The Dusk Network has been flying under the radar over the past few months but has more recently been generating quite a bit of interest.
It is flying hot off the heels of a recent Binance listing and trading volumes reflect this. The project is trying to take the concept of privacy based blockchains and bring it to the world of digital securities and STOs.
Yet, is all this hype overdone?
In this Dusk Network review, I will give you everything you need to know about the project. I will also look at the long term potential and use cases for DUSK tokens.
What is the Dusk Network?
The Dusk Network is a privacy blockchain that is focused on the issuance of digital securities, aiming to make trading compliance automatic, while maintaining individual user privacy and auditability. According to Jelle Pol, business lead of the project:
Dusk Network was created to digitize regulated (financial) markets. Built from the ground up to tackle the challenge at the deepest layer
The protocol combines a custom-built consensus mechanism and zero-knowledge cryptography to provide both compliance and confidentiality. The goal is to create a platform that removes the expensive middlemen found in traditionally regulated markets but still maintain regulatory approval.
The Dusk Network has recently moved to a public testnet and has plans on becoming a blockchain protocol that allows for easy deployment of Zero-Knowledge dApps, which would make it the backbone of a global, permissionless dApp ecosystem.
The Dusk Network Goals
Dusk was created for use in the financial industry, with a combination of necessary privacy and compliance with regulations.
While there are several potential use cases for the Dusk Network, the primary initial adoption strategy is focused on the Security Token (STO) market, which they feel will benefit from the addition of a privacy and compliance-focused blockchain built specifically for the needs and challenges of the STO space.
In order to become the primary blockchain used for STOs, it is critical for the team to provide for both the privacy of transactions and compliance requirements. Privacy of transactions is one of the key elements of regulated markets.
Consider the following example: Any large movements of Bitcoin from various whale wallets can cause huge spikes in Bitcoin volatility, either upwards if there is a large purchase, or downwards when there is a large sale. If Bitcoin were a regulated asset like a stock, the transparency of the blockchain and transactions would be not only discouraged by regulators but could also be considered as leading to market manipulation, a practice that is illegal in any regulated market.
 Benefits of Dusk Network. Image via Dusk Website
Benefits of Dusk Network. Image via Dusk WebsiteWhile the privacy of transactions is important in maintaining an orderly market, compliance is equally important in legal market trading. This means checks for traders such as KYC and AML, which combat money laundering, as well as restrictions on the country of residence, amount of assets being issued, whether assets can be fractional, and other details of a healthy asset market.
It’s important to know that as a layer 0 protocol the Dusk Network differs from other similar solutions such as PolyMath which acts like a for-profit middleman in the STO market, which need to charge fees and make money to be successful.
When you use those platforms you must also pay the fees, which can run into the hundreds of thousands of dollars for new STO campaigns. In contrast, the Dusk Network is a protocol which makes their security token standard open to all, just like the ERC-20 standard on Ethereum was open to all for use in their ICOs.
That makes Dusk free to use, which is a vast improvement for projects looking to launch an STO.
Dusk Network and Zero-Knowledge
The Dusk Network makes use of Zero-Knowledge cryptography as a means for validating a wide variety of network operations. This includes transactions, right to access a service, right to participate in blind bidding auctions and much more.
In addition, using zero-knowledge cryptography means users can participate without revealing their identity or any details of transactions while providing proof of correct computation in a trustless manner. All of these verifications are handled by browser nodes.
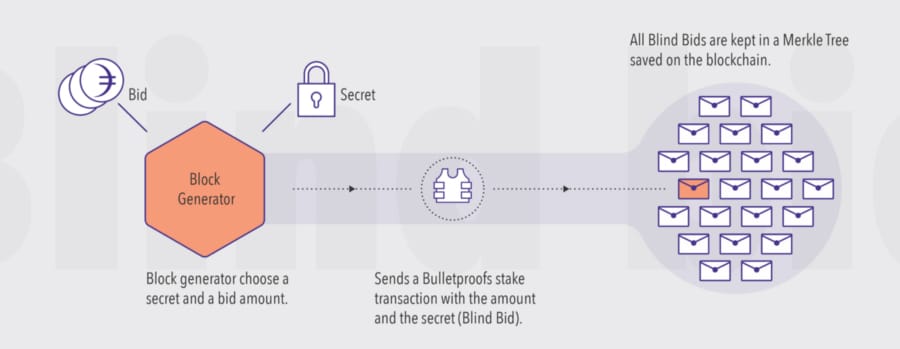 Blind Bind on the Dusk Network. Image via Blog.
Blind Bind on the Dusk Network. Image via Blog.These nodes compete with each other by staking an undisclosed amount of Dusk tokens to participate in the block selection process. This generates compliance to the process as it generates the zero-knowledge proof that transactions in the block have occurred.
The shifting of the workload of verifying (and eventually generating) zero-knowledge proofs allow the community to add computational power, thus leveraging game theory principles and bringing Dusk one step closer to becoming fully browser-based.
Privacy Features
Dusk uses a wide variety of technologies to maintain privacy in the network while also minimizing the potential for data breaches or transaction and account detection. The list of features used includes:
- Stealth Addresses;
- Ring Confidential Transaction Signatures;
- An Anonymous Network Layer;
- Non-Interactive Verifiable Secret Sharing;
- Cryptographically Committed Provisioners;
- A Segregated Byzantine Agreement (SBA) consensus algorithm.
All of which is incorporated into a low-latency gossip network using garlic routing and a non-repliable datagram to prevent occurrences of IP address propagation.
The entire network is secured with the Segregated Byzantine Agreement consensus protocol. The SBA protocol is a permission-less algorithm that includes statistical block finality.
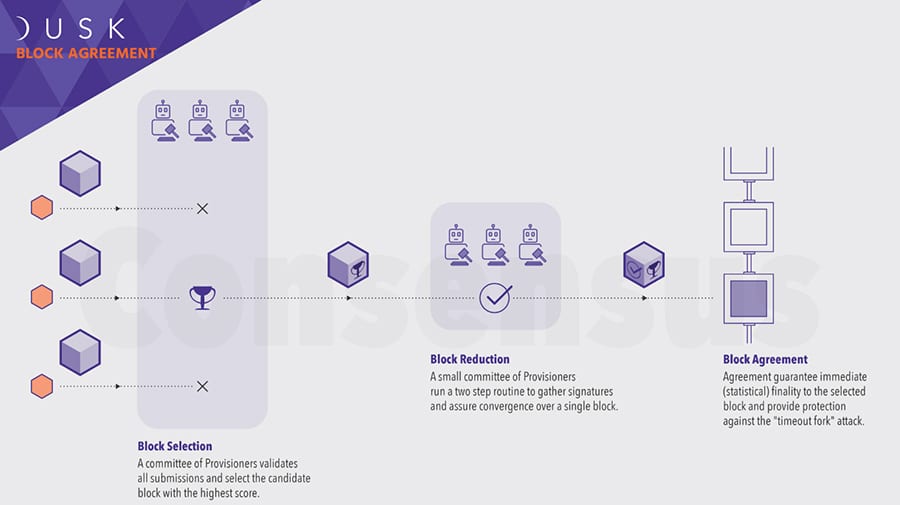 Overview of the Dusk Network Consensus
Overview of the Dusk Network ConsensusIt also includes the unique Proof of Stake consensus known as Proof of Blind Bid, which allows block generators to stake tokens anonymously. SBA compliments many of the ideas first introduced by the Byzantine Agreement consensus including the concept of stealth time-locked transactions to protect from Sybil attacks.
A further benefit of SBA is that it only allows the usual transactional nodes to compete for block generation. All of the network and computationally intensive tasks are relegated to non-transactional nodes called Provisioners.
This hardens the Dusk Network as it decreases the amount of network communication, decreases the probability of network partitioning and helps maintain the overall availability of the Dusk Network.
The Dusk Team
The Dusk team is comprised of a variety of technical and business experts, but the leadership of the team comes from the founders Emanuele Francioni and Fulvio Venturelli.
Emanuele Francioni serves as the project and tech lead for the Dusk Network. His background is in robotics and automation engineering, and he holds a Master of Engineering degree from Universita degli Studi di Roma Tre.
He is not only the founder of the Dusk Network, but also developed the Segregated Byzantine Agreement consensus mechanism. Prior to creating the Dusk Network he spent 15 years working in the tech industry. His last assignment was with TomTom where he was a Master Engineer. He is also heavily involved in the blockchain sector in general and holds the position of Executive Director at Web 3 Ventures.
 Some of the Dusk Team Members
Some of the Dusk Team MembersFulvio Ventureli is the lead researcher at Dusk Network and he holds a degree in IT Engineering from Sapienza Universita di Roma. He has more than 20 years experience in the IT field and has worked for international tech companies such as TomTom, Amazon, and Excite. Like his co-founder, Fulvio is also heavily involved in the blockchain space and holds the position of Executive Director at Web 3 Ventures.
Besides the technical team at the Dusk Network, there is also a business team, which is led by Jelle Pol, a third co-founder of the Dusk Network. He graduated from Rotterdam School of Management with a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration.
He went on to receive a Master of Science in Business Information Management and later a Technology MBA from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology. He has spent his entire career since 2015 working in the blockchain space.
In addition to the founders, there are 17 other team members, most of whom are either blockchain engineers, cryptographers, or other technology professionals. The team is also supported by a 9-member advisory board who bring extensive business experience to the project.
The DUSK Token
The DUSK token is an ERC-20 token that can be used for staking and consensus on the network, and will also be used to pay network fees, to deploy dApps and as gas.
It will also be used as a reward for consensus participants. It will be possible to trade DUSK for any of the XSC tokens in a one-way exchange or via atomic swaps, and it will also be used for on-chain governance within XSC. In Dusk Network, block rewards are paid through the emission of DUSK defined in the protocol.
The team held an ICO through Bitfinex back in November 2018, long before the Tokinex platform was launched by Bitfinex. It wasn’t a huge success, raising just $8 million versus a hardcap of $14.4 million.
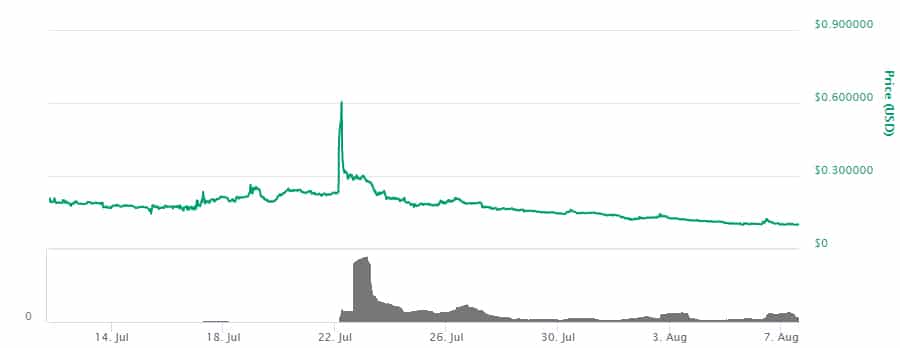 DUSK Token Performance. Image Via CMC
DUSK Token Performance. Image Via CMCHowever, investors may have been wise to buy more of the ICO token as the price of the DUSK token has gained roughly 75% in USD terms since the ICO.
Tokens were sold for $0.05760 during the ICO period, and as of August 7, 2019, are selling at $0.101 which is significantly lower than prices hit during July 2019.
Unfortunately, CoinMarketCap only has price data going back to July 11, 2019. Since then the price of DUSK tokens have been as low as $0.0.98772 on August 5 and as high as $0.674791 on July 22.
Buying & Storing DUSK
The DUSK token was recently listed on Binance, and that’s the exchange with the greatest trade volume as well. There are also small volumes at HotBit, Bittrex, and Ethfinex. Interestingly given that the ICO was held through Bitfinex, they do not currently list the token.
Given that Binance has over 90% of the volume for the token, it could great a risk from a "key exchange" perspective. If there was ever a situation in which trading on Binance were to cease, then the open market liquidity could drop with it.
 Register at Binance and Buy DUSK Tokens
Register at Binance and Buy DUSK TokensHaving said that, the turnover on Binance's books is much stronger than similar sized altcoins. This means that order book liquidity is quite strong and can hence absorb large block orders without too much slippage.
Currently, DUSK tokens can be stored in any ERC-20 compatible wallet. The mainnet is scheduled to launch in the fourth quarter of 2019, and a native DUSK wallet is expected to be available at that time, although there hasn’t been much in the way of details regarding the wallet from the Dusk team.
Dusk Development
One of the most important questions that I like to ask about a project is how much development work they have been pushing.
While progress on protocol design can sometimes be hard to quantify with a simple metric, there are a number of different "rules of thumb" that one can use to determine this.
One of the most direct ways is to look into their GitHub repositories and observe their coding activity. Below are the number of code commits to their two most active repositories.
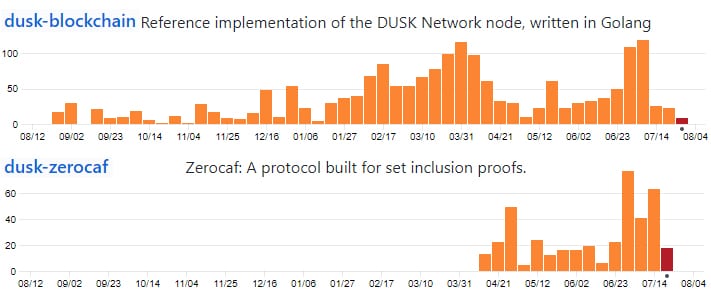 Code Commits to select Repos over 12 months
Code Commits to select Repos over 12 monthsAs you can see, there has been a pretty decent flow of commits to these repositories. There are also a further 10 other repos but these have much less commit flow. This is about the average level that I have observed on other projects.
Dusk Network Roadmap
While the code repos are a great way to determine the current state of the project, I always like to take a look at a project's roadmap.
Apart from giving us a sense of where a project is headed, they also allow us to determine whether they have been able to meet previous milestones that were laid out.
In the past few quarters, the project has rolled out both their private testnet and public testnet in rapid succession. These appear to have been pushed out in time and in accordance with their whitepaper.
Looking forward, below are some of the most interesting updates that we can expect from their updated roadmap:
- Q3 2019: Release of the Zero Knowledge Virtual Machine Architecture & the Deployment of Confidential Security Digitization.
- Q4 2019: Integration of the Zero Knowledge Virtual Machine. We can also expect the release of the GUI wallet, the regulator API as well as the eventual Mainnet launch.
- Q1 2020: If all goes according to plan then in early 2020 we can expect to see research on horizontal scaling and the implementation of the P2P ZK Channel.
There are also plans in the roadmap that will increase adoption of the network including dApp deployment, Security Trading integration and issuance of the XSC.
It will be interesting to see how the project progresses over the coming few months. If they are able to keep to their timelines then it could provide a positive boost for the project. If you want to keep up to date then you should keep an eye on their blog.
Conclusion
With so many different infrastructure projects coming into the blockchain space it’s fair to wonder what Dusk brings that’s unique and whether or not we need a Dusk Network.
One factor in favor of Dusk is that it’s the only protocol being created specifically to serve the security token market. Plus, the team seems to have put extensive thought into what’s needed for such a network to be successful, and they seem to understand the market. Plus the technology being developed for the project is very impressive.
In fact, the technology is so advanced it is quite hard to grasp. Have a look at the whitepaper and you’ll know what I mean. However, even as complex as the technology is, the Dusk team is good at explaining it in fairly simple terms.
And I believe it is positive that they are focusing pretty exclusively on security tokens before exploring other use cases. This could help them corner that part of the blockchain ecosystem.
That focus is a big deal because I see too many projects trying to tackle too many features at once. With any startup the more focused the team is I think the more success they can have from the start. And then they can build on those successes.
I think the Dusk Network has potential, but obviously, we have to wait until the launch of the mainnet to see how successful the team is in marketing this solution and launching STOs.



