In the cryptocurrency space Ethereum stands as a prominent and pioneering platform, facilitating the development of decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts. However, the path to innovation within the Ethereum ecosystem is not without its challenges. Before any ground-breaking innovation can go live on the Ethereum mainnet, it must undergo rigorous testing and development on test networks, known in short as "Testnets."
In the journey to create and deploy Ethereum blockchain improvements, developers face a daunting challenge - the need to ensure the reliability, security and functionality of their creations without risking real assets. This is where Ethereum Testnets step in as invaluable tools.
These Ethereum Testnets provide a vital intermediary step before core devs or individual dApp developers can launch their projects on the mainnet. Testnets allow developers and blockchain enthusiasts to use these specialized testing environments without any fear of damaging the live network and placing real crypto assets at risk.
The deployment of code and execution of transactions on the Ethereum mainnet require meticulous preparation and scrutiny, which requires the use of multiple different Testnets, which we will cover in this article.

Testnets provide a secure, sandboxed space where code can be rigorously tested, thoroughly experimented with and diligently debugged. This critical phase in the development process is essential to avoid potentially catastrophic bugs, which could have devastating consequences.
The consequences of a catastrophic Layer 1 bug in mainnet Ethereum would be incredibly damaging to the cryptocurrency space as Ethereum's prominence within the blockchain world cannot be overstated.
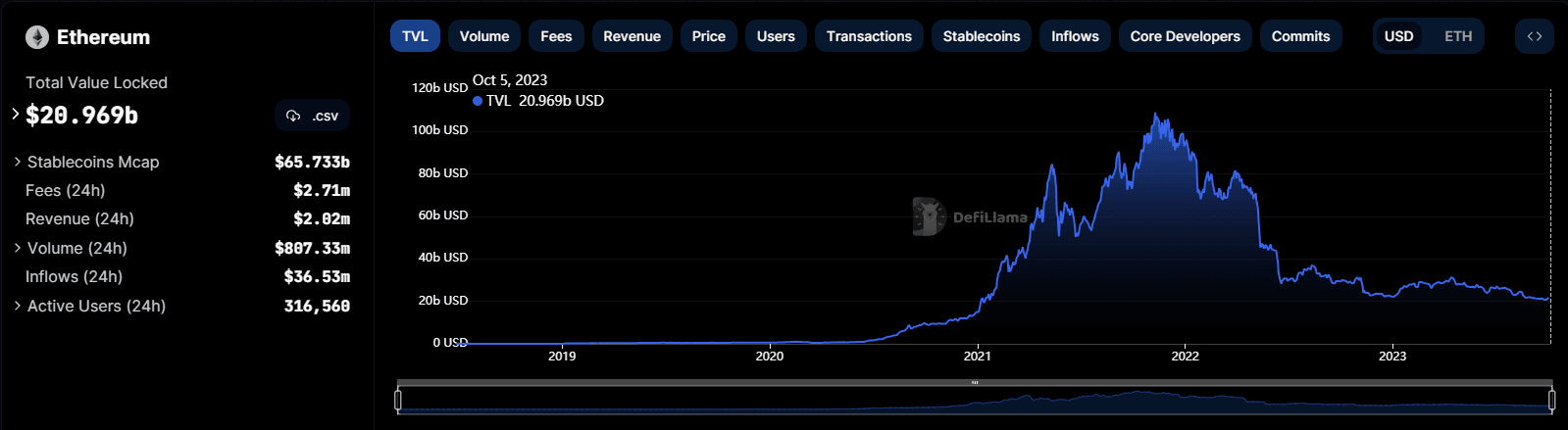 ETH TVL, Image via Defillama
ETH TVL, Image via DefillamaEthereum secures a staggering $20.96 billion in Total Value Locked (TVL) and supports a vast network of 31 different Layer 2 solutions that all secure back to the Ethereum Layer 1. Consequently, if anything were to happen to Ethereum’s Layer 1, all of the Layer 2’s would also be compromised.
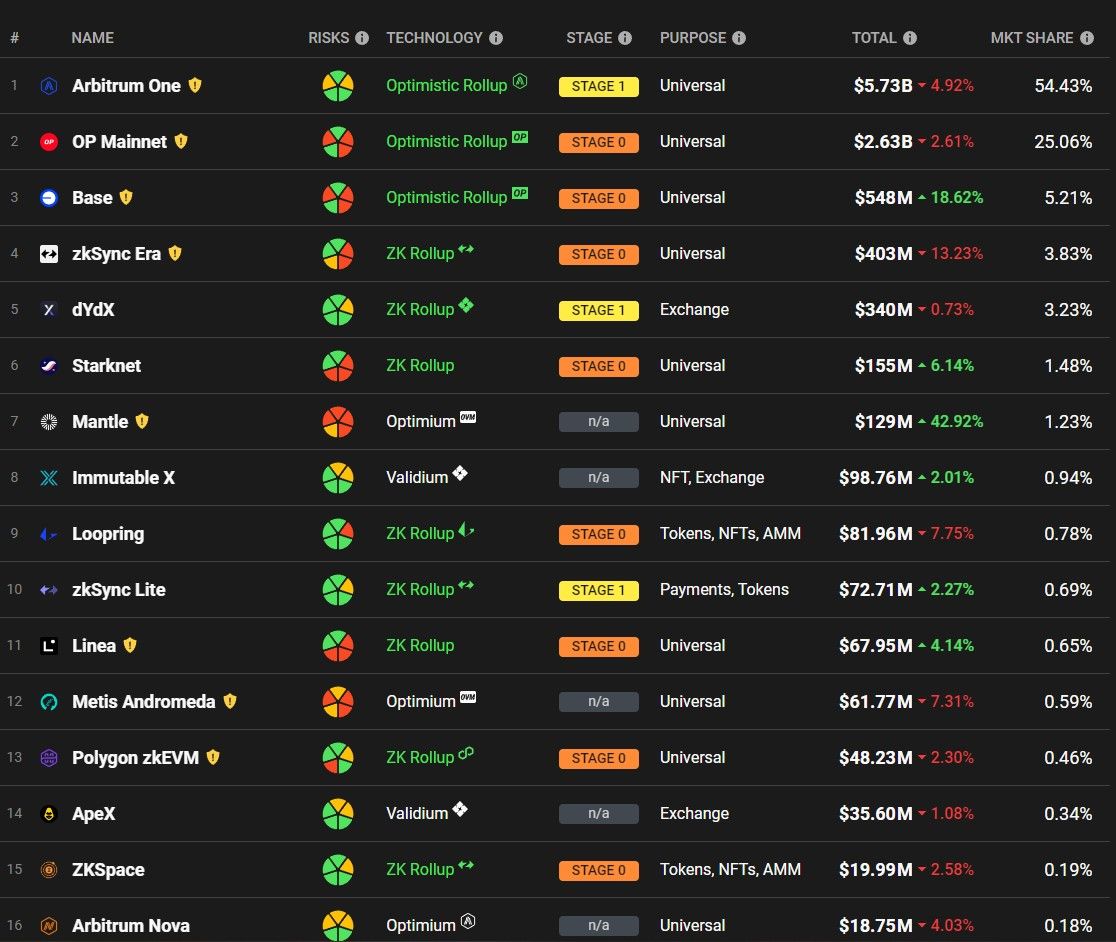 A Look at Just a Few of the Protocols That Rely on Layer 2 Solutions. Image via L2Beat
A Look at Just a Few of the Protocols That Rely on Layer 2 Solutions. Image via L2BeatIn this article, we will delve into the world of Ethereum Testnets, shedding light on what they are, how they operate, their diverse applications, the inherent value they bring to the blockchain ecosystem and an exploration of the various Testnets available today.
This article will cover:
- What Ethereum Testnets Are: We'll start by demystifying the concept of Testnets, explaining their role as separate blockchain networks designed for testing and experimentation.
- How They Work: Taking a look at the technical underpinnings of Ethereum Testnets, exploring the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and consensus mechanisms that power these networks.
- What They Are Used For: Discovering the wide array of use cases Ethereum Testnets serve, from smart contract development and quality assurance to educational purposes and protocol upgrades.
- Why They Are Useful: Delving into the intrinsic value of Testnets, including their role in risk mitigation, accelerated development and community collaboration.
- How Many Testnets There Are: Getting an overview of the main Ethereum Testnets, with each catering to different needs and use cases.
- What is the Future of Ethereum Testnets: How will new and existing Testnets be added and removed?
Hopefully, by the end of this guide, you'll have a good understanding of Ethereum Testnets and their pivotal role in facilitating the development and growth of the Ethereum ecosystem. Whether you're a blockchain developer, enthusiast or simply curious about the inner workings of Ethereum, this guide will provide you with the knowledge needed to understand Testnets and what their purpose is.
What are Ethereum Testnets?
Ethereum Testnets are specialized blockchain networks designed to replicate the core functionality of the main Ethereum network, also known as the "mainnet." The primary difference lies in the currency used within these test networks.
Instead of real Ether (ETH), they use test Ether tokens, often referred to as "Testnet Ether" or "test ETH." These test Ether tokens are supposed to hold no actual monetary value as they can be obtained without any cost, allowing users to engage in various activities without the fear of losing real funds. Testnet ETH is also designed to be free or cheap to acquire as it allows developers to make lots of test transactions at virtually no cost.
Although Testnet ETH should be valueless as it can be created with relative ease, there are actually secondary markets that exist where Testnet ETH does have a surprisingly high market value as they have become scarce or hard to obtain.
An example of this would be Goerli ETH which is facing deprecation and at the time of writing is trading at $0.03312 with a 24-hour trading volume of $1668.
As stated by Coingecko:
“Goerli Testnet is one of Ethereum Chain's many Testnets that serves as a test environment for Ethereum developers and is facing deprecation. It should also be noted that these Testnet tokens can be obtained for free as it is meant for testing of Ethereum smart contract in a sandbox environment.”
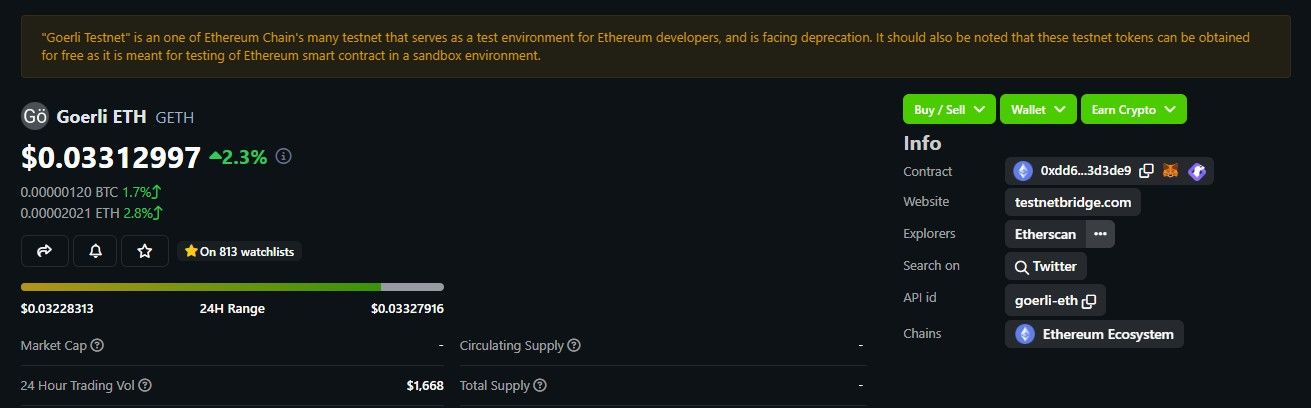 Image via Coingecko
Image via CoingeckoEthereum Testnets serve as invaluable tools for developers, businesses and anyone interested in Ethereum's capabilities. They enable experimentation, testing and exploration of smart contracts, decentralized applications (DApps) and other blockchain features without the financial risks associated with the mainnet.
How do Testnets Work?
Testnets come in a variety of flavours, with the most common being Rinkeby, Goerli, Sepolia and more recently, Holesky. Each Testnet offers a slightly different environment to cater to specific testing needs. For instance, Ropsten (now deprecated) used a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism similar to the old mainnet, while Rinkeby employs a proof-of-authority (PoA) consensus mechanism and Goerli combines aspects of both. Developers can choose the Testnet that best suits their project's requirements.
Accessing a Testnet typically involves using specialized wallets or development tools. Once connected, users can create and deploy smart contracts, interact with DApps, simulate transactions, and test various blockchain-related functionalities. The open nature of Testnets fosters collaboration, community feedback and iterative development, ultimately contributing to the stability and security of applications before they are deployed on the main Ethereum network.
Ethereum Testnets are essential components of the Ethereum ecosystem that allow developers to test and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) without using real Ether (ETH) on the main Ethereum network and serve as a safe environment for experimentation. Here's how Ethereum Testnets work:
- Testnet Networks: Ethereum has multiple Testnet networks, each serving a different purpose. The most commonly used Testnets include Holesky, Goerli and Sepolia. Each of these networks mimics the Ethereum mainnet to varying degrees but uses Testnet Ether, which has no real-world value.
- Testnet Ether (tETH): Testnets have their own native cryptocurrency called "Testnet Ether" (tETH) or other Testnet-specific tokens. These tokens are freely available and can be obtained from faucets or other Testnet resources. Unlike real Ether, tETH is usually distributed for free and has no monetary value.
- Similar Blockchain Structure: Testnets replicate the structure of the Ethereum mainnet, including block generation, transaction processing and smart contract execution. They use the same underlying technology, such as the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and the same consensus algorithms (proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, depending on the Testnet).
- Faucets: Testnet Ether can be obtained from faucets, which are online tools that distribute tETH for free. Users often need to provide a Testnet address to receive the tokens. Faucets are available for each Testnet and developers can use them to acquire tETH for testing.
- Gas Fees: Just like the mainnet, Testnets require gas fees to process transactions and execute smart contracts. However, since tETH has no real-world value, the gas fees are minuscule and affordable. Developers need tETH to pay for gas when testing their applications.
 Rinkeby Testnet Transaction, Image via StackExchange
Rinkeby Testnet Transaction, Image via StackExchange- Development and Testing: Developers can deploy smart contracts and DApps on Testnets using the same tools and methodologies they would use on the mainnet. They can test their code, simulate interactions, and ensure that everything works as expected without risking real Ether.
- Community Support: Testnets have active developer communities that provide support, information, and resources to help developers navigate the testing environment. You can find Testnet block explorers, forums, and other tools to monitor and interact with the Testnet.
- Network Upgrades: Testnets are periodically upgraded to test new Ethereum protocol upgrades and changes before they are implemented on the mainnet. Developers and network validators participate in these upgrades to ensure they are safe and effective. Examples include the already implemented Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 so called EIP1559 which introduced a fee burning mechanism.
- Resetting and Pruning: Testnets may be reset or pruned periodically to maintain their performance and cleanliness. This means that Testnet data can be erased, and tETH balances can be reset to prevent accumulation and misuse.
Ethereum Testnets provide a controlled and risk-free environment for developers to experiment with Ethereum smart contracts and DApps. They mimic the mainnet's functionality while using Testnet-specific tokens that have no real value, making it a safe space for development and testing.
What Are Different Testnets Used For?
Each Testnet will be designed for specific use cases or developer needs, as such, different Testnets will be used by different people for different tasks. Let’s break them down and take a look:
Sepolia Testnet
Sepolia is a Testnet primarily designed for developers and testers who want to interact with the Ethereum network without the constraints and complexities of the mainnet. Sepolia is the recommended default Testnet for application development and was designed to simulate harsh network conditions. Sepolia offers the following benefits and features:
- Sepolia is suggested as the default Testnet: Developers who are building applications on a specific blockchain platform are recommended to use Sepolia. It’s designed for testing decentralized applications, smart contracts and other EVM functionality.
- Permissioned Validator Set: The Sepolia network employs a permissioned validator set. In a permissioned network, validators are chosen and controlled by specific entities, often client teams and testing teams. These validators are responsible for confirming and adding new transactions to the blockchain. Having a permissioned validator set provides more control and security, making it suitable for testing and development purposes.
- New Testnet with Small State and History: Sepolia is described as a relatively new Testnet. This means that it hasn't been in existence for very long, and as a result, the blockchain's state (current data and account balances) and history (past transactions and events) are quite small. This is in contrast to older Testnets or the mainnet, which may have accumulated a large amount of data over time.
- Quick to Sync: Because Sepolia's state and history are small, it's much quicker to synchronize (sync) with the network. Syncing refers to the process of downloading and updating a node's copy of the blockchain to match the current state of the network. In Sepolia's case, this process is fast and efficient.
- Minimal Disk Space Requirement: Running a node on the Sepolia Testnet doesn't require a lot of storage space. This is advantageous for developers who want to set up a node quickly and interact with the network directly without having to allocate a significant amount of disk space for storage.
Holesky Testnet (Replacing Goerli in 2023):
Holesky is replacing Goerli as a Testnet for staking, infrastructure and protocol development and went live on 28 September 2023. Holesky is an impressive new Testnet and is the first long-standing, merged-from-genesis, public Ethereum Testnet whose main function is to replace Goerli as a staking, infrastructure and protocol-developer Testnet in 2023.
Holesky is specifically designed for thorough staking trials, infrastructure assessments and direct protocol developer testing, mirroring mainnet functionalities for precise evaluations.
Holesky aims to increase the number of validators on the Ethereum mainnet and test how changes affect its stability. The Ethereum Foundation’s DevOps team has several plans for Holesky.
- Test the network more thoroughly by having twice as many active validators as the main Ethereum network.
- Improve the way inflation works using methods from the Sepolia testnet.
- Start with a strong base of 1 million validators for better testing.
- Encourage teams to run many of these validators, aiming for each team to handle around 100,000, ensuring the testnet works as intended.
Goerli Testnet
Goerli is a widely used Ethereum Testnet with the following key purposes:
- Open Validator Set: Goerli features an open validator set, allowing stakers to participate and test network upgrades. This openness makes it suitable for developers and projects interested in testing their staking setups.
- Large State: Goerli has a larger state compared to some other Testnets, which is useful for testing complex smart contract interactions and scenarios that require a substantial amount of data.
- Longer Sync and Storage Requirements: Because of its larger state, Goerli may take longer to sync and requires more storage space to run a node. This means it's better suited for users who require a more comprehensive testing environment and are willing to invest in the necessary resources.
In summary, Ethereum Testnets are specialized networks designed for specific use cases and developer needs. They cater to different tasks and audiences.
- The Sepolia Testnet, recommended for application development, offers benefits like a permissioned validator set, a small state and history, quick synchronization and minimal disk space requirements.
- Holešky Testnet, replacing Goerli in 2023, focuses on staking, infrastructure, and protocol development, aiming to be the first long-standing public Ethereum Testnet.
- Goerli Testnet is widely used and features an open validator set and a large state but requires longer sync times and more storage space.
These Testnets serve distinct purposes, allowing developers and users to test various Ethereum network aspects based on their specific needs and resource availability. The choice of Testnet depends on your testing requirements and resource constraints.
Why Are Testnets Useful?
Ethereum Testnets are often overshadowed by the mainnet's spotlight but they play a pivotal role in the world of blockchain and Ethereum ecosystem development. They serve as invaluable sandboxes for developers and stakeholders alike, offering a controlled environment to experiment, test, and refine Ethereum-based applications.
First and foremost, Testnets are instrumental in mitigating risks associated with deploying smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum mainnet. The blockchain ecosystem is a high-stakes arena, with real-world assets and substantial economic value at risk. By allowing developers to deploy and assess their creations on Testnets, the Ethereum community can identify vulnerabilities, bugs and security loopholes before they potentially wreak havoc on the mainnet. This risk mitigation aspect is pivotal in preserving the integrity and trustworthiness of the Ethereum network.
In the fast-paced world of blockchain, developers are constantly innovating and iterating their projects. Testnets provide a rapid and cost-effective means to validate ideas and deploy prototypes. Without the burden of real-value transactions, developers can experiment freely, implement upgrades, and fine-tune their codebase with agility. This accelerated development cycle on Testnets not only reduces time-to-market but also fosters a culture of innovation, ensuring that Ethereum remains at the forefront of blockchain technology.
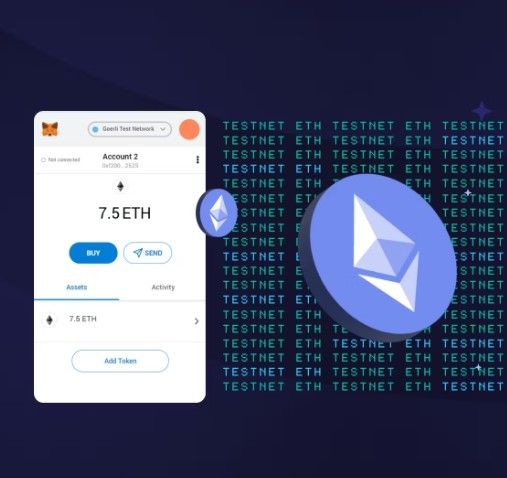 Image via Argent
Image via ArgentFurthermore, Testnets are powerful tools for community collaboration. Ethereum is built on the principle of decentralization and a vibrant ecosystem of developers, enthusiasts and stakeholders. Testnets create a common ground where this diverse community can collaborate, test new features, and provide feedback. Developers can engage with the broader Ethereum community, seeking input and insights that can enhance their projects. This open and collaborative approach ensures that Ethereum evolves in a direction that benefits its users and maintains community-driven governance.
Ethereum Testnets are far more than just staging grounds for developers; they are indispensable pillars of the Ethereum ecosystem. They play a pivotal role in risk mitigation by identifying vulnerabilities early, facilitating accelerated development by providing a safe playground for innovation and fostering community collaboration by encouraging open dialogue and feedback. As Ethereum continues to evolve, Testnets will remain a cornerstone of its success, ensuring that it remains a secure, innovative and community-driven blockchain platform.
What is the Future of Ethereum Testnets?
The Ethereum community is facing a challenge with the rapid deprecation of Testnets, causing frustration among application developers and infrastructure providers. To address this issue, a proposal has emerged from discussions within the Testnet workgroup. The proposal aims to create a more predictable Ethereum Testnet Lifecycle, providing stability and clarity for all stakeholders in the ecosystem.
The central idea of the proposal is to establish a predictable schedule for launching and maintaining Ethereum Testnets. Here are the key points:
- New Testnets Every Two Years: Ethereum would launch a new Testnet every two years on a predefined date, such as October 1st, 2023, 2025, 2027, and so on.
- Testnet Lifetime Limit: Testnets will have a maximum lifetime of five years, comprising four years of active testing and one additional year of long-term support if necessary.
- Goerli Support Extension: Depending on the outcome of discussions regarding supply issues, Goerli's long-term support may be extended for another two years until 2024.
The current approach of abruptly deprecating multiple Testnets with little notice ahead of the merge has caused frustration. Currently, only two major Testnets are available: Goerli (permissionless) and Sepolia (permissioned). Goerli has attracted more users due to its better infrastructure, creating a network effect.
The proposal suggests limiting the lifetime of public Ethereum Testnets to four years after genesis, with the possibility of extending it by one year for heavily used networks, reaching a maximum of five years.
Additionally, a new Testnet will be launched every two years. This ensures that at least two public Testnets will always be available to all stakeholders, reducing the frequency of application migrations to every four years.
The Predictable Ethereum Testnet Lifecycle proposal aims to bring stability and predictability to the Ethereum Testnet ecosystem. By establishing a clear schedule for launching and maintaining Testnets, it seeks to reduce frustration among application developers and infrastructure providers, ensuring a smoother transition for the Ethereum community during network upgrades and changes.
 Timeline of Ethereum Testnet Lifecycles, Image via GitHub
Timeline of Ethereum Testnet Lifecycles, Image via GitHubSummary
Ethereum Testnets serve as crucial elements in the world of blockchain development, providing a secure and controlled environment that benefits both developers and users. This article sheds light on their importance, encompassing their role as distinct blockchain networks designed for experimentation and highlights their technical intricacies, their wide-ranging applications in smart contract development and quality assurance and their undeniable value in risk mitigation and community collaboration.

After gaining insight into the various Ethereum Testnets currently in existence, you should be better prepared to harness the full potential of these testing platforms and actively contribute to the Ethereum ecosystem. Testnets play a pivotal role in ensuring the ongoing growth and innovation within Ethereum, which in turn fuels progress in the broader cryptocurrency space.
The future of Ethereum Testnets looks promising, with a proposed Ethereum Testnet Lifecycle that promises predictability. Under this proposal, new Testnets will be launched every two years, each with a maximum lifespan of five years. The commitment also involves maintaining at least two public Testnets, reducing the need for frequent application migrations. All in all, these collective efforts aim to create a smoother and more predictable experience for the Ethereum developer community during Testnet network upgrades.
Hopefully this article will have provided some basic understanding of what Ethereum Testnets are and how they work. Testnets are easily accessible through EVM-compatible wallets, such as MetaMask, so try it out and get involved!





