Rari CapitalFor centuries, the traditional insurance business model has proven to be an incredibly resilient one. However, traditional insurance is starting to feel the effects of digitisation as emerging, innovative technologies have gradually come to life on the scene and are progressively changing the way consumers interact with businesses and how services are delivered. One of these technologies is, of course, blockchain.
Blockchain technology is a decentralised and distributed public ledger that first emerged when Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin to the world, spearheading the dynamic ecosystem of cryptocurrencies that we know and love today. In its simplest form, blockchain can be described as follows:
Picture a spreadsheet that is duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. Then imagine that this network is designed to regularly update this spreadsheet and you have a basic understanding of the blockchain.” - BlockGeeks
As defined in the Bitcoin Whitepaper, blockchain stores, shares and synchronises data as ‘chains of blocks’ using cryptographic techniques. These blocks on the blockchain are comprised of digital pieces of information that exist in three parts.
The first is stored information about transactions, such as date, time and the dollar value of the transaction. The second is stored information about who is participating in the transaction. The third is stored information that distinguishes one block from the other.
 Blockchain Stores, Shares And Synchronises Data As Chains Of Blocks, Opening Up Some Exciting Opportunities In Business
Blockchain Stores, Shares And Synchronises Data As Chains Of Blocks, Opening Up Some Exciting Opportunities In Business
Thus, because blockchain databases essentially act as large storage points for synchronised, recorded information, blockchain technology opens the door for improved processes in many industries, including supply chains, healthcare and insurance.
By leveraging its distributed ledger technology (DLT), blockchain seeks to optimise efficiency, security and transparency for the entire crypto industry and it could potentially even come to totally disrupt the way insurance is done today. In fact, using open-source, public ledgers and fortified cybersecurity protocols, blockchain is poised to revolutionise traditional insurance parametres from the ground up, as it aims to facilitate a new, on-chain, trustless insurance model.
 Blockchain Is Set To Optimise The Security, Efficiency And Transparency Of The Insurance Industry
Blockchain Is Set To Optimise The Security, Efficiency And Transparency Of The Insurance Industry
Blockchain has seen multiple use cases throughout the years, from peer-to-peer payment coins to fine art tokenisation. But there is now a group of up-and-coming blockchain-based projects that aims to catapult blockchain to a whole new level in the crypto hemisphere, with a grade of complexity rivalling traditional businesses and financial structures.
We are of course talking about the emerging DeFi insurance protocols. Given the recent momentum in the crypto markets, paired with the huge capital gains made by individual projects and investors, it was only natural for insurance to make its way into the digital asset space, as there is most definitely a growing need and use case for it, especially in DeFi.
The Potential Of Blockchain Insurance
In this day and age, we’re so used to having insurance for our medical bills, lives and cars, but the multi-trillion dollar insurance industry also covers lots of other things, including crypto. Despite insurance being such an incredibly well-established industry, it is by no means perfect and it can potentially pose some problems to its clients, such as inefficiencies, fraud, human error, and most concerning of all, cyber attacks.
For instance, according to a 2015 KPMG report, Anthem Insurance revealed a data breach that exposed the sensitive data of 78.8 million customers, which resulted in the entire industry losing $375 million due to identify fraud.
 Traditional Insurance Models Can Expose Clients To Unnecessary Risks, Such As Data Breaches And Identity Fraud
Traditional Insurance Models Can Expose Clients To Unnecessary Risks, Such As Data Breaches And Identity Fraud
On the other hand, blockchain’s ability to generate trust in a trustless ecosystem through the use of public ledgers and fortified cybersecurity protocols, indeed has positive implications for the insurance industry’s future growth and sustainability. In fact, alongside the benefits for big data and artificial intelligence, the potential that comes with leveraging the power of blockchain in insurance mechanisms will most likely stem from three main components:
- Smart Contracts
- Advanced Automation
- Cybersecurity
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts allow blockchain network participants to transfer pretty much anything of value without the need for a third party intermediary. Similarly to physical, real-world contracts, smart contracts stipulate the rules between two entities, but in a decentralised environment. Moreover, unlike physical contracts, smart contracts can track insurance claims and hold both entities accountable, a major infrastructural advancement from traditional insurance systems.
 Smart Contracts Establish Pre-Set Rules Between Two Parties In A Permissionless Environment
Smart Contracts Establish Pre-Set Rules Between Two Parties In A Permissionless Environment
Thus, insurance policies could potentially be written as coded, decentralised smart contracts in which, for instance, an individual agrees to pay the insurance company in return for the company’s promise to help cover the individual’s future expenses in a specific area.
Smart contracts could therefore prove to be quite the step-up for insurance, as they would allow for the creation of immutable data based on an insurance policy owner’s records that can immediately accept or refuse any insurance claims made to the company.
For example, in the case of fraudulent claims on behalf of the policy owner, or if the insurance company no longer agrees to cover a condition previously agreed upon, the insurance smart contract can immediately dissolve and the premium payment will be transferred back to the client.
This process would indeed be mutually beneficial for both entities and would establish trust in a trustless environment, as all data would be transparent and any deviation from the agreement would result in the dissolution of the smart contract.
Advanced Automation
Because the traditional insurance ecosystem contains millions of individual insurers worldwide, it is relatively easy for the industry to become clogged-up with inefficiencies stemming from human error, paperwork and poor communication between parties.
Blockchain’s DLT technology can automate the somewhat outdated traditional insurance mechanisms, saving endless hours of bureaucracy and paperwork while reducing human error overall, as all data is safely stored and compartmentalised on-chain.
Cybersecurity
Blockchain’s ability to preserve and safeguard sensitive data constitutes the heart and soul of its technology and is deeply emblematic of its inherently disruptive nature. At present, in the 21st century, our data is pretty much tampered with on the daily and leveraged by big data corporations for their own monetisation purposes, no big surprise there!
However, blockchain’s ledgers are natively decentralised, meaning that they are relatively tamper-proof, cannot be easily corrupted and no central authority can control them. While blockchain data is encrypted, it is also completely transparent and visible to all on-chain members, or nodes.
This means that all nodes on the blockchain can view a particular individual’s transactions, which in turn allows them to verify the soundness of their actions and identify any malicious behaviour before it potentially becomes a threatening issue across the network.
 Given Its Ledger Transparency, Blockchain Nodes Can Identity Any Malicious Behaviour On-Chain Before It Can Pose A Major Threat To The Network
Given Its Ledger Transparency, Blockchain Nodes Can Identity Any Malicious Behaviour On-Chain Before It Can Pose A Major Threat To The Network
Through smart contracts, protocol automation and cybersecurity, insurance can develop into a thorough on-chain ecosystem set to utterly advance the industry’s propositions not only within the digital asset space, but in the realm of traditional coverage as well.
The Need For Insurance In DeFi
At the time of writing, there is over $70 billion locked in Decentralised Finance (DeFi) protocols, and despite it being a new, emerging ecosystem offering trustless and permissionless financial services to millions of people worldwide, DeFi comes with some surprisingly big risks. Essentially, because of the general lack of regulation, the DeFi space has at times been haunted by severe protocol hacks, stolen funds and millions of dollars worth in assets being lost forever.
 The Value Locked In DeFi Has Grown Exponentially, But So Has Its Exposure To Hacks And Attacks
The Value Locked In DeFi Has Grown Exponentially, But So Has Its Exposure To Hacks And Attacks
Perhaps the biggest hack in crypto history was the one suffered by Tokyo-based cryptocurrency exchange Coincheck, in which the exchange lost $532 million in digital assets, or about $420 million in NEM tokens.
Throughout 2020, over $120 million was stolen via hacks or exploits of DeFi platforms, and the year 2021 has also seen no shortage of malicious behaviour in the space with three different DeFi protocols, Rari Capital, Value DeFi and Larva Labs’ Meebits NFT project, being heavily exploited with $22 million lost in May.
In March 2021 PAID Network, a DeFi platform aimed at real-world businesses, was exploited in an ‘infinite mint’ attack that sent the PAID token crumbling from its price of $2.80 at the time to a low of $0.05, but quickly bounced back to $2.60 within a matter of days.
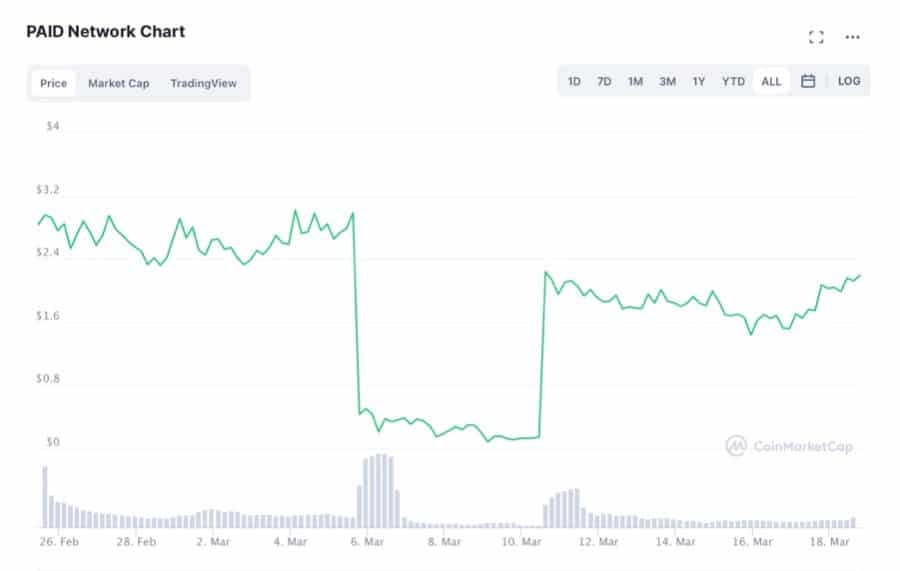 The PAID Network Exploiter Netted $3 Million From An Infinite Mint Attack. Image via CoinMarketCap
The PAID Network Exploiter Netted $3 Million From An Infinite Mint Attack. Image via CoinMarketCap From lending and borrowing protocols to yield farming, users have more of their assets than ever before locked up in some of the most widely-recognised DeFi platforms and, as interest for DeFi continues to grow from both institutional investors and the traditional finance sector, the need for sustainable coverage frameworks and DeFi insurance mechanisms to be put in place is at an all-time-high.
Top DeFi Insurance Protocols
To remedy this, a few exciting projects have emerged in the crypto space looking to take the utility of blockchain coverage to an entirely new level. These projects have established themselves as the current leaders in the digital asset insurance vertical, and these projects are:
- Nexus Mutual
- Bridge Mutual
- iTrust Finance
While there are of course many other up-and-coming projects looking to tap into the growing industry of crypto insurance, such as Polka Cover, Etherisc, Insured Finance, Cover Protocol and Unslashed Finance, this piece will primarily focus on arguably the most well-established in the space: Nexus, Bridge and iTrust.
Nexus Mutual
Given the general lack of regulation in the crypto space, hackers and attackers are always on the lookout for discrepancies in new, shiny DeFi platforms that have just launched and entered the market.
It is important to note that it isn’t just the smaller, perhaps less experienced crypto teams who are susceptible to hacks, as in fact even some of the most popular DeFi protocols are regularly targeted by these attackers. On February 4th 2021, for example, DeFi protocol Yearn.Finance reported that its V1 yDAI vault was compromised and exploited by a hacker who managed to get away with almost $3 million in crypto assets.
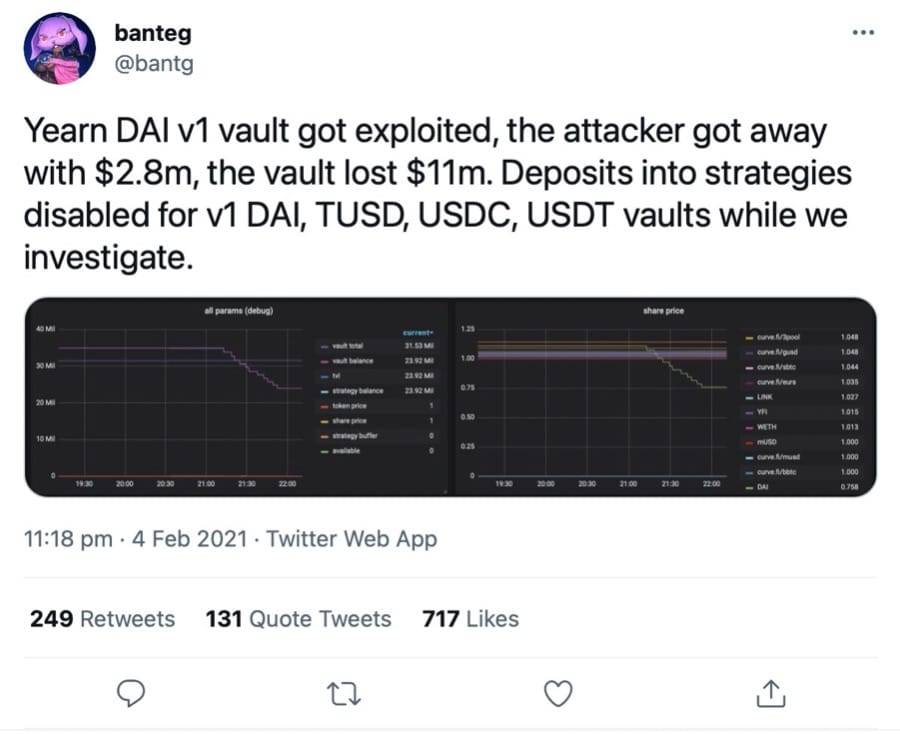 Yearn’s DAI Vault Was Exploited Causing A Loss Of $11 Million In Assets. Image via Twitter
Yearn’s DAI Vault Was Exploited Causing A Loss Of $11 Million In Assets. Image via Twitter The need for protection and coverage in the Decentralised Finance framework is therefore becoming increasingly important, and insurance protocol Nexus Mutual aspires to do just that. By harnessing the power and network effect of the Ethereum blockchain, while adopting ‘A People-Powered Alternative To Insurance’ philosophy, Nexus Mutual seeks to deliver the infrastructure necessary for crypto users to get covered against smart contract failure and exchange hacks.
 Nexus Mutual, The People-Powered Alternative To Insurance. Image via NexusMutual.io
Nexus Mutual, The People-Powered Alternative To Insurance. Image via NexusMutual.io Unlike traditional insurance companies, Nexus Mutual is community-centric and is run by its members. This decentralised insurance protocol leverages smart contract functionality to synthesise a community-oriented business model founded on the importance of community governance in determining the outcome of any one insurance claim.
As the project’s name implies, Nexus Mutual is a mutual like any other. Essentially, an insurance mutual is a firm that is entirely owned by its policyholders. Any profits earned by a mutual insurance company are either retained within the company or rebated to policyholders in the form of dividends or reduced future premiums.
Examples of traditional mutuals are Mutual of Omaha, Prudential, MassMutual and Northwestern Mutual, for instance. On the other hand, a stock insurance company is owned by investors who have purchased company stock, and any profits generated by the stock insurance company are distributed to the investors without necessarily benefitting policyholders. A typical example of this is Allianz, in which any profits generated are distributed to shareholders regardless if they are policyholders or not.
 Mutual Of Omaha, A Fortune 500 Mutual Insurance And Financial Services Company
Mutual Of Omaha, A Fortune 500 Mutual Insurance And Financial Services Company
There are of course advantages and disadvantages to both, and Nexus Mutual incorporates the features of each. However, due to how young and nascent the project still is, its current applications are somewhat limited. Thus far, the applications that are effectively available have sparked interest across the DeFi space and attracted many blockchain enthusiasts.
This is primarily because Nexus Mutual doesn’t provide users with protection against earthquakes, car damage or long-term disability, but its main focus resides in coverage and protection against smart contract failure, a rather pressing issue in the emerging world of blockchain infrastructure.
Despite smart contracts relying on their tamper-proof, solid architecture, even they are at times subject to vulnerabilities. This could be in the form of exchanges being hacked, a specific token wallet malfunctioning, or even human error in the codebase. Nexus Mutual aspires to create an insurance safety-net against potential smart contract failures, allowing members of its community to buy cover for smart contract related risks.
Community Governance
Community members are responsible for assessing the risk associated with each smart contract on Nexus. In this instance, in case of an exploit, community members will be asked to vote on whether the claims are legitimate or fabricated, and if a payout should be structured.
Members can stake their NXM tokens, Nexus Mutual’s native asset, with certain DeFi smart contracts proportional to how secure the members deem the smart contract to be. The more NXM a contract has staked, the cheaper it is for users to buy coverage. Basically, this happens because Nexus Mutual community members have technically put their capital at risk to say that a specific smart contract is reputable and relatively low-risk.
This essentially creates a community-driven insurance protocol in which users who stake their NXM assets in high-risk contracts risk losing a portion of that stake in the event of the smart contract being hacked or compromised. Kayleigh Petrie, Nexus Mutual’s Director of Engagement, explains this process as follows:
Staking with Nexus Mutual is more knowledge based than with other DeFi systems and therefore should be undertaken only by members who are prepared to risk losing their stake if there is a claim on that smart contract. It should be considered as active rather than passive staking. - Kayleigh Petrie, Nexus Mutual Medium
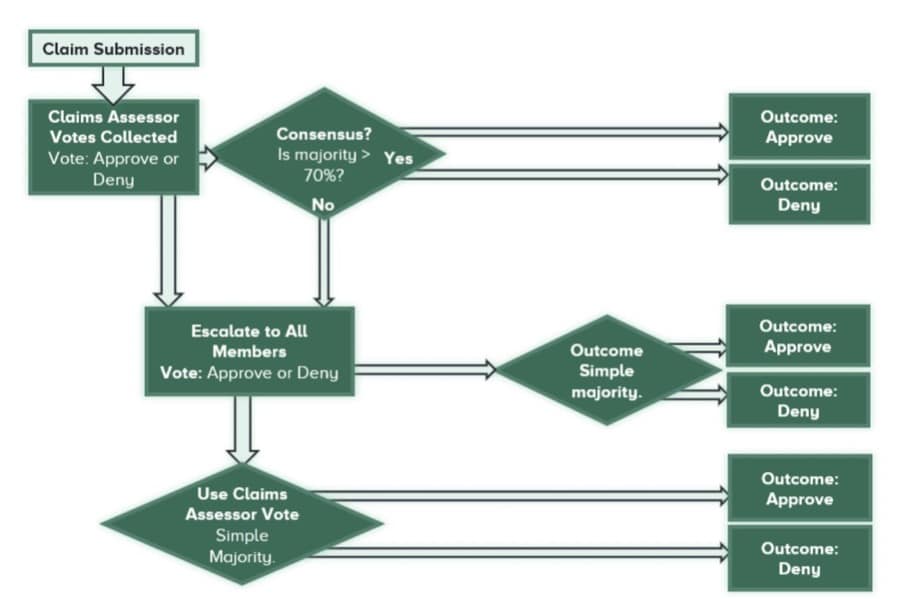 A Visual Of The Nexus Mutual Insurance Claim Procedure. Image via Nexus Mutual Whitepaper
A Visual Of The Nexus Mutual Insurance Claim Procedure. Image via Nexus Mutual Whitepaper As previously mentioned, when a claim is made, NXM holders are asked to vote on whether the claim of a smart contract hack, for instance, is legitimate. Voting with the broader community consensus earns holders more NXM tokens while voting against the majority will lock voters’ tokens for a period of time.
Getting Covered With Nexus Mutual
Nexus Mutual’s community members can gain access to a variety of interesting insurance programs and buy coverage against a particular risk. In order to do so, users will need to:
- First, Go to NexusMutual.io
- Click On ‘Buy Cover’ from the home page.
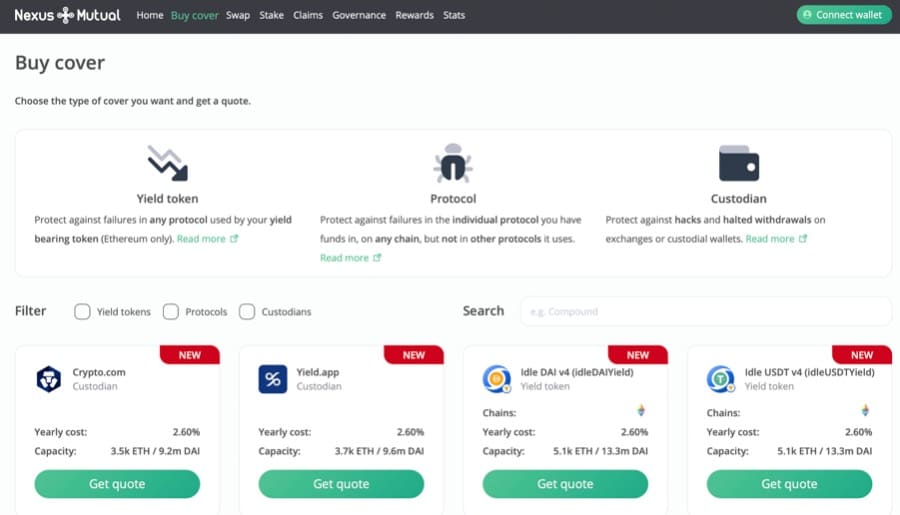 Image via NexusMutual.io
Image via NexusMutual.io - Choose which protocol they want coverage for. The range is rather broad and includes all the major DeFi protocols, such as Uniswap, PancakeSwap, Curve, Yearn.Finance, SushiSwap and Anchor Protocol, among others.
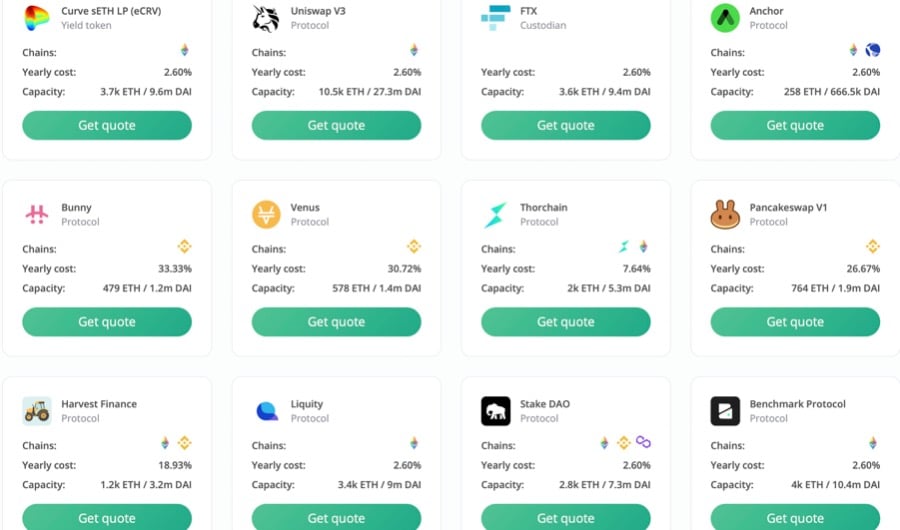 Image via NexusMutual.io
Image via NexusMutual.io - Connect Metamask, WalletConnect or Ledger Wallet to the platform and Click ‘Get A Quote’.
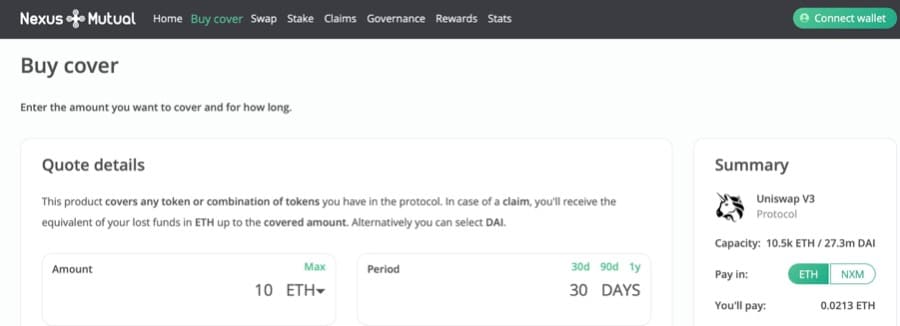 Image via NexusMutual.io
Image via NexusMutual.io In this scenario, we have selected ‘Get A Quote’ for a 30 day period insurance on Uniswap v.3. For insurance on asset value up to 10 ETH, Nexus Mutual has quoted 0.0213 ETH.
- After having completed this step, users will be required to become platform members, if they are not already.
- To initiate the process, users will need to Click on ‘Become a member’.
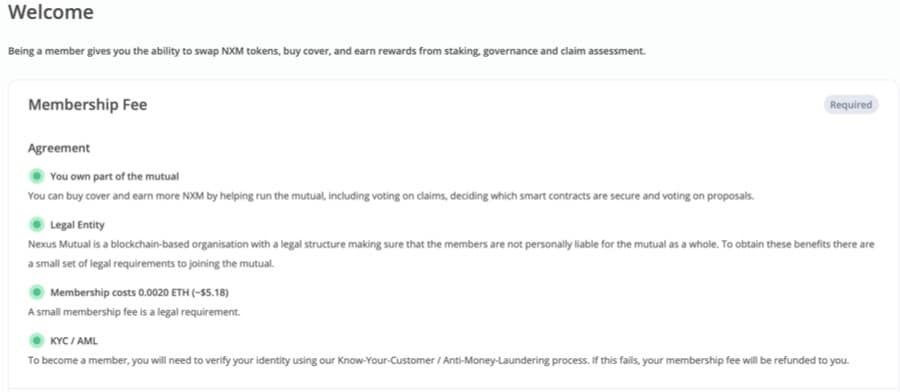 Image via NexusMutual.io
Image via NexusMutual.io - Joining Nexus entails paying a 0.0020 ETH fee, equating to approximately $5.18 at the time of writing. The process furthermore entails undergoing a standard KYC/AML procedure for protocol security. After all, this is an insurance project!
- Once members, users can progress onto purchasing NXM tokens from the platform itself in order to participate in governance and smart contract risk voting through NXM staking.
Bridge Mutual
Bridge Mutual is a decentralised and DAO-managed risk coverage platform that provides insurance for stablecoins, centralised exchanges, smart contracts, as well as other services. Bridge Mutual allows users to buy coverage for their funds, provide insurance liquidity in return for profits and rewards, vote on insurance claims and their respective payouts, and receive compensation for evaluating claims fairly.
 Bridge Mutual, A Decentralised And DAO-Based Insurance Protocol. Image via BridgeMutual.io
Bridge Mutual, A Decentralised And DAO-Based Insurance Protocol. Image via BridgeMutual.io Furthermore, Bridge Mutual enables any user to build insurance liquidity pools for any smart contract, service or exchange at any one time. Other users can then purchase coverage policies to insure themselves against potential rug pulls, protocol hacks or exploits that result in the permanent loss of funds. Stablecoins are also insurable on Bridge Mutual and coverage for stablecoins protects users against any potential devaluation that moves the asset away from the $1 mark.
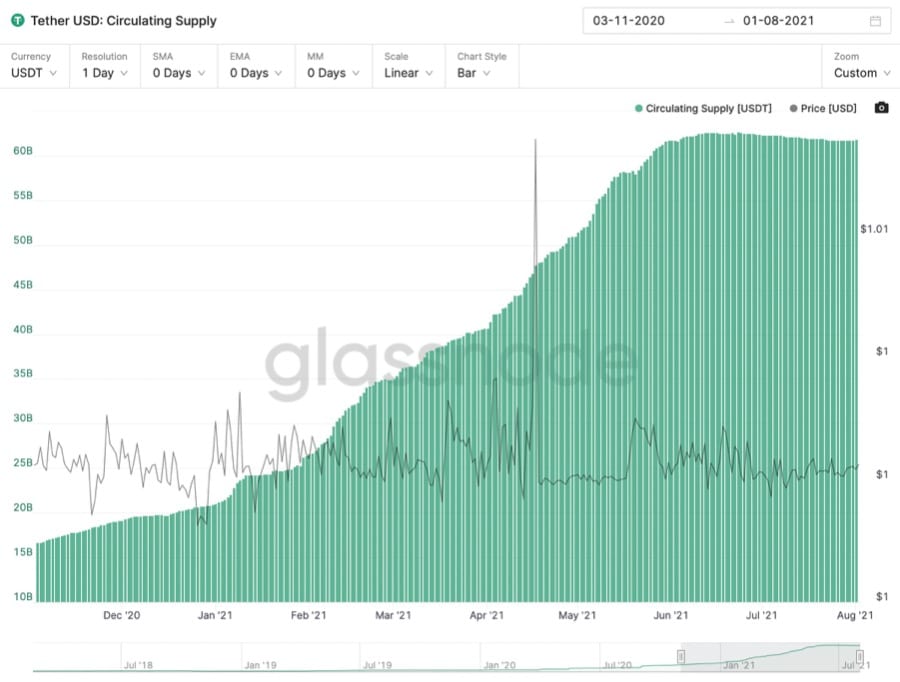 The Circulating Supply Of The USDT Stablecoin Has Been Steadily Increasing Throughout 2021. Image via GlassNode
The Circulating Supply Of The USDT Stablecoin Has Been Steadily Increasing Throughout 2021. Image via GlassNode Throughout 2021, the volume and circulating supply of stablecoins have absolutely skyrocketed. Over this same period, the asset value of loans in DeFi lending and borrowing protocols has also been on a steep upward trend.
However, the increased value of the DeFi ecosystem as a whole has also incremented the number of protocol attacks on behalf of malicious actors, with quite a few news-worthy hacks happening on the regular. Bridge Mutual was designed to be a long-term, viable solution to these issues, and it seeks to provide a decentralised, scalable and comprehensive ecosystem of smart contracts to insure stablecoins, centralised exchanges, smart contracts, as well as other crypto and DeFi products.
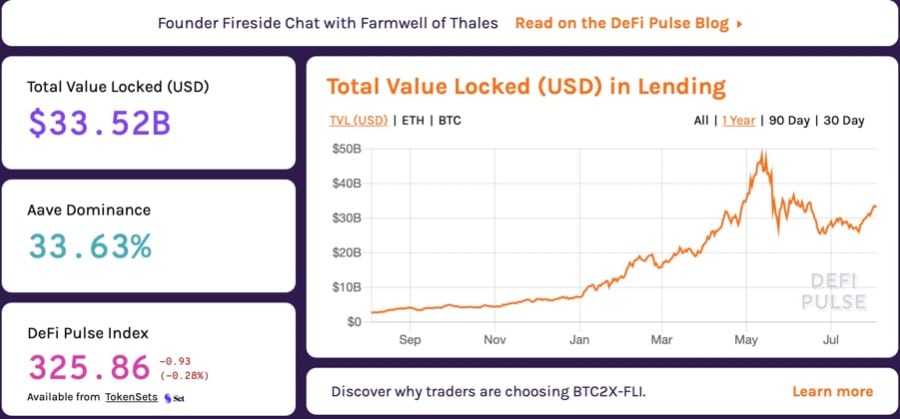 The Total Value Locked (TVL) In DeFi Lending Protocols Has Also Been Increasing Throughout 2021. Image via DeFiPulse
The Total Value Locked (TVL) In DeFi Lending Protocols Has Also Been Increasing Throughout 2021. Image via DeFiPulse Bridge Mutual offers users:
- On-chain investment strategies to return yields to its users.
- Clear profit-sharing incentives.
- No KYC (Know Your Customer) or personal ID requirements.
- Scalability and cost-efficiency via Polkadot and its cross-chain interoperability features.
- A team of dedicated and experienced insurance lawyers, developers and financial experts.
Users can join the Bridge Mutual ecosystem by purchasing BMI tokens, Bridge Mutual’s native asset, and staking their tokens in the coverage liquidity pools. Funds within coverage pools will be simultaneously invested on-chain in other DeFi protocols such as Aave and Curve Finance. Users seeking asset insurance can utilise the Bridge Mutual platform to quickly gain access to quotes and purchase coverage for a wide variety of smart contracts, stablecoins and exchanges.
 From The Bridge Mutual dApp Dashboard Users Can Buy BMI Via Uniswap, Purchase Policies Or Provide Coverage. Image via BridgeMutual App
From The Bridge Mutual dApp Dashboard Users Can Buy BMI Via Uniswap, Purchase Policies Or Provide Coverage. Image via BridgeMutual App On the Bridge Mutual dApp users can:
- Swap Assets via Uniswap v.3.
- Buy Insurance Policies for multiple DeFi solutions.
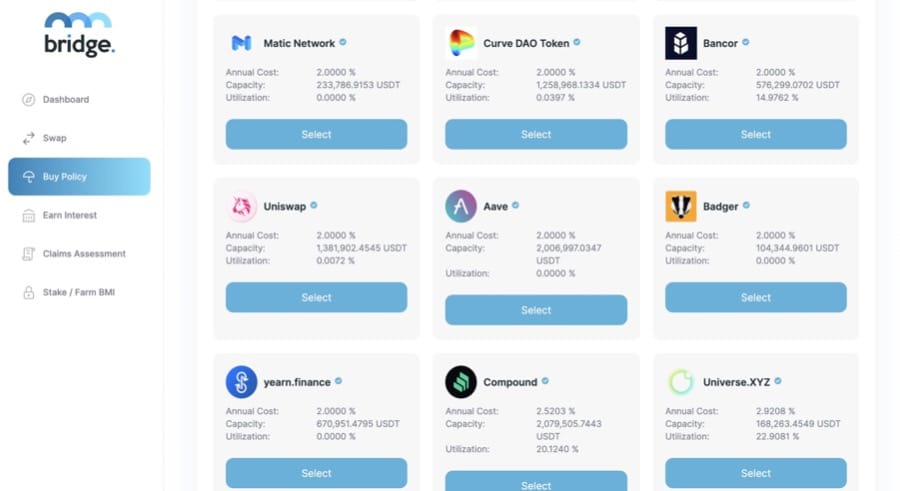 Image via BridgeMutual.io
Image via BridgeMutual.io - Earn interest on staked assets deposited in coverage pools.
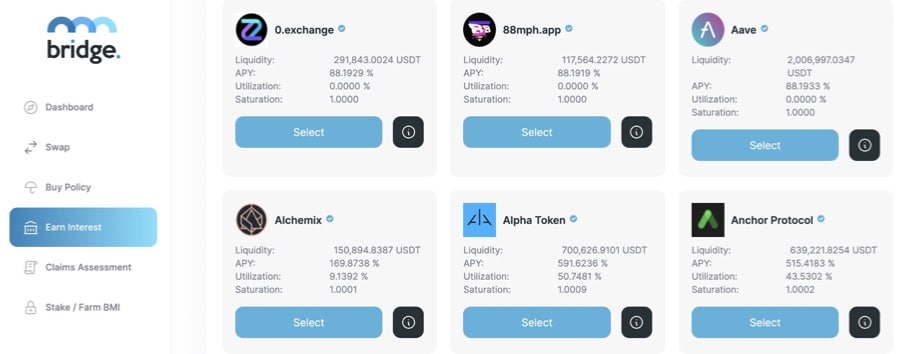 Image via BridgeMutual.io
Image via BridgeMutual.io - Earn rewards by assessing insurance claims fairly.
- Stake and farm BMI tokens for a current APY of 19.3%.
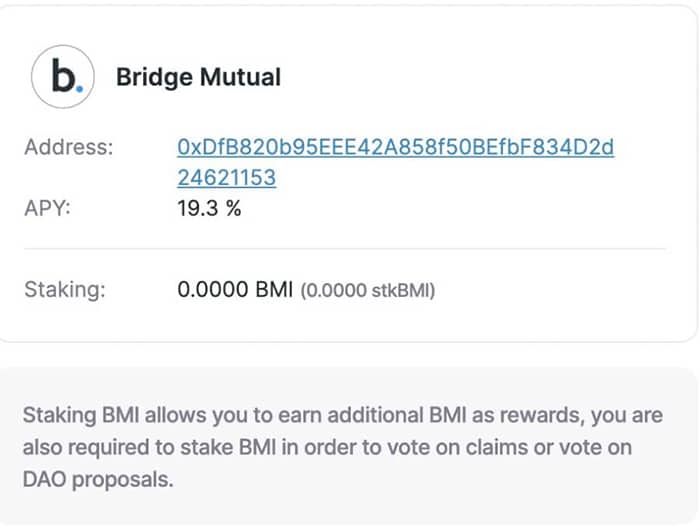 Image via BridgeMutual.io
Image via BridgeMutual.io If a claimable event occurs and a user wishes to create a claim to collect on their coverage, they can do so on the Bridge Mutual platform directly. In fact, claims on stablecoins are settled immediately, whereas claims on smart contracts or exchanges are settled through a three-step voting process within a 6-week timeframe.
iTrust Finance
iTrust Finance is a decentralised and permissionless protocol that is merging crypto asset staking infrastructures with risk management systems.
iTrust.finance seeks to improve efficiency and usability in the DeFi Market. Maximising cover capacity and accruing token rewards for stakers in the DAO; increasing the overall market value of the underlying insurance protocol - iTrust Finance Whitepaper
iTrust Finance implements a Decentralised Autonomous Organisation (DAO) mechanism to alleviate some of the bottlenecks inhibiting the DeFi insurance sector from achieving growth and advancing its value propositions. iTrust primarily focuses on three major cornerstones in the DeFi coverage ecosystem, with these being:
- Efficiency
- Higher Returns
- Simplicity
iTrust Finance manages risk and simplifies the overall process of participating in DeFi protocols, offering users a simple to use platform that is backed up by a risk-assessed and managed set of DeFi strategies. In an exciting move, while also leveraging a DAO-based infrastructure, iTrust Finance has teamed up with other insurance protocols in the space, with perhaps the most notable one being Nexus Mutual.
 iTrust Finance, The Risk-Managed Staking DeFi Protocol. Image via iTrust.Finance
iTrust Finance, The Risk-Managed Staking DeFi Protocol. Image via iTrust.Finance Furthermore, to achieve a greater level of efficiency, iTrust is building higher coverage capacity for insurance protocols while enabling lower premiums and increased adoption. iTrust will provide a number of token Vaults to manage the staking of Nexus Mutual’s native asset NXM, and of its wrapped counterpart wNXM, to increase coverage liquidity.
When users stake their NXM or wNXM in an iTrust Finance Vault, they will receive staking tokens representative of their amount in the Vault. These Vaults provide an onboarding ramp to increase insurance liquidity and cover capacity, as they allow stakers to access the synthetic counterpart of an asset, while preserving the value of their underlying tokens. For instance:
- User X interfaces Metamask with the iTrust Finance platform.
- User X deposits 1 wNXM into Vault A.
- User X receives 1 iTrust Vault A token in their Metamask wallet.
- iTrust then stakes the 1 wNXM on the Nexus Mutual platform.
Thus, Nexus Mutual benefits from increased cover capacity and user X benefits from the rewards obtained through staking wNXM. In the near future, iTrust Finance will also allow users to provide insurance liquidity through staking ETH and BTC.
iTrust Finance provides a number of Vaults with varying staking strategies to suit the risk appetite of the particular staker. Currently, iTrust offers two Vaults for users to stake into:
- Vault A: An index of all the contracts available on Nexus Mutual.
- Vault B: A low-risk, high-reward Nexus strategy developed by the iTrust Finance DAO.
In practice, this works as follows:
- User Y stakes 1 NXM into Vault B.
- User Y receives 1 iTrust Vault B token, as a representation of the NXM staked.
- iTrust Finance then stakes User Y’s NXM across multiple contracts available in Vault B.
- iTrust Finance will accrue the rewards generated from User Y’s NXM.
- User Y, in turn, will receive a share of the iTrust Governance Tokens
(iTG) proportional to the amount of NXM initially staked.
These mechanisms are designed to onboard more and more stakers into the iTrust Finance ecosystem, with the goal of allowing users to simply stake their tokens and receive their rewards almost instantaneously. In fact, more often than not, DeFi stakers aren’t able to collect their rewards efficiently, due to high gas fees, network inefficiencies and protocols restrictions.
In addition, iTrust Finance Vaults create additional liquidity for insurance protocols such as Nexus Mutual by allowing users to stake their capital and receive rewards, while also redeploying NXM and wNXM to provide extra cover liquidity.
Conclusion
While the traditional insurance business model has proven to be incredibly resilient and somewhat timeless, blockchain-based coverage is slowly but surely starting to take over. There are quite a few up-and-coming projects in the space looking to completely disrupt the insurance industry, not just in crypto but in real-world environments as well.
Given the general lack of regulation in the crypto markets, hackers and attackers are always on the lookout for discrepancies in new DeFi platforms. With so many hacks occurring throughout 2020 and 2021, the need for DeFi insurance protocols is obviously dire.
Besides providing coverage to protocols in the space, blockchain insurance could actually facilitate and optimise the process of traditional insurance through its DLT technology, smart contract applications, automation features and cybersecurity measures. While it is indeed still a relatively young and nascent market, blockchain-based insurance could also come to utterly revolutionise outdated coverage systems and change the way people do crypto and DeFi.



