Decentralized finance apps, or DeFi, was the big thing in crypto in 2020. People got caught up in the craze of yield farming and peer-to-peer lending, with dozens of new apps and exchanges being created as a result. Now in 2021 that phase is considered to be more mature and the latest craze in 2021 is in non-fungible tokens, or NFTs.
Certainly NFTs are not all that new. It’s been possible to create these unique digital creations for years, but only recently have they become more popular among blockchain enthusiasts, artists, and collectors. With NFT valuations skyrocketing in 2021, the most expensive NFT sold for $69.3 million, the interest in NFTs has exploded among the creators of NFTs and collectors alike.
While the NFT craze seems to have peaked earlier in 2021, it is still a growing and very popular space, and there’s plenty of room for new creators with a unique take on creativity and digital artworks.
Given the potentially massive prices for some NFTs it’s certainly understandable that more creators are interested in getting involved and create their own NFT or collection of NFTs. Fortunately there are now tools that make it much easy to create your own NFTs and profit from the growing world of digital collectibles.
The following guide on how to mint an NFT will give you all you need to create your very first NFT. With the new knowledge, skills, and hopefully confidence you can then expand on your new-found abilities into other platforms or marketplaces.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via Shutterstock It might surprise you to learn that the process of minting your own NFT in 2021 is not as technical as you might have thought. With the tools we’ll inform you of, and some basic skills with a computer, you can soon be the latest proud new NFT creator.
As with any technical undertaking however, it’s good to have a complete understanding before jumping in. Which is why we’ve created the following comprehensive guide to getting started in the process of minting your own NFT.
Let’s get started.
What Is an NFT?
As mentioned above, non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have been around for some time. The very first type of NFT was actually created as part of the Bitcoin protocol and they were known as “colored coins.” These were digital representations of real-world assets created on the Bitcoin blockchain. They never really caught on however, mostly due to the creation of the Ethereum blockchain and mass adoption of the ERC-20 standard, and later the ERC-721 standard.
 Colored coins were the very first NFTs. Image via Bitcoin.com
Colored coins were the very first NFTs. Image via Bitcoin.com Because blockchain technology is well known as a great way to prove the authenticity and ownership of an asset it is a perfect match for the non-fungible token, which needs to be unique, authentic and have a proven chain of ownership. Because humans have a tendency to collect things, and to appreciate unique one-of-a-kind collectibles, the explosion of NFTs was only a matter of time.
NFTs use existing token standards to set unique identifiers that establish the authenticity, uniqueness, and ownership of a digital token or asset. The most commonly used blockchain for NFTs in 2021 is the Ethereum blockchain, but as indicated by the Bitcoin example above it is possible to create NFTs on other blockchains, and in the future one of these could overtake Ethereum as the primary chain for NFTs.
The difference between an NFT and blockchain based cryptocurrencies is that the NFTs are unique and cannot be exchanged equally like a cryptocurrency. For example, one BTC is identical to any other BTC. This is known as fungibility, and it is one of the defining features of currency, whether crypto or fiat. Non-fungible tokens then are those tokens that cannot be exchanged equally with other tokens, making them unique.
This is possible due to the transparency and immutability of the blockchain, whereby we are able to trace the timestamp of the creation of the token, who created that token, who the current owner is, and many other unique identifiers. All of these characteristics are stored on the public blockchain ledger and cannot be changed or manipulated in any way.
This makes the NFT an ideal creation when rarity and ownership proof is needed. This is why NFTs have gained popularity among collectors and artists.
For NFT Creators
Creators of NFTs get to enjoy a great degree of flexibility that’s often not available when using conventional methods for receiving value from the sale of their art, videos, music and others. When using NFTs a creator is able to side-step the middle-men that are involved in the traditional art sale scene and access the global marketplace directly.
Using a reputable NFT marketplace will allow the creator to streamline what can otherwise be a very resource-intensive and expensive process. All of this means the creator gets to keep a larger share of the profits from their creativity and effort.
 Creators are the backbone of the NFT ecosystem. Image via Medium.com
Creators are the backbone of the NFT ecosystem. Image via Medium.com In addition, NFTs can provide creators with passive income and a stream of future payments. You see, an NFT can be created in such a way that a commission is paid to the creator any time the NFT is sold. For example, you could program in a clause that pays a 5% commission to the creator whenever the NFT is sold. That means 10 or even 50 years from now if the NFT is sold you, as the creator, receive 5% of the sale price – even if it is $1 million or more!
For NFT Collectors
Collectors of artwork and investors can appreciate the NFT for its transparency and immutability that avoids the possibility of counterfeits, and provides proof of ownership.
While it is true that copies of any digital artwork, including NFTs, can be made, the fact that the authenticity of the original artwork is always preserved makes the NFT a unique and valuable item even if copies are made. After all, there are thousands of copies of the Mona Lisa in existence, but the original maintains its value because it is the original.
In the same way that copying the Mona Lisa doesn’t diminish the value of the original, copying an NFT also does not diminish its value.
Should You Create an NFT?
As you probably have already seen there are a number of benefits to creating an NFT of your digital or real-world artwork. Because of the transparency and immutability that comes with NFTs you gain an increased control over your intellectual property.
And having your artwork as an NFT opens up a global network of marketplaces and art collectors interested in your creations. NFTs are the gateway to a decentralized and democratized world of art and digital item collectors.
How to Create an NFT
Now that we have all the background information out of the way you’re probably interested in creating your own NFT. However there are still some factors that could influence your decision regarding where you will create your first NFT.
Because even though Ethereum as best-known as the blockchain for NFTs, there are growing communities of NFT marketplaces and creators on a number of other blockchains. Those blockchains being used for NFTs include:
 There are a number of blockchains that support the creation of NFTs. Image via Bitcoin.com
There are a number of blockchains that support the creation of NFTs. Image via Bitcoin.com - Ethereum
- Binance Smart Chain
- Polkadot
- EOS
- Flow by Dapper Labs
- Cosmos
- Tron
- Tezos
- WAX
Note that currently when you mint an NFT on one blockchain it is pretty much not possible to transfer them to another blockchain. However as the technology improves and things such as cross-chain bridges become more popular and numerous it could be possible in the future to move an NFT to pretty much any blockchain that supports their creation and storage.
However that’s all speculative, so for now you might want to carefully consider which blockchain you are going to use. There are certainly pros and cons to creating NFTs on each of the various blockchains that offer support for them.
Because Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for NFT creation currently we are going to exploring minting NFTs on Ethereum in this guide. Binance Chain is also becoming quite popular and in the future we might create a separate guide that focuses on minting Binance Smart Chain (BSC) NFTs. One of the benefits to using BSC is that the transaction fees are much smaller than those on the Ethereum blockchain.
 Binance will soon launch an NFT marketplace. Image via YouTube.com
Binance will soon launch an NFT marketplace. Image via YouTube.com One of the considerations is that the blockchain you choose to mint your NFT on will also determine which marketplaces you are able to use. The Ethereum blockchain has some of the largest NFT marketplaces, which include OpenSea, Rarible, and Mintable.
If you decide to go with the Binance Smart Chain you’ll choose between marketplaces such as BakerySwap, Treasureland, and Juggerworld.
How to Mint an NFT on Ethereum
Because the Ethereum network is most used for NFTs it has become quite easy to mint one on Ethereum. All that’s required are an account at the marketplace you’re going to use, an Ethereum compatible wallet, and some ETH stored in that wallet. Many people like to use either MetaMask or Trust Wallet as their Ethereum wallets, although there are many other possibilities.
 OpenSea is the top Ethereum NFT marketplace. Image via OpenSea.io
OpenSea is the top Ethereum NFT marketplace. Image via OpenSea.io Because Open Sea is the most popular Ethereum NFT marketplace, and MetaMask is among the most popular ETH wallets, we are going to use these two in our explanation of how to mint an NFT.
How to Mint NFTs on OpenSea
Before you head off to the OpenSea site make sure you’ve created a MetaMask wallet and that it contains some ETH that you will use during the NFT creation process.
The first obvious step once your wallet is set is to head over to the OpenSea website. Once there locate the “Create” button on the left side of the website and click it.
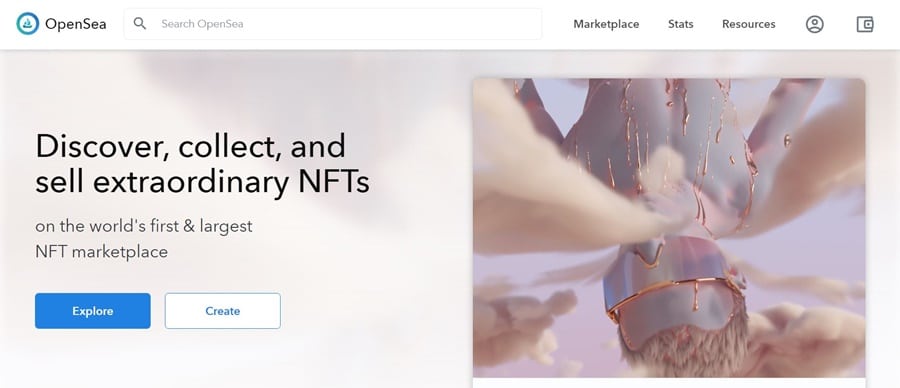 Get started minting NFTs at OpenSea. Image via OpenSea.io
Get started minting NFTs at OpenSea. Image via OpenSea.io You’ll be taken to a screen asking you to connect your MetaMask wallet (you can also choose from other supported wallets). Click to sign in and then follow the prompts to connect your wallet. You may be required to digitally sign a wallet message to confirm your ownership of the wallet address.
Once that’s down you’ll be taken into the “My Collections” screen on OpenSea, where you’ll be able to create a new collection.
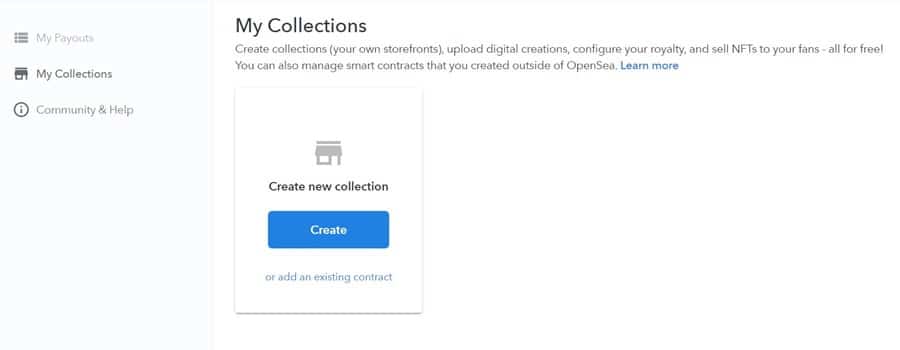 Get ready to create a new NFT! Image via OpenSea.io
Get ready to create a new NFT! Image via OpenSea.io Click on the “Create” button and you’ll get a popup asking for you to upload the logo for your collection as well as a title and an optional description. Note that during this step you are not creating an NFT and all of these can be changed at a later time.
Once you’ve created the collection details it will show up in you’re My Collections screen. Clicking on it will take you to a new screen where you’ll be able to actually create an NFT. Click the “Add New Item” button.
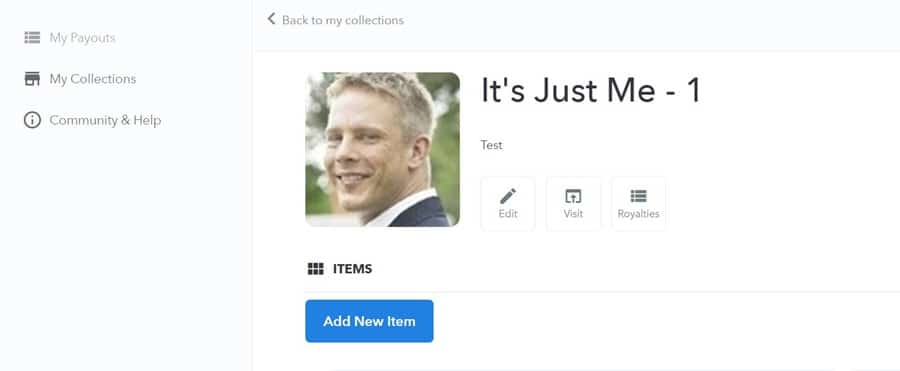 A shiny new NFT.
A shiny new NFT. After clicking the button you’ll receive a popup asking you to sign the transaction, and after clicking “Sign” you’ll be taken to the page where you can upload your Image, Video, Audio, or 3D Model. Currently the file formats supported are JPG, PNG, GIF, SVG, MP4, WEBM, MP3, WAV, OGG, GLB, and GLTF with a max file size of 40 MB.
Add the name and description (optional) of your file. You can also include an external link if you have a website where you are featuring your works. Otherwise OpenSea will create an internal link to the item within its own website.
Once you have submitted the necessary information, you can go ahead to upload the image, art, audio or 3D model. There are also options to set special properties for the uploaded item, as well as levels and stats. You can also set the item with unlockable content or mark it as explicit or sensitive content.
After you are done with all the extra customization, click Create to mint the NFT.
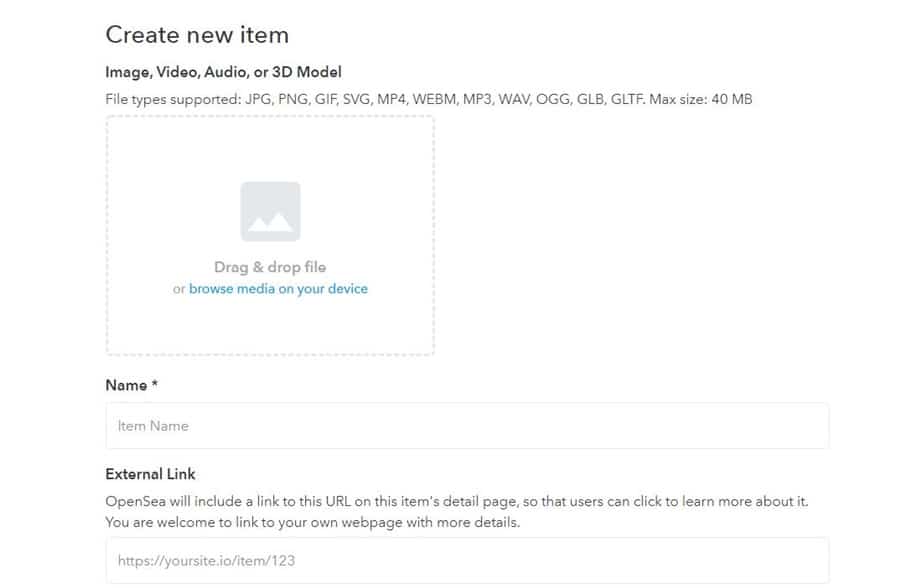 Adding a new item in Opensea.
Adding a new item in Opensea. You will have to confirm the creation of the NFT on your wallet by signing another message. Immediately after the confirmation, your NFT should appear as a collectible on your wallet.
You can then list the NFT on the marketplace by clicking the Edit button. This will take you to a page where you can choose the ERC-20 token you want to receive as payment and set a royalty clause.
Conclusion
See, minting your own NFT is not all that challenging. If you can create a wallet, you can create an NFT too. It’s really not much more difficult than creating an account at ebay or Amazon and uploading items to sell.
While we used OpenSea as a guide to minting an NFT you’ll find the process is quite similar on any other platform, regardless of which blockchain they support. So if you’re interested in participating in the NFT ecosystem as a creator why not get out there and start minting your own NFTs.



