The Decentralized Finance realm is constantly evolving. The Ethereum network is the nucleus of DeFi, so when it receives a foundational update, the effects permeate the entire crypto space.
One such upgrade was Ethereum 2.0, a.k.a Ethereum Beacon Chain Upgrade, a.k.a Ethereum's much-anticipated migration to the Proof of Stake consensus system. The upgrade was profound in many ways; it introduced ETH burning, added a new utility to Ether, improved the network's decentralization, and drastically reduced its carbon footprint.
With Ethereum 2.0, the liquid staking paradigm entered the cryptosphere. Liquid staking sought new utility for staked Ether by minting synthetic Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) pegged to staked liquidity. Soon, users began leveraging LSTs to secure new networks and introduced the restaking narrative.
This article reviews Puffer Finance, which is a liquid staking and restaking protocol simultaneously. Moreover, Puffer has devised a mechanism that lets a staker or an Ethereum node operator participate in Ethereum's consensus process with as low as 1 ETH, rather than the standard 32 ETH, along with additional protocol benefits.
This Puffer Finance review will unpack the project to explain the technology behind it so that readers can learn to integrate it into their DeFi strategy.
Puffer Finance Review Summary
Puffer Finance is an Ethereum-native liquid restaking protocol. It has developed a mechanism that drastically reduces the requirements to participate in Ethereum PoS consensus; it further enhances return by rehypothecating staked in EigenLayer with an integrated restaking mechanism and has also established anti-slashing measures to preserve user's staked funds.
The Key Features of Puffer Finance Are:
- EigenLayer powered restaking: Puffer Finance utilizes EigenLayer to enable restaking, allowing stakers to earn additional rewards beyond traditional PoS earnings.
- Participating in restaking with as low as 1 ETH: Puffer Finance lowers the barrier to entry by enabling participation in restaking with a minimum of just 1 ETH.
- Anti-slashing mechanisms: Puffer's Secure-Signer technology uses Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) to protect validator keys and prevent slashing penalties.
- Validator Tickets: Validator Tickets (VTs) are a novel approach that provides liquidity and flexibility, allowing validators to trade their staking rights on the secondary market.
- Native Liquid Restaking Tokens (nLRTs): nLRTs, such as pufETH, offer a dual-source reward system that includes traditional PoS rewards and additional restaking rewards.
Challenges of Staking in Ethereum
While offering attractive rewards and contributing to network security, staking in Ethereum presents several challenges that can deter individual participants. Here, we discuss the primary obstacles associated with staking in Ethereum.
High Barrier to Entry
The Ethereum Beacon Chain mandates that users must set up a full validator node and stake a minimum of 32 ETH to participate in staking. This requirement poses a significant barrier for many potential stakers. Accumulating 32 ETH is a substantial financial commitment, especially considering the fluctuating price of ETH. Beyond the financial requirement, setting up and maintaining a validator node demands technical expertise and appropriate hardware, which adds to the complexity and cost. This high entry threshold excludes many potential participants interested in contributing to the network's security and earning staking rewards.
Capital Locked in the Staking Contract
Once staked, the 32 ETH is locked in the Ethereum staking contract for the duration of the staking period. This lock-up period renders the staked capital inaccessible for other uses, which can be a significant drawback. During this time, stakers might miss out on potentially more lucrative opportunities in the DeFi space that could offer better returns than staking. The immobility of staked funds is one reason behind the growing popularity of liquid staking tokens. These tokens represent the staked ETH and can be used in other DeFi protocols, providing liquidity and additional yield opportunities while still earning staking rewards.
Centralization of Validator Pools
The emergence of liquid staking protocols like Lido and Rocket Pool has led to significant amounts of ETH pooling, creating a potential centralization risk. While these protocols are designed to democratize access to staking and increase participation, their success can inadvertently lead to a concentration of staking power.
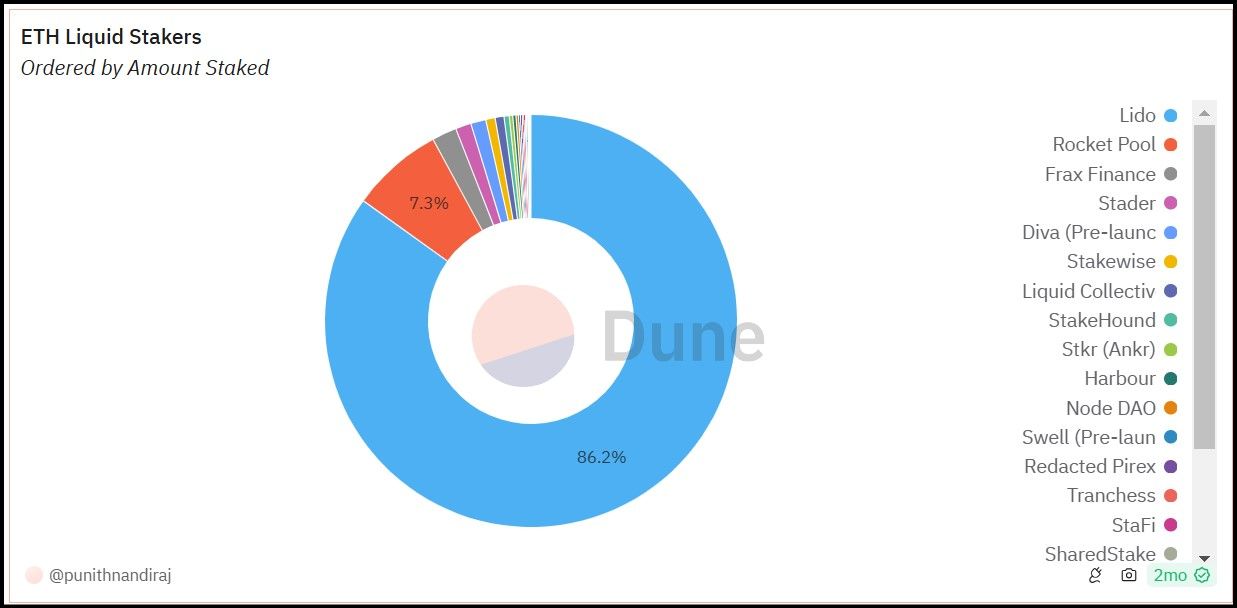 A Dune Analytics Chart Illustrates Lido Dominance Over Ethereum Staking
A Dune Analytics Chart Illustrates Lido Dominance Over Ethereum StakingThis centralization, even if unintentional, poses risks to the health and security of the Ethereum network. The dominance of a few large validator pools can undermine the decentralization ethos of blockchain technology and make the network more vulnerable to collusion and attacks.
Puffer Finance Addresses These Challenges
Puffer Finance aims to mitigate these challenges through innovative mechanisms. By allowing users to participate in staking with as little as 1 ETH, Puffer significantly lowers the barrier to entry. Furthermore, Puffer's approach enables stakers and node operators to earn rewards not only from Ethereum staking but also from additional restaking activities through EigenLayer's Actively Validated Services (AVS). This method ensures that the staked ETH can be rehypothecated, providing additional utility and potential returns within the DeFi ecosystem.
Puffer employs a unique system of validator tickets to address the centralization issue. These tickets act as temporary passes for nodes to participate in staking, limiting the concentration of staking power and promoting a more decentralized network. The specifics of validator tickets and their impact on centralization will be explored in greater detail later in this review.
What is Puffer Finance?
Puffer Finance is a native liquid retaking protocol (nLRP) on Ethereum. Puffer allows ETH holders to participate in Ethereum staking without setting up proprietary validator nodes. Moreover, Puffer further accrues additional rewards as a native restaking protocol built on top of EigenLayer.
 Puffer Finance Homepage
Puffer Finance HomepageWhat is Native Restaking?
Native retaking is better understood against other liquid staking protocols in the Ethereum ecosystem. Restaking is the practice of exposing one's ETH holdings to two sets of slashing conditions – One by the Ethereum mainnet and another by staking it in Actively Validated Services like EigenLayer. The additional slashing conditions help secure more networks after the Ethereum mainnet and earn the holder additional rewards through transaction fees and commissions.
To participate in restaking, a user first gets their hands on some liquid staking tokens like stETH (Staked ETH). Liquid staking protocols like Lido and Rocketpool issue LSTs. They accept ETH deposits from the user and stake them in the Ethereum network on their behalf. The Liquid Staking Protocol then mints some LST tokens to represent the user's deposit, which they may use in a myriad of ways in DeFi.
When the user leverages the LSTs to secure more networks further, the strategy is restaking. EigenLayer is the most famous restaking protocol. It accepts Liquid Staking Tokens from the leading LST protocol as deposits and uses them to sponsor AVSs that secure additional networks. Overall, restaking is a two-step process:
- Acquire LST tokens by staking ETH using liquid staking protocols.
- Staking LSTs on EigenLayer for restaking incentives.
Put simply, Puffer Finance combines this two-step process into one protocol. Users on Puffer Finance can stake their ETH with the protocol and reap staking and restaking rewards. Since Puffer alleviates the need to access multiple protocols, it has termed its strategy native restaking.
Native restaking can potentially make staking simpler and more efficient. Since Puffer manages both Ethereum staking and restaking, it may be able to provide more significant economic incentives to its users and reduce friction in the experience of restaking.
Puffer Finance's Unique Features and Incentives
Puffer finance is unique in a multitude of ways. It offers features that simplify restaking for non-technical users and establishes measures to mitigate technical roadblocks like slashing and decentralization. On Puffer, users have to simply provide liquidity in Ether to the protocol, which takes care of every technical setting to ensure a frictionless restaking experience.
Here are some of Puffer's standout features:
- Permissionless: Puffer allows anyone with adequate hardware to participate in retaking to join the Puffer protocol as a node operator.
- Low Barrier: Puffer has reduced the amount of ETH one needs to participate in Ethereum staking to as little as 1 ETH.
- Restaking Exposure: Node operators on Puffer can increase their staking rewards through integrated restaking via EigenLayer.
- Secure:
- Puffer has established an anti-slashing mechanism to mitigate losses and penalties while participating in staking.
- It has introduced a new concept of validator tickets, allowing the protocol to align node operator incentives.
- It has deployed a security council to reduce inactivity risk.
- Puffer establishes strict rules about who can operate AVSs.
- It adjusts risk by switching between multiple EigenLayer AVSs.
- Puffer caps the protocol's staking size to 22% to protect Ethereum's credible neutrality.
The Puffer Finance Solution
This section will distil the Puffer Finance Architecture. It comprises several roles, including stakers, node operators, restaking operators, and Guardians that work together to facilitate a sustainable restaking economy. Let's understand the value flow in Puffer Finance with the following architecture flowchart:
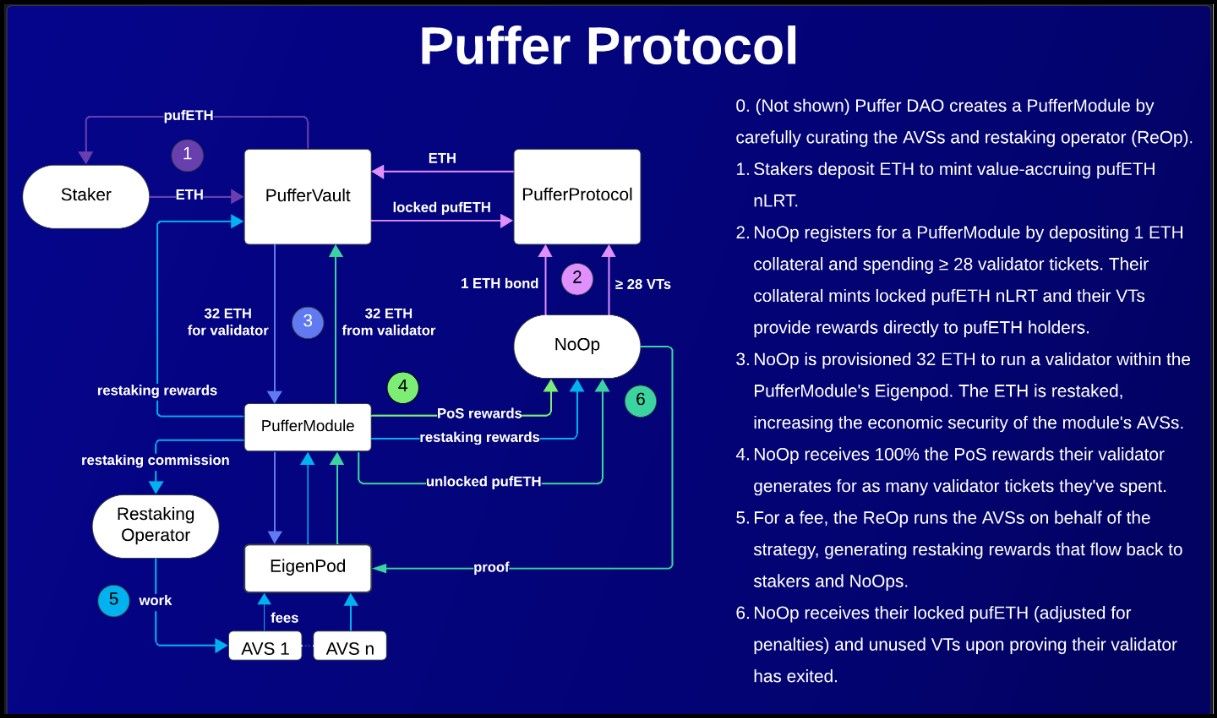 The Puffer Architecture | Image via Puffer Finance
The Puffer Architecture | Image via Puffer FinancePufferModules
The participation requirements for entering Ethereum's PoS consensus or joining EigenLayer as a native restaker are that a participant has to operate a full node and stake 32 ETH in the network. Puffer breaks this requirement with the PufferModule.
A PufferModule is a smart contract in the Puffer protocol that controls an EigenPod as a native restaker in the EigenLayer protocol. EigenPods are contracts with which users stake 32 ETH, operate EigenLayer AVS, and reap restaking benefits.
Instead of a single node operator staking 32 ETH on Puffer, every PufferModule comprises several smaller node operators (NoOps) who perform Ethereum PoS validation. Several NoOps contribute as low as 1 ETH each to enable a module's participation in EigenLayer. Puffer begins with several empty PufferModules that NoOps gradually populate.
Staking ETH
Stakers are another participant in the Puffer Protocol. Stakers are users who hold ERH and want to earn liquid staking and restaking rewards. The process begins with stakers depositing their ETH in the PufferVault. Then, the vault mints pufETH, a native liquid restaking token representing the user's ETH deposits.
Native Liquid Restaking Tokens (nLRTs)
Ethereum's constantly evolving staking landscape has given rise to a new token model: the native Liquid Restaking Token (nLRT). This modern take on liquid staking provides a unique advantage over its predecessor, the LST. Fundamentally, an nLRT is an LST that delivers traditional PoS rewards and boosts these with additional restaking rewards.
nLRTs are Different from LRTs
nLRTs generate their restaking rewards through native restaking on EigenLayer. The additional capability makes them more functions than traditional LSTs. Essentially, nLRTs tokenize restaked LSTs within a Liquid Retaking Protocol (LRP) like Puffer Finance.
Liquid Restaking Token rewards are divided between the liquid staking and restaking protocol. In contrast, nLRTs earn both Ethereum PoS rewards and restaking rewards simultaneously under one protocol.
pufETH
nLRTs, including pufETH, provide a diversified stream of rewards. They encompass both traditional Ethereum PoS rewards and allow holders to earn rewards from restaking services. This dual-source reward system positions nLRT holders to potentially outearn their LST counterparts.
Stakers deposit ETH to the PufferVault contract to mint the pufETH nLRT. At the protocol's inception, pufETH's conversion rate was one-to-one and is expected to increase over time. Assuming the protocol performs well, i.e., accrues more rewards than penalties, the amount of ETH redeemable for pufETH will increase. This mechanism ensures that pufETH holders can benefit from the protocol's success while enjoying enhanced liquidity and earning potential.
For instance, if the user receives 1 pufETH, it represents a deposit of 1 ETH in the protocol. Then, if the protocol performs profitably and earns 0.2 ETH from staking and restaking services, then 1 pufETH is valued at 1.2 ETH. Instead of directly paying wallets holding pufETH, Puffer distributes rewards through value appraisal of pufETH.
In summary, pufETH combines the benefits of traditional LSTs with additional advantages from restaking rewards, simplified DeFi integration, and a novel approach to managing validator performance and decentralization challenges.
Registering NoOps
Node Operators (NoOps) are Puffer participants running validator nodes participating in Ethereum's PoS consensus and earning rewards. NoOps deposits 1 ETH and a novel ERC-2 token called Validator Tickets as collateral to the Puffer protocol contract. In return for their deposit, the protocol mints pufETH, which remains locked in the protocol for their participation. NoOps can also alternatively deposit pufETH tokens directly in the protocol.
Validator Tickets
Validator tickets are a novel innovation of Puffer Finance. It is an ERC-20 token that serves as a sort of temporary license, allowing NoOps to reap Ethereum's PoS rewards. Validator tickets are minted when a user deposits ETH using the Puffer protocol. The user can use VTs to either participate as node operators in the Puffer protocol or sell it to others who need it for extra rewards.
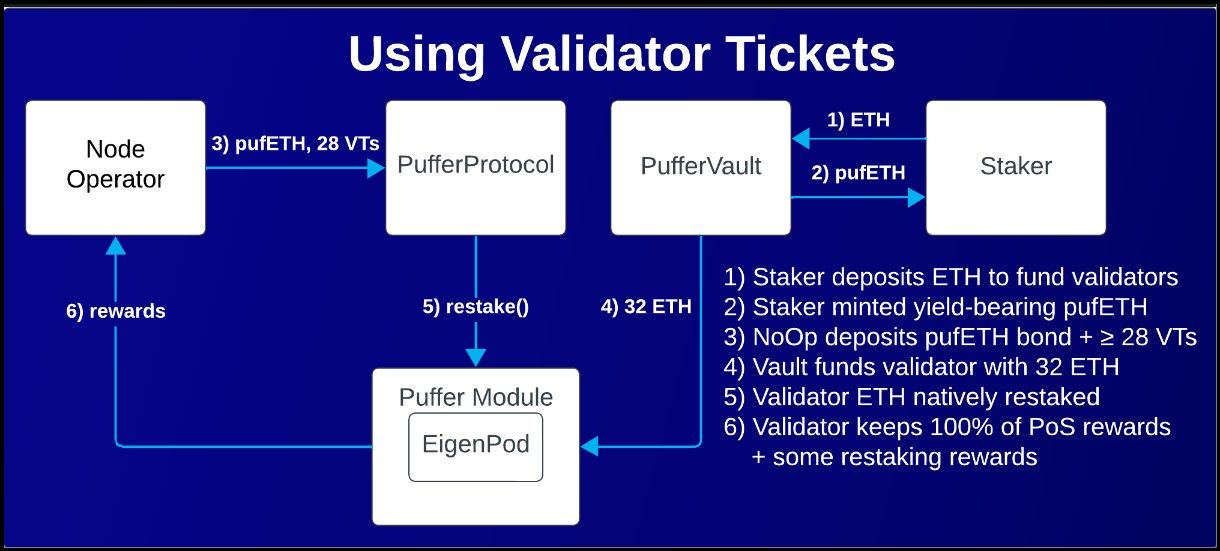 VT Architecture Explained in Puffer Docs
VT Architecture Explained in Puffer DocsVTs are bonds. A NoOp deposits at least 1 ETH and 28 VTs to participate as an Ethereum validator on Puffer. The protocol collects ETH from stakers and NoOps. Once it has 32 ETH, it is prescribed to a node operator and entitles it to 100% of the PoS rewards for as many days as the number of VTs deposited. This mechanism allows Puffer to enable node operators to participate in Ethereum consensus without staking the full 32 ETH themselves. The Puffer protocol burns the used VTs.
This new approach neatly tackles two traditional problems:
- Rug-pooling: With NoOps entitled to all the MEV they generate, there's no longer a need to police or penalize them for rug-pooling.
- Lazy NoOps: Since stakers get a proxy for PoS rewards upfront via minting VTs, they aren't adversely affected if a NoOp underperforms.
Restaking Rewards
Restaking operators may also be node operators that execute EigenLayer AVSs on the PufferModule's behalf and receive commissions for their services. Restaking operators keep a portion of the fees and rewards collected from AVSs and return the rest to the Puffer protocol, which goes towards enhancing the value of pufETH. This mechanism allows stakers to simply deposit ETH in the protocol and gain exposure to both Ethereum PoS rewards and restaking rewards by virtue of pufETH value accrual. This arrangement also allows node operators to earn more rewards than through Ethereum PoS alone without needing additional hardware. NoOps can access their rewards through the protocol withdrawal process.
Exiting Puffer Protocol
When a NoOp exits the Puffer, the protocol calculates penalties related to inactivity or slashing if the validator has incurred any. The corresponding bond in pufETH is burned, and the rest is returned to the node operator. The protocol also returns any unused VTs to the node operator.
Conclusion
Validator tickets are central to the Puffer Finance protocol. Puffer integrates liquid staking and restaking under one paradigm through the issuance and sale of validator tickets.
On Puffer Finance, users can participate on multiple levels with very low entry barriers and earn rewards for securing blockchain networks. As stakers, users are rewarded in PoS rewards and restaking rewards for simply holding pufETH, which is a step up from traditional liquid staking protocols.
Additionally, users with access to node-worthy hardware can participate as Ethereum validators and restaking operators by depositing significantly less than the standard 32 ETH requirement and earning rewards by collecting PoS commissions and fees from AVSs.
Puffer outsources Actively Validated Services to EigenLayer, which is the leading restaking protocol in Ethereum. This strategy ensures Puffer's access to robust networks that pay consistent AVS fees, reducing restaking risks to which Puffer operators are exposed.
Puffer Security Measures
The Puffer Protocol has implanted several security measures to safeguard stakers and NoOps from unwarranted penalties and slashing. Moreover, the Puffer protocol includes Guardians, a group of trusted entities that function as a DAO and are tasked with critical duties that ensure the smooth functioning of the Puffer protocol.
Puffer Anti-Slashing Technology
Puffer's Secure-Signer is a remote signing tool backed by an Ethereum Foundation grant, designed to prevent slashable offenses using Intel SGX. It leverages Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), which provide confidentiality and integrity guarantees. Currently implemented as an Intel SGX enclave, Secure-Signer ensures that code is executed without tampering and data remains encrypted and protected. Puffer plans to diversify its hardware by implementing Secure-Signer on AMD's SEV TEE and other future technologies to mitigate points of failure.
How Does Secure-Signer Work?
Secure-Signer can be used locally with the consensus client or on a remote server. For node operators with SGX-enabled hardware, setting it up is straightforward: install and run Secure-Signer, then configure the consensus client to use it as the remote signer.
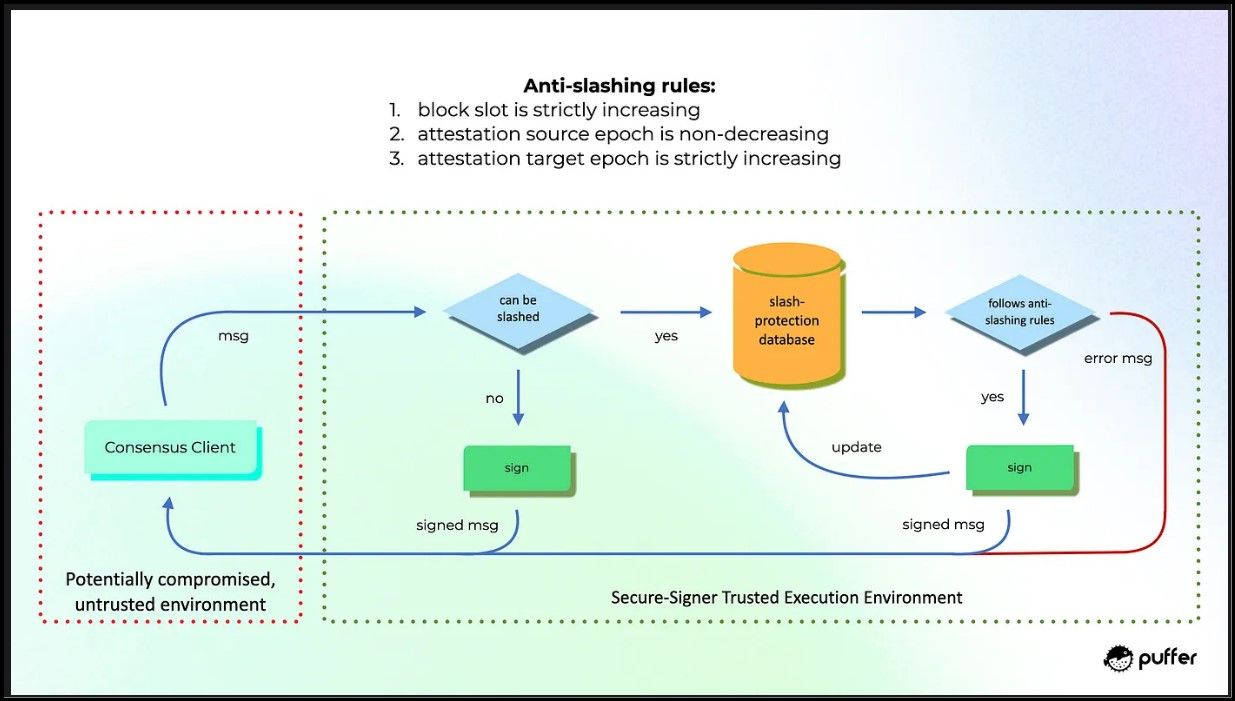 Puffer Secure Signer Implements Anti-Slashing Techniques | Image via Puffer Docs
Puffer Secure Signer Implements Anti-Slashing Techniques | Image via Puffer Docs To prevent slashing, Secure-Signer generates and stores all BLS validator keys in its encrypted memory, which is only accessible during runtime. This means the keys can't be misused or exposed, protecting against accidental slashes from double-signing. Additionally, Secure-Signer keeps an integrity-protected database of all previously signed materials, ensuring all signatures follow these rules:
- Proposal check: The current slot must be greater than the previous slot.
- Attestation check: The source epoch must be greater than or equal to the previous source epoch.
- Attestation check: The target epoch must be greater than the previous target epoch.
These checks are enforced even if the node's operating system is compromised, preventing slashing due to software bugs or other issues.
Why Use Secure-Signer?
Secure-Signer provides a robust and efficient way to protect validator keys, similar to using a hardware wallet for cryptocurrencies. By using Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), Secure-Signer reduces the risk of slashing, helping maintain the security and integrity of the Ethereum network. It is designed to benefit all validators by decreasing the likelihood of mass-slashing events, making it a valuable tool for the Ethereum community.
Guardians
Guardians are a set of trusted Puffer community members that function as a DAO. Their economic intentions are deeply aligned with the success of the Puffer protocol and serve the following essential duties:
- Ejecting Validators: They eject the validators of the node operators that perform their validation duties poorly. The Guardian removes the validators in these cases to protect the integrity of the Puffer protocol:
- If a validator's deposit in the Ethereum Beacon Chain falls below a DAO-designated threshold.
- Validator's PufferModule is slashed due to an AVS violation.
- The validators runs out of VTs.
- Provisioning or Skipping Validators: If a NoOp registration is done incorrectly, it is the responsibility of the Guardians to identify, penalize and skip such NoOp registrations.
- Returning Validator Bonds: When a validator exits the Puffer protocol, it is the Guardian's job to return its bond and burn the consumed VTs.
All actions of the Guardians are executed after a supermajority agreement between them.
Roadmap to Decentralization
Puffer seeks to achieve greater decentralization by automating the role of Guardians with smart contracts. However, the intricate nature of their responsibilities means that automating guardians hinges on a bunch of Ethereum EIPs, which are listed as follows:
- EIP-7002: It will enable the triggering of guardians with smart contracts.
- EIP-4788: Allows many Guardian operations to be replaced via a zero-knowledge proof.
- EIP-2537: Reduces the trust dependencies on Guardians by enabling on-chain registration validation.
Until these EIPs are adopted in the Ethereum mainnet, the role of Guardians remains central to the Puffer protocol.
Puffer Protocol Risks
Puffer Finance employs novel techniques that have not been used extensively in DeFi before while the protocol still remains under development. Therefore, if you're considering Puffer Finance for restaking, these risks are worth consideration:
Validator Tickets (VTs)
- Novelty Validator Tickets (VTs) represent a new concept in the staking industry. While this innovation can offer significant advantages, such as improving decentralization and providing additional liquidity, it also faces the challenge of gaining trust within a landscape dominated by established practices. The adoption of VTs requires validators and stakers to understand and accept this new paradigm, which may take time and education.
- Increased Capital Requirement: VTs require more upfront ETH compared to the traditional bond-only model. However, Puffer mitigates this concern by offering the lowest bond requirement among all permissionless Liquid Staking Providers (LSPs) at 11 ETH. This makes the additional ETH requirement relatively minor in the broader context of staking. Despite the need for more initial capital, the reduced bond requirement makes participation more accessible compared to other protocols.
- The value of VTs is subject to market dynamics, including execution rewards and the size of the validator set, which can cause fluctuations in consensus rewards. However, the daily repricing of VTs helps to mitigate volatility. Moreover, the liquidity of VTs allows them to be traded on the secondary market, providing an additional layer of flexibility and risk management for stakers.
Specific Risks Associated with Puffer Finance
- Slashing Penalties for Validator Misconduct: One of the primary risks in any staking protocol is the potential for slashing penalties due to validator misconduct, such as double-signing or being offline. Puffer addresses this through its Secure-Signer technology, which significantly reduces the risk of such penalties by protecting validator keys and ensuring adherence to proper signing protocols. However, the risk of slashing still exists and can impact stakers.
- Reliance on EigenLayer for Restaking: Puffer Finance relies on EigenLayer for its restaking functionality. While EigenLayer is a robust platform, this dependence introduces a risk factor. Any issues or vulnerabilities within EigenLayer could affect Puffer's operations and the security of staked assets. Ensuring the reliability and security of EigenLayer is crucial for the smooth functioning of Puffer Finance.
- Platform Development Stage: Puffer Finance is still under development, which inherently comes with uncertainties and potential risks. The platform may face technical challenges, security vulnerabilities, or delays in feature rollouts. Early-stage projects often encounter bugs and require iterative improvements. Users must be aware of these risks and consider them when deciding to participate in the protocol.
In summary, while Puffer Finance offers innovative solutions and significant potential benefits, it is essential for users to understand and consider these risks. The combination of new technologies, reliance on external platforms, and the developmental stage of Puffer Finance introduces various risk factors that should be carefully evaluated.
Puffer Finance Review: Closing Thoughts
Puffer Finance is an intriguing innovation in an incredibly nascent restaking niche in DeFi. It is a testament to the scope of innovation in DeFi. The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade introduced PoS, then came liquid staking protocols and lowered the barriers to Ethereum staking.
Now, solutions like Puffer Finance are further innovating in the staking niche to enhance the ROI in staking. These developments are healthy for the Ethereum ecosystem at large. As staking becomes more accessible and solutions like Puffer make it more lucrative, more Ether will get staked in Ethereum. Therefore, innovations like Puffer are making Ethereum more secure and improving Ether's value proposition in the long run.





