Kava has been generating quite a bit of interest in the DeFi industry lately. There are many that think it could shake up the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem.
The project wants to create the world's first dedicated DeFi platform offering colleteralized debt and stablecoins for all the major crypto assets. Built on tendermint core and powered by Cosmos, the project is also coming hot off a successful Binance IEO in 2019.
However, is it really all that it is being chalked up to be?
In this Kava review I will attempt to answer that by giving you everything you need to know. I will also look at the long term use cases and adoption potential of the Kava token.
What is Kava?
The Kava platform is being called “DeFi for Crypto” as it is designed to offer using collateralized loans based on a variety of different cryptocurrencies.
It’s a cross-chain platform that offers a service similar to that of Maker DAO, but where Maker supports ETH and eventually ERC-20, Kava is capable of providing collateralized debt positions on any cryptocurrency theoretically.
The platform has already garnered the support of many major players within the crypto ecosystem, including projects like Cosmos and Ripple, and hedge funds such as Arrington Capital.
To provide its service Kava uses both a stablecoin (USDX) backed by crypto-asset collateral and a staking token (KAVA) used for voting and governance.
Kava works using Interledger to integrate diverse blockchain networks, which allows new users to access this group of diverse networks. Through Kava, a wallet user is able to send payments cross-chain and to complete seamless asset swaps right within the wallet.
 Some of the benefits of the Kava Platform
Some of the benefits of the Kava PlatformMoreover, exchanges can also use the Kava solution to allow users to retain control over their blockchain assets while transacting directly with the exchange’s order book.
It’s this application that Kava is best known for currently. Their cryptocurrency swap application called Switch allows for the nearly instantaneous swap of cryptocurrencies, even those based on different blockchains.
Kava is developing a stablecoin backed by Ripple, which will be used to power the collateralized debt positions (CDP) offered by Kava. Like Maker, the Kava platform will allow users to lock their cryptocurrencies into a CDP and receive USDX stablecoins in return.
Additionally, the Proof-of-Stake Kava blockchain has recently launched its mainnet. This blockchain is expected to include many different Cosmos based cryptocurrencies and is meant to improve the DeFi services available to users.
Kava is closely related to Cosmos since it is powered by the Tendermint consensus engine, the same as Cosmos.
Additional Crypto Support
The first hurdle being overcome by Kava is to extend the Cosmos DeFi to Ripple, but there has already been progress made towards supporting Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
That progress is in the form of the Interledger based Switch application mentioned earlier, which allows users to seamlessly and nearly instantaneously swap cryptocurrencies from different blockchains.
Of course, Kava is recognizable in its similarity to MakerDAO, with its Dai stablecoin and the use of collateralized debt positions to provide stability, governance, and leverage from a number of collateral sources.
 Benefits of Cosmos for the Kava platform
Benefits of Cosmos for the Kava platformKava has been built on Cosmos as a Proof-of-Stake blockchain that allows users to stake tokens and participate as validators in the network, providing governance for the network. It adds the USDX stablecoin, which is issued by the CDP and can be backed by any number of digital assets.
The Kava project has previously stated that one of their major goals is to provide DeFi benefits to assets that otherwise wouldn’t have been able to access DeFi.
Kava intends on extending DeFi capabilities through decentralized leverage and hedging. In order to realize this vision, they use the USDX stablecoin as the store of value that can be backed by many different assets.
The multi-chain framework used by Kava gives users access to liquidity from a large number of backing assets. The Kava platform sports a user-friendly interface, which makes accessing DeFi for a number of different assets far more trivial. The only concern among users is that there may be some trade-offs in ease of use versus security.
 Use Cases for the Kava Network. Image via Steemit
Use Cases for the Kava Network. Image via SteemitAs is true of most stablecoins, the success of Kava will in many ways be tied to its ability to maintain decentralization through a large array of validators, and its ability to attract enough liquidity to maintain the peg zone for USDX.
Kava has launched its mainnet and is expecting to launch the testnet for the CDP platform. They have already on-boarded over 100 validators for the network, which will help maintain the decentralization we referred to above.
CDP Platform Process
The primary product for Kava will be its CDP Platform, which is expected to launch on its testnet in the first quarter of 2020. This is where users will be able to collateralize crypto assets and receive USDX in return.
The CDP Platform works very similarly to MakerDAO but differs in that the Kava CDP Platform will allow users to collateralize many different assets, not just Ethereum.
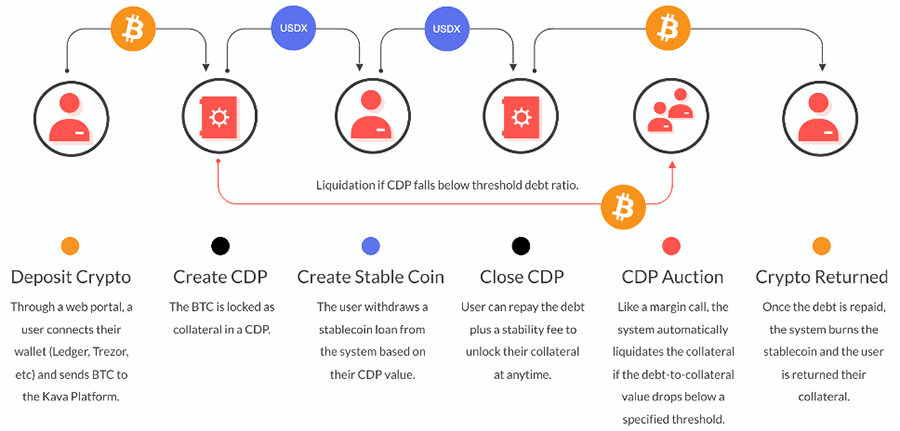 How the CDP Process Works at Kava
How the CDP Process Works at KavaThere are five steps in the CDP process, and a potential sixth step if the debt-to-collateral value drops below the specified threshold. These steps are as follows:
- The user deposits their cryptocurrency by sending it to the Kava Platform.
- The Kava Platform accepts the cryptocurrency and locks it in a smart contract as collateral.
- The smart contract issues the USDX stablecoin to the user as a loan based on the value of the deposited cryptocurrency.
- The user is able to repay the debt, plus a stability fee, at any time, unlocking their collateral and having it returned to them.
- When the collateral is returned the system automatically burns the USDX stablecoins.
- The sixth step is optional and only occurs if the debt-to-collateral ratio falls below a pre-set threshold. If this occurs the system will automatically liquidate the collateral to repay the loan.
Now that you have a good idea of how the Kava platform works, let's take a look at the team behind the project.
The KAVA Team
The Kava team has been working on the platform since 2017, and while it has undergone changes in that time, some of the original members remain as leadership for the project.
The CEO of Kava, and one of its co-founders, is Brian Kerr. After graduating from San Francisco State University with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration he went on to found Fnatic Gear, the first company making Esports hardware and apparel designed by Esports players for Esports Fans.
 Kava Team, From Left: Brian Kerr (CEO), Scott Stuart (Product Manager) & Ruaridh O'Donnel.
Kava Team, From Left: Brian Kerr (CEO), Scott Stuart (Product Manager) & Ruaridh O'Donnel.In addition to his role at Kava, he is also an advisor for DMarket.io, a blockchain-based decentralized digital asset marketplace, and Snowball, the world's first smart crypto investment automation platform.
The blockchain development lead, and a second co-founder of Kava, is Ruaridh O’Donnell. After receiving a Master’s Degree in Physics from the University of Glasgow in 2015 he spent time as an engineer and data analyst for Levelworks before helping to found Kava.
The team is quite open with their community so if you wanted to get more information about the project then you could always jump into the Kava Labs telegram group. If you wanted more general updates from the team then they also have an official Twitter.
The KAVA Token
The KAVA token is the native token behind the network. There will be a total supply of 100 million KAVA that will be minted with the genesis block. There are a two main use cases for the KAVA token and those are for governance and staking / validation.
In terms of governance, KAVA works about the same as the MKR token in the Maker Dao Ecosystem. KAVA holders can vote on proposals to change the blockchain or the system parameters. These include parameters such as the total amount of USDX, accepted collateral types, collateral to debt ratios etc.
Given that KAVA uses the tendermint consensus mechanism, it is a staking blockchain. This means that users can delegate their voting rights to validators who will secure the network. In exchange for this, they will earn fees from the transactions as well as stability fees paid by users when closing the CDPs.
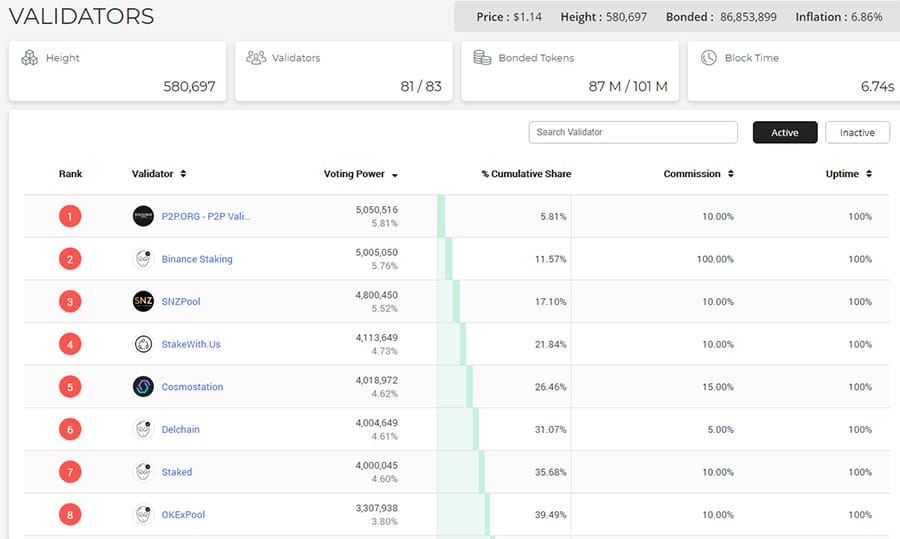 Validators on the Kava Platform. Image via Mintscan
Validators on the Kava Platform. Image via MintscanThe amount of staking returns that a user can earn will really depend on the amount of KAVA that has been staked. If the staked amount is low the APR for a KAVA validator will rise to a maximum of 20%. Conversely, if there are a lot of users who are staking then rewards will drop to a minimum of 3%.
Key point to note here as well is that those who are running the validator nodes may charge an additional commission for their services. So, this is an additional cost that you need to consider when looking around for a validator.
Perhaps your best bet for validating is using that staking pool setup by the Binance Exchange. Currently this pool is offering about 14% - 16% annual yield for those who are staking on it. Given that they are stored at Binance, it is generally more secure than most of the other alternatives.
Binance IEO & Token Trading
Most recently Kava conducted an Initial Exchange Offering on Binance, and it was fairly successful. Better than other recent Binance IEOs, but nowhere near the performance of the first Binance IEOs.
One possible reason for the early returns – KAVA coins were up 180% within days of release – was the wave of shilling on Twitter and other social media platforms. It was almost like warping back to 2017, with tons of anonymous users spreading hype and FOMO about the newest Binance IEO.
The IEO was held on October 23 and 24, and the pricing for KAVA tokens was $0.46. The project was able to sell 6.52 million KAVA tokens, raising $3 million. That’s just 6.52% of the total supply of 100 million KAVA.
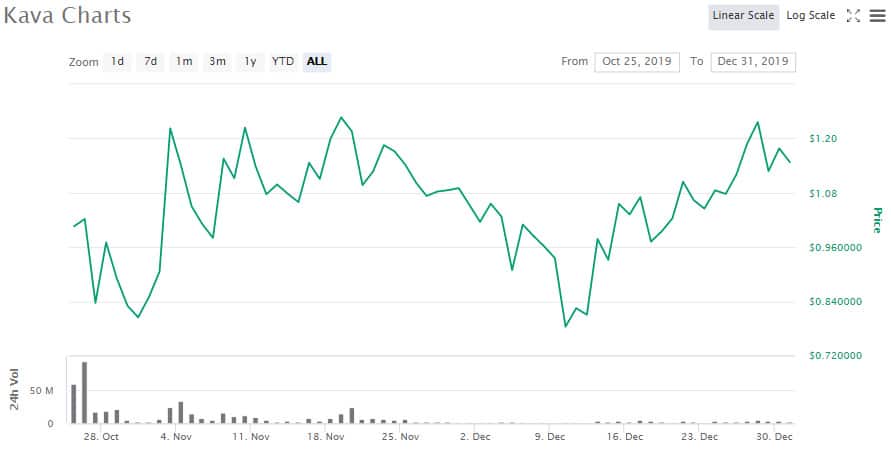 KAVA Token Price Performance. Image via CMC
KAVA Token Price Performance. Image via CMCThe coin shot up following the IEO, giving the early investors a return of roughly 250% in just 24 hours. After immediately falling off those highs the coin spent the next three weeks trading higher in choppy trade, eventually reaching an all-time high of $1.29 on November 19, 2019.
After dropping back to $0.80 by December 10, 2019, the coin has since rallied again and as of December 30, 2019, it is trading back at $1.16, for a 250% return. While that might not be as good as the early IEOs hosted on Binance, it is better than the most recent token sales and is certainly nothing to complain about.
It is notable that the coin has not only held its value but also held early gains. That indicates the project is at least perceived to have real value.
KAVA Exchanges & Storage
When it comes to exchange listings, KAVA only really does any sizable volume on two exchanges. These are Binance and Bilaxy. On Binance you can trade it against Bitcoin, Binance Coin and USDT whereas on Bilaxy you can only trade it against Tether.
This is not really the best picture for general market liquidity. With 50% of the trading volume split evenly between these two exchanges it means that if ever token trading were to cease on one, KAVA liquidity could collapse.
 Register at Binance and Buy KAVA Tokens
Register at Binance and Buy KAVA TokensIt also makes it harder for general price discovery to take its course. With less exchanges to arbitrage out mispricings, it means that the price of KAVA could deviate from a "true" value with relative ease.
When it comes to wallet support, the Kava team is working on a Trust Wallet integration which is not released yet. However, given that KAVA is built on Cosmos, you can use most of the wallets that support ATOM.
These include the likes of Lunie and Cosmostation with both allowing you to delegate your KAVA and earn the staking returns. We have actually completed a list of the best Cosmos ATOM wallets which you can also take a peak into.
Development & Roadmap
One of the best ways to determine the development progress of a project is to look into their open source repositories. By observing coding activity, you can get a nice benchmark.
Hence, I decided to dig into the Kava Labs GitHub and observe their total activity. Below are the total commits to the top 3 most active repos over the past 12 months.
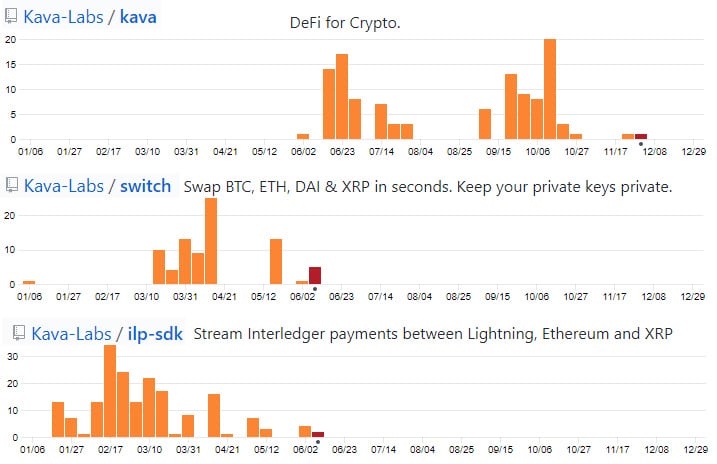 Total Commits to Select Repos over past Year
Total Commits to Select Repos over past YearAs you can see there has been quite a bit of development although this has been on the rather light side. This is also surprising for a project that has just launched their mainnet.
Perhaps there is still some work that is taking place in private repositories that is yet to be pushed. Indeed, this blog post seems to list a number of important development milestones that have been reached.
When it comes to the roadmap, the next most important thing to look forward to is the launch of the CDP Testnet in the first few weeks of January. For the rest of the year, these are what is planned:
- Q2: Cross-chain assets in CDP system on mainnet
- Q2: Integrate custodial BTC Peg into CDP system testnet
- Q3: Integrate both custodial and non-custodial BTC Peg into CDP system mainnet
It will be interesting to see if they can meet these milestones. All eyes will be on the CDP testnet in the beginning of the year. If you want to keep up to date with the developments then you can follow their official blog.
Conclusion
Kava is an interesting DeFi project, but I’m not certain we need another project similar to MakerDAO. On the other hand, it is good to have access to a collateralized debt position platform that will be able to utilize any crypto asset.
During my research for this piece, it did seem to me that details regarding the project, its founders, and its advisors, was scant at best. The website has little information and the white paper is little better. The project claims to have been in existence since 2017, but there is almost nothing on them prior to the announcement of the Binance IEO.
On a positive note for investors in the KAVA coin, the return has been good until now, and the coin is holding its value.
Until the launch of the CDP Platform in the first quarter of 2020 I will remain somewhat skeptical of the project. Even after that, I would really like to get my hands on more details regarding the project and the team behind the project. Until then there are just too many blank spaces for my liking.



