The POA network is an open-source public side-chain of Ethereum that has been getting quite a bit of interest from the community lately.
The platform offers a framework for smart contracts which provides developers with an easy and effective way to code on Ethereum standards while leveraging the POA network. The team hopes that this will allow for greater scalability and interoperability.
However, with so many similar protocols and frameworks, can the POA network really compete?
In this review of the POA network, we will give you everything that you need to know about the project. We will dig into the technology, roadmap and development. We will also look at the potential for long term adoption of POA tokens.
The POA Network Tackles Network Scalability
One of the key struggles and focus of 2018 for blockchain technology is the question of scalability for blockchains and their networks. Until now scalability has been a consideration, but not one that needed to be addressed as their simply weren’t enough users to make scalability an issue. That all changed in December 2017 as blockchain usage exploded, especially on the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks.
Even when network congestion is low a Bitcoin transaction can take up to 10 minutes, and during December 2017 some transactions were taking over a full day to be validated. This delay has kept Bitcoin from entering the mainstream as most people can’t accept such a large delay when making payments or transferring money to others. Let’s face it the 21st century is the century of instant gratification.
Another issue that comes with network congestion is higher transactions costs. It’s unbelievable for cryptocurrency users to see fees that can be in excess of 20% during times of congestion. After all, one of the selling points of cryptocurrencies is supposed to be that they are an inexpensive way to transfer assets.
Some solutions have come forward, such as Plasma, which is an off-chain solution that borrows trust from the main chain, and of course the POA Network.
The POA Network Sidechain Solution
The POA Network was designed as a clone of Ethereum and was meant to be its own public blockchain. This means it isn’t simply sidechain technology, and it comes with its own consensus mechanism known as proof-of-authority. With the POA Network there is a notary system in place that is used to solve any node trust issues that might arise.
 Ethereum and xDai sidechains with the POA Network. Source: POA Network Blog
Ethereum and xDai sidechains with the POA Network. Source: POA Network BlogThis works because any validator in the network goes through the full KYC process. Validators on the POA Network are public personalities, in many cases professors at various universities. This means the POA network is not fully decentralized, however it is trustable.
One of the most interesting implementations being developed by the POA Network is the Bridge solution, which allows tokens to move between the Ethereum mainnet and other blockchains. The POA Network believes that this type of cross-chain interoperability is one of the keys to making blockchain technology useful in business settings and everyday use.
The POA20 Bridge
Te POA20 standard is the implementation of the first ever cross chain bridge, which allows POA tokens to be moved onto the Ethereum mainnet quickly and easily through an interoperability protocol. POA20 is the representation of POA tokens as ERC20 tokens. These POA20 tokens have the same properties as ERC20 tokens and can be used in the same manner.
This creation of cross-chain bridges has shown that two standalone blockchains are able to interact in a safe and secure manner, and it sets up a whole range of use cases that hadn’t been possible without the ability of blockchains to interact in this way with each other. For one thing, scalability issues are resolved with the addition of cross-chain bridges.
The POA Network and Gaming
One of the identified use cases for the POA Network is in building online games that will be able to scale massively while also receiving security protections from the Proof-of-Authority consensus.
One of the benefits to gamers is the minimal transaction costs offered by using the POA Network. Additionally, the POA Network is three times faster than Ethereum, even for ERC-721 tokens.
The recent addition of bridging technology is the most exciting part of the POA Network for gamers. It will allow players to easily transfer tokens and other assets from one blockchain to another and back again. In practice this means game items can be transferred from one game to another seamlessly.
POA Network Dapps
Ceremony – This dApp is used when on-boarding a new validator to create an initial key which is securely distributed to the new validator. The dApp is then used to transfor that initial key into the set of keys used for participation in network governance, to receive validation rewards, and to actually validate transactions.
Governance – The POA Network uses U.S. notaries as validators, and all governance decisions are made through the platform’s Governance dApp to record all transactions to the blockchain. Validators are also empowered to make their own suggestions using the Ballots dApp. It’s a secure and transparent system that is very efficient.
Validators – The network validators are U.S. notaries, and transparency is provided by the Validators dApp, which publishes information regarding validators to the blockchain. This information includes the name and notary license of the validator, as well as their address and all information is confirmed using existing KYC regulations.
Bridge Monitoring – The Bridge Monitoring dApp allows users to confirm the existence of two matching contracts on the two blockchains. This dApp helps keep track of deposit, withdrawal and balance changes and/or differences.
Ballots Stats – User are able to monitor all the voting statistics on the POA blockchain using a command line dApp. This is important for maintaining transparency and validator accountability.
BridgeJS – This dApp allows users to deploy their own bridges to move ERC-20 tokens between the Ethereum and POA Network chains.
Network Stats – Rather than digging through statistics on your own, you can use the Network Stats dApp to see important network statistics in an easy to read format. These statistics include average block time, current block number, the number of active nodes and more.
BlockScout – When you want to drill down into blockchain transactions the BlockScout dApp is your friend. You can use the dApp to view account details, to see pending transactions or search through completed transactions, and to view interactions with blockchain smart contracts.
Testnet Faucet – This is a dApp used to mint tokens on the POA Network testnet. This type of minting is used to create tokens for experimenting with use cases in the test environment.
Token Wizard – The token wizard is used to create new tokens and launch ICOs. By answering step-by-step questions in the wizard a user can create, deploy and publish an ICO in just minutes.
Howey Wizard – This dApp is a planning tool for the ICO process. By answering a few simple questions a user can determine if a token qualifies as a security or not.
Proof of Physical Address – This dApp is used to link an Ethereum wallet address and a users physical address and is used to provide trustability of validators. Users can add their address in the dApp and a postcard is sent to them. The postcard contains a unique cod that can then be entered in the dApp and complete the verification process.
Proof of Bank Account (in development) – This dApp will allow for the linking of an Ethereum wallet address and a bank account number. Users prove ownership of both the wallet address and the bank account to complete the linking process.
Other POA Network dApps in development:
- Mana-Ethereum
- Honey BadgerBFT Consensus
The POA Token
The POA Network (operating as the Oracles Network at the time) conducted an ICO on November 17, 2017, raising $12.6 million by selling roughly 175 million POA tokens at $0.0724 each. The POA token wasn’t publically traded until February 28, 2018, debuting at $0.63. Price fell quickly after the debut, dipping below $0.28 by March 18.
 Register at Binance and Buy POA Tokens
Register at Binance and Buy POA TokensIt quickly recovered and rose over the next two months, nearly hitting $0.85 in May 2018, before getting caught in the broad based cryptocurrency bear market. From that all-time high in May the coin dropped steadily and significantly (with a small October 2018 bounce), and as of January 10, 2019 it is trading at just $0.025786 per token.
Nearly all of the trading volume in POA is on Binance, and while the coin is listed on a few other exchanges the small volume at these other exchanges makes them unsuitable for buying POA at competitive rates.
POA works with a large number of wallets since it is part of the Ethereum ecosystem. In addition to hardware wallets Trezor and Ledger, it is also supported by MetaMask and MyEtherWallet or MyCrypto. It also works with other wallets like Nifty Wallet and Trust wallet, among others.
Development
In order to get the best sense of how much work is being done on the POA network, it helps to take a look at the project's GitHub repo. This will give us a rough estimate of how much code is being pushed and how many more updates we can expect from the project.
Given the scope of the POA network, there were over 84 repositories on their official GitHub. We decided to look into those that have been the most active over the past 12 months. Below we have three of these repos and the total code commits that occurred over the period.
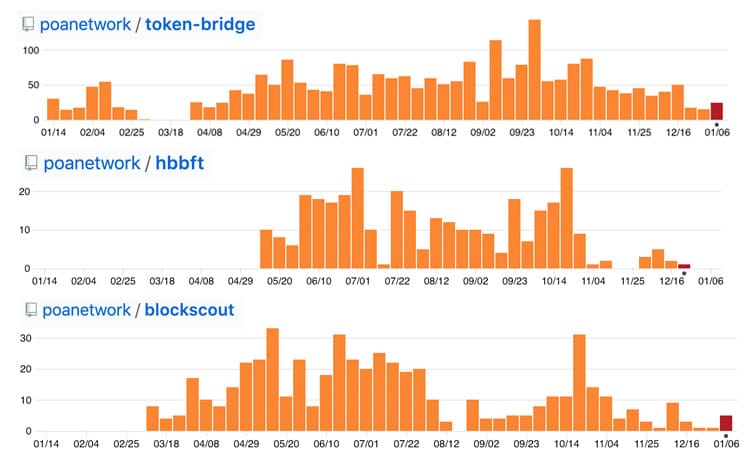 Three of the most active GitHub repos in the POA Network
Three of the most active GitHub repos in the POA NetworkAs you can see, the developers and POA network community have been quite busy. In fact, if we were to take a look at the rankings of POA in terms of other project's GitHubw, we are sitting at 59 which makes the POA network between Bitshares and Factom.
Irrespective how much work has been done on the protocol, one cannot rely on past developer performance to extrapolate anything into the future. Hence, it helps to take a look at the roadmap of a project to get a sense of what we can expect to see.
Roadmap
There are on the POA network for 2019. These relate to the core protocol, to the Mana-Ethereum, to TokenBridge and BlockScout. We won't delve into all of them right now but we can take a quick look into the POA Core Roadmap.
There are three areas that the POA network developers would like to improve when it comes to the core protocol. Firstly, they want to increase general adoption through the creation of more dApps. They also want to develop support for a new client on the the POA core.
There are also core updates that pertain to the consensus algorithm. For example, they want to upgrade the POA core testnet from the AuthorityRound consensus to the HoneyBadgerBFT (HBBFT). This will make the POA network consensus more resilient to outside attack. You can read about the about HBBFT here.
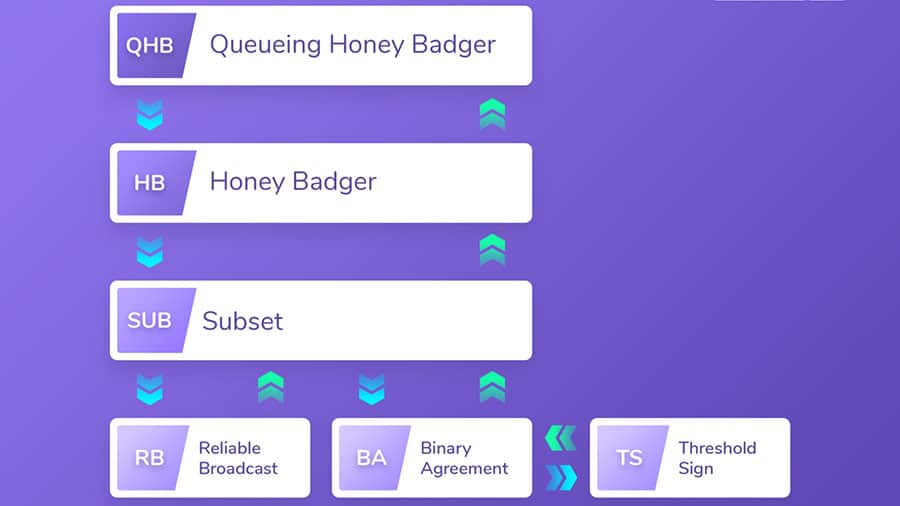 HBBFT Architecture on the POA Network. Image Source:POA Network Blog
HBBFT Architecture on the POA Network. Image Source:POA Network BlogWhen it comes to governance on the POA network, the developers are looking to increase the number of network validators. This is one step closer to reducing centralisation on the network. Lastly, the team would like to use the self-sustainabilty model of the POA core through the emission fund to support R&D and other operations on the net.
Conclusion
The POA Network is providing enterprises with a simple and useful way to issue tokens and conduct a crowd sale or ICO. They have also simplified the KYC process, and the use of Proof-of-Authority consensus brings trusted validators into any blockchain ecosystem.
The addition of Bridges brings a new level of interoperability for blockchains, one that the POA Network feels is necessary for the technology to grow and evolve. As leaders in this area, if they are correct, they could soon be one of the leading blockchain projects.
The POA Network team certainly is excited about what can be accomplished with Bridges, and have become increasingly optimistic about what the future will bring for the project.



