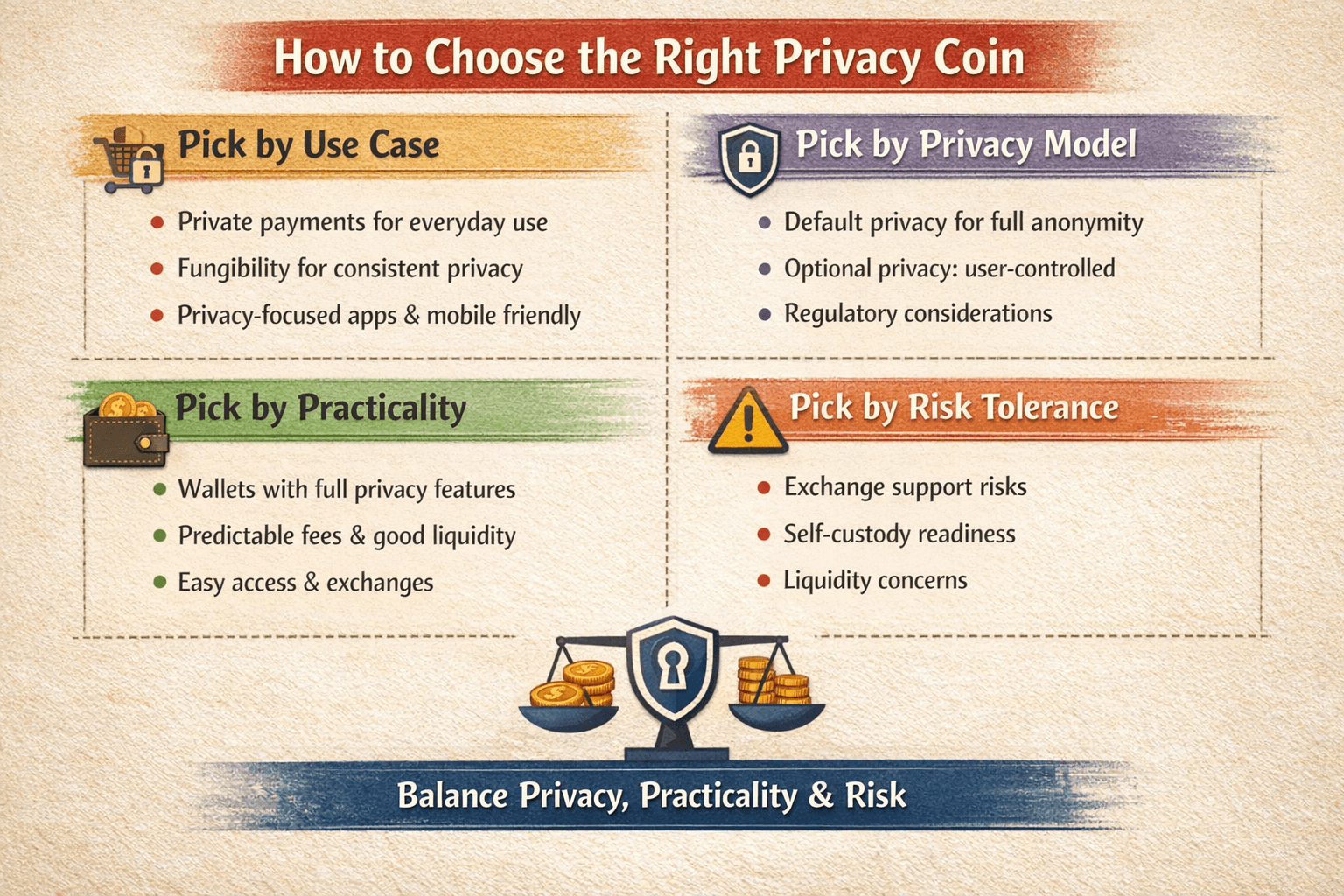 You Can Use This Simple Graphic To Choose The Right Privacy Coin For Your Neds
You Can Use This Simple Graphic To Choose The Right Privacy Coin For Your NedsPick by Use Case
- Everyday private payments: Choose coins with default privacy so sender, receiver, and amount are hidden automatically
- Fungibility matters: Consistent privacy reduces user error and uneven anonymity
- Privacy inside apps: Look for networks built for confidential computation, not just private transfers
- Mobile or lightweight use: Some coins are optimized for frequent use without running a full node
- Payment privacy expectations vary by use case, especially retail payments vs settlement, as noted by the Bank for International Settlements
Pick by Privacy Model
- Default privacy: All transactions follow the same rules, larger anonymity sets, fewer mistakes
- Optional privacy: Disclosure is possible, but privacy depends on user behavior
Pick by Practicality
Ask:
- Does the wallet support full privacy features by default?
- Are fees predictable enough for regular use?
- Is liquidity sufficient in your region?
- Wallets and exchanges change faster than protocols
- Practical access often matters more than theoretical guarantees
Pick by Risk Tolerance
- Avoid fragile exchange support if delistings would break your plan
- Privacy-by-design systems suit users comfortable with self-custody and variable liquidity
- Compliance pressure concentrates at the exchange layer.
Privacy Coins vs Bitcoin
Bitcoin and privacy coins solve different problems. One optimizes for transparency and verifiability. The other optimizes for confidentiality and fungibility. Lining them up side by side makes the trade-offs obvious.
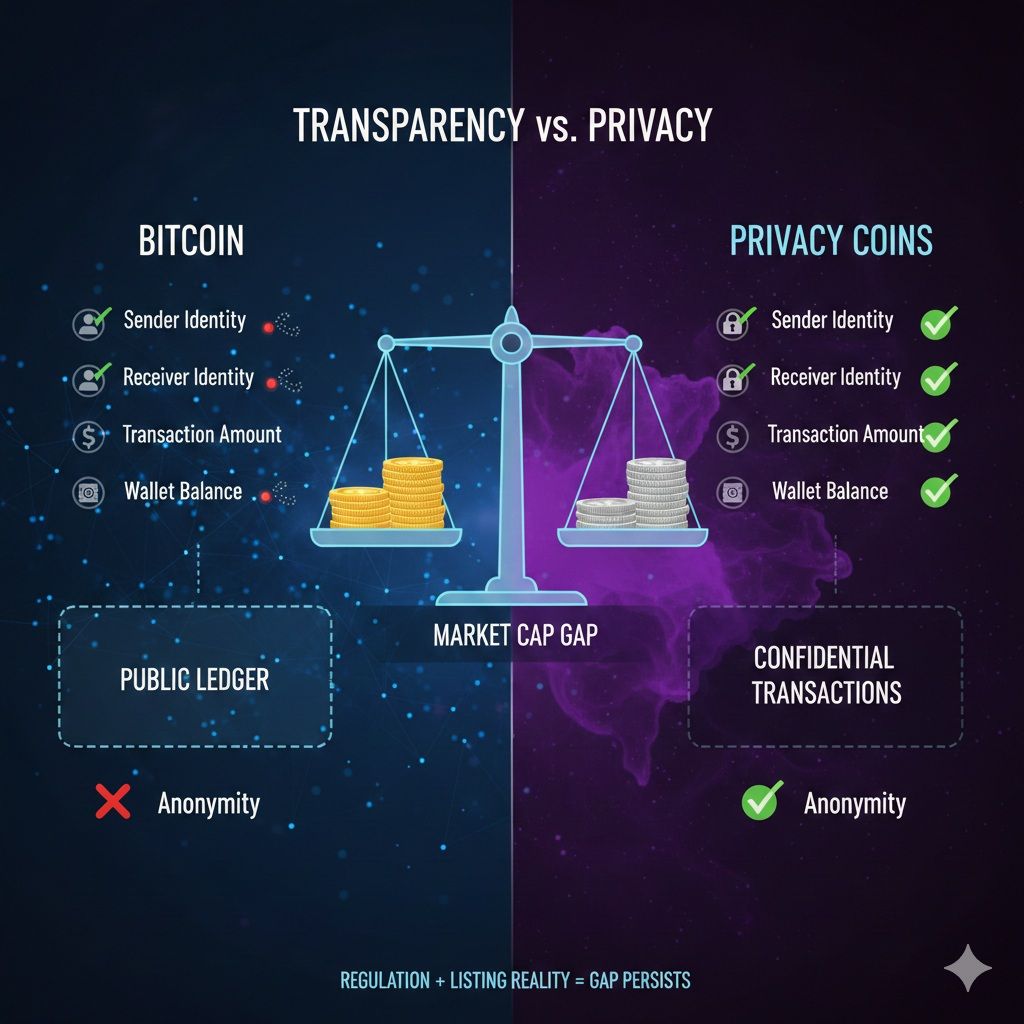 Privacy Coins Remain Niche But Purpose-Built
Privacy Coins Remain Niche But Purpose-BuiltTransparency and Traceability
Bitcoin transactions are transparent by design. Every transaction, amount, and address relationship is recorded on a public ledger that anyone can inspect. Bitcoin’s own documentation describes this openly in its explanation of the UTXO transaction model.
This transparency enables verification and auditability, but it also enables tracing. Address reuse, transaction graphs, and timing patterns allow observers to cluster activity over time.
Privacy coins take the opposite approach. They hide key data at the protocol level, such as sender, receiver, and amount. This design choice limits what can be inferred from the blockchain alone and reduces long-term data leakage.
Public institutions acknowledge that transparent ledgers expose behavioral patterns. The European Central Bank discusses how transaction-level transparency can reveal sensitive user information in its analysis of privacy considerations in digital payments.
Use-Case Split
Bitcoin is widely positioned as:
- A settlement network
- A store of value
- A censorship-resistant payment rail
Its transparency supports these roles by making supply, issuance, and transaction validity easy to verify.
Privacy coins are better suited for:
- Confidential payments
- Situations where fungibility matters
- Use cases where financial exposure creates risk
This split mirrors traditional finance. Public markets emphasize disclosure. Private transactions emphasize confidentiality. Both exist because they serve different needs.
Adoption and Market Positioning
Bitcoin’s market capitalization and liquidity are orders of magnitude larger than those of privacy coins. That gap persists for structural reasons, not technical ones.
Regulators, custodians, and financial institutions are more comfortable integrating transparent systems. Privacy-by-default assets introduce compliance complexity at the exchange and custody layer.
Global standard setters have noted this asymmetry. The Financial Stability Board explains how regulatory expectations shape crypto-asset market structure and access in its report on global regulatory frameworks for crypto-asset activities.
As a result:
- Bitcoin benefits from broad institutional adoption
- Privacy coins remain niche but purpose-built
Conclusion
Privacy coins are not “better Bitcoin.” They are purpose-built tools for a different job: reducing transaction traceability and restoring basic financial confidentiality on-chain. If you need privacy always on, default-private systems tend to be more reliable because they remove user choice as a failure point. If you need selective disclosure, auditability, or app-level privacy, optional models and confidential smart contract networks can fit better, but only if your wallet and workflow support them end-to-end.
The practical reality is that most risk concentrates at the access layer. Listings change, regions differ, and liquidity can thin out quickly. So the right question is not “Which privacy coin is best?” It’s “Which privacy model matches my use case, and can I still buy, hold, and use it safely where I live?”
If you treat privacy as a stack, not a switch, you will make better choices. Strong on-chain privacy helps, but sensible wallet habits, self-custody, and realistic expectations about regulation matter just as much.





