In traditional finance, treasuries have always been used as the bedrock of stability. Corporations, governments, and institutions maintain reserves, whether in cash, bonds, gold, or foreign currencies, to ensure liquidity, hedge against risk, and safeguard long-term strategies. These reserves aren’t glamorous, but they quietly build the health and resilience of entire enterprises.
Now, as decentralized finance (DeFi) and the web3 ecosystem grow, a new category has emerged, known as Ethereum treasuries. These are reserves of ETH, the native currency of Ethereum, set aside by corporates, DAOs and institutions.
Just like their traditional counterparts, they provide stability and liquidity, but unlike fiat treasuries, ETH can be staked to generate yield, deployed into DeFi for returns, or transparently allocated through smart contracts and on-chain governance.
Unlike Bitcoin treasuries, which are largely passive “digital gold,” Ethereum treasuries offer yield, governance influence, and DeFi interoperability. Thus, making ETH a balance-sheet item, and an important one at that.
This article explores how Ethereum treasuries have developed, who’s leading the trend, how they function, and what the future might hold.
TL;DR — Ethereum Treasuries
- Ethereum treasuries are reserves of ETH held by corporates, DAOs, and institutions to provide stability, liquidity, and long-term balance-sheet strength, similar to how traditional treasuries hold cash, bonds, or gold. The largest holders are BitMine Immersion, SharpLink Gaming, and The Ether Machine.
- Unlike Bitcoin treasuries, which are mostly passive "digital gold", Ethereum treasuries are productive assets since ETH can be staked for yield, deployed in DeFi, or allocated through on-chain governance.
- The category has scaled rapidly, from about 116,000 ETH in 2024 to over 3.6 million ETH ($15B+ in August 2025), representing roughly 2.8% of Ethereum’s circulating supply.
- Challenges include ETH price volatility, smart contract risks, governance capture, and fragmented regulations, though adoption is pushing ETH closer to mainstream reserve status.
- Bottom line: Ethereum treasuries extend the idea of reserves beyond passive storage, creating yield-generating, transparent, and governance-active balance-sheet assets that could become standard in both DeFi and corporate finance.
👉 Ethereum treasuries are not just reserves, they are productive financial tools that merge stability with on-chain yield and governance, making them a new cornerstone of Web3 finance.
Ethereum Treasuries Today: Market Data and Leaders
Ethereum treasuries have grown into a multibillion-dollar category in just a few years.
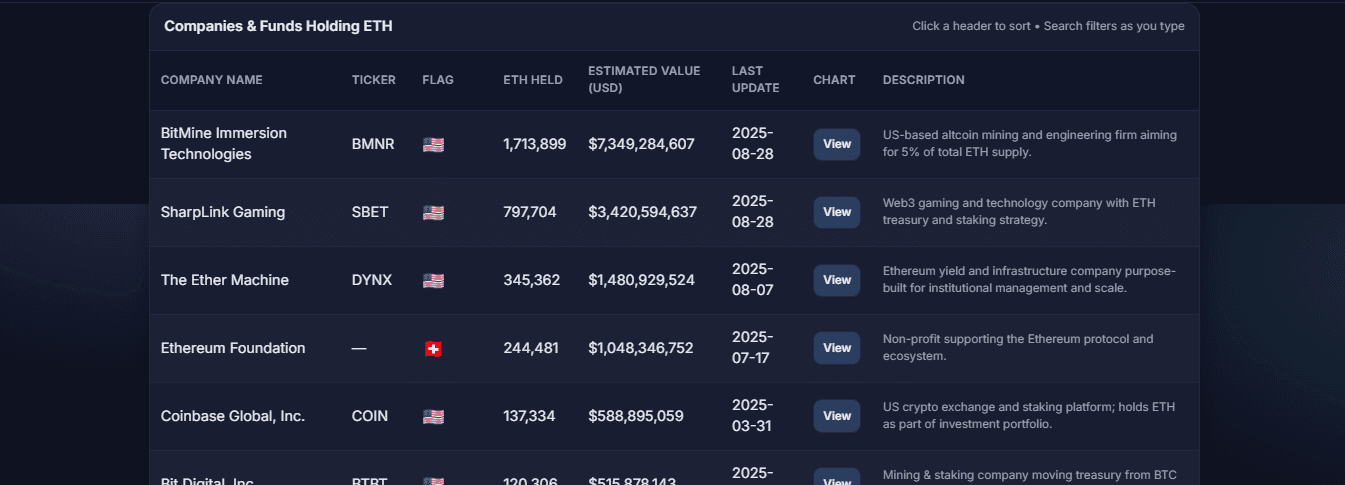
As of early 2024, tracked treasuries amounted to around 116,000 ETH. As of Aug. 30, 2025, 17 companies hold over 3.6 million ETH, representing roughly 2.8% of Ethereum’s circulating supply, according to EthereumTreasuries.net. At an ETH price of about $4,288.05, this translates to over $15.5 billion in balance-sheet value.
BitMine Immersion is the largest corporate ETH holder, followed by SharpLink Gaming, with The Ether Machine rounding out the top three ETH holders, EthereumTreasuries.net. All of these companies are based in the U.S.
| Company Name | ETH Held | Estimated Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| BitMine Immersion Technologies | 1,713,899 | $7,502,044,425 |
| SharpLink Gaming | 797,704 | $3,491,693,995 |
| The Ether Machine | 345,362 | $1,511,711,639 |
| Ethereum Foundation | 244,481 | $1,070,137,344 |
| Coinbase Global, Inc. | 137,334 | $601,135,638 |
| Bit Digital, Inc. | 120,306 | $526,601,017 |
| 180 Life Sciences ETHZilla | 82,186 | $359,742,915 |
| BTCS Inc. | 70,028 | $306,525,161 |
| Fundamental Global Inc. | 47,331 | $207,176,307 |
| Ether Capital Corp. | 46,274 | $202,549,627 |
| Intchains Group Limited | 7,023 | $30,740,935 |
| Exodus Movement, Inc. | 2,729 | $11,945,324 |
| GameSquare Holdings, Inc. | 1,818.84 | $7,961,390 |
| Vault Ventures PLC | 711.93 | $3,116,246 |
| Entreparticuliers.com | 459 | $2,009,126 |
| Mogo Inc. | 146 | $639,068 |
| Neptune Digital Assets | 140 | $612,805 |
Here's our video on the topic:
Ethereum Treasuries vs Bitcoin Treasuries
Bitcoin and Ethereum treasuries both serve the crucial purpose of corporate and institutional balance-sheet diversification in the digital asset age. However, their roles, strategies, and economic profiles differ widely, reflecting the unique characteristics of each cryptocurrency.
| Category | Bitcoin Treasuries | Ethereum Treasuries |
|---|---|---|
| Core Role | Digital Gold – store of value, reserve asset | Productive, yield-generating treasury |
| Top Corporate Holder | MicroStrategy: 632,000 BTC (~$69B mid-2025) | BitMine Immersion |
| Other Major Holders | MARA Holdings, Riot Platforms, Trump Media | Mix of corporates, funds, ETF inflows |
| Total Holdings | ~1,000,936 BTC held by public firms (~4.8% of total BTC supply) | ~3.3M ETH held by public firms + ETFs (~3.5–5% of circulating ETH supply) |
| Strategy | Buy-and-hold, passive approach (store-of-value, no direct yield) | Staked and/or deployed in DeFi for 3–5% yield, governance participation, liquidity |
Bitcoin Treasuries: The Digital Gold Standard
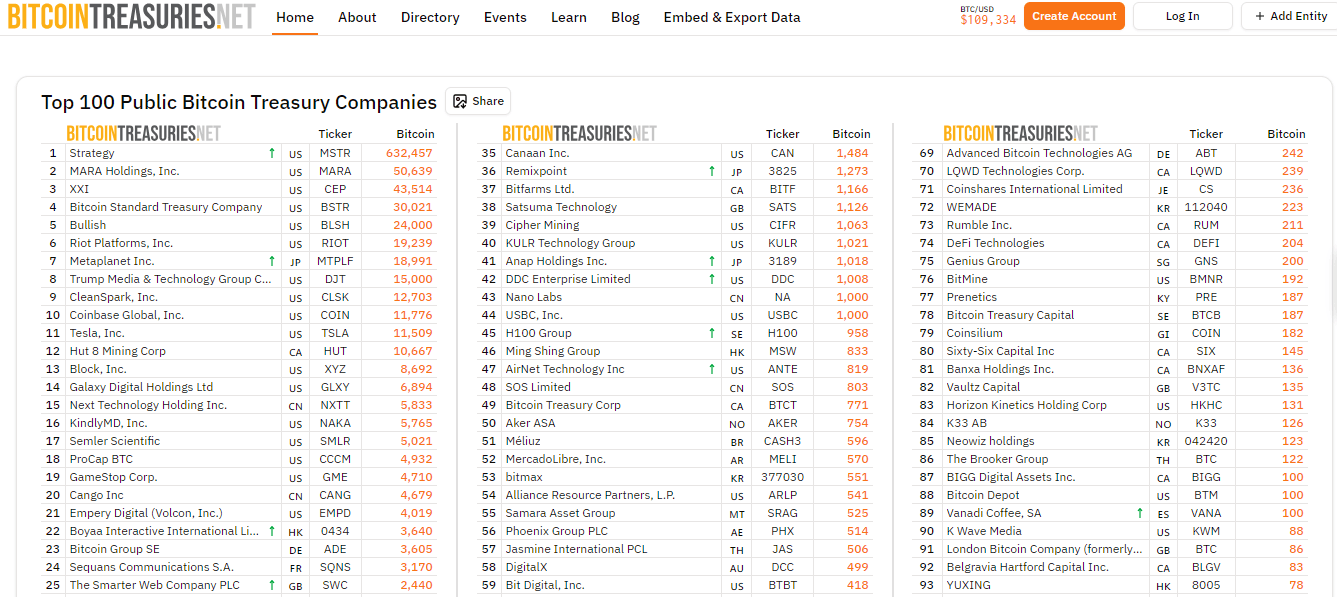
Bitcoin treasuries have become famous and widely recognized, anchored by leaders such as MicroStrategy, the largest public corporate holder with over 632,000 BTC valued at around $69 billion as of mid-2025.
 Top Bitcoin Treasury Holders. Image via Bitcoin Treasuries
Top Bitcoin Treasury Holders. Image via Bitcoin TreasuriesOther major Bitcoin holders include MARA Holdings and Riot Platforms, each holding tens of thousands of BTC, alongside notable newcomers like Trump Media. In total, public companies hold about 1,000,936 BTC, or roughly 4.8% of Bitcoin’s total supply, illustrating significant institutional confidence.
Bitcoin treasuries primarily follow a buy-and-hold strategy, mirroring traditional corporate gold or FX reserves. Bitcoin is held as a store of value, with no mechanism for generating yield directly on the asset, making it a passive treasury. This passive approach has earned Bitcoin the moniker “digital gold,” valued for its scarcity, decentralization, and security.
Ethereum Treasuries: Productive and Yield-Generating
Ethereum treasuries, by contrast, represent a new breed of productive treasury management. While Ethereum shares Bitcoin’s use case of diversification, its proof-of-stake consensus mechanism allows ETH holders to stake their tokens and earn annual yields of 3–5%, adding income generation to treasury value.
Public Ethereum treasury firms collectively hold over 3.3 million ETH, worth approximately $15 billion at current prices, representing about 3.5% to 5% of the circulating ETH supply when combined with ETF inflows.
Top ETH treasury companies such as BitMine Immersion and SharpLink Gaming lead the charge in deploying ETH not only as a financial reserve but as a yield-bearing and governance-participating asset, with portfolios actively staked or partially allocated to DeFi protocols to enhance returns.
Ethereum treasuries thus embody a fundamentally different philosophy: they are productive assets that combine the security and value proposition of ETH with on-chain participation, liquidity optimization, and governance influence. This creates additional layers of potential return and ecosystem integration that Bitcoin treasuries lack.
Case Studies: Top Ethereum Treasury Companies
Numbers are useful, but let’s take a look under the hood at how some of the top companies use ETH treasuries and how they operate in practice.
 BitMine, SharpLink, And Coinbase Lead Ethereum Treasury Holdings. Image via Ethereum Treasuries
BitMine, SharpLink, And Coinbase Lead Ethereum Treasury Holdings. Image via Ethereum Treasuries1. BitMine Immersion: ETH Treasury at a Glance
Why It Matters
- Scale comparable to sovereign wealth funds.
- Goes beyond standard corporate diversification.
Dual Treasury Model
- Core — Staking: predictable, steady yield.
- Layer — DeFi: liquidity pools, stablecoin swaps, yield farms.
Market Impact
- Transparent purchases and treasury growth.
- Considered a bellwether for institutional ETH adoption.
3. Coinbase
Dual Role
- Holder of ETH for its own treasury.
- One of the largest global custodians & staking providers.
Industry Influence
- Oversees millions of ETH staked by clients.
- Shapes custody, staking rewards, and disclosure standards.
- Makes ETH productive, not idle capital.
Institutional Impact
- As a US-listed company, ETH disclosures face regulatory scrutiny.
- Bridges crypto-native practices with traditional finance norms.
- Anchor of legitimacy for corporates considering ETH exposure.
4. Bit Digital
From BTC Mining to ETH Staking
- Pivoted from pure Bitcoin mining as BTC margins tightened.
- Adopted Ethereum staking to generate recurring on-chain yield.
- Treasury now contributes to operating income via staking rewards.
Nuanced Treasury Design
- Staked tranche: predictable returns and stability.
- Liquid tranche: agility for DeFi opportunities and volatility management.
- Balances income generation with strategic flexibility.
Why It Matters
- BTC remains a store-of-value reserve; ETH adds programmable, yield-bearing utility.
- Signals a broader shift toward multi-chain corporate treasuries.
- Shows BTC and ETH can be complementary tools, not either/or bets.
DAO Treasuries (MakerDAO, Uniswap, Aave)
 DAOs Redefine Governance Through Transparency And Smart Contracts. Image via Shutterstock
DAOs Redefine Governance Through Transparency And Smart Contracts. Image via ShutterstockSome of the largest decentralized organizations provide a clear view of how different strategies shape on-chain balance sheets.
MakerDAO has diversified heavily into real-world assets. Instead of concentrating on ETH, its treasury leans on U.S. Treasuries, with about $1.2 billion currently allocated to government bonds as part of DAI’s reserve backing. While not an ETH-heavy treasury, it shows how DAOs are blending on-chain and off-chain assets to stabilize operations.
Uniswap stands out as one of the largest DAO treasuries overall, with an estimated value of $3.73 billion in 2025. The majority of this treasury is in UNI tokens, but it also includes a meaningful mix of ETH, USDC, DAI, and OP, positioning Uniswap as one of the most capital-rich organizations in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Aave has taken a balanced approach, actively managing its holdings through its own lending protocols. Its treasury is worth about $132.7 million (excluding AAVE) and $329 million (including AAVE). Roughly 44.6% of that treasury is in ETH and related tokens, according to BlockBeats. This makes Aave one of the more ETH-exposed DAO treasuries, especially compared to MakerDAO’s real-world asset focus.
How Ethereum Treasuries Work?
 Ethereum Powers DeFi, NFTs, And Web3 Innovation Globally. Image via Shutterstock
Ethereum Powers DeFi, NFTs, And Web3 Innovation Globally. Image via ShutterstockEthereum treasuries are structured systems designed to balance security, liquidity, and returns. Their mechanics combine elements familiar from traditional treasury management, like diversification and governance, with blockchain-native tools such as staking contracts, automated smart contracts, and DeFi integrations.
Understanding these mechanics is key to seeing why Ethereum treasuries are more dynamic than their Bitcoin counterparts.
Treasury Structure and Components
At the foundation, every treasury is defined by its structure and mix of assets. Corporate treasuries often rely on custodians such as Fireblocks, Anchorage, or Coinbase Custody to hold ETH securely.
These custodians use solutions like MPC (multi-party computation) or multi-sig wallets to reduce single points of failure. In contrast, DAOs operate treasuries fully on-chain, typically through vaults such as Gnosis Safe, where token holders collectively authorize movements.
Hybrid approaches are also emerging. Some corporates retain custody of the bulk of their ETH but delegate smaller pools to DAO-like frameworks for community-based allocation. This allows them to test on-chain governance models without exposing their entire reserve.
While ETH dominates, most treasuries diversify. Common components include:
- ETH (core holding): The backbone of every Ethereum treasury, often staked for yield.
- Stablecoins (USDC, DAI): Held for operational liquidity and protection against volatility.
- ERC-20 governance tokens: Strategic holdings tied to ecosystem partnerships, giving voting rights in other protocols.
- Layer 2 assets or derivatives: Some treasuries already experiment with rollup tokens or stETH derivatives, increasing flexibility.
This mix creates resilience. ETH provides upside, stablecoins maintain stability, and governance tokens extend influence across DeFi ecosystems.
Role of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts sit at the center of Ethereum treasuries. They reduce reliance on intermediaries and allow for real-time, automated management of reserves. Their roles can be broken into three categories:
1. Automation of Liquidity and Yield
Smart contracts automate routine tasks like deploying ETH into staking pools, reallocating funds when conditions change, or harvesting yield from DeFi strategies. For example, a DAO treasury can automatically restake rewards without human intervention, ensuring constant compounding. Automation reduces costs and minimizes the delays associated with manual decision-making.
2. Governance Protocols
In DAO treasuries, smart contracts execute governance-approved decisions. Token-holder votes on platforms like Snapshot or Aragon can be tied directly to treasury contracts, ensuring that once a proposal passes, the allocation happens without human bottlenecks. This preserves transparency and so every move is recorded on-chain and verifiable.
3. Risk Points
Automation brings efficiency, but also risk. If a contract contains a bug or an exploit, an attacker can drain reserves instantly. The infamous 2016 DAO hack showed how devastating poorly audited contracts can be.
Governance capture is another risk. If a few whales control voting tokens, they can direct treasuries for their own benefit. These risks highlight why many treasuries combine automation with controls like time delays, audits, and insurance.
Smart contracts make Ethereum treasuries faster, cheaper, and more transparent, but they also introduce a new category of risks that corporates must carefully manage.
Treasury Liquidity and Yield Optimization
Beyond storage and governance, Ethereum treasuries are designed to work their capital. Liquidity and yield optimization are central features that distinguish them from traditional treasuries.
Direct staking forms the baseline, with validators offering annual yields of 3–5%. This is a low-risk, steady income source that ties directly into Ethereum’s proof-of-stake consensus.
Liquid staking protocols like Lido and Rocket Pool add another layer. They allow ETH to be staked while issuing derivative tokens such as stETH or rETH, which can then be traded or used in DeFi. This provides both yield and liquidity, enabling treasuries to access capital without unstaking ETH.
Some treasuries go further into DeFi strategies:
- Yield farming: Supplying stETH or ETH into liquidity pools on protocols like Curve to earn trading fees plus incentives.
- Leveraged staking: Borrowing against stETH to acquire more ETH, restaking it, and compounding yield.
- Stablecoin swaps: Converting staking rewards into USDC or DAI for liquidity management.
Yields in these strategies can climb into double digits (10–14%) during favorable markets. But with higher return comes higher risk: smart contract exploits, liquidity crunches, or cascading liquidations can wipe out capital.
The challenge for treasury managers is balance: ensuring steady, predictable revenue while carefully allocating only a portion of reserves into higher-risk DeFi plays. For corporates, transparency and sustainability matter more than chasing maximum APY.
Governance and Risk Management in Ethereum Treasuries
The effectiveness of an Ethereum treasury depends on how they are managed. Governance determines who makes the decisions, while risk management ensures those decisions protect and grow capital without exposing it to unnecessary threats. For corporates and DAOs alike, the way a treasury is governed can be the difference between long-term sustainability and rapid capital loss.
 The Effectiveness of an Ethereum Treasury Depends on How They Are Managed. Image via Shutterstock
The Effectiveness of an Ethereum Treasury Depends on How They Are Managed. Image via ShutterstockTreasury Governance Models
Governance frameworks differ depending on whether the treasury belongs to a DAO, a corporate entity, or a hybrid.
- DAO Governance: Most DAOs rely on token-holder voting to decide treasury allocations. Platforms like Snapshot and Tally record votes that are then executed through treasury smart contracts. While this system is transparent and inclusive, it has drawbacks. Low participation rates can leave decisions in the hands of a small minority. For example, MakerDAO has seen critical debates where only a handful of large holders determined outcomes, raising concerns about “governance capture.” This makes DAOs both open and fragile as well as visible to all, but vulnerable if power concentrates.
- Corporate Governance: Corporations usually fall back on committee-based decision-making led by CFOs, boards, or treasury managers. This mirrors traditional finance, with tighter accountability, established controls, and clear lines of responsibility. It is less transparent to the public but aligns more closely with regulatory and investor expectations. Shareholders often prefer this clarity, even if it lacks the democratic openness of DAOs.
- Hybrid Models: Some firms are experimenting with blends of both. For instance, they may allocate the majority of their ETH through a traditional treasury committee while setting aside a smaller pool for community-driven initiatives using DAO-style governance. This model allows corporates to test on-chain governance without putting their entire balance sheet at risk.
Ultimately, the model chosen reflects trade-offs between transparency, accountability, and flexibility.
Risk Management Strategies
Managing risk is central to any treasury strategy. For Ethereum treasuries, risks arise not only from market volatility but also from custody, insurance, and liquidity constraints.
- Custody: Secure storage is the first line of defense. Multi-signature wallets (such as Gnosis Safe) require multiple parties to sign off before funds can be moved, thereby reducing the risk of unilateral theft. MPC (multi-party computation) custody, offered by providers like Fireblocks and Anchorage, goes further by splitting cryptographic keys across different parties. Cold storage remains a fallback, where ETH is kept offline and away from immediate attack vectors, though it limits liquidity.
- Insurance: Treasury insurance is an emerging field. Decentralized protocols like Nexus Mutual and Unslashed Finance allow treasuries to hedge against smart contract exploits or validator slashing events. While adoption is not yet widespread, these solutions add a critical safety net, especially for DAOs managing billions of dollars transparently on-chain.
- Liquidity: Liquidity management is especially important in Ethereum staking. Unstaking ETH can take days or weeks if network queues are congested. During periods of volatility, this lag can trap treasuries in illiquid positions just when flexibility is most needed. To counter this, many treasuries use liquid staking derivatives (stETH, rETH) that can be traded or used in DeFi while underlying ETH remains staked.
Each of these strategies adds a layer of protection but also involves trade-offs: stronger custody can reduce flexibility, and more insurance coverage can eat into yields. Treasury managers must weigh safety against efficiency.
Accounting and Reporting
Accounting rules bring Ethereum treasuries firmly into the world of traditional finance. In 2023, the FASB (Financial Accounting Standards Board) updated its guidelines, requiring companies to mark crypto assets to their fair market value. This means that ETH price movements flow directly into income statements.
- Impact in Bull Markets: A rising ETH price inflates balance sheets and can turn treasuries into profit centers, boosting quarterly earnings.
- Impact in Bear Markets: The reverse is true; price declines show up as losses, even if the ETH remains untouched and continues generating staking yield.
This accounting treatment introduces volatility into corporate financial reporting. For a company like Coinbase, which must file regular SEC reports, this means that ETH reserves directly affect investor sentiment and stock performance.
To manage this, corporates often pair treasuries with detailed disclosure policies explaining staking yields, liquidity management, and hedging strategies to reassure investors. Some even publish proof-of-reserves reports or commission independent audits of their smart contracts, bridging the gap between traditional accounting and blockchain-native transparency.
Regulation and Policy Landscape
 Regulatory Authorities Oversee All Cryptocurrency Transactions. Image via Shutterstock
Regulatory Authorities Oversee All Cryptocurrency Transactions. Image via ShutterstockEthereum treasuries are currently in the midst of mixed regulatory environments.
The US GENIUS Act supports corporate digital asset adoption, while the Investment Company Act complicates holdings if treasuries cross 40% into “securities.”
The EU’s MiCA framework sets consistent standards across member states. On the other hand, Asia’s approach varies as Singapore and Hong Kong encourage corporate treasuries, Japan permits gradual adoption, and China restricts them.
Audited proof-of-reserves and quarterly disclosures are likely to become standard for ETH treasuries in regulated markets.
Future of Ethereum Treasuries
Ethereum treasuries are still in their early stages, but the direction is clear. As more institutions and DAOs experiment with ETH reserves, new models are emerging that could reshape how digital assets are managed at scale.
Opportunities in DeFi Treasury Solutions
A new wave of “Treasury-as-a-Service” providers is emerging. Platforms like EigenLayer and Figment let institutions put idle ETH to work while keeping control. These services simplify staking, restaking, and yield strategies for corporates that lack in-house expertise.
Cross-chain treasury tools are also taking shape. Firms can balance assets across Ethereum, Layer 2s, and even other blockchains for stability and flexibility. This reduces dependence on a single network and opens up yield from multiple ecosystems.
DAOs remain the most active treasury innovators. Many are experimenting with automated allocations, community-driven governance, and diversified reserves. Their practices could influence how traditional companies manage digital treasuries.
Challenges Ahead
Price volatility still looms large. ETH can swing quickly, creating liquidity risk for any firm holding a large stake.
Governance attacks and smart contract exploits are another danger. Treasuries tied to protocols must navigate security vulnerabilities that don’t exist in traditional finance. Regulation is also fragmented. Rules for digital assets differ across regions, making global treasury management complex.
Market Implications
Large ETH treasuries may help stabilize the price. Staking removes supply from circulation, creating steady pressure toward scarcity.
At the same time, corporate and DAO treasuries bring Ethereum closer to mainstream adoption. They show crypto can be more than speculation; it can be infrastructure.
The trend also mirrors sovereign wealth funds. Just as nations use reserves to secure the future, Ethereum treasuries could become strategic economic tools for the digital era.
Conclusion
Ethereum treasuries are reshaping how organizations think about reserves. Traditional treasuries focus on holding; Ethereum treasuries add yield, transparency, and network alignment. Whether managed by corporates or DAOs, they combine financial prudence with blockchain-native mechanics.
If Bitcoin was the first step toward digital treasuries, Ethereum extends the concept into productive reserves. Over the next decade, ETH treasuries could sit alongside traditional reserves as part of standard financial practice.





