The crypto market never sleeps. It runs 24/7, lets you trade fractional amounts of assets, and imposes no limits on leverage or geographic access, making it a perfect arena for speculators. But it’s not just the accessibility that draws traders in. Crypto is also one of the most volatile markets in the world, and that volatility means it’s possible to generate meaningful returns in short periods if you know what you’re doing.
These traits have made crypto an increasingly popular space for day traders, who thrive on fast-paced, short-term trades. Day trading, in this context, typically refers to strategies that exploit intraday price movements—sometimes holding positions for just minutes or hours.
If you’re new to trading and want to understand how this strategy works in the world of crypto, this article will walk you through the core concepts, tools, risks, and techniques you need to get started.
Key Takeaways
- Crypto day trading offers high-risk, high-reward potential, but the majority of traders lose money without proper skill, strategy, and discipline.
- Day traders operate in short timeframes, rely on technical analysis, and must react quickly to market shifts in a 24/7 trading environment.
- Scalping, momentum trading, and range trading are popular strategies that depend on execution speed, liquidity awareness, and volatility.
- Tools like TradingView, CoinGlass, bots, and order book tracking are essential, but mastering the basics beats relying on fancy software.
- Risk management is non-negotiable: use stop-losses, position sizing, and emotional control to avoid blowing up your account.
- Most beginners should avoid day trading until they’ve gained experience with long-term investing, TA basics, and market structure fundamentals.
- Understanding how derivatives, leverage, and funding rates affect price action is key for any serious crypto day trader.
- Profitable trades are rare and unpredictable. Success comes from preparation, not constant trading or chasing losses.
What Is Crypto Day Trading?
In traditional finance (TradFi), intraday trading involves closing all positions before the market closes each day. Traders profit from short-term price movements, often relying on large order volumes rather than significant price swings, since daily fluctuations tend to be modest.
Crypto markets, however, never close. There’s no central authority to force settlement, yet "day trading" persists as a popular strategy, now defined by its behavior rather than exchange mandates. Crypto day traders typically:
- Operate in small timeframes (minutes to hours).
- Use large orders to capitalize on thin margins.
- Execute frequent trades, sometimes hundreds daily.
- Churn capital rapidly, recycling funds for compounding gains.
- Make spontaneous decisions based on real-time data.
Unlike TradFi, crypto’s 24/7 nature and extreme volatility amplify both opportunities and risks, requiring relentless attention.
Who Should Consider Day Trading Crypto?
Day trading is not for everyone. It clashes with the "buy and hold" mindset of value investors, who bet on long-term asset appreciation. Day traders, by contrast, obsess over one question: "Is this asset mispriced right now?"
Ideal Candidates for Crypto Day Trading
- Experienced Traders: Proficiency in technical analysis (e.g., candlestick patterns, order flow) and fundamentals (e.g., news catalysts, liquidity shifts) is essential.
- Risk-Tolerant Individuals: Volatility can wipe out accounts quickly; emotional discipline is non-negotiable.
- Those With Time/Resources: Monitoring charts, news, and macroeconomic trends is a full-time job.
- Algorithmic Traders: Bots thrive in high-frequency, math-driven environments.
Who Should Avoid It
- Passive Investors: If you prefer "set-and-forget" strategies, stick to hodling or dollar-cost averaging.
- Beginners Without Mentorship: Jumping into day trading without backtesting or guidance is gambling.
- Underfunded Traders: Fee drag and slippage erode small accounts fast.
Reality Check: Studies show most day traders lose money. Success demands skill, discipline, and a willingness to adapt—not just luck.
How Crypto Markets Work: A Quick Primer
In traditional markets, day trading is wrapped in regulatory red tape. U.S. traders face the Pattern Day Trader (PDT) rule, which limits accounts under $25,000 to three day trades in five business days. In India, intraday capital often can’t be recycled within the same session. Stocks also settle at market close, capping how quickly traders can reallocate funds.
Crypto operates differently. There’s no centralized authority, no forced settlements, and no rules limiting trade frequency or leverage usage. Instead, crypto day trading is governed by your strategy, capital discipline, and how well you manage risk.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockKey Mechanics of Crypto Day Trading
Leverage: Amplifying Gains (and Losses): Crypto exchanges often offer leverage of 10x–100x.
- Example: A 10x long on BTC turns a 1% price move into 10% profit—or loss.
- Overleveraging risks liquidation: positions are auto-closed when collateral dips below margin thresholds.
Derivatives: Trading Beyond Spot: Perpetual futures crypto day trading due to their deep liquidity and high leverage limits.
- Traders use them to speculate, hedge, or profit from price drops via inverse contracts.
- These markets offer deep liquidity and flexible position management.
Volatility: The Double-Edged Sword: With swings of ±20–30% in hours, volatility fuels opportunity—but also magnifies risk.
- Traders exploit this using breakout, mean reversion, or momentum strategies.
- Concepts like delta and vega matter more in options, but volatility basics help across the board.
Liquidity & Slippage: Thinly traded coins can slip heavily on large orders.
- Tip: Stick to deep markets (e.g., BTC/USDT)
- Use limit orders,
- Check order book depth.
These nuances may be immaterial for long-term traders but can make or break a day trader's portfolio.
The Day Trader’s Toolkit
- Technical Analysis: RSI, MACD, candlesticks
- News Tracking: Reacting to ETF approvals, exploits, or macro shocks
- Automation: Bots can execute faster and with fewer emotional errors
Day trading crypto is unique because markets never close, there is no regulator to monitor your strategies, and it involves global participation. Crypto markets often react to world events instantly, leaving no room for error and high scope for unexpected market turns.
Setting Up for Day Trading Success
Day trading crypto profitably requires speed, precision, and an edge over the market. Unlike passive investing, success hinges on real-time information processing, disciplined execution, and rigorous preparation. Here’s how to set yourself up for success:
1. Preparation: Anticipating the Market
Pre-Market Research
- Analyze macroeconomic trends (e.g., Fed rate decisions, Bitcoin ETF flows).
- Monitor crypto-specific catalysts (e.g., exchange listings, protocol upgrades, regulatory news).
- Review overnight price action in correlated markets (e.g., Nasdaq, gold for BTC).
Directional Bias
Formulate a thesis (bullish/bearish/range-bound) before the trading day begins.
Use tools like:
- TradingView for chart patterns.
- CoinGecko for token-specific news.
- Crypto Twitter/Telegram for sentiment shifts.
Key Mindset:
"The best traders don’t predict—they react faster and smarter than the crowd."
 Day Trading Crypto Profitably Requires Speed And Precision. Image via Shutterstock
Day Trading Crypto Profitably Requires Speed And Precision. Image via Shutterstock2. Asset Selection: Less Is More
Focus on 2-3 high-liquidity assets (e.g., BTC, ETH, SOL) to minimize cognitive overload.
Why? Tracking multiple assets dilutes attention, increasing errors. Avoid "shiny object syndrome"—ignore low-cap coins unless you specialize in them.
Pro Tip: Master one asset’s price behavior before expanding your portfolio.
3. Choosing the Right Exchange
Spot Trading
Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) like Binance, Kraken, or Coinbase are ideal due to:
- Deep liquidity (minimal slippage).
- Low fees (0.1% or lower for makers).
- Fast execution (critical for scalping).
Avoid DEXs for day trading—high gas fees and slow settlements kill profitability.
Derivatives Trading
- CEX Perpetuals (Binance, OKX) offer:
- Leverage (up to 100x)—but use sparingly (5-10x is safer).
- Tight spreads in BTC/ETH markets.
- Onchain Perps (e.g., Hyperliquid) are viable for:
- Censorship-resistant trading.
- Lower KYC hurdles.
- Still lagging CEXs in liquidity for most pairs.
Regional Note: Check if your preferred exchange is legally available in your country (e.g., Binance is banned in the U.S.)
Check out our top picks for the best crypto exchanges for day trading.
4. Essential Tools & Resources
| Tool | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Platform | Executing trades swiftly | Binance, Coinbase, Hyperliquid |
| Charting Software | Technical analysis | TradingView, CoinGlass |
| News Aggregators | Tracking catalysts | CoinTelegraph, The Block |
| Wallet | Self-custody (if needed) | Ledger (cold), Trust Wallet (hot) |
| Internet | Low-latency connection | Fiber optic, backup mobile hotspot |
Capital Requirements:
- Spot trading: Start with at least $5K–$10K to absorb fees/slippage.
- Derivatives: Smaller accounts (~$1K) can use leverage—but risk liquidation.
5. The Myth of "Sophisticated Tools"
- You don’t need expensive bots or AI to succeed.
- Master the basics first:
- Candlestick patterns (doji, engulfing).
- Support/resistance levels.
- Order book reading.
- Advanced tools help later:
- Algorithmic scripts (e.g., 3Commas).
- On-chain analytics (Glassnode, Nansen).
Golden Rule: “A skilled trader with a simple setup outperforms a novice with all the tools.”
Core Strategies for Crypto Day Traders
Excelling in any financial market requires a strong grasp of both the technical and fundamental drivers of price. But the degree to which these factors influence market action depends on the timeframe.
Over long horizons, fundamentals—things like project strength, network growth, and token utility—tend to drive price. That’s why value investors often disregard short-term price swings, trusting that strong fundamentals will win out over months or years.
For day traders, the opposite is true. In short-term windows (minutes to hours), fear, greed, supply, demand, liquidity, and technical forces become far more influential. A good earnings report might not move an asset intraday, but a sudden liquidity vacuum or liquidation cascade certainly will.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockThat’s why technical skills are non-negotiable for day traders. Without them, you’re gambling. Good technical trading is about reading patterns in price movement and judging the probability of what will happen in the next few time frames. Here are four core strategies that will sharpen your understanding of how this works in crypto markets:
Scalping
Scalping is the art of capturing tiny price movements—fractions of a percent—over very short periods.
- Traders might open and close a position in seconds or minutes.
- It demands quick execution, low-latency tools, and constant monitoring.
Example: A BTC/USDT trader sees a large bid wall emerge in the order book at $65,000. They quickly enter a long position and sell a few points higher once the bid is filled and the price ticks up.
Momentum Trading
Momentum trading rides the strength of an existing move.
- Traders identify strong trends and “go with the flow.”
- Success hinges on entering early enough to capture most of the trend, while managing exit points as momentum fades.
Example: Ethereum breaks a key resistance level with rising volume and positive funding rates—signals that momentum traders use to enter longs.
Range Trading
Range trading profits from markets moving between predictable support and resistance levels. The trader buys near support and sells near resistance—often repeating the cycle multiple times a day.
Example: Solana bounces between $140 and $145 for several hours. A range trader buys at $140 and sells at $145 repeatedly until the range breaks.
Risks and Considerations
- Patterns aren’t guarantees: Just because a setup appears doesn’t mean the outcome is certain. All technical patterns reflect probabilities, not certainties.
- Pattern bias: If you look for a pattern, you’ll often convince yourself one is there. It takes discipline to avoid false signals.
- Over-reliance: No pattern overrides common sense. Blindly following indicators without considering context (liquidity, news, funding) is a fast path to losses.
- Execution risk: Markets move fast. Slippage, latency, and poor fills can erode even the best setups.
Success comes from combining technical setups with sound risk management, fast execution, and situational awareness.
Arbitrage in Crypto Day Trading
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets—buying low in one place and selling high in another. In crypto, where fragmentation is common, these opportunities often arise.
Common crypto arbitrage types:
- CEX vs. DEX spreads: Sometimes DEX prices lag centralized exchanges by a few seconds, letting traders exploit the gap.
- Cross-network arbitrage: A token trading at $2.05 on Arbitrum may trade at $2.08 on Solana, offering a small but repeatable edge.
- Stablecoin spreads: Even stablecoins (USDT, USDC) sometimes trade at slight premiums across ecosystems, though profits here require large capital due to razor-thin margins.
Execution tip: Holding liquidity across multiple venues helps you act quickly—actual on-chain bridging often takes too long. Market-makers and professional arbitrageurs pre-fund accounts on multiple centralized exchanges (CEXes) and blockchains to capitalize on opportunities instantly.
Technical Analysis for Beginners
At its core, technical analysis (TA) is the study of market psychology through price charts. It’s about using historical price action to judge the likelihood of future moves, without needing to analyze the project’s fundamentals. The tool of choice for most traders is the candlestick chart, which visually represents an asset’s price behavior over any given timeframe.
Each candlestick shows four key data points: the opening price, closing price, highest price, and lowest price during that period. But more than data, a candlestick tells a story—if you know how to read it.
The body of the candle shows how decisive traders were.
- A long body signals strong momentum in one direction—longs overpowering shorts, or vice versa.
- A short body means the market was balanced; bulls and bears reached a near agreement on price.
The wicks (shadows) reveal market sentiment.
- Long wicks signal indecision: traders pushed the price beyond the open/close but were ultimately rejected.
- Short or absent wicks show conviction: price held firmly during that period.
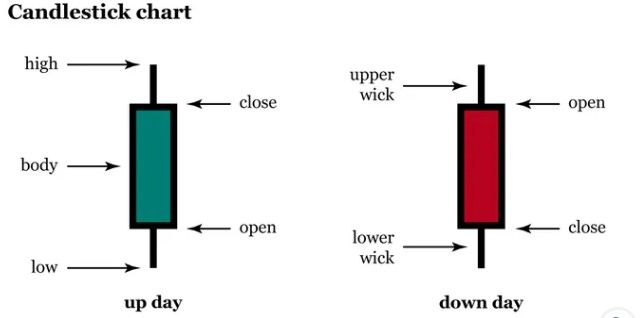 Anatomy of a Candlestick | Image via Britannica
Anatomy of a Candlestick | Image via BritannicaThe key is to first understand what a single candle “says.” Then zoom out: what story does a sequence of candles tell? Does a cluster of strong bullish candles signal growing momentum? Is a long upper wick near resistance showing rejection?
Patterns are important, but a good technical analyst doesn’t just memorize formations. The real skill is understanding how much weight to give a pattern, based on its context:
- A bullish pattern at the market bottom is more meaningful than one at a local top.
- A breakout candle on BTC may be more trustworthy than the same candle on a thinly traded memecoin.
In other words, a poor analyst hunts for patterns. A good analyst reads patterns in context. A great analyst reads the narrative of the chart itself over time, tracking the behavior of market participants in that asset. And because each market behaves differently, becoming truly skilled at TA requires consistent observation, watching how traders behave in that specific market across cycles. There’s no shortcut.
If you’d like to go deeper, check out these articles from The Coin Bureau:
- How to Read Crypto Candlestick Charts?
- How to Use TradingView to Analyze Cryptocurrencies
- Beginner's Guide To Crypto Technical Analysis
- Best Crypto Research Tools
Risk Management Essentials
Good risk management is what separates consistent traders from those who blow up their accounts. It’s not about winning every trade — it’s about protecting your capital so you can trade another day. Here are the essentials:
- Use Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Never enter a position without a clear exit plan. Set stop-losses to cap downside risk and take-profit levels to secure gains. Don’t move these levels mid-trade unless new information justifies it.
- Focus on Net Profit: Trying to “win” every trade often leads to poor decisions. The goal is to be net profitable over time — learning when to cut losses or exit is key.
- Position Sizing and Leverage: Never deploy all your capital into a single trade. Keep position sizes modest and use leverage sparingly. Over-leveraging is one of the fastest ways to liquidate your account.
- Don’t Overdiversify: Diversification works for long-term investing, but for day trading, it can dilute your focus and returns. It’s better to specialize in a few assets you understand well.
- Watch for Slippage on Illiquid Tokens: Avoid low-liquidity tokens, especially if you’re a beginner. Slippage can turn what looks like a good setup into a losing trade.
- Manage 24/7 Exposure: Crypto markets never sleep. Avoid going offline with large open positions — especially leveraged ones. If you must, use limit orders and hard stop-losses.
- Don’t Overload on Indicators: Too many technical indicators often produce mixed signals. Find a simple combination that works for the asset you’re trading — less is often more.
- Trust Your Gut: If your instinct contradicts what your indicators say, don’t ignore it. Experience and common sense often catch things that tools can’t.
- No Position is Also a Position: Sitting out can be the smartest move. Forcing trades in poor market conditions or during unclear setups leads to losses.
Mastering these risk management principles won’t guarantee profits, but they will protect you from unnecessary losses and give you a foundation to improve as a trader.
 Good Risk Management Is About Protecting Your Capital. Image via Shutterstock
Good Risk Management Is About Protecting Your Capital. Image via ShutterstockPsychology of a Day Trader
At its core, successful day trading is a mindset—one built on discipline, probability thinking, and emotional control. The best day traders approach each session with clear intent, not random action.
- Probability over certainty: Every trade is a probability bet—never a guarantee. A skilled trader weighs setups in terms of risk vs. reward, knowing that even perfect signals sometimes fail. This mindset helps them avoid emotional reactions to losses.
- Clear directional view: Before entering the market, an effective day trader already has a defined view of the asset’s likely direction and has mapped out potential trade setups. They don’t chase moves impulsively or improvise mid-session.
- Emotional detachment: Losses aren’t taken personally, and wins aren’t celebrated prematurely. Day trading rewards those who can stay objective, without ego clouding decisions.
- Selective participation: They don’t force trades daily. If the market isn’t offering clear opportunities, they sit out. Patience often separates consistent traders from those who burn out.
- Discipline with exits: A disciplined trader sticks to take-profit targets—even if it means missing further gains. FOMO after the fact leads to poor decision-making.
- No chasing missed entries: If a trade setup is missed or invalidated, it’s left alone. Chasing late entries is often how good ideas turn into bad trades.
- Portfolio perspective: Many day traders also maintain long-term positions to hedge volatility and absorb setbacks. They understand that day trading is just one piece of a broader investment picture.
- Key market truth: Most of a trader’s profits often come from a few standout trades that occur unpredictably. The goal isn’t to win daily—it’s to stay prepared and show up consistently when opportunity does arise.
Common Mistakes New Day Traders Make
Day trading may seem exciting, but for many new traders, the learning curve is steep. Here are four of the most common mistakes that beginners make, often costing them money and confidence.
Overtrading and Chasing Losses
New traders often fall into the trap of making too many trades, thinking more action equals more profit. In reality, overtrading usually leads to burnout and unnecessary risk exposure. After a losing trade, many also try to “win it back” immediately, a behavior known as revenge trading. This emotional approach compounds losses rather than correcting them.
Ignoring Market News and Macro Factors
Charts don't exist in a vacuum. Economic reports, interest rate decisions, geopolitical events, and even tweets from influential figures can move markets sharply. Ignoring the broader context means you’re trading blind. A simple news alert or economic calendar check can save you from trading into volatility you didn’t see coming.
Trading Without a Plan or Strategy
Winging it might work once or twice, but consistent success in day trading requires a defined system. That includes knowing when to enter and exit a trade, how much to risk, and what your profit targets are. Without a trading plan, every decision becomes emotional, and that’s when discipline breaks down.
Neglecting Fees and Slippage
Even if your trades are mostly profitable, hidden costs can quietly erode your gains. Frequent trading racks up fees, and during volatile periods, you may experience slippage, where your order executes at a worse price than expected. These small losses add up over time and can turn a break-even strategy into a losing one.
 Day Trading May Seem Exciting But The Learning Curve Is Steep. Image via Shutterstock
Day Trading May Seem Exciting But The Learning Curve Is Steep. Image via ShutterstockCreating Your Own Day Trading Plan
There’s no universal blueprint for successful day trading. If there were, markets would be easy—and they aren’t. Every trader approaches the market with their own unique style, preferences, and risk tolerance. The key is finding a process that works for you.
A good trading plan is personal. It evolves through observation, experience, and reflection. But most effective plans do share a few core elements:
- Time for research: Successful traders dedicate ample time each day to preparing—reviewing charts, reading the news, and understanding market context before placing a trade.
- Defined spend and loss limits: Setting daily limits—on both position size and maximum acceptable losses—keeps you from spiraling when things go wrong.
- Pre-mapped key levels: Many traders identify support, resistance, and key zones for the day ahead of time. This creates a framework for reacting to price action in a structured way.
- Constant sentiment monitoring: Markets shift quickly, especially in crypto. Tracking sentiment across news, funding rates, and order books helps you stay one step ahead.
- Reliable information sources: Having a set of trusted feeds—whether from Twitter, private groups, Discord servers, or news aggregators—keeps you informed without drowning in noise.
- Mobile readiness: Since crypto trades 24/7, having trading accounts accessible on your phone allows you to react to sudden changes when away from your main setup.
Above all, consistency matters. Building a plan and sticking to it helps filter emotional decisions and reduces randomness in your trading process.
And as markets evolve, so should your plan—adapting to new conditions, tools, and lessons learned along the way.
How Much Can You Earn from Crypto Day Trading?
Estimating potential earnings from crypto day trading is nearly impossible—it depends heavily on your capital, skill, discipline, number of trades, and use of leverage.
Profit as a multiple of price moves
Suppose Bitcoin jumps 10% in a day. With 10× leverage, a trader could amplify that into a 100% return on the position. With 50× leverage, that same move becomes 500%. Of course, leverage works both ways—losses are amplified just as quickly. But that doesn't translate to consistent profits. Real-world outcomes depend on trade frequency, entry accuracy, execution speed, and even transaction costs and slippage.
The Reality: Most Traders Lose Money
Multiple studies confirm the sobering truth:
- Only 3%–20% of day traders manage to turn a profit, up to 95% lose money in TradFi
- Another source states that over 97% of traders lose money over time, with fewer than 1% truly profitable.
- FINRA data shows 72% of day traders end the year with losses, and only 13% stay consistently profitable at six months.
- In India’s equity intraday market, 70% of intraday traders lost money, with 80% of high-frequency traders losing.
These numbers highlight how difficult it is to make consistent gains.
Bottom Line
- Profit potential is high, especially with leverage, but so is the risk.
- Most day traders lose money, and only a tiny percentage remain profitable long-term.
- Estimating earnings with absolute numbers is misleading. The real question is: Can you develop the discipline, edge, and mindset to be in that rare minority?
The rare big paydays are unpredictable and come from being consistently prepared, not straight-line daily wins.
Final Thoughts
Crypto day trading is often presented as a fast path to wealth, but the reality is very different. Successful day trading demands more than a flashy strategy or a set of indicators. It requires sharp technical skills, deep market understanding, strict risk control, and the ability to read price action in context—skills that only develop through years of market experience.
For beginners in trading, the truth is simple: you should not attempt day trading. Even seasoned long-term investors face a steep learning curve when transitioning to short-term strategies. A beginner day trader should first build a solid foundation through active investing, gaining years of experience reading market behavior, and understanding risk.
In particular, crypto day trading hinges on understanding not just spot markets, but the full dynamics of derivatives markets — perpetuals, funding rates, open interest, and how these tools impact price action. Mastering how derivatives drive short-term trends is essential—not only to trade them but also to analyze market structure.
The bottom line: if you’re not yet an experienced spot trader with strong conceptual knowledge of crypto derivatives, stay out of day trading. The odds are stacked against new traders. But with time, education, and discipline, you can gradually build the foundation to approach these markets with skill and caution.





