Welcome crypto-naut! It looks like you have ventured here looking for a way to earn passive income by staking your Ethereum. Instead of letting your Ethereum sit in your wallet and collect proverbial dust, this article will show you how to put your ETH to work for you and earn a bit of passive interest income while also contributing to the security and future of the Ethereum ecosystem that we all know and love.
This article is going to show you where and how you can stake your Ethereum to earn some of that sweet APY on your ETH holdings. In the interest of keeping this article less than textbook length, I will be providing links to step-by-step, in-depth tutorials for each of the mentions in this article.
Disclaimer: I hold Ethereum as part of my personal portfolio.
What is Ethereum Staking?
Without getting too deep into the weeds on this one, as it is a hefty topic, I’ll provide a quick summary of what the Ethereum upgrade was about and why we needed it. If you are already well versed in the world of Ethereum, feel free to skip this section or check our article that provides a thorough deep dive into all things Ethereum 2.0 related or you can also find Guy's opinion on Ethereum 2.0 staking.
 Photo of Ethereum Logo Image via thefutureisnow
Photo of Ethereum Logo Image via thefutureisnow For those who don’t know, Ethereum underwent a much-needed upgrade as it evolved from the proof-of-work consensus mechanism to Ethereum 2.0, which is now running on the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
Why this has been a much anticipated and vitally important upgrade is that Ethereum basically powers the entire DeFi space, sustaining entire virtual worlds such as Decentraland and the Sandbox, also providing the network backbone that most of our beloved NFTs and crypto domains are hosted on, not to mention that nearly half of the top 100 cryptocurrencies are all Ethereum ERC20 tokens.
 Image Showing a Mere Fraction of the Entire Ethereum Ecosystem Image via Reddit
Image Showing a Mere Fraction of the Entire Ethereum Ecosystem Image via Reddit With all of this activity on a rapidly growing Ethereum network, it has been known since Ethereum’s inception back in 2015 that the network would need to upgrade to proof of stake eventually if they wanted to keep up with the growing demand of the scaling Ethereum ecosystem.
What this has to do with staking, is that those who stake their Ethereum are contributing to the Ethereum network itself, becoming validators of the network and contributing to the security of the blockchain, processing transactions and storing information by adding blocks to the new consensus model for Ethereum 2.0. As a reward for their participation and support, those validators or stakers receive interest on their staked coins.
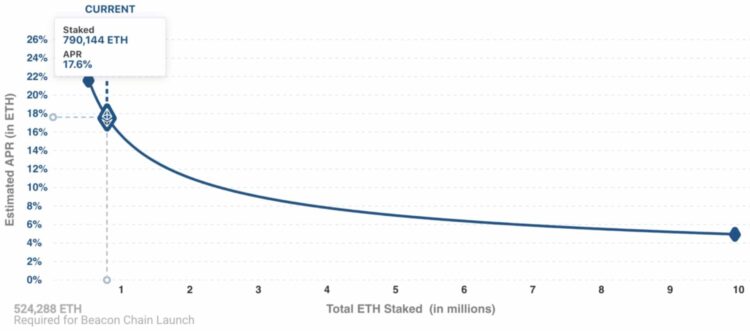 The Ethereum Staking APY Returns Chart Showing Diminishing Returns as more ETH is Staked Image via extropy.io
The Ethereum Staking APY Returns Chart Showing Diminishing Returns as more ETH is Staked Image via extropy.io How Much Can You Earn Staking Ethereum?
The APY earned on staking Ethereum fluctuates depending on the number of participants and the amount of ETH that is being staked, not to mention it will also vary depending on the staking platform and method used. The rewards received are dynamically calculated based on the state of the network upon epoch completion.
Network-level reward rates are a function of the total amount of ETH staked and average percentage of uptime for validators. This is shown in the image above, highlighting that the total APY for staked Ethereum is set to a fixed rate, with early stakers getting in with a nice 21% return, with that rate diminishing as more stakers come onto the scene as the APY technically remains fixed, but needs to be allocated equally among validators so the amount of ETH rewards received will diminish over time, resulting in a variable APY per individual validator.
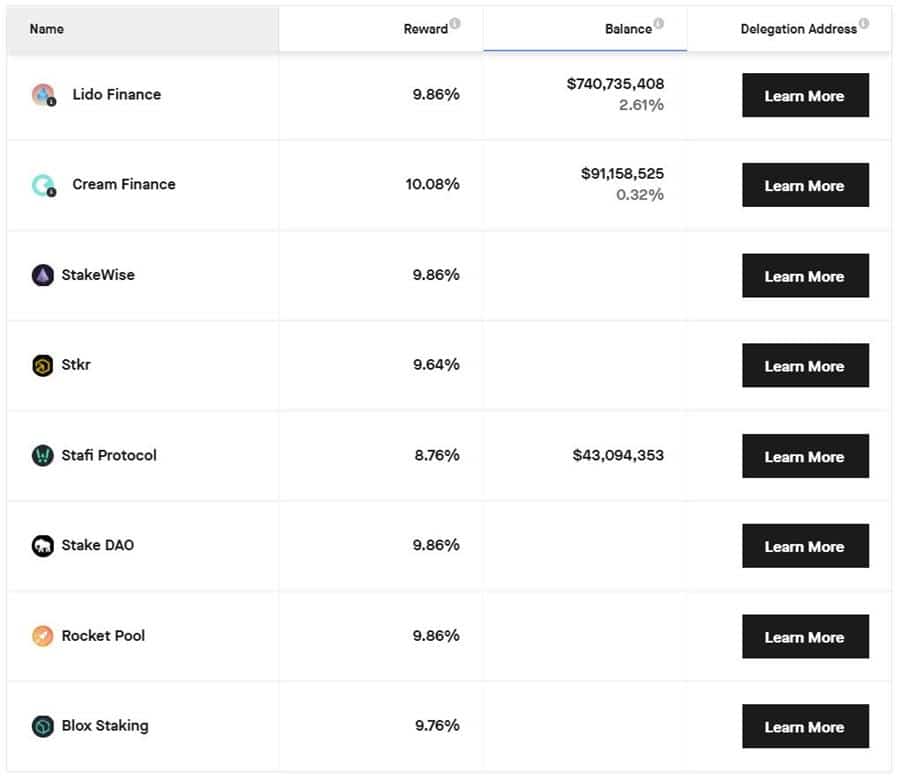 Pretty sweet staking rewards. Image via StakingRewards.com
Pretty sweet staking rewards. Image via StakingRewards.com Current Ethereum staking rewards range between 4-20% on exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase and Kraken, as they advertise at the time of writing, though it is important to note that the higher interest rates went to the newcomers, with interest rates now being on the lower end of that scale. The APY for those wanting to run their own validators or utilize staking pools can expect between a 4-10% APY.
What are the Risks Involved?
Staking Ethereum isn’t all sunshine and rainbows, unfortunately, similar to any investment vehicle offering returns, there are always risks involved and Ethereum staking is no different. There is a small risk of losing funds through slashing.
Those choosing to become their own validators can also lose funds by being offline more than 50% of the time and not performing their staking duties correctly, having a mild penalty of not receiving the rewards that they were expecting. Validators can also lose their funds by publishing contradictory information about the chain, in which case the validator is slashed and ejected from the system.
The amount slashed will be between 1 ETH and the entire staked amount, harsh but fair as this normally only happens in cases where a validator is acting maliciously.
 Ethereum Co-Founder and Lead Developer Commits $1.5 Million for Staking on Ethereum 2.0 Image via criptomercato.it
Ethereum Co-Founder and Lead Developer Commits $1.5 Million for Staking on Ethereum 2.0 Image via criptomercato.it The other major risk is market risk and applies to the fact that staked Ethereum is subject to a delay when users go to unstake, meaning that your Ethereum is not immediately accessible to be able to sell until the unstake is complete. The time it takes to unstake Ethereum can vary depending on several factors, including the number of requests in the queue and whether the unstaking is partial or full. The average time for a full unstaking request can range from 17 days to weeks or even months. Partial withdrawals, on the other hand, can take about 4.27 days to process. It's worth noting that the unstaking process is done on-chain on the Ethereum network, which means that the time it takes to complete the request is subject to network congestion and other factors.
Ethereum staking is not suitable for short-term traders or holders and should only be utilized for people who want to stake their Ethereum long-term. Liquid staking is available, where Ethereum Stakers can receive a sort of IOU token equal to the amount of their staked ETH so they still have liquid access to their staked capital, but the IOU tokens received in return aren't quite the same thing as holding the original Ethereum asset itself.
An example of market risk would be if Ethereum skyrocketed to 10k tomorrow, then plummeted back down to five hundred dollars. Staked Ethereum is not available to be sold for profits at 10k, nor would users be able to get out of the asset and jump a sinking ship should the value of Ethereum continue to drop. Ethereum stakers are at the complete mercy of the market, and many are hesitant to stake their Ethereum as the profit that can be made by selling Ethereum during a bull market will likely be worth more than the APY you can earn by staking it.
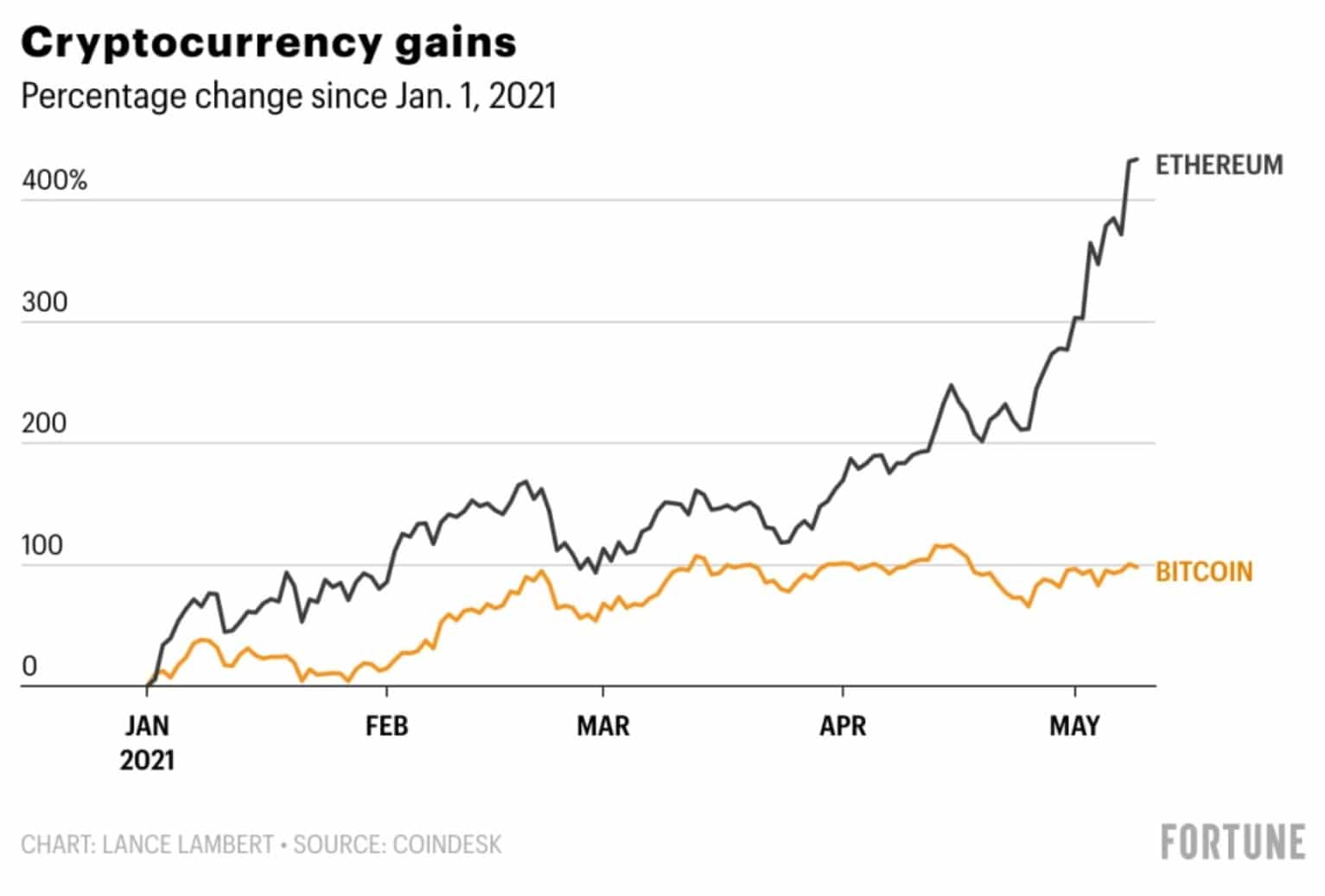 2021 Ethereum Returns Showing That Ethereum Gains are Higher Than Staking Returns Image viaFortune.com
2021 Ethereum Returns Showing That Ethereum Gains are Higher Than Staking Returns Image viaFortune.com How/Where can you stake Ethereum?
This can be a bit of a loaded question with no “one size fits all” answer. There are multiple different methods you can use to stake Ethereum, and different places you can go for staking. Not all staking methods are created equal. Here I will cover the different ways you can stake, and the most popular places to stake, beginning with the most difficult to set up and most costly in terms of initial setup and amount of ETH needed.

Become your own Validator
Yes, for the most die-hard and “OG’s” in the Ethereum space, setting up your own validator node is the most decentralized and effective method for staking your Ethereum, but it isn’t going to come cheap or easy, and you definitely do not want to choose this method if you are not technically savvy, don’t hold 32 ETH, or won’t have access to continuous internet uptime.
 Ethereum 2.0 Validator Machine Image via medium.com/coinmonks
Ethereum 2.0 Validator Machine Image via medium.com/coinmonks People who choose this option generally do so because they want to directly support the Ethereum network and contribute to the security and functionality of Ethereum, ensuring the future success and prosperity of the Ethereum ecosystem. To become a validator and set up a node for ETH staking, all you need to have is a cool 32 ETH kicking around, which is only $52,300 dollars at the time of writing. Easy enough, right? Let me just smash open the old piggy bank and collect the coins buried in my couch cushions and I’ll get that 52k in two shakes of a lamb’s tail.
Say you do have a lovely bag of 32 ETH sitting around, you will also need some hardware to become a validator, which in this case, will need to be a dedicated computer set up for staking, with software installed that will allow you to run a terminal command that will pull the Ethereum 2.0 node onto that machine. If this is the path that you would like to take, here is a full detailed guide on how to run your own validator node.
 Computer Screen Showing What Running an Ethereum Validator Node Looks Like Image via voskcointalk.com
Computer Screen Showing What Running an Ethereum Validator Node Looks Like Image via voskcointalk.com What about the options for those of us who aren’t tech-savvy, don’t want the hassle of running our own nodes, or don’t have a money tree kicking around to be able to buy the 32 ETH needed for staking? Well, luckily there are plenty of alternatives, starting with the simplest solution which is staking with a centralized platform.
Centralized Staking on an Exchange
The quickest and easiest way to start staking Ethereum is on centralized exchanges. Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase all offer Ethereum staking, with no minimum amount of Ethereum required to get started, assuming you are trying to stake at least more than 0.0001 ETH that is. All you need is an account with one of these exchanges which many people already have, hold some Ethereum in that account and choose the staking option.
Note that liquid Ethereum staking is not available in every jurisdiction, so you will need to check with your exchange of choice to find out if you are located in one of the supported regions. Some exchanges such as Binance will provide users with BETH tokens at a 1:1 ratio to the amount of ETH staked to help ensure users have access to liquid capital while their Ethereum is staked.
Many users prefer this method as the BETH tokens are liquid, so while the ETH is locked away being staked, users are free to transact with their BETH as they would with regular ETH, swapping for other assets, or participating in BETH yield farming to further increase their rewards. Here is a guide on Binance ETH staking.
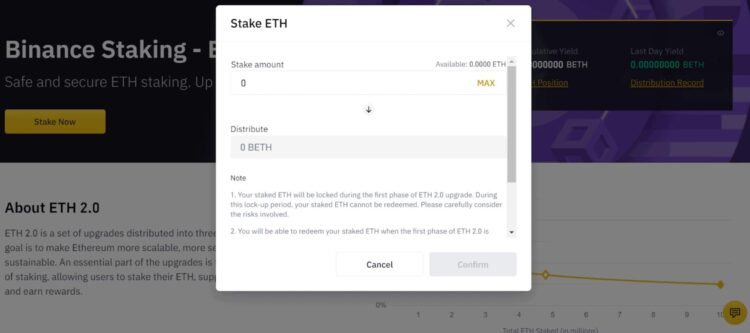 The Ethereum Staking Process Shown in Binance When Users go to Stake Their Eth Image via Binance
The Ethereum Staking Process Shown in Binance When Users go to Stake Their Eth Image via Binance Similar to Binance, Kraken also offers liquid Ethereum Staking to users with a low minimum balance to get started of just 0.00001 ETH. Kraken provides a similar method of staking to users where users who stake their Ethereum will receive a pegged token representing the value of the Eth they staked at a 1:1 ratio.
This token is called ETH2.S and can be used as users would use regular ERC20 tokens. Note that while staking Ethereum is available on Kraken for users located in America and Canada, liquid staking and the distribution of ETH2.S is not available. Be sure to double-check supported regions before getting involved. Here is the guide to ETH staking on Kraken.
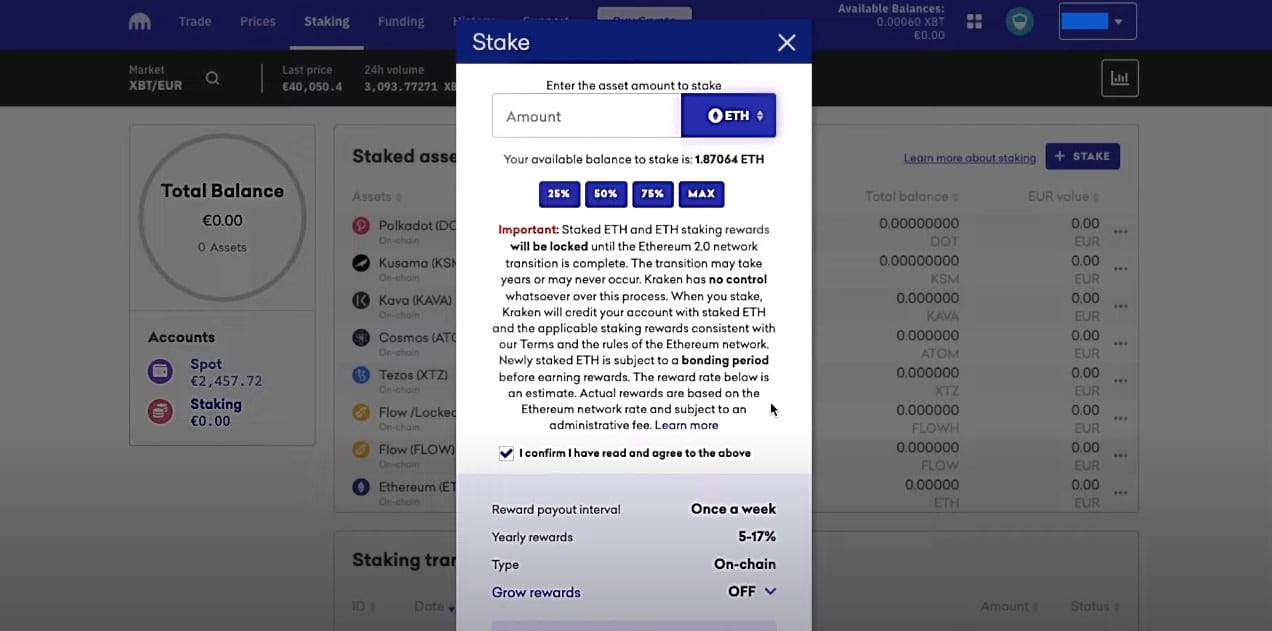 Kraken’s ETH Staking Screen Providing a Warning and Explanation about Ethereum 2.0 Staking Image via Kraken
Kraken’s ETH Staking Screen Providing a Warning and Explanation about Ethereum 2.0 Staking Image via Kraken Staking Pools
The next way that users can get involved in staking Ethereum if they have under 32 ETH is by joining and getting involved with staking pools. On that note, you can check out the best Ethereum staking pools.
There are multiple staking pools to choose from, too many to cover here, but I’ll mention a couple of top choices for you to consider. Staking pools are protocols that can contribute to validator nodes, collecting Ethereum from multiple participants until the 32 ETH are needed to begin staking.
A great thing about Staking pools and why the majority of users prefer this method is that they can hold their ETH safely off of centralized exchanges and still participate in staking. The most popular staking solution in this category is Lido.
Lido
Lido is a fantastic option as users can stake the Ethereum that they hold in their own non-custodial wallet such as Metamask, Coinbase Wallet, Trust Wallet and even Ledger, which is a real game-changer. Be sure to check out our review on why we think Ledger is one of the best options for storing and even staking crypto.
Similar to Binance and Kraken, Lido offers liquid staking which is a great, decentralized way to participate in Ethereum staking without locking up your capital. While your Ethereum will still be locked, users will receive stETH at a 1:1 value of the amount of ETH they staked, plus rewards. stETH tokens are minted upon deposit and burned when redeemed back for Ethereum. The stETH tokens can be used as one would use regular ERC20 tokens available to swap or sell.
Lido’s Ethereum staking feature also comes supported and preinstalled in the mobile wallet Argent, for ultimate convenience. You can find a full tutorial on how to use Lido with a software wallet, and how to use Lido with Ledger hardware wallet.
 Ethereum 2.0 Staking Supported Natively in Argent Wallet Through Lido Image via Argent
Ethereum 2.0 Staking Supported Natively in Argent Wallet Through Lido Image via Argent ANKR
ANKR is another fantastic platform offering many different DeFi services including node hosting for over 50 different blockchains and provides an easy way to get involved with Ethereum staking pools. ANKR offers ETH staking through their decentralized staking protocol Stkr, which is a smart contract allowing users to get involved in ETH staking with less than 32 Ether, but a minimum of 0.5 ETH is needed.
The STKR system has two staking options available for users to choose from, they can simply be a requester, or staker, where someone else runs the node for you, sharing the profits, or users can also choose to be a node provider even if they do not hold 32 ETH, earning higher rewards by combining their ETH with users who are only contributing ETH to make up the 32 needed.
ANKR provides liquid staking similar to Lido and works with Metamask, Trust Wallet, Bitkeep, Math Wallet, imTOKEN, and others.
Users who choose to stake ETH will receive aETH token in return at a 1:1 peg to the value of their deposited Ethereum which can then be traded on exchanges such as SushiSwap and Uniswap freeing up liquidity for Ethereum stakers. Here is a full tutorial on how to get involved with staking Ethereum with Ankr.
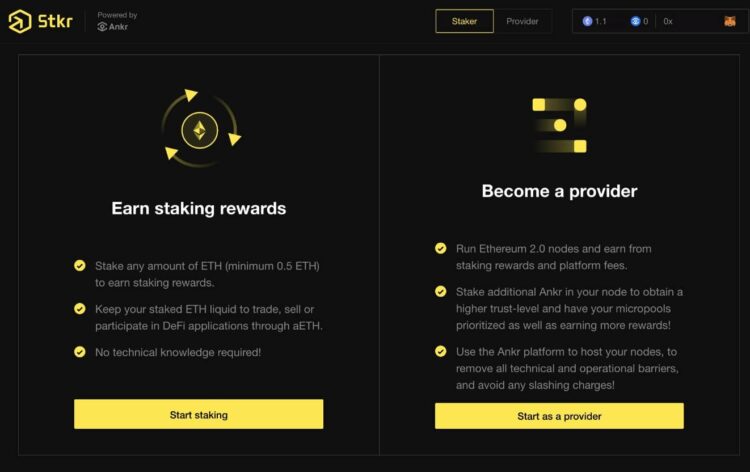 Ankr’s Stkr screen Showing the Different Staking Methods Available for ETH 2.0 Image via reddit.com/r/Ankrofficial
Ankr’s Stkr screen Showing the Different Staking Methods Available for ETH 2.0 Image via reddit.com/r/Ankrofficial Validators as a Service (VaaS)
The final option I would like to cover is for those Ethereum holders that maybe do hold the 32 ETH required to run their own node, but maybe lack the technical knowledge and equipment, or simply do not have the time or desire to run their own node. This is where a Validator as a Service company can come into play. There are service companies out there that are happy to run a validator node on your behalf for a flat fee, monthly fee, or percentage of your profits.
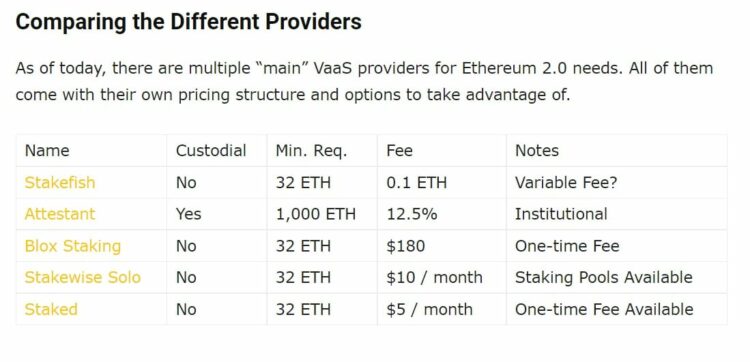 List of a few Validator as a Service Company who Offer Hosted Ethereum Validator Services Image via cryptomode
List of a few Validator as a Service Company who Offer Hosted Ethereum Validator Services Image via cryptomode People who choose this method will pay the service company to maintain and run the validator node on their behalf, leaving the ETH holder no need to invest in the hardware, nor have the know-how on how to set up, maintain, or run their own node. The drawbacks being that the funds are obviously still illiquid while staked, and users are opening themselves up to third-party risk as they need to trust the company running the node, and hope they won’t go bankrupt or disappear overnight.
It is also worth mentioning that some of these services charge quite a high premium for this service, and the costs fluctuate greatly between providers so be sure to shop around for the best deal and ensure the service provider is reputable. Two highly rated, reputable, and reasonably priced VaaS companies to consider are Staked and Stakefish.
Closing Thoughts
Those are the most common methods that can be utilized by Ethereum holders who want to stake their funds. The process of staking Ethereum may not be suitable for short-term holders or traders as the loss of access to Ethereum for an unknown period of time during the unstaking process could result in traders missing out on short-term price movements.
Staking Ethereum is mainly utilized by long-term Ethereum holders who are interested in capital appreciation over time and true supporters of the network as they want to see the future of DeFi flourish and are passionate about the Ethereum ecosystem.
If you are interested in earning interest on your Ethereum holdings without staking, then platforms such as SwissBorg and Yield.App may be more suitable for you. You can find more information on yield generation platforms in our Top 6 CeFi Platforms article.





