In a world where money is power, those that wield it often hold the monopoly over policies and rules of finance in society. For centuries, this has been within the grasp of state bodies and a few powerful private individuals and corporations that can influence this money flow.
Well, that was until Decentralised Finance (DeFi) moved into the financial neighbourhood. DeFi, which was fathered by ‘Cryptocurrency’ (another OG bad boy in the financial district), wrested the power to create and govern financial instruments and policies away from centralised intermediaries and state bodies and delivered it unto the hands of an almost truly global decentralised market run by a serendipitous collaboration of global participants.
DeFi is emerging as one of the most desirable go-to solutions that offers services such as lending and borrowing to yield farming, from high APY staking protocols to margin trading for individuals globally. The visible growth of DeFi can be seen in the rise of the Total Value Locked (TVL) in Defi from a ‘mere’ $600 million at the beginning of 2020 to almost $250 billion at the beginning of 2022.
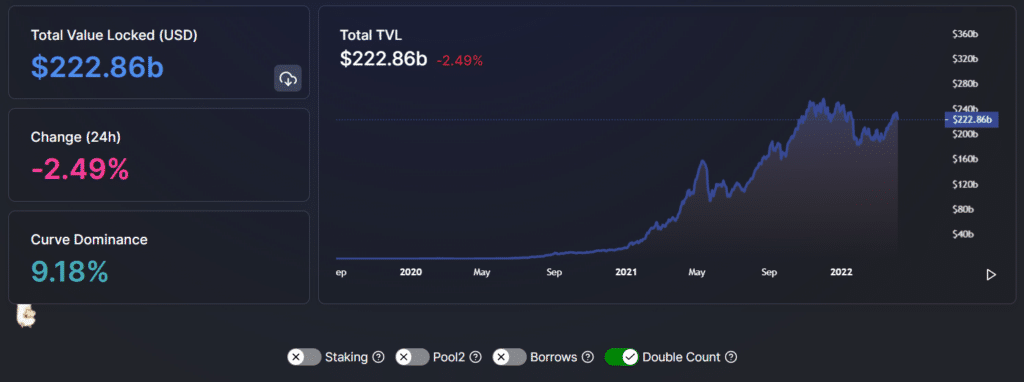 Growth of Defi TVL from 2020 to 2022 via Defi Llama
Growth of Defi TVL from 2020 to 2022 via Defi Llama
While most of the TVL is concentrated in the Ethereum ecosystem, there has been a gradual shift of TVL to other chains such as Terra, BSC, Avalanche, Solana, Fantom, and more over the past year. To truly be on the cusp of identifying and predicting long-term blockchain ecosystems in a multichain world, it is pertinent to keep an eye on market leaders in newer blockchains and ecosystems.
A couple of weeks ago, on March 19th, Solana’s Serum DEX briefly overtook BSC’s Pancakeswap in daily trading volume. Most of this trading volume can be attributed to two DEXs leveraging Serum on the Solana blockchain- Atrix and Mango Markets.
In this article, we will explore one of these DEXs- Mango Markets. This decentralized derivatives exchange offers margin and perpetual trading for its users. We will be exploring the products Mango Markets offers along with its innovative DeFi governance and cutting-edge trading features that rival the ones provided by centralized exchanges.
What is ‘Mango Markets’
Mango Markets is a decentralized derivatives exchange built on the Solana blockchain. Its user-friendly interface allows users to lend, borrow, swap, and leverage trade crypto assets. Mango Markets allows assets deposited on the platform to be cross-collateralized, which means that assets can be shared as collateral between borrow/lending and leverage trading. These assets will automatically earn interest and serve as available collateral to leverage trade or withdraw a borrow.

Mango wants to combine CeFi's liquidity and usability with DeFi's permissionless innovation at a lower cost to the end-user than both presently offer. Mango achieves this by providing users with an on-chain limit order book style trading system on its interface. Presently, this is a rare feature among DeFi platforms as most of them use a constant product AMM swap feature to enable decentralized trading.
Moreover, since Mango is built on the Solana blockchain, it can utilize the shared order book of the Serum DEX for spot margin trading, while perpetual futures are traded on Mango's own order book. Mango Markets also has its own governance token called MNGO, which allows its holders to vote for decisions within the Mango DAO.
At the time of writing, according to DeFi Llama, 'Mango Markets' occupies the 13th place in overall TVL within the Solana ecosystem, with over $175 million in assets locked on its platform.
Pros and Cons
Pros
- The cross-margin feature allows for more capital efficiency
- Completely decentralized – no KYC requirements.
- Built on Solana- Low latency and transaction cost
- Mango users unlock the highest level of savings on Serum DEX trading fees due to its aggregate deposits of MSRM.
- Email alerts and Risk Calculator Features are available
- Account Delegation enabled.
- Downloadable trade history in csv format for tax filings
Cons
- A low number of trading pairs supported
- Deposit interest rates aren't incredibly competitive
- Less beginner-friendly than centralized exchanges
Team & History
Mango Markets is currently managed by the Mango DAO and is the brainchild of Dafydd Durairaj and Maximilian Schneider.
 Dafydd presenting at the Pyth workshop in Chicago via Twitter
Dafydd presenting at the Pyth workshop in Chicago via Twitter
Dafydd Durairaj is a seasoned developer with a long history of building algorithmic trading and market maker solutions for financial markets. Dafydd was initially inspired to create an on-chain derivatives exchange after coming across dYdX in 2019.
However, he held back on creating a project because he felt that Ethereum was just too slow and expensive to guarantee the best user experience for on-chain derivatives and margin trading at the time.
This changed in 2020 when Dafydd came across the Serum Dex built on Solana. He finally felt that the right opportunity to create an on-chain derivatives exchange that provided users with the best experience and low latency had arrived.
He initially named the project ‘Leverum’, a name choice that was indicative of its product- leverage trading on Serum. Dafydd then created and published a video showcasing ‘Leverum’, hoping that it would catch the attention of Sam Bankman-Fried (SBF).
While the video may or may not have caught the attention of SBF, it did catch the attention of someone else who would become instrumental in the creation of Mango Markets as we know it today- Maximilian Schneider.
 Interview of Dafydd and Maximilian with Project Serum Podcast via Youtube
Interview of Dafydd and Maximilian with Project Serum Podcast via Youtube
Maximilian, a software engineer and the co-founder of Mango Markets, describes himself as a serial entrepreneur who was pulled into the world of crypto during the DeFi summer of 2020. Maximilian, intrigued by the video and concept, approached Dafydd to discuss the project in greater detail.
Through their discussions and mutual love for building leverage trading products, the duo realized they could create an even better protocol if they began working together on the project. They then decided to rebrand the project to ‘Mango Markets’, staying true to the theme of ‘food-based’ Defi protocols in the space.
AMM vs Order Book
Before we begin looking at Mango Markets, let us understand the different market-making mechanisms. Specifically, there have been two predominant market-making mechanisms employed by different crypto exchanges (CeFi and DeFi) over the years- AMM and the Order Book method. So let’s take a look at how they work and their differences.
 AMM vs Order Books via Medium
AMM vs Order Books via Medium
AMM
AMM stands for Automated Market Maker. This mechanism is commonly employed by decentralized exchanges to facilitate swaps of token pairs.
It was first born in the paper “Improving Front Running Resistance of X *y = K Market Makers”, written by Ethereum’s co-founder Vitalik, and has become increasingly popular with several DeFi projects. For example, projects like Uniswap, Sushiswap, Pancakeswap, etc., use an AMM mechanism.
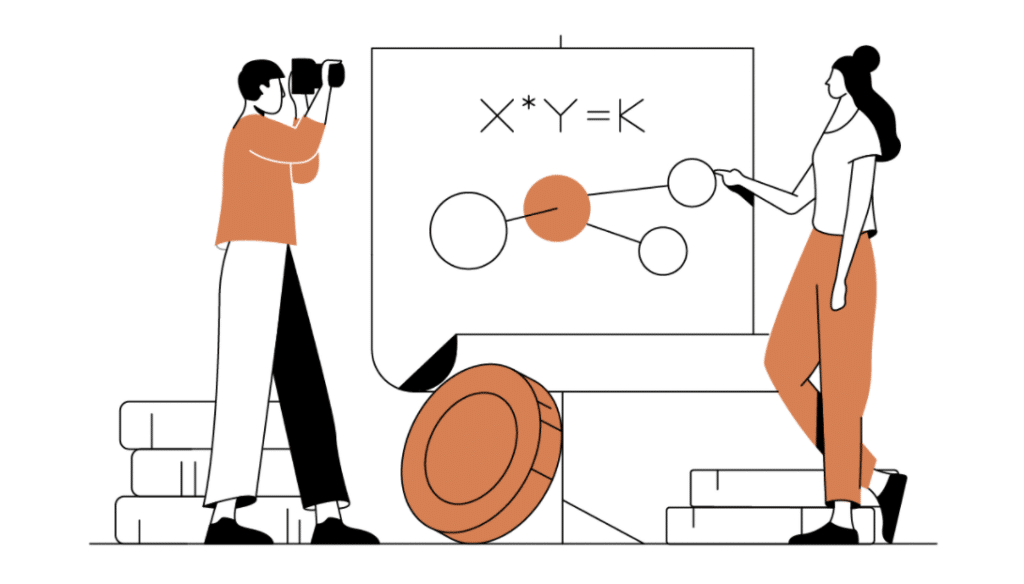 Constant Product AMM via Chaindebrief
Constant Product AMM via Chaindebrief
The value of assets in AMMs are determined using the simple mathematical formula of x*y = k. Then, these assets are arranged into liquidity pools, which are rebalanced as users trade to add or take liquidity from one side of the pool.
Order Books
The order book mechanism is usually seen on centralized crypto exchanges such as Binance, FTX, Kucoin, etc.
Order book exchanges allow users to set buy/sell orders at specific prices instead of the market price. This offers users the ability to pre-set trades at specific price points, creating a stress-free trading experience.
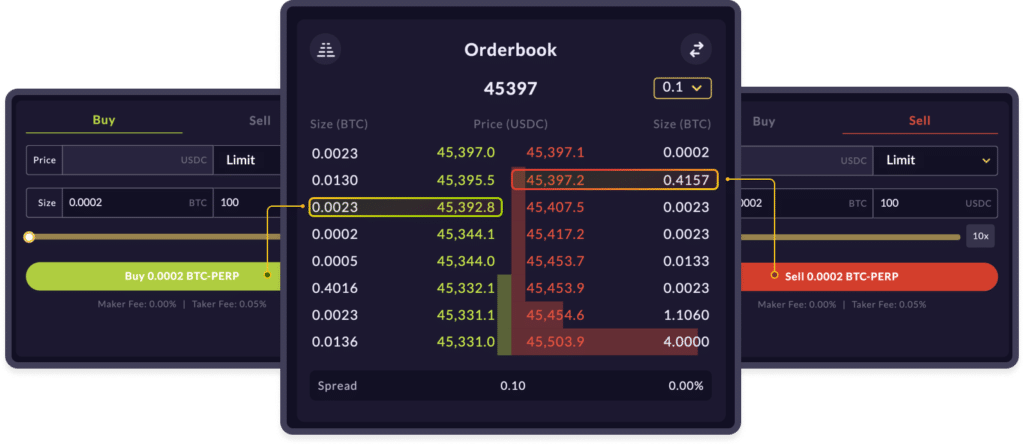 Order Book via Mango Markets
Order Book via Mango Markets
In exchanges using order books, the user interface displays all the pending buy/sell orders for a particular asset placed by platform users. These orders are typically matched by the centralized exchange hosting them, for which the exchange takes a fee. In decentralized exchanges using an order book, this order matching function is typically carried out by a smart contract on the platform.
Differences
While there are a slew of differences between these mechanisms, it would be inappropriate to assert that this makes one better than the other. Both mechanisms have their own place in the broader DeFi ecosystem. Each tends to suit the needs of a specific type of trading over the other.
Having said that, let us look at the differences between the two mechanisms.
Trade Placement- Order Books allow their users to place limit orders. This means the user can choose to define the price they would like to buy or sell their assets. The control rests with the trader.
AMMs, on the other hand, generally do not provide the user with the ability to place limit orders; rather, the trader has to be careful with the time at which he places his swap order. As a result, the trader does not have the same degree of control over the price the order executes relative to an order book exchange.
Trade Execution- When a limit order is placed on the order book, the user can expect the order to execute at that same price. However, this also means that certain orders can remain unfilled for a long time if the intended price target is not achieved.
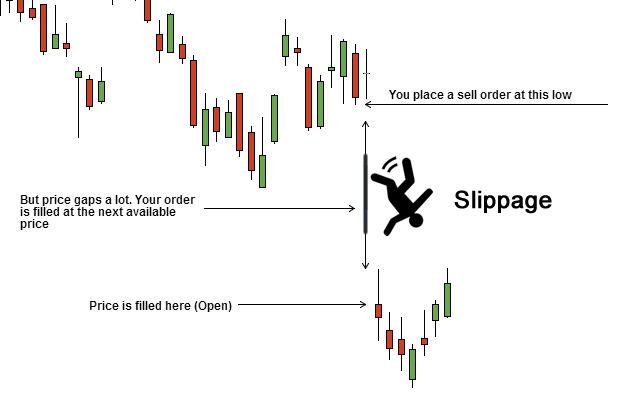
Slippage via Chaindebrief
AMMs offer the user instant liquidity; however, this comes with a cost- ‘slippage’. Slippage is the difference between the price at which you initiate the swap transaction versus the price at which it actually does.
This means that you could end up with a higher or lower number of tokens than you wished to purchase. This is especially true for relatively large orders compared to the pool size.
Participation- Order book exchanges limit the participation of their users to only trading assets. However, AMMs offer their users the additional opportunity to provide liquidity to their trading pools and earn a cut of the trading fees charged by the platform for doing so.
Risks- AMMs suffer from two significant risks- failed transactions and impermanent loss. AMM transactions can fail due to a variety of reasons, but the most common cause is exceeding the slippage tolerance. Impermanent loss is a risk that is faced by liquidity providers in AMMs. It refers to the relative loss of funds because of volatility in a trading pair.
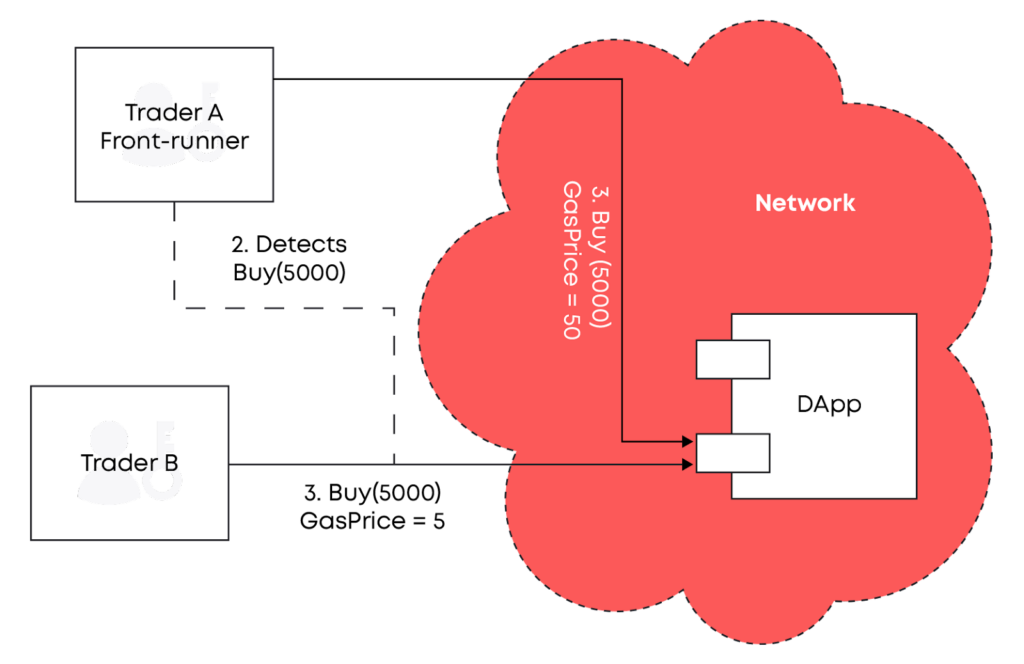
Front Running via Blaize
Order book exchanges face the risk of unfilled limit orders. Users typically have to pay a gas fee when cancelling their limit order in on-chain order books. This can get quite expensive on certain blockchains.
Both mechanisms also suffer from one common risk- ‘front running’. ‘Front running’ occurs when certain parties (usually miners) who have access to information on pending transactions place an order that would earn them a profit based on a pending trade.
Is it safe?
You can find the official audit reports from the Mango Protocol documentation.
The Mango program also has a $70m DAO controlled treasury for insurance on v3 deposits. When there are bankrupt accounts, the insurance fund will pay off losses incurred by token lenders or perps contract participants.
Getting Started
To use the full range of features on Mango Markets, users will need two things-
- A Solana-based wallet like Solflare, Phantom, etc. and,
- A Mango Account
To get started using Mango Markets, users will first need to connect their Solana-based wallet and then create a Mango Account on the platform to deposit funds.
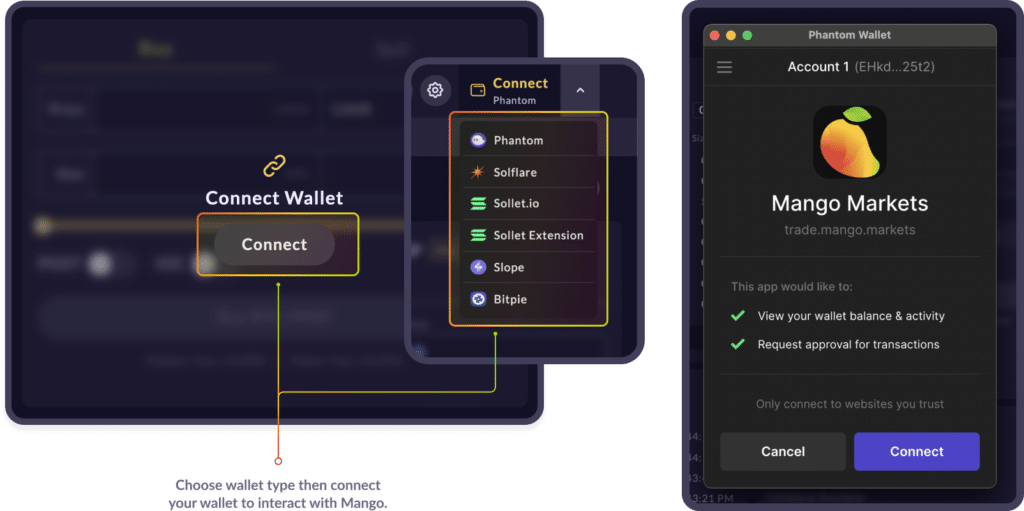 Connecting Solana Wallet via Mango Markets
Connecting Solana Wallet via Mango Markets
To create a Mango account, users will need to click on the deposit button and pay a small fee of 0.035 SOL (~roughly $4 at today's price). The funds deposited within the Mango account are considered "collateral", meaning users can margin trade and borrow funds depending upon the value of the assets deposited in the account.
Moreover, the funds within the account are cross-collateralized, which means that assets can be shared as collateral between borrowing/lending and leverage trading. These assets will automatically earn interest and serve as available collateral to leverage trade or withdraw a borrow.
Products
Now that we've understood how to get started using the platform let us look at Mango's products.
Mango primarily offers four products:
- Spot Margin
- Perpetual Futures
- Lending and Borrowing
- Swap
Spot Margin
What is Spot Margin trading?
Margin trading essentially involves borrowing money to make bigger bets on the price movement of a specific crypto asset or asset pair, such as SOL-USD, for instance.
 Spot Margin Interface via Mango Markets
Spot Margin Interface via Mango Markets
Crypto traders can borrow funds and bet on the price of a crypto asset moving in a specific direction, either up or down (also known as a long or short position, respectively). They can execute their trades on an exchange’s spot market with or without margin.
The amount a user can borrow usually depends on the collateral deposited and the leverage the particular exchange allows its users to take. Leverage is generally expressed as a multiplier on the deposited collateral.
How is Spot Margin trading on Mango Markets?
The Spot margin trading on Mango Markets is facilitated through the order book mechanism via Serum DEX, and users can take up to 10x leverage. This feature allows users to take a long or short position in the spot market by borrowing assets based on the collateral held in the account. Assets on Spot Margin have different maximum and maintenance leverage specifications.
For example, if a user holds $100 worth of SOL in their account, the platform will allow him to borrow and trade assets worth up to $1000 (around 10x).
 Double check your spot order- Margin box
Double check your spot order- Margin box
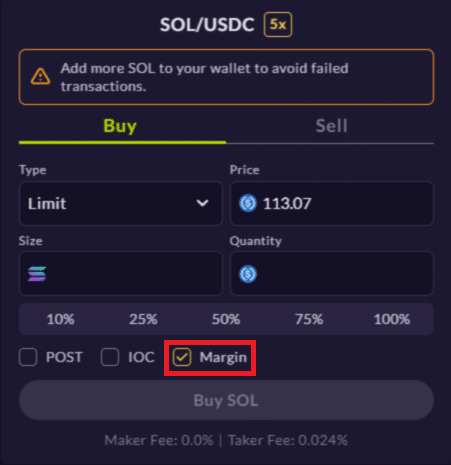
On Mango, the margin option is enabled by default; therefore, funds are automatically borrowed for leverage trading.
If you would like to place a margin/leverage trade, simply place an order for your desired amount. If the required capital is beyond your deposits, funds will be borrowed for the position (as long as account health is eligible).
Conversely, if you do not want to take margin trade, uncheck the margin box before you place your spot order.
Types of Orders in Spot Margin on Mango Markets
Market Order- These orders are executed immediately at either the highest bid price for sell orders or the lowest ask price for buy orders.
Limit Order- Limit orders allow users to specify the price at which the order must execute.
Immediate or Cancelled (IOC) Order- If an order is placed and not filled within seconds, it's cancelled. This allows users to save on gas by removing the need for manual cancellation if their limit order is not executed. IOC orders will always be the 'taker'.
POST Order- These limit orders are added to the order book and earn maker fees if filled. POST orders will always be the 'maker'.
Is Margin Trading risky?
All forms of leverage trading are risky. Since you borrow funds in a margin trade, not only are your profits multiplied but so are your losses.
 Account Health via Mango Markets
Account Health via Mango Markets
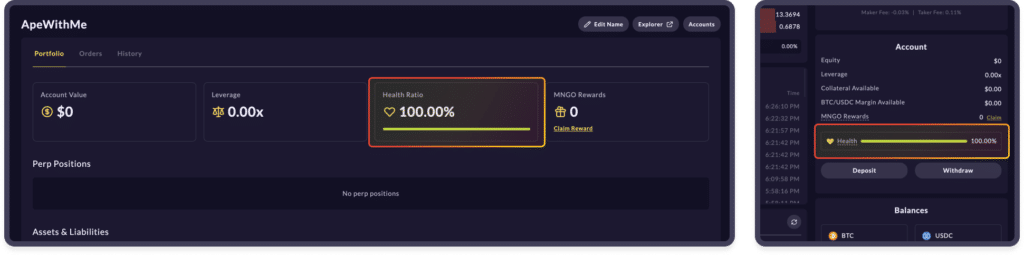
This means that if you're not mindful of your' account health', you can trigger a 'liquidation' event. Account health represents the likelihood of liquidation risk for an account. It is also used to determine if a user is eligible for a new margin position.
Every Mango account must maintain an account health above 'zero'. A 'liquidation event' occurs when the user's deposited collateral can no longer sustain the position's risk. Open positions are closed until the account health rises back above zero. Sometimes, in extremely leveraged accounts, the entire collateral deposited by the user can be wiped out.
Perpetual Futures
What are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual Futures are synthetic trading markets that use stablecoins as collateral to allow investors exposure to liquid assets. By trading perpetuals, users can participate in market movements, reduce risk, and profit by longing and/or shorting with leverage on a futures contract. A futures contract is a financial derivative contract, which means that its value is derived from the underlying asset's performance.
Unlike standard futures contracts, a perpetual futures contract has no expiration date. This avoids the need to re-establish a long or short position regularly. As a result, perpetual contracts' pricing must be tied to the spot prices of their underlying assets.
This price anchoring of perpetual futures is achieved through a 'funding rate' mechanism. This mechanism balances perpetual swaps' short and long positions by rewarding or discouraging trades. Consider it a rebate or tax that balances the demand for perpetual contracts on both the short and long sides.
How is Perpetual Future trading on Mango Markets?
Mango Markets offers perpetual futures built on the Mango protocol through its order book. Similar to spot margin trading, users are allowed to take leverage on their collateral to execute perpetual future trades.
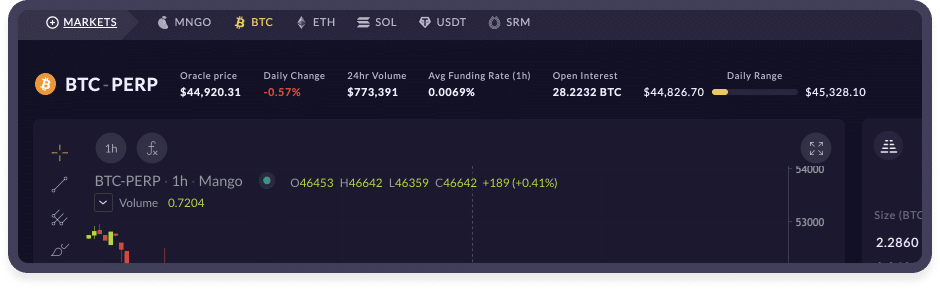 Perpetual Futures via Mango Markets
Perpetual Futures via Mango Markets
Perpetuals on Mango allow initial leverage of up to 10x and maintenance leverage of 20x. If the value of your position (or collateral) falls and your leverage exceeds 20x, your account will be eligible for liquidation. Assets on Perpetual Futures have different maximum and maintenance leverage specifications.
Mango’s funding rate mechanism is computed continuously as a daily difference in the index price and current book price (current midpoint of the bids & offers). When the future market is trading above the oracle price, longs will have to pay shorts. When below the oracle price, shorts will pay longs. This rate is continually calculated and paid roughly every 5 seconds and is shown above the market as an hourly rate.
While there have been many trading strategies employed in DeFi, certain traders have taken advantage of positive funding rates to generate yield by maintaining a delta neutral position through longing an asset on spot and shorting the asset on perps.
Types of Orders in Perpetual Futures on Mango Markets
In addition to the market order, limit order, IOC and POST order types that we’ve already seen in Mango’s Spot Margin feature, perpetual futures offer six more order types:
 Stop Loss Stay Comfy via Twitter
Stop Loss Stay Comfy via Twitter
Stop Loss Order- If the price falls below a specified level, this order will initiate a market order. The 'Trigger Price' box is where you set the price threshold. You might use a stop-loss order to exit a position to mitigate downside risk if the price falls 20% below the entering price.
Stop Limit Order- A stop-limit order is similar to a stop loss, except it is triggered at a specific price target rather than a market price. The limit order's price is set in the 'Price' box.
Take Profit Order- If the price rises above a certain level, a take profit order will trigger a market order. This can profitably close a portion or all of a position.
Take Profit Limit Order- This order works similarly to a 'take profit order', but a limit order is placed with a specified price instead of a market order.
Reduce Only Order- This ensures that an order will only be executed to reduce or close a position and never increase or open a new position. Check the Reduce Only box above the buy/sell button to apply.
Slide Order- This is a limit order that will set your price one tick more or less than the opposite side of the book.
Is perpetual future trading risky?
Perpetual Futures carry the same risks as Spot Margin trades. Additionally, traders using perpetual futures must also be mindful of their position's funding rate.
However, Mango Markets offers various features such as 'email health alerts' and 'risk calculators' that help the user stay informed of the possible risk of liquidation at any point in time.
Mango can automatically email users if their account health drops below a specified threshold. This is the best way to profit from 20x leverage and still enjoy a day at the beach without stress. The feature is available on the accounts page.
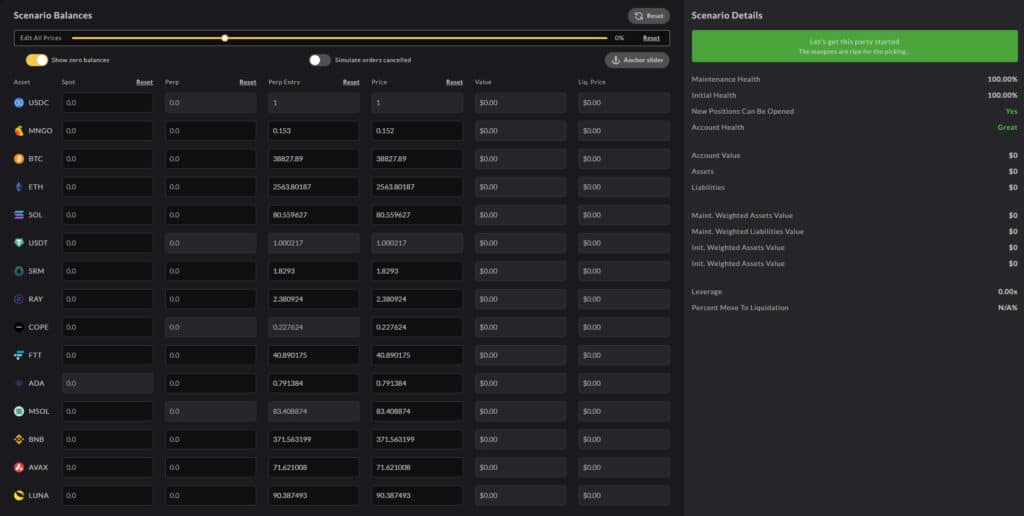 Mango Risk Calculator- Quick Tools (Top Left), Scenario Input (Bottom Left), and Scenario Details (Right) via Mango Markets
Mango Risk Calculator- Quick Tools (Top Left), Scenario Input (Bottom Left), and Scenario Details (Right) via Mango Markets
Traders can use the ‘Risk Calculator’ available on the Mango website to predict and estimate the various scenarios. The calculator allows users to input different future prices and simulate cancelled orders.
Lending and Borrowing
Remember the funds we deposited in the Mango account we created at the beginning of this article? Guess what? They automatically start earning interest as soon as they are deposited!
Mango’s cross-margin model allows its users to avail the benefits of its lending and borrowing program with the same assets used as collateral. This allows the funds to be freely used without any lock-up period.
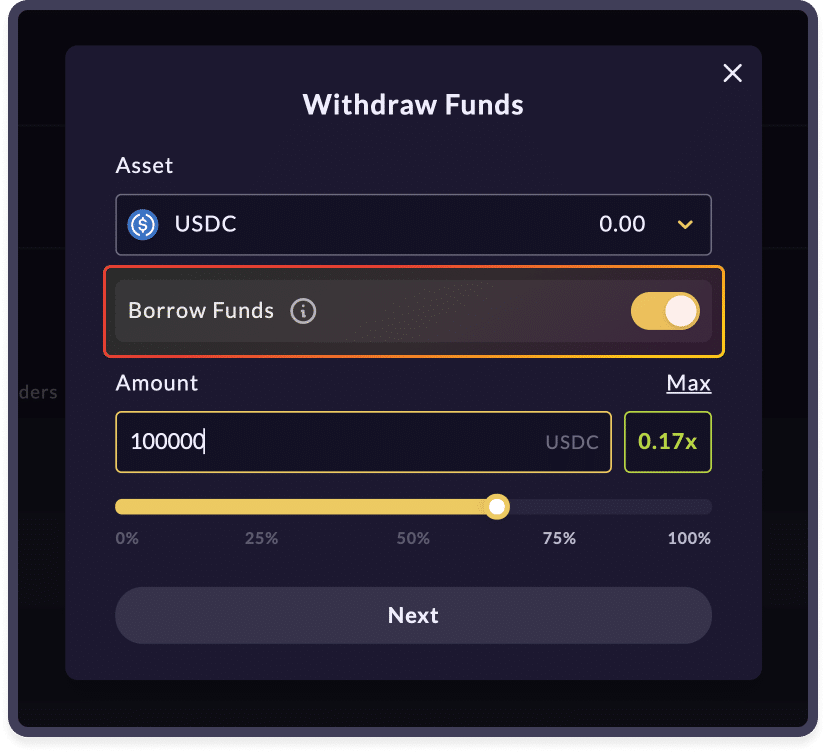 Borrow funds via Mango Markets
Borrow funds via Mango Markets
Users can deposit assets on the account and borrow against them instead of selling them. To do that, you need to simply click 'Withdraw' under the Account tab or "Borrow" under the Borrow tab.
Once that's done, the UI will prompt you to select the asset you wish to withdraw and borrow and toggle 'Borrow Funds' on. Once you select the amount you want to borrow, click next. The final transaction page will highlight the account risk and leverage taken.
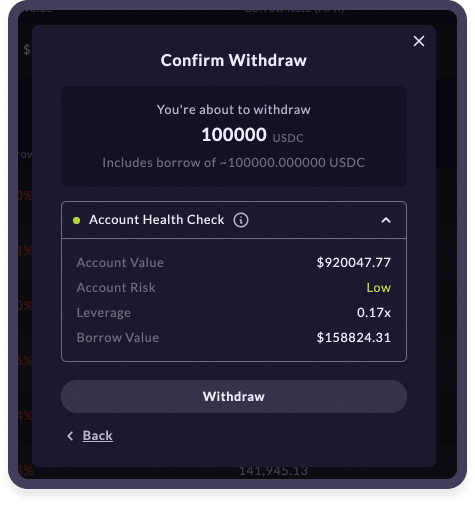 Borrowing Transaction Confirmation
Borrowing Transaction Confirmation
Be careful not to take on too much leverage as interest is continuously paid on your ‘borrows’ from your deposits. Make sure to monitor interest rates as they recalculate based on pool utilisation.
Once you’re satisfied, click confirm. Congrats, you’ve successfully borrowed funds on Mango.
Swaps
For AMM users, Mango offers a familiar feature called ‘Swaps’, which allows users to swap for any Solana asset. However, unlike native liquidity pools in AMMs, Mango’s swap feature is integrated with the Jupiter Aggregator- the key liquidity aggregator for Solana.
 Swap Feature via Twitter
Swap Feature via Twitter
The Jupiter Aggregator Integration allows Mango’s swap feature to compare pricing and routes across all Solana dApps, ensuring you receive the best deal possible. These transactions occur in your linked wallet and are unrelated to your Mango account.
Account Delegation
‘Account Delegation’ is a star feature of Mango Markets. This feature allows users to delegate ‘trading’ control of their ‘Mango accounts’ to different wallet addresses. To prevent the theft of funds, the control is purposefully limited to the ‘trading’ of assets. Delegates cannot withdraw funds from the original owner’s mango account.
However, this does not prevent the delegate from liquidating your account or draining your capital via malicious trading, so only use this feature with trusted entities. A Mango Account can have at most one delegate. The owner of the Mango Account continues to have complete control of the Mango Account irrespective of delegation.
 Let that 'expert' trader, trade on your behalf. Image via Pinterest
Let that 'expert' trader, trade on your behalf. Image via Pinterest
Some of the best use cases of this feature are:
- Individuals may fund an account and delegate access to a friend that is an expert investor. The friend can make trades on their behalf.
- Users can set up full access on a hardware wallet (e.g., Ledger) while delegating access to a hot wallet (e.g., Phantom). This makes trade execution easier and ensures safe custody of the deposited capital. The same strategy could be applied to a core wallet and mobile wallet pair, so trading remotely is possible without sacrificing security.
- DAOs or other entities can deposit funds into an account and choose individuals to allocate those funds on their behalf. Mango recently used this feature to purchase mSOL for the treasury.
Fees
Margin trading- By pooling SRM in Mango, Mango traders save a lot of money on Serum DEX trading fees. The tier structure of Serum establishes price rates based on the amount of SRM in an account; the more SRM in an account, the fewer fees you pay and the more money you receive as a manufacturer. The highest tier is 1 MegaSerum (MSRM), which is unattainable for most people.

Trading Fee Meme via Twitter
Fortunately, Mango uses a generously deposited MSRM, which allows all users to achieve the top tier and benefit from it when trading on the platform.
Perpetual Futures trading- Mango currently charges 'takers' on the platform a 5bps fee. There is no fee for providing a limit order into the book that is later executed as a 'maker', although 'makers' do receive rebates of 4bps. Use the POST order option to ensure your limit order gets executed as 'maker'. However, this comes at the cost of time for the order to execute.
Lending and Borrowing- Mango does not take a fee for borrowing or lending. However, the specified interest rate is applicable on borrowed assets.
Swaps- Since swaps on Mango use the Jupiter Aggregator, the fees charged are the lowest possible across Solana.
Fee Discounts- Users of perp trades with at least 10k MNGO in their account are now only charged 4bps taker fees and receive 3bps maker rebates. Anyone without 10k MNGO should create an account using a referral link. They will then automatically receive a 0.2bps (around 4% of the trading fee) discount on taker orders (4.8bps vs. 5), and 0.8bps (approximately 16% of the trading fee) of fee revenue will flow to their referral source. This incentivizes users to refer more people and onboard more users to the platform.
MNGO Token
$MNGO is the governance token for the Mango DAO. The token was initially launched through a public IDO with the majority of $MNGO (around 90%) locked in the DAO treasury- in which token holders vote on how the funds should be utilized. The remaining 10% was split, with 5% being put up for a public sale and the other 5% allotted to the project's founders.
 MNGO token via Marginatm
MNGO token via Marginatm
The current circulating supply is around 1 billion $MNGO tokens.
Utility
Apart from being used to avail fee discounts, as mentioned earlier, the MNGO token is used primarily in voting for or against proposals in the DAO. For example, any change to the Mango code must be via a proposal in the DAO. Furthermore, the proposal must have attained a minimum of 100 million MNGO 'Approve' votes for a successful vote, with the 'approve' votes outnumbering the 'decline' votes.
Unlike other DEX protocol tokens on chains like Ethereum, $MNGO token holders do not receive a share of the protocol revenue. Instead, all protocol revenue is sent to the Mango DAO vault.
Token Launch
On August 10th, 2021, 5% of the total MNGO supply (500,000,000 MNGO) was put up for sale to anyone who possessed SPL-USDC and a Solana native wallet. There were two token vaults, one for users to deposit USDC and one that held 500,000,000 MNGO tokens.
The amount of USDC deposits in the vault determined the price per MNGO during that time. The launch had two stages, each lasting 24 hours. During the first stage, users could deposit and withdraw USDC into and out of the vault. During the second stage or the "grace period," users could only withdraw USDC, meaning the price of MNGO could only go down. This allowed users who no longer wanted to purchase MNGO to withdraw their investment while also preventing whales with large amounts of capital from artificially inflating the price.
At the peak of the IDO, there were 570M USDC in the vault, pricing MNGO at $1.14 per token. By the end of the grace period, the majority of this capital was withdrawn, resulting in a much lower price per MNGO. Upon completion, the IDO raised 70M at $0.14/MNGO. All proceeds went directly to the DAO treasury for use as an insurance fund in the event of extreme volatility causing excess losses in the system.
Price History
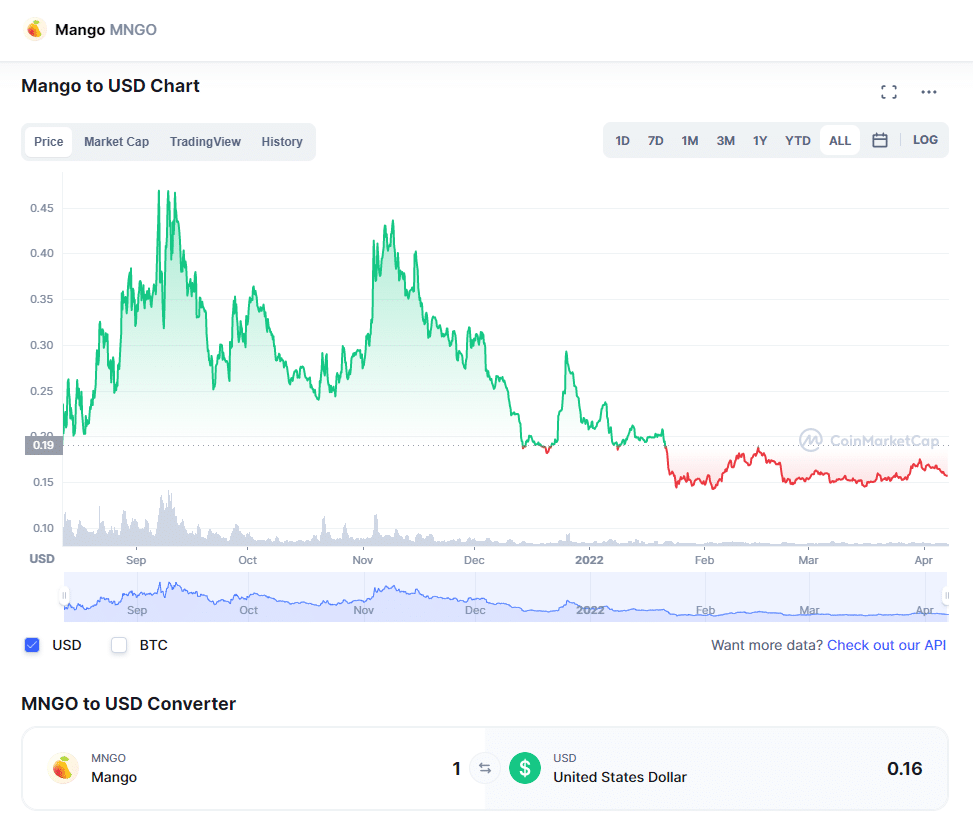 MNGO Price History via CoinMarketCap
MNGO Price History via CoinMarketCap
According to CoinMarketCap, the current price of the MNGO token is $0.156. The MNGO token reached an all-time high of $0.51 in September 2021. However, the token seems to be currently trading close to its all-time low of $0.14.
Where to buy $MNGO?
$MNGO can currently be bought on both centralised and decentralised exchanges. The available markets are listed below
CEXs- Gate.io and Kraken
DEXs- Mango Markets, the Jupiter Aggregator, Raydium Swap and DEX, and Orca Swap.
Can I stake $MNGO?
There is no protocol staking mechanism. However, there are ways to earn yield. For example, $MNGO can be deposited in your mango account to earn interest. Current rates are shown in APR.
Mango DAO
Mango Markets is managed by the Mango DAO, whose governance token is $MNGO. For any changes to the Mango code, it must be passed via a proposal on the governance forum. Governance proposals made on the Mango governance forum are separated into four categories: grants, listings, governance, and feedback.
Anyone with 0.01% of the Mango tokens staked (100,000 $MNGO) can create a proposal. To vote for or against a proposal, one must lock MNGO tokens in a smart contract for the "voting period."
 Mango DAO meme via Twitter
Mango DAO meme via Twitter
MNGO can be locked for up to 5 years to receive increased voting weight in the DAO up to 2x. Voting weight is calculated linearly based on a locking period. Locked tokens cannot be withdrawn until lockup expires.
Any Mango token staker can vote for or against proposals. Official proposals are not merely suggestions; they are executable code. A minimum of 2% of the total MNGO token supply (100 million $MNGO) needs to be cast for a proposal to be eligible for approval.
All proposals are subject to a 3 day voting period. If a majority and at least 2% of the total Mango Token supply are cast for the proposal, it is queued in the timelock and can be implemented after 2 days.
Community Tool- Mangolorians
Mangolorians is a community project built by the users- Waterquarks and Klossie that helps Mango traders monitor liquidity and other metrics on a historical/real-time basis. The project currently provides order book analytics & historical data for Mango Markets.

Merchandise- Mango Market Caps
Mango Markets has its own line of tokenized merchandise called Mango Market Caps ($MCAPS), redeemable for limited edition wearable ‘Caps’.
The merchandise sale took place last year in April. The sale featured 500 $MCAPS tokens sold on a bonding curve. $MCAPS is a token that entitles you to 1 genuine limited-edition cap, shipped globally. The $MCAPS token can be sold back at any time or can be burnt to redeem a genuine cap.
 Current Price of MCAPS.
Current Price of MCAPS.
Currently, around 42 caps are left for sale, while 41 $MCAPS have been burnt and redeemed out of the 458 $MCAP tokens sold. The sale started at $15 USDC and currently stands at a dynamic price of 2883.06 USDC.
The merchandise does not currently offer owners utility, governance, or protocol rights. Although the $MCAP tokens were sold as a collectible with no promise of any utility, a brief scan of the discord reveals that some MCAP owners have proposed a DAO or added utility for MCAP holders.
 MCAPS vs Tungsten Cube meme via Twitter
MCAPS vs Tungsten Cube meme via Twitter
While what comes out of it is yet to be seen, I’m interested to see whether limited edition crypto fashion merchandise (MCAPS, Unisocks- SOCKS) can achieve the same level of demand and community that non-crypto fashion merchandise (such as the ones seen in the sneaker industry) have achieved.
This seems like a distant possibility or even a joke in a fast-paced industry such as crypto. But you never know; only time shall tell.
Community & Education
Mango Markets has a strong community of almost 78 thousand followers on Twitter and over 6000 members on discord.
The platform has an exhaustive tutorial series in its official documentation.
Conclusion
Mango Markets seems to be currently one of the best derivatives trading protocols on the Solana blockchain. With v4 of Mango Markets expected to go live sometime within the next three months, users can expect to see the optimisation of current features, new features and new asset markets.
Some of the features currently offered by Mango Markets, such as Account Delegation, email alerts and its optimised perpetuals market, are the best in the Solana ecosystem. With Solana becoming the next hot destination for DeFi due to its fast throughput and low latency, the future of protocols like Mango Markets is bright.




