Aster is a non-custodial perpetuals platform built for traders who already understand leverage, margin, and liquidation risk. It prioritizes execution privacy, capital efficiency, and flexible trading across crypto and stock perpetuals, combining multi-chain settlement, hidden orders, and yield-bearing collateral into a single modular system.
This guide is a full, end-to-end breakdown of how Aster works in practice. It covers the platform’s architecture, Simple vs Pro trading modes, fee and funding mechanics, yield-bearing collateral, the ASTER token, and how Aster compares to peers like Hyperliquid. Along the way, it highlights where Aster creates real edge and where risk concentrates.
The goal is not to sell Aster as a default choice, but to explain it clearly enough that you can decide whether it fits your trading style. By the end, you should understand who Aster is built for, how to use it without blind spots, and why its design choices matter in today’s perpetual market.
Verdict (30-Second Summary)
Verdict: Aster is a multi-chain perpetuals DEX built for pro-grade execution, pairing hidden limit orders and on-chain settlement with a dual-mode UX (Simple vs Pro). Fees are typically ~0.01%–0.08% depending on mode/role, leverage ranges from up to 1001x in Simple on select pairs (and lower caps in Pro/stock perps), and it supports BNB Chain, Ethereum, Solana, and Arbitrum.
Rule of thumb: this is perps infrastructure, not passive investing.
Who It’s For
- Active perps traders who care about execution tools (orderbook controls, modifiers, brackets).
- Multi-chain users who want to trade on BNB Chain, Ethereum, Solana, or Arbitrum without living in bridge limbo.
- Privacy-conscious execution where hiding size/price until fill matters (alpha-sensitive entries/exits).
- Traders who want stock + crypto perps in one interface, 24/7 exposure, and Pro-style controls.
- Users who can use yield-bearing collateral intelligently (and understand haircuts, redemption friction, and stress behavior).
Who It Isn’t For
- Cold-storage-only users who rarely trade and just want long-term holding.
- Set-and-forget beginners looking for “buy and chill” simplicity.
- Anyone uncomfortable with funding math, liquidation mechanics, or oracle-driven mark price risk.
Quick Facts
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| What it is | Next-generation decentralized perpetual and spot exchange with Simple and Pro trading modes, MEV-resistant routing, hidden orders on advanced interfaces, and non-custodial settlement across multiple chains. |
| Backers | Backed by YZi Labs (spun out from Binance Labs) and other strategic investors aligned with the BNB Chain ecosystem. |
| Listing | ASTER listed on Binance with a Seed Tag in early Oct 2025; also tradable on major CEXs such as MEXC and Gate, alongside the native Aster DEX. |
| Leverage | Up to 1001x leverage in Simple Mode on supported pairs (primarily on BNB Chain and Arbitrum); Pro Mode offers high leverage with pair-specific caps and advanced order types. |
| Fees | On-chain perps currently use a 0.08% open/close fee for most crypto pairs on BNB Chain, plus a small fixed execution fee per transaction; forex pairs use lower percentage fees. |
| Chains | Core deployment on BNB Chain and Arbitrum for Simple Mode, with Pro Mode live on BNB Chain, Ethereum, and Solana; Aster Chain (own Layer-1 for perps) is in active development. |
| Privacy | MEV-resistant order routing and hidden/iceberg order options on advanced interfaces to reduce information leakage for large trades. |
| Collateral | Supports yield-bearing collateral such as liquid-staked BNB (asBNB) and a native yield-generating stablecoin (USDF) to improve capital efficiency. |
| Token | ASTER, primarily a BEP-20 token on BNB Chain, used for governance, trading fee discounts, staking rewards, and revenue-share programs; total supply 8,000,000,000 ASTER. |
| Airdrop | Initial airdrop allocation of 704,000,000 ASTER (8.8% of supply) was claimable between Sep 17 and Oct 17, 2025 with withdrawals from Oct 1, 2025; later “Stage 3” and “Aster Crystal” phases added new claim windows from Dec 15, 2025–Jan 15, 2026 and Dec 22, 2025–Feb 1, 2026 respectively, distributing an additional 200M+ ASTER to eligible users. |
Taken together, these numbers position Aster as a fast-scaling contender rather than a mature, stability-first venue. That context becomes especially important once Aster is placed side by side with the current perps benchmark, Hyperliquid.
Aster vs Hyperliquid (via DefiLlama)
| Metric | Aster | Hyperliquid |
|---|---|---|
| 24h Perp Volume | $4.27 billion | $9.26 billion |
| 30d Perp Volume | 127.04 billion | $173.13 billion |
Data current as of Jan. 29, 2026.
What Is Aster?
 Explaining Aster’s Core Purpose And Design
Explaining Aster’s Core Purpose And DesignAster is a multi-chain perpetuals DEX built to deliver pro-grade trading through a tightly integrated stack, rather than a collection of loosely connected tools.
The platform offers dual trading modes, Simple and Pro, supports hidden limit orders for execution privacy, 24/7 stock perpetuals alongside crypto markets, and settles positions, P&L, and liquidations fully on-chain in a non-custodial manner. Users connect a wallet, choose between BNB Chain, Ethereum, Solana, or Arbitrum, post collateral, including yield-bearing options, and execute trades that ultimately settle transparently on-chain. Off-chain routing logic handles MEV mitigation and hidden order matching, allowing Aster to improve execution quality without sacrificing settlement guarantees.
The platform began attracting outsized attention in late 2025, driven by a rapid-dominance narrative. During its token launch and hidden orders rollout, Aster briefly surged past Hyperliquid in daily volume and fee generation. That momentum was fueled primarily by strong BNB Chain traction and ecosystem alignment, rather than reliance on heavy promotional campaigns or short-lived marketing incentives.
Behind the protocol itself sits a deliberate choice around visibility. Aster is tied to established players in the broader crypto ecosystem. Still, it maintains a product-first posture that prioritizes delivery and infrastructure over individual personalities or constant public-facing branding.
Team & Backing
The project traces its roots to Astherus, a DeFi yield protocol that secured seed investment from YZi Labs, formerly Binance Labs, in November 2024. That early backing provided technical and ecosystem support before Astherus merged into what eventually became the Aster perpetuals platform. In September 2025, Binance founder CZ confirmed that he serves in an advisory capacity focused on product and technical direction. Several former Binance staff members contribute to the project, while YZi Labs retains a minority position through private investment vehicles.
Despite those connections, the founding team and core contributors operate under a pseudonymous and deliberately low-profile model. The emphasis remains on product execution, on-chain delivery, and system reliability rather than public personas, frequent AMAs, or personality-driven narratives.
Legitimacy Snapshot
Rather than relying on trust alone, Aster’s credibility can be evaluated through public data and independently verifiable signals.
Claims here are drawn from primary sources such as CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap for listings and token information, and Arkham for entity-level flow analysis where available.
On-chain activity is substantial, with more than $125B in 30-day volume, roughly $359M in TVL, and transparent settlement flows that can be inspected across four chains via public explorers. On the market access side, ASTER is listed on major centralized exchanges, including Bybit, which hosted first-listing campaigns, as well as Gate.io, KuCoin and MEXC. On the decentralized side, liquidity is visible on PancakeSwap for BNB-based pairs and Uniswap for Ethereum.
Public communication channels also remain active and accessible. Official documentation is published at docs.asterdex.com, updates are shared through the @Aster_DEX account, and API documentation is detailed enough to signal serious developer integration rather than superficial tooling.
What remains unverified follows a familiar pattern for pseudonymous teams. The full private cap table, internal control structures, and upgrade key management are not publicly disclosed. These gaps are not unusual, but they are areas worth monitoring as on-chain governance and upgrade mechanisms mature.
Why Aster Exists
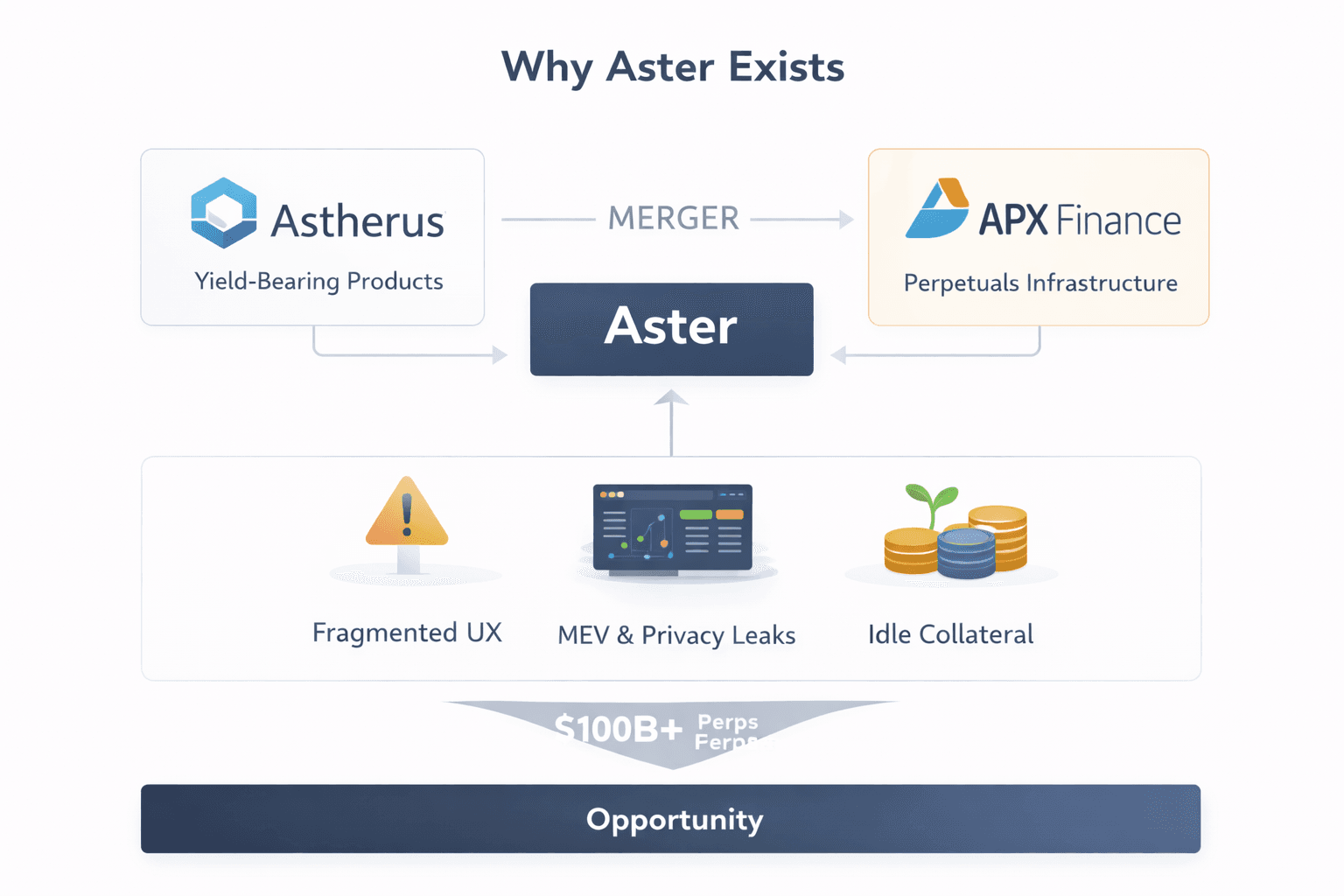 The Problem Aster Was Built To Solve
The Problem Aster Was Built To SolveAster did not appear in a vacuum. It emerged from the 2024 merger of Astherus, which focused on yield-bearing products, and APX Finance, which built perpetuals infrastructure. That combination was deliberate, aimed squarely at persistent friction in DeFi perpetuals trading.
Despite multi-billion-dollar monthly volumes, perp activity remains fragmented across chains, exposed to privacy leaks through visible order books, weighed down by idle collateral, and wrapped in clunky UX that forces traders to bridge assets or constantly switch chains. By unifying high-leverage perpetuals with yield-bearing assets under a single non-custodial umbrella, Aster targets a slice of the $100B+ perps market while addressing execution quality and capital efficiency head-on. The design emphasizes MEV resistance, pooled liquidity across chains, and multi-chain access that does not rely on bridges as a default workflow.
To understand how cross-chain transfers work and the risks involved, read our cross-chain bridges overview.
This origin story matters because it explains why Aster’s feature set feels intentional rather than layered on over time. To see that more clearly, it helps to break down where existing perp rails fail in practice.
What Breaks on Today’s Perps Rails
At the system level, most current perp DEXs expose traders to structural inefficiencies that quietly erode edge. These problems compound as size, leverage, and activity increase.
Fragmented UX forces users to hop between chains or bridge assets just to access liquidity or preferred markets. Visible order books leak intent, making traders vulnerable to MEV bots that sandwich orders or front-run directional flow. Order flow often routes through centralized aggregators, creating additional information leakage outside the trader’s control.
Risk tooling also lags behind reality. Retail users rarely get real-time portfolio liquidation previews across positions, leaving them reactive rather than proactive during volatility. At the same time, posted collateral frequently sits idle, generating no yield while funding costs continue to accrue. During strong trends, this combination amplifies carry costs and worsens drawdowns.
These issues are not isolated bugs. They are systemic traits of how most perp stacks are currently assembled.
Aster’s Proposed Edge
Aster’s response is not a single feature but a coordinated design shift. The platform combines dual-mode trading, a Pro orderbook for granular control, and a Simple 1001x one-click mode for speed, allowing different execution styles within the same system.
Hidden orders conceal size and direction until fill, reducing MEV exposure. Yield-bearing collateral, such as BNB and USDF, helps offset carry costs rather than leaving margin dormant. Market scope extends beyond crypto into U.S. stock perpetuals, with leverage reaching up to 100x and settlement still handled in crypto.
Crucially, settlement remains non-custodial and on-chain across supported networks, while execution logic operates without forcing users into constant bridging or chain-switching loops. The goal is to remove friction without sacrificing control, and to let execution quality scale alongside leverage rather than breaking under it.
With the problem framing in place, the next step is to learn how Aster’s architecture actually delivers on these promises, starting with its dual-mode trading system and multi-chain settlement design.
How Aster Works
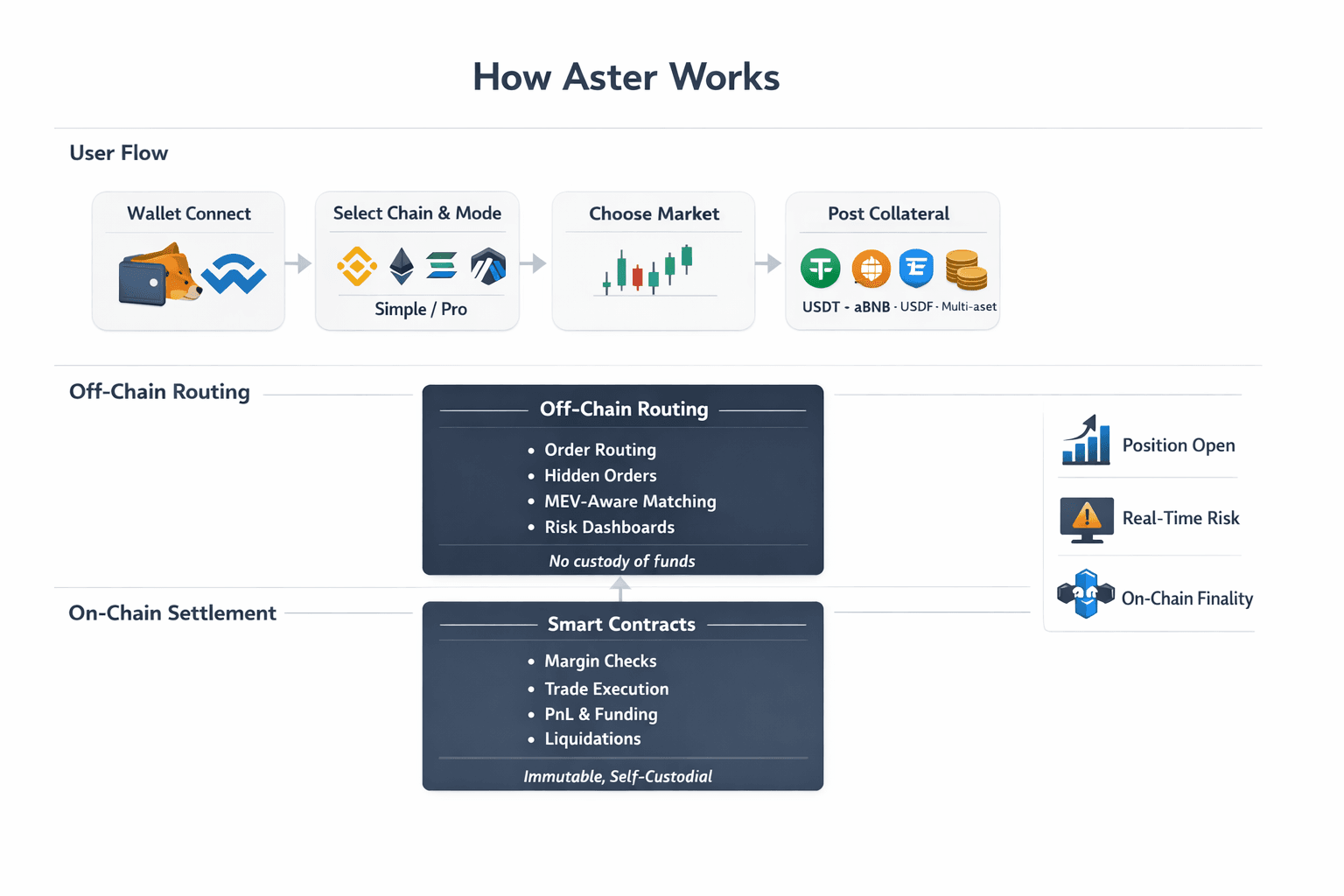 Breaking Down Aster’s Core Operational Mechanics
Breaking Down Aster’s Core Operational MechanicsUnder the hood, everything flows through a single, repeatable cycle that stays consistent regardless of chain or mode.
- The process starts by connecting a self-custodial wallet such as MetaMask or via WalletConnect.
- From there, the user selects a chain, BNB Chain, Ethereum, Solana, or Arbitrum, chooses a trading mode, Simple or Pro, and picks a market.
- Collateral is then deposited or approved, whether that is USDT, yield-bearing assets like asBNB or USDF, or multi-asset collateral in Pro mode.
- Once collateral is posted, automated margin checks run before any order is accepted.
- Orders, either visible or hidden, route through MEV-aware matching logic designed to reduce information leakage.
- Trades execute and settle with positions, PnL, and liquidations finalized directly on-chain.
- Funding updates occur per block in Simple mode and on scheduled intervals in Pro mode, while liquidation risk can be monitored in advance through real-time previews.
The split between responsibilities is intentional. On-chain components handle immutable settlement, collateral custody, and liquidation mechanics. The off-chain routing layer never touches user funds, but it powers hidden orders, optimal execution paths, and risk dashboards. The result is pro-grade control without sliding into CEX-style custody or opaque internal accounting.
This hybrid model sets the foundation, but the real user choice emerges at the next layer: Aster’s dual trading modes.
Simple vs Pro
Rather than forcing all users into a single interface, Aster deliberately splits the experience between accessibility and depth. Simple and Pro are not cosmetic skins; they are two lanes designed around different risk tolerances and execution needs.
Simple mode, branded as “1001x,” focuses on speed and guardrails. It offers one-click entries on select high-liquidity pairs such as BTC and ETH on BNB Chain and Arbitrum. Auto-liquidation buffers and the absence of manual order management make it suitable for aggressive scalps where execution speed matters more than customization. The trade-off is sensitivity. At extreme leverage, even a 0.10% adverse move can wipe a 1001x position, making this lane unforgiving despite its simplicity.
Pro mode unlocks the full orderbook workstation. Traders gain access to hidden limits, bracket orders, multi-collateral margining, and portfolio-level risk views. This lane supports precision execution and cross-margin efficiency, but it comes with a steeper learning curve. Users must manage shortcuts, shared risk across positions, and advanced time-in-force settings. Where Simple reduces error risk by limiting choices, Pro expands flexibility at the cost of complexity.
The distinction cuts both ways. Simple sacrifices customization to provide guardrails, lowering operational friction for less experienced users or speed-focused scalpers. Pro trades ease of use for depth, which becomes essential for larger position sizes, stock perpetuals, or traders managing correlated exposures.
Mode selection feeds directly into Aster’s deeper UX layers. Pro’s orderbook and hidden orders form the platform’s sharpest edge, while Simple offers a fast lane for traders who already understand the risks and want minimal friction.
If you want a deeper breakdown of how the top UXs of top decentralized exchanges compare, see the best decentralized exchanges analyzed on Coin Bureau
Taken together, these dual modes represent Aster’s strongest UX decision. A Pro-grade workstation for precision traders sits alongside a Simple 1001x lane for aggressive scalpers, each with distinct mechanics, risk profiles, and ideal use cases. That separation lets users self-select based on skill, intent, and tolerance rather than forcing a one-size-fits-all interface.
Dual Trading Modes Deep Dive
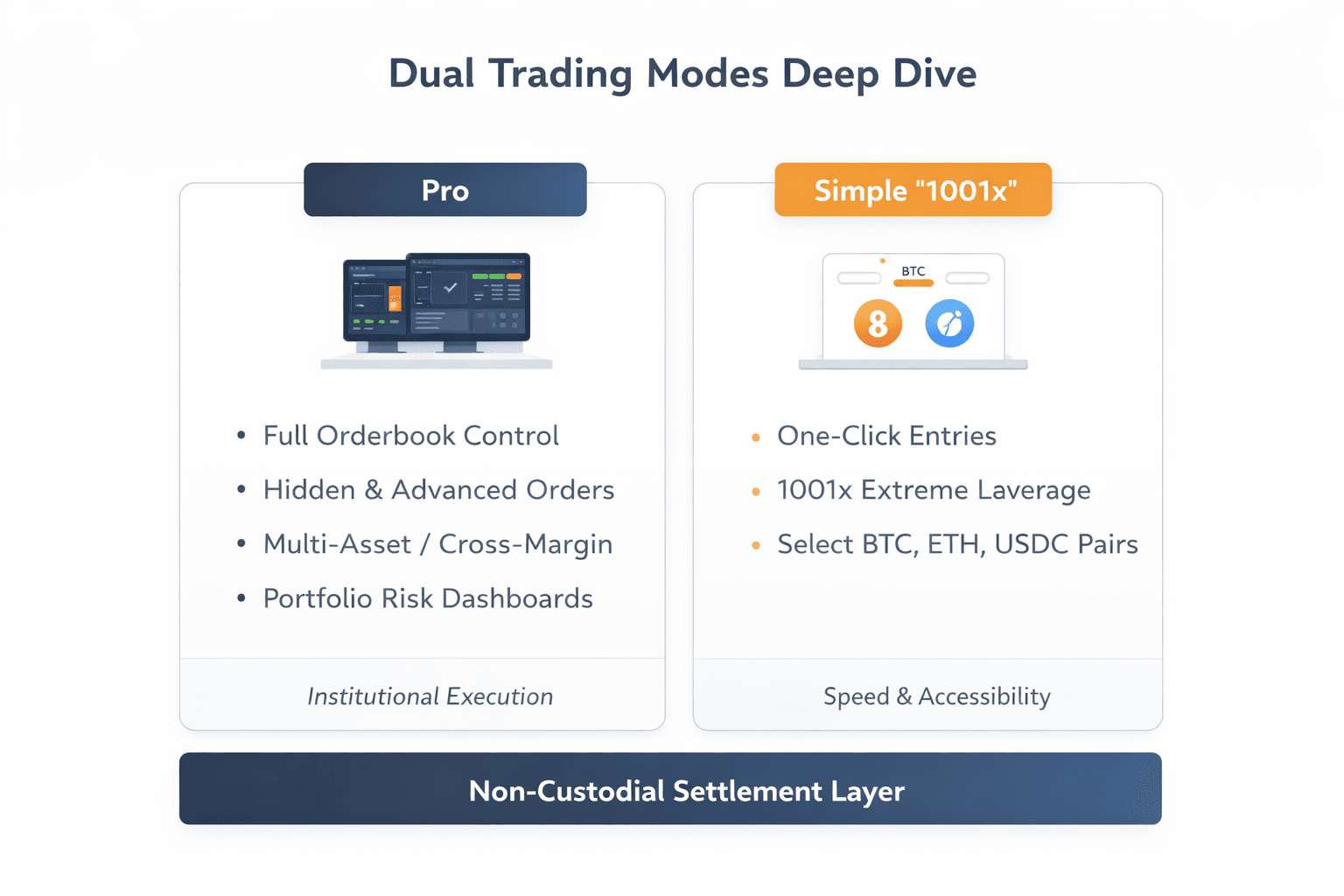 Inside Aster’s Simple And Pro Trading Modes
Inside Aster’s Simple And Pro Trading ModesAster’s most defining product decision is its refusal to force all traders into a single experience. Instead, it deliberately splits trading into two lanes, Pro and Simple, each optimized for a different relationship with leverage, speed, and control.
Pro mode delivers institutional-style execution with full orderbook control, hidden orders, multi-collateral margining, and portfolio-level risk dashboards. Simple mode, branded as “1001x,” strips trading down to one-click entries on select markets, prioritizing speed and accessibility at extreme leverage. Both modes share the same non-custodial, on-chain settlement layer, but the user experience, risk profile, and failure modes differ meaningfully.
This bifurcation allows experienced traders to maximize efficiency without compromise, while newer or speed-focused users avoid common execution mistakes like mis-sized orders or mistimed exits. Pro mode anchors Aster’s reputation as a serious perp DEX, so it makes sense to start there.
Read our beginner’s guide to crypto trading to understand key concepts and tools.
Aster Pro
At its core, Aster Pro functions as a full-featured orderbook environment built for deliberate execution. The interface exposes real-time market depth, supports both single-asset and multi-asset margin modes, and surfaces portfolio-level risk views, including aggregate liquidation prices across positions.
Before execution, users can preview funding and fee impacts, reducing surprises after fills. Order support includes standard limits, hidden limit variants, stop and trailing orders, post-only options, and advanced modifiers. Visual tooling assists with position sizing, margin ratios, and unrealized PnL across the portfolio.
Single-asset mode isolates risk per position using USDT-only collateral, resulting in cleaner liquidation math and simpler mental models. Multi-asset mode pools yield-bearing assets like asBNB and USDF, applying haircuts to shared margin balances. This enables cross-margin efficiency but increases correlation risk, as stress in one position can propagate across the portfolio.
Pro mode rewards precision and discipline. It offers flexibility that scales with position size and complexity, but it assumes the user understands how shared risk behaves under volatility.
Single-Asset Mode
Single-asset mode exists for traders who want strict compartmentalization. Each position uses USDT collateral in isolation, preventing losses in one market from cascading into others.
This setup is especially useful for testing new markets, experimenting with strategies, or maintaining clean risk silos. Liquidation is triggered independently based on entry price and leverage. For example, a 20x BTC perpetual position would liquidate after roughly a 5% adverse move, without affecting other positions.
The trade-off is lower capital efficiency. Collateral cannot be reused across positions, but the clarity and containment it provides often outweigh that cost for disciplined risk management.
Multi-Asset Mode
Multi-asset mode flips the emphasis toward capital efficiency. Instead of isolating positions, it accepts a mix of collateral types such as USDT, as BNB, and USDF into a unified margin pool.
Chain-specific haircuts are applied, typically in the 10% to 20% range for yield-bearing assets, to account for additional risk. This allows traders holding complementary exposures to net margin more efficiently, reducing redundant collateral requirements.
The risk is structural. Under-collateralization in one leg can liquidate the entire portfolio, not just a single position. Multi-asset mode demands continuous monitoring, especially during correlated drawdowns or rapid funding shifts.
This mode favors experienced traders who understand portfolio-level dynamics and are comfortable trading efficiency for tighter risk coupling.
Simple mode takes the opposite approach entirely.
Aster Simple/“1001x.”
Aster Simple, marketed as “1001x,” is designed for speed above all else. It removes upfront deposit flows and minimizes decision points. Users connect a wallet, select BTC, ETH, or USDC pairs on BNB Chain or Arbitrum, choose leverage from 1x to 1001x, and enter with a single click.
To spot thin liquidity before it distorts price action, see our low liquidity crypto indicators guide.
Liquidity is provided by an Automated Liquidity Pool (ALP), which acts as a counterparty to positions and manages hedging internally. At extreme leverage, liquidation sensitivity becomes brutal. A 1001x position can be wiped out by a 0.10% adverse price move. Manual stop placement is unnecessary because the system auto-closes positions via pool mechanics.
Fees in Simple mode differ from traditional maker-taker models. Execution fees typically fall in the 0% to 0.05% range and are paired with leverage-based and PnL-based close fees rather than flat commissions. This structure aligns costs with usage intensity, but it makes frequent micro-scalping expensive if misused.
Simple mode lowers the entry barrier but raises the consequence curve. It is easy to enter and very easy to lose.
Oracles & Pricing Sources
Pricing in Aster aggregates feeds from Pyth, Chainlink, and Binance Oracle to derive mark prices. Circuit breakers exist to limit extreme desyncs, but oracle divergence remains a real liquidation vector.
During periods of volatility, gaps of 0.5 percent or more between feeds can occur. In Simple mode’s high-speed environment, these discrepancies matter more, as liquidation thresholds are razor-thin at high leverage.
Understanding Oracle behavior is essential. Even correct directionality does not guarantee survival when leverage magnifies small pricing differences.
Dumb Mode
“Dumb Mode” pushes Simple mode to its extreme. It removes even slippage controls, enabling true one-tap entries aimed at bots and ultra-short-term traders who prioritize latency above all else.
This mode is not safer. It is faster. It exists for users chasing nano-second edges in highly liquid markets, where customization is a liability rather than a feature.
The contrast is intentional. Pro mode offers control. Simple mode offers speed. Dumb Mode offers raw access.
What ties these lanes together is Aster’s hidden orders layer. By addressing MEV and visibility risks at the execution layer, Aster elevates both modes beyond standard public orderbooks. That hidden execution capability is the platform’s real differentiator, and it deserves focused attention next.
MEV Protection & Hidden Orders
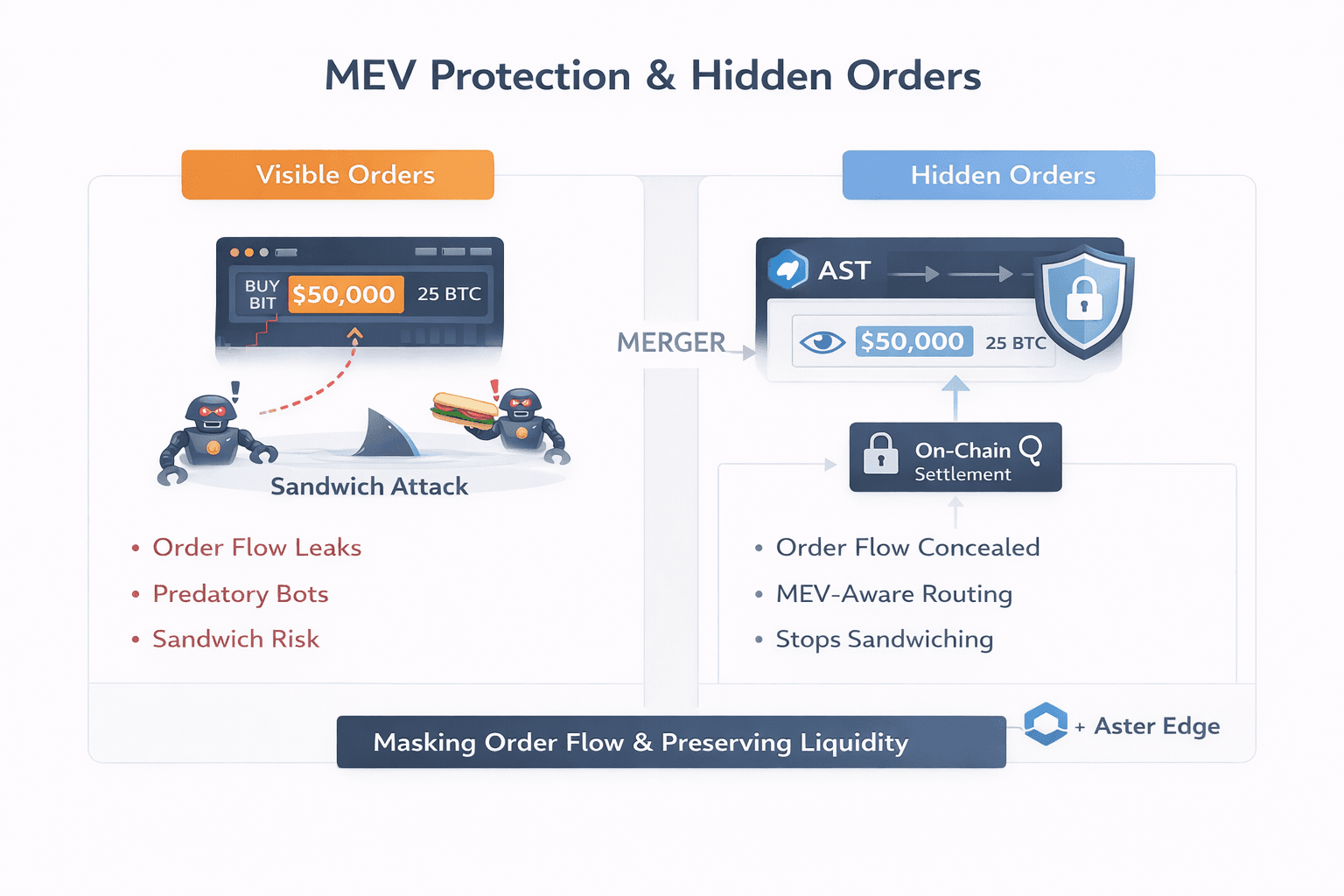 How Aster Reduces MEV And Order Exposure
How Aster Reduces MEV And Order ExposureTo understand why hidden orders matter, you have to start with how visible orders behave on-chain.
A large BTC limit buy sitting in a public orderbook broadcasts intent. MEV bots read it instantly. That signal invites sandwich attacks, adverse selection, and stop-hunting behavior, while leaked order flow increasingly resembles the predatory dynamics seen in centralized venues.
Aster’s response is a combination of hidden limit orders and MEV-aware routing. Hidden orders fully conceal both size and price until a match occurs. Instead of broadcasting intent to the mempool, orders are committed off-chain through Aster’s routing layer before settlement, sharply reducing signaling and sandwich risk. This approach avoids dark pools or fragmented liquidity, preserving access to the main book while stripping away visibility that MEV bots depend on.
The privacy layer integrates directly into Pro mode’s order book. Traders can tap into primary liquidity while remaining invisible, which materially changes execution outcomes for larger tickets, structured entries, or alpha-sensitive strategies.
How Hidden Orders Work
At a mechanical level, a hidden order is a limit-only instruction that never appears in the public book. Neither price nor size is visible. The order waits inside the matching engine and fills only when the opposing flow arrives. For example, a market seller can hit your hidden BTC buy at $50k without anyone knowing that liquidity was resting there beforehand.
Everything remains concealed until after the fill. That eliminates the residual footprints left by iceberg orders and reduces impact compared to visible limits. Mempool handling leans on privacy-preserving techniques, including ZK-based components, to further limit information leakage during execution.
There are still boundaries. Hidden orders cannot manufacture liquidity or protect against structural conditions. Thin books, wide spreads, oracle shocks, low-liquidity hours, or major news events can still result in slippage or missed fills. This is not a tool for illiquid assets or macro-event spikes. It works best when paired with sufficient depth and normal market conditions.
For traders who want to use it actively, the deployment flow is simple and repeatable, which highlights Pro mode’s execution polish.
Step-by-Step: Place a Hidden Order on Aster Pro
Placing a hidden order follows a consistent sequence designed to hold up under pressure.
- Start by connecting your wallet and selecting the desired perpetual market, leverage, and position size within the Pro interface.
- Next, set your limit price. Hidden orders are strictly limited-only. If you are scaling or managing exits, add take-profit or stop-loss brackets at this stage.
- Then toggle the “Hidden Order” option. The system applies invisibility automatically.
- From here, select modifiers such as reduce-only or specific time-in-force settings to control how the order behaves if conditions change.
Before confirming, review the order in the Open Orders panel. The eye-slash icon confirms that the order is invisible to the public book. Once placed and confirmed on-chain, the position settles normally after fill, with public visibility only post-execution.
There are a few common mistakes worth avoiding:
- Hidden orders cannot be market orders or stops. Always use reduce-only for closing trades to prevent accidental exposure increases.
- Double-check time-in-force settings to avoid stale orders hanging during volatility. When conditions are unstable, test with a smaller size before committing to full exposure.
Hidden orders are most powerful in Pro mode, but Aster’s broader appeal comes from how this privacy layer scales across assets and chains.
Hidden execution delivers Aster’s privacy edge, but its reach extends beyond crypto-native markets. That breadth becomes clearer when mapping supported assets, where stock perpetuals introduce a distinct twist to the platform’s market lineup.
Markets, Chains & Supported Assets
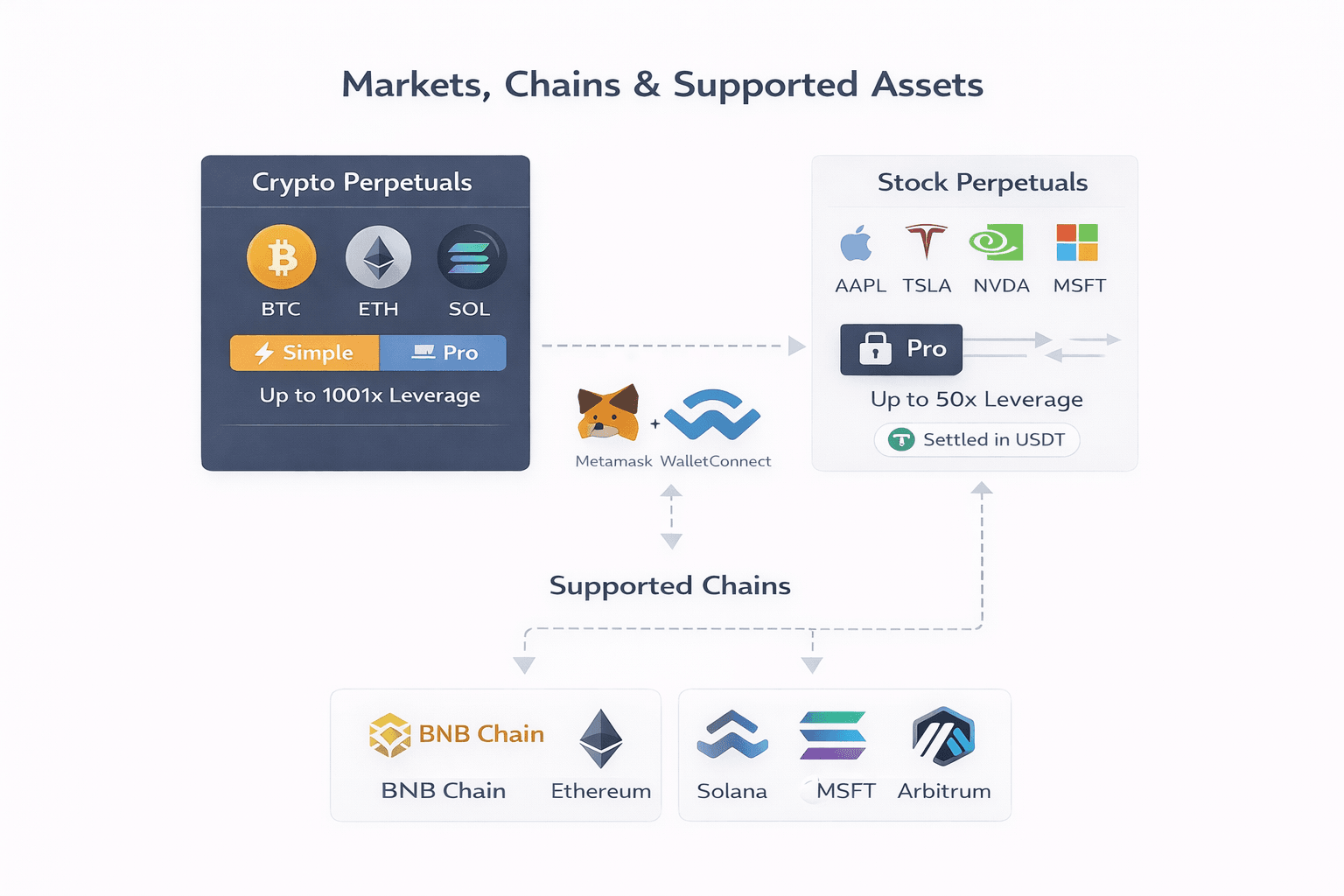 Supported Markets Chains And Assets Overview
Supported Markets Chains And Assets OverviewThe platform brings crypto and stock perpetuals into a single dashboard, but it does so through native multi-chain deployments rather than abstraction layers that hide reality.
Wallet connection determines the active chain, and liquidity routing happens intelligently in the background. That reduces the need for manual bridging, but it does not eliminate chain-specific behavior. Users still interact with native gas tokens, RPC performance, and congestion patterns on each network.
Crypto perpetuals are available across both Simple and Pro modes with deep liquidity. Stock perpetuals, by contrast, live exclusively in Pro mode, operate with lower leverage bands, and are settled in USDT using Pyth-based pricing. The result is TradFi-style exposure without brokers, custody accounts, or market-hour constraints.
“Unified” smooths the experience, but it does not erase the underlying realities. Gas spikes on Ethereum or congestion on Solana can still affect execution and cost, and Aster does not attempt to mask those trade-offs.
Supported Chains
Chain selection shapes both execution characteristics and operational risk, so Aster’s deployment choices are intentional.
The platform currently runs on BNB Chain, which acts as the core liquidity hub, Ethereum for deep L1 liquidity and market credibility, Solana for low-latency execution, and Arbitrum for L2 efficiency. Scroll is in testing, signaling continued expansion rather than a static footprint.
After connecting a wallet, users select the desired chain from a dropdown. It is important to match wallet configuration to the network, such as using Phantom for Solana and MetaMask for EVM-based chains. Gas fees are paid in native tokens, BNB, ETH, or SOL, depending on the chain. Testing with a small size first is recommended to avoid RPC mismatches or configuration errors that can surface during volatile periods.
For a practical look at how the two wallets stack up, read our Solflare vs Phantom guide.
Crypto Perps vs Stock Perps (24/7)
Aster treats crypto and stock perpetuals as first-class instruments, but they operate under different constraints.
Crypto perpetuals cover major assets such as BTC, ETH, and SOL. These markets are available in both Simple mode, with leverage scaling up to 1001x on select pairs, and Pro mode, where leverage generally tops out around 100x or slightly higher, depending on liquidity. Trading and funding run continuously, without session breaks.
Stock perpetuals are Pro-only. The lineup includes large-cap names like AAPL, TSLA, NVDA, MSFT, and AMZN. Leverage typically reaches up to 50x, with recent defaults closer to 10x as standards normalize. Positions are settled in USDT and track real-time indices via Pyth oracles. The key distinction is availability. These instruments trade 24/7, without traditional market close gaps, creating exposure patterns that do not exist in spot equities.
Market Specs That Matter
Tick sizes vary by instrument. Stocks generally trade in larger increments, such as $0.01, while crypto pairs use finer granularity. Funding cadence also differs, running every one to eight hours in some markets or per block in others. Leverage caps range widely, from as low as 10x on illiquid pairs to 1001x on flagship BTC markets in Simple mode.
Notional limits matter as well. On flagship pairs, maximum notional exposure can approach or exceed $1 million, but these limits shift as liquidity conditions change. Specs grow, so previewing them in-app before trading is essential rather than relying on static assumptions.
These markets pair naturally with Pro’s order suite, where precise execution becomes the difference between theoretical edge and realized results. Up next is a closer look at order types and modifiers that give traders control over that execution layer.
Order Types on Aster Pro
 Available Order Types On Aster Pro Explained
Available Order Types On Aster Pro ExplainedExecution is where the edge either compounds or quietly leaks away. Aster Pro treats order types as a coordinated toolkit rather than a menu of isolated buttons, mirroring the depth of centralized pro platforms while settling fully on-chain.
To learn how different order types work in trading, check out our educational guide on crypto order types.
Core Orders
Before diving into individual order types, it helps to anchor them in intent. Each order serves a different market state, and reviewing funding and liquidation shifts before placing size is part of the workflow rather than an afterthought.
- Market orders execute immediately at the best available bid or ask. They work best on highly liquid pairs like BTC and ETH during calmer hours, where slippage often stays below 0.05 percent. They should be avoided during gaps or fast-moving news events.
- Limit orders fill at your specified price or better. They form the backbone of value-based execution and can be paired with the hidden toggle to reduce signaling and MEV exposure.
- Stop Market orders trigger a market fill once a predefined price is breached. These are commonly used for breakout entries or crash hedges, with buffers in the 0.5 to 1 percent range depending on volatility.
- Stop Limit orders trigger a limit order instead of a market fill. This adds price control at the cost of execution certainty, which matters in fast or thin conditions.
- Trailing Stop orders dynamically adjust as the price moves in your favor, such as trailing by 1 percent, allowing trends to run without constant manual intervention.
- Post-Only orders cancel automatically if they would take liquidity. This preserves maker status and can unlock rebates up to roughly 0.01 percent when providing passive liquidity in ranges.
- Hidden Limits conceal price and size until matched. These are limit-only orders designed for alpha-sensitive entries where visibility itself is a risk.
Modifiers That Prevent Accidents
Once the core order is defined, modifiers add guardrails. These settings are visible in the advanced panel and exist to reduce operational errors rather than increase complexity.
- TP/SL References allow users to choose between “Mark” price, which is funding-adjusted and generally safer, and “Last” price, which can be faster but noisier during volatility. This choice directly affects how take-profit and stop-loss brackets trigger.
- Reduce-Only prevents an order from increasing exposure. It is essential for exits, blocking accidental position adds from fat-finger inputs or mis-clicks.
- TIF (Time-in-Force) controls order lifespan. GTC keeps orders live until canceled, IOC fills immediately or cancels the remainder, and FOK requires full execution or nothing. GTC suits patient limits, while IOC and FOK are better aligned with scalps.
When stacked correctly, these tools create self-managing structures. A hidden limit entry combined with a trailing stop, referenced to the Mark price and flagged as reduce-only, plus a post-only modifier on entry, forms a complete bracket that runs without constant supervision.
Fees & Funding
 Aster Fee Structure And Funding Rates Explained
Aster Fee Structure And Funding Rates ExplainedBefore comparing headline rates, it helps to understand how Aster actually charges users in practice. Costs split cleanly into three layers:
- Trading fees on entry and exit
- Funding payments that accrue while holding leverage
- Mode-specific mechanics that change how and when those costs apply
Execution fees on Aster remain competitive, generally ranging from 0.01% to 0.08%. The real cost emerges when leverage, holding time, and funding skew interact. For example, a 50x position paying +0.05% hourly funding compounds to roughly 2.4% per day, regardless of how cheap the entry fee looks. This is why funding dominates outcomes once trades extend beyond short windows.
Aster’s structure deliberately rewards makers in Pro while optimizing Simple for ultra-fast scalps. The table below reflects the current breakdown directly from Aster’s documentation.
Fee Table by Market Type
| Market Type | Execution Mode | Maker Fee | Taker Fee | Funding Cadence | Hidden-Order Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crypto perps | Simple (1001x) | 0.005% (as low as) | 0.04% (as low as) | Every block; funding exchanged continuously between longs and shorts (premium index in Simple mode) | Not specified separately in docs; standard maker/taker fees apply | Up to 1001× leverage on selected pairs; ~5% fee discount when paying with $ASTER |
| Crypto perps | Pro | 0.01% (as low as) | 0.035% (as low as) | Hourly funding (dynamic funding rate mechanism) | Not specified separately; standard maker/taker schedule applies | Advanced order types (orderbook perp contracts) with optional ~5% fee discount using $ASTER |
| Stock perps | Pro | 0% | 0% | Typically every 8 hours (sessionless funding schedule) | N/A (no trading fees under current zero-fee campaign) | Zero-fee promo on tokenized US equity perps; max leverage ~50×; notional caps and Harvest/points rules apply |
One point outweighs the table itself: maker and taker fees are entry-level math. Funding determines reality. A 20x BTC long in a +0.1% hourly funding regime pays roughly 2.4% per day in carry, completely dwarfing a 0.035% taker fee.
Funding Cadence Differences
Funding cadence is where Simple and Pro diverge structurally, and misunderstanding this is a common source of losses.
- Simple per-block funding updates continuously. Liquidation prices drift with every BNB or Arbitrum block. In mild skew, this can translate to roughly 0.02% drift per 100 blocks. This structure punishes holds beyond short durations but enables sub-second scalps where funding impact remains minimal.
- Pro scheduled funding resets on predictable eight-hour intervals. This allows traders to time entries and exits around funding windows, making Pro better suited for swing or positional trades where funding is modeled explicitly.
- Implication: Simple is built for fast flips and momentum bursts. Pro is built for structure, sizing, and duration, provided funding resets are respected.
Fee Discounts
Once baseline costs are understood, discounts become incremental rather than decisive.
Paying fees in ASTER unlocks roughly a 5% discount, with VIP1 or higher required. VIP tiers are volume-based. Around $10M in 30-day volume unlocks an additional 0.005% maker rebate, scaling toward –0.02% at higher tiers.
Promotions rotate and should never be assumed. Zero-fee stock perp campaigns appear periodically, and Simple’s dynamic close fees vary by position. Always verify live conditions in-app before sizing.
In isolation, Aster’s fees are competitive but not uniquely cheap. The differentiator that we have not talked about yet is yield-bearing collateral. By allowing margin to earn yield, Aster partially offsets negative funding, turning margin from a pure cost center into a mild tailwind for traders who manage leverage and duration deliberately.
Aster Earn & Yield-Bearing Collateral
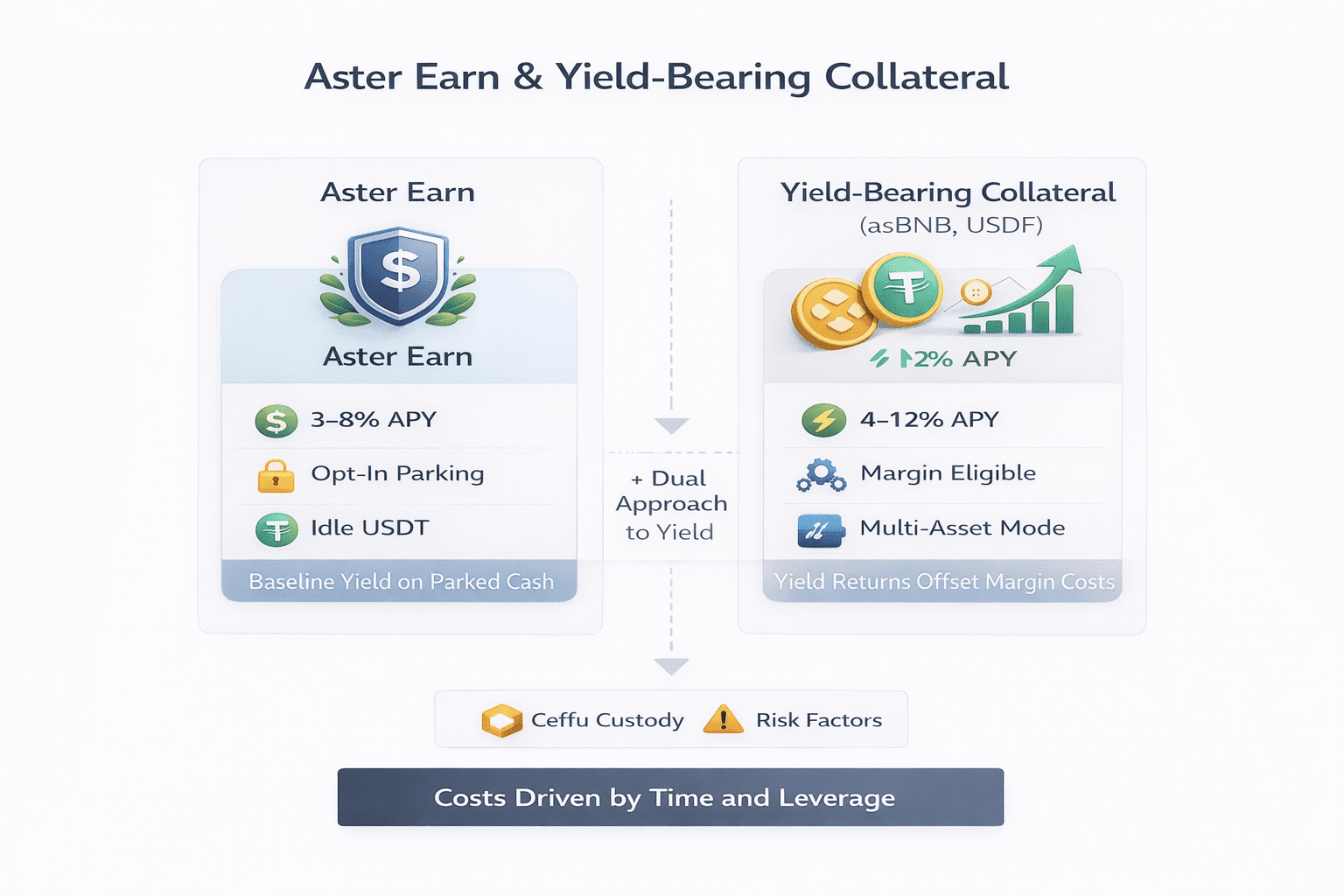 How Aster Converts Collateral Into Yield Streams
How Aster Converts Collateral Into Yield StreamsBefore treating yield as a benefit, it’s important to separate two very different mechanisms that Aster groups under the same umbrella. Earn and yield-bearing collateral solve different problems and carry different risk profiles.
Aster Earn provides a baseline yield, roughly in the 3% to 8% APY range, on idle USDT held via Ceffu custody. This is opt-in parking, not margin-eligible collateral. Yield-bearing collateral, by contrast, embeds returns directly into Pro’s multi-asset margin system, typically targeting 4% to 12% annualized returns. The distinction matters. Earn suits parked cash. Yield collateral exists to offset funding drag while trading, but it introduces custody, strategy, and basis risks that need to be sized deliberately rather than assumed away.
Yield-Bearing Collateral (asBNB, USDF)
When posted as margin in Pro’s multi-asset mode, yield-bearing assets change how carry behaves over time.
Users can post asBNB, a staked BNB wrapper, or USDF, a delta-neutral yield stable, as collateral. Yield auto-rebases to principal. For example, a 6% APY yield can offset roughly –0.03% funding on long positions, improving net carry without relying on price appreciation.
Haircuts apply to these assets, typically in the 15–25% range, which raises liquidation thresholds compared to plain USDT collateral. This makes the margin more efficient over time but also tighter in stress scenarios.
Core risks remain explicit. Exposure to Ceffu custody introduces counterparty considerations. Yield strategies can underperform due to hedge drift or unfavorable funding environments. Redemptions are not instant. In stressed conditions, queues can stretch from one to seven days. The correct way to use this stack is to test with very small positions before scaling.
USDF Mechanics (High-Level, Non-Marketing)
To understand where USDF’s yield comes from, it helps to look at the mechanics rather than the headline rate.
- Mint: Deposit USDT and receive USDF at a $1 peg.
- Deployment: Assets are custodied by Ceffu and deployed into a delta-neutral strategy, typically combining a perpetual short with a spot long.
- Rewards: Yield streams compound weekly to holders, with a rough 7–10% target depending on market conditions.
- Peg: Arbitrage mechanisms enforce stability. Redemptions carry roughly a 0.1% fee and usually settle in one to two days, with a seven-day maximum observed during heavy outflows.
- Stress reality: If the peg deviates by around 5%, collateral haircuts can approach 20%, accelerating liquidations despite ongoing yield. This is not a “set and forget” instrument.
Used correctly, these efficiency layers reward traders who actively model funding and collateral behavior. Used carelessly, they magnify complexity at exactly the wrong moment.
Yield mechanics help offset costs, but they are not the glue that holds Aster together. That role belongs to the ASTER token, which ties governance, discounts, and long-term incentives into a single system.
ASTER Token
 ASTER Token Economics Utility And Risk Overview
ASTER Token Economics Utility And Risk OverviewASTER is not a decorative governance token. It is designed to sit at the center of protocol control, fee flows, and long-term alignment.
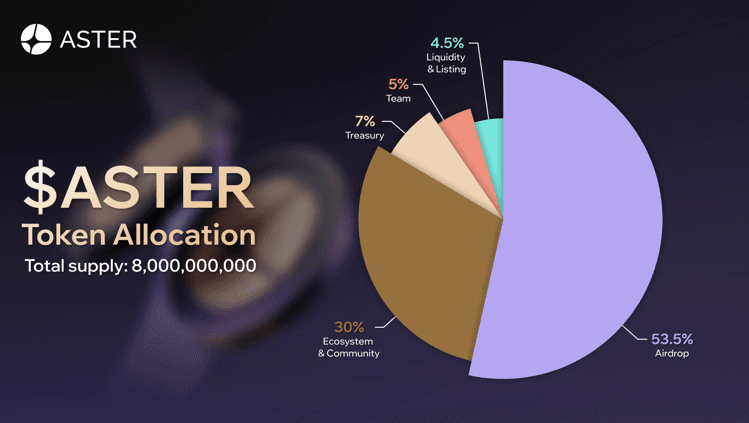
ASTER governs fee parameters, chain expansions, treasury deployment, and upgrade decisions. Protocol revenue is routed toward buybacks and staking rewards, creating a feedback loop intended to support value over time rather than rely purely on emissions. Total supply is capped at 8,000,000,000 ASTER. Of this, 704M tokens (8.8%) were unlocked at the October 2025 TGE for airdrop qualifiers via Spectra points and Gems. The remaining supply follows structured cliffs and vesting schedules to smooth distribution. Unclaimed airdrop allocations are redirected into future rewards rather than recycled immediately.
Aster Token Allocation Overview
Understanding supply pressure starts with how tokens are distributed and when they unlock. The table below captures the full allocation with vesting context.
| Category | % Supply | Amount (M ASTER) | Vesting / Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airdrop | 53.5% | 4,280 | 704M TGE unlock (Spectra/Gems); remainder released over 80 months via governance |
| Ecosystem & Community | 30% | 2,400 | APX migration + grants and marketing; 20-month linear vest (post-swap rate decay) |
| Treasury | 7% | 560 | Fully locked post-TGE; unlocks only via governance |
| Team | 5% | 400 | 12-month cliff (0% year one), followed by 40-month linear vest |
| Liquidity & Listing | 4.5% | 360 | 100% TGE unlock for CEX/DEX liquidity bootstrap |
Why this matters:
A heavy airdrop allocation (53.5%) combined with APX migration captures early traders without VC dominance. Treasury and team locks limit immediate dump risk. The ecosystem’s linear vesting introduces a steady supply through 2027, making governance decisions around unclaimed tokens and emissions worth monitoring closely.
Token Utility
Once allocation is clear, the utility defines whether the token accrues relevance beyond speculation.
- Governance: ASTER holders vote on initiatives such as fee parameters, revenue buybacks, treasury usage, and chain expansion decisions.
- Incentives: Airdrops, staking rewards, and APX → ASTER swaps, with decay mechanics applied over time.
- Revenue Share: A portion of protocol fees, funds, buybacks,s and governance-directed distributions to holders.
- Ecosystem Growth: Grants and marketing initiatives draw from the 30% ecosystem pool.
This mix ties usage, participation, and protocol revenue into a single incentive loop rather than splitting value across disconnected tokens.
Tokenomics Breakdown
 Detailed Breakdown Of ASTER Token Supply
Detailed Breakdown Of ASTER Token SupplyBefore moving into Airdrop specifics, this allocation benefits from a visual snapshot.
The dominant 53.5% airdrop slice highlights the community-first tilt. The 30% ecosystem share reflects ongoing development and liquidity incentives. Treasury, team, and listings appear as thinner segments, reinforcing the absence of outsized insider allocation.
Key takeaways remain consistent. Airdrops prioritize traders and early participants. Ecosystem allocation supports APX upgrades and liquidity over a defined window. Treasury remains locked unless governance approves release. Listing liquidity unlocks at TGE to support depth. Revenue buybacks, controlled jointly by the foundation and governance, act as a stabilizing counterbalance post-launch.
For a simple breakdown of how crypto airdrops work, see our guide to airdrops.
Airdrop Details + Claim Window
With distribution framed, the airdrop mechanics themselves are straightforward.
The 53.5% pool includes 704M ASTER unlocked at TGE for Rh/Au Spectra point earners and Gems participants. The remaining allocation vests gradually over roughly 80 months. APX holders convert into ASTER through a decaying swap mechanism, encouraging early participation. Unclaimed tokens recycle back into reward pools rather than being burned or redistributed arbitrarily.
The claim window opened at TGE in October 2025 and has since closed. No token approvals were required during claiming. Phishing risk remains the primary threat vector.
How to Buy ASTER
 Steps To Buy ASTER Token
Steps To Buy ASTER TokenASTER primarily trades against USDT and is accessible through both centralized and decentralized venues, each with different trade-offs.
Centralized exchanges offer speed, liquidity, and fiat on-ramps, making them more approachable for newer users. Decentralized exchanges appeal to self-custodial users who want to avoid KYC, but they require comfort with gas fees, slippage, and contract verification. BNB Chain acts as ASTER’s native liquidity hub, generally offering the lowest fees and smoothest execution.
This is not advice. Always check fees, spreads, and regional limits before proceeding.
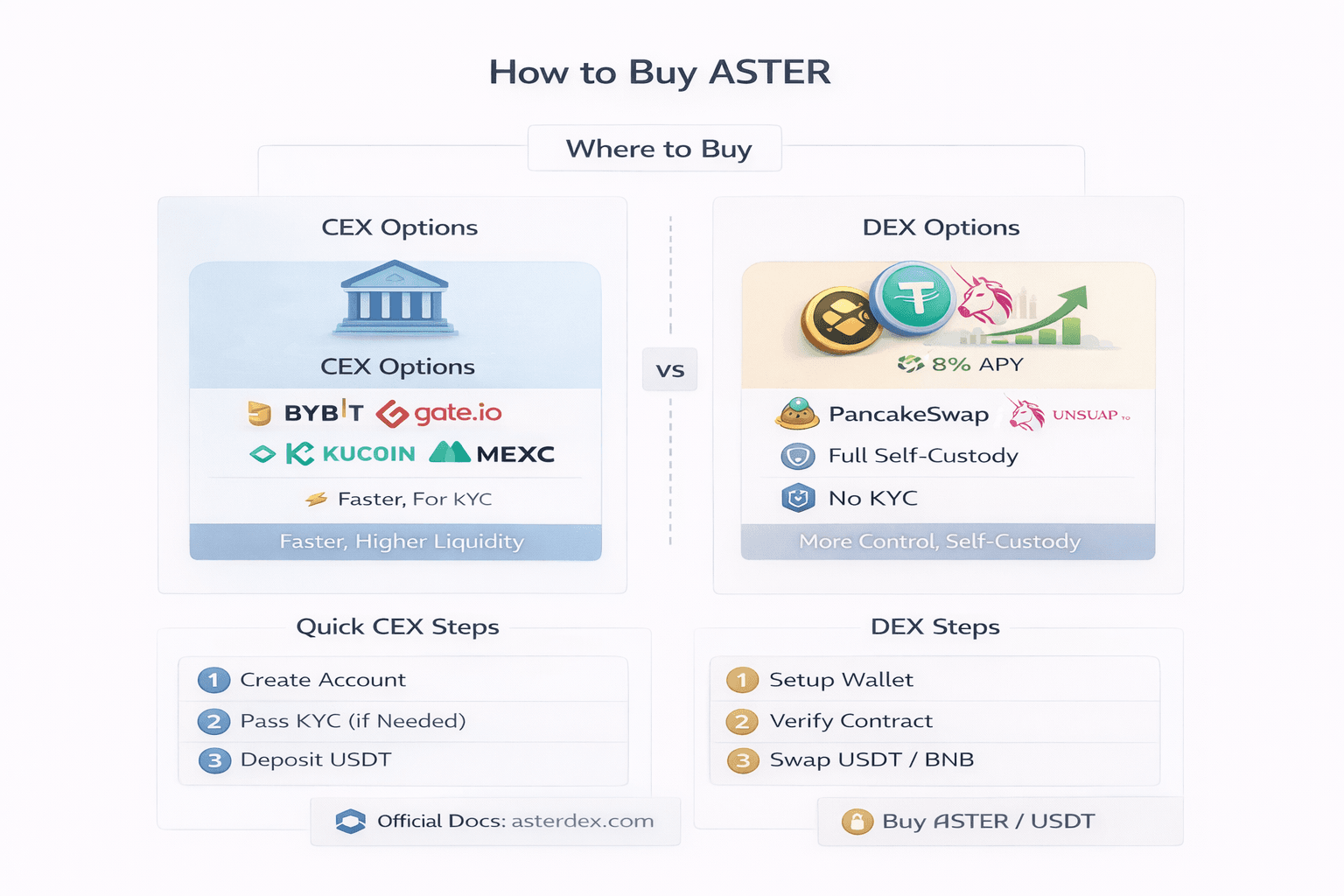
Where to Buy
Before choosing a venue, it helps to align the purchase path with your priorities: convenience versus control.
- CEX options provide the highest liquidity and easiest fiat access. ASTER/USDT is listed on major platforms including Bybit, Gate.io, KuCoin, MEXC, and HTX. Typical spot taker fees sit around 0.1%, with frequent trading campaigns or fee incentives.
- DEX options support full self-custody. PancakeSwap V3 on BNB Chain and Uniswap V3 on Ethereum allow ASTER swaps using USDT or BNB. Slippage typically ranges from 0.3% to 1% for trades above $1,000, depending on liquidity and timing. Always verify the contract address via official documentation before swapping.
A simple rule applies here. Choose CEX for speed and fiat access. Choose DEX for no-KYC control, but only after verifying contracts through asterdex.com or official docs.
Quick CEX Steps
For users starting with a centralized exchange, the process is straightforward and usually takes 5–15 minutes after setup. Security should be prioritized from the start.
- Create account+security: Sign up on Bybit, MEXC, or Binance. Enable two-factor authentication using Google Authenticator and set a withdrawal whitelist limited to one or two trusted addresses.
- KYC (where required): Upload ID and selfie. Approval typically takes 5–30 minutes. KuCoin often allows small buys without full verification.
- Deposit USDT: Fund the account via card with a 2–5% fee, bank transfer with minimal cost, or P2P options such as UPI in India on supported platforms.
- Buy ASTER/USDT: Use the spot market. Market orders fill instantly; limit orders give price control.
- Withdraw to personal wallet (recommended): Send ASTER to MetaMask or Trust Wallet on BNB Chain. Copy addresses carefully and start with a small test transfer, such as $10.
- Mini security checklist: Enable 2FA everywhere, never share seed phrases, whitelist withdrawals, install apps only from official sources, and activate anti-phishing codes.
For an updated look at top trading platforms, see our best crypto exchanges review.
DEX Steps
For users comfortable with self-custody, DEX access removes intermediaries but adds responsibility.
DEX usage requires a wallet and gas fees, typically a few dollars in BNB or ETH. BNB Chain is often preferred for lower costs.
- Wallet setup: Use MetaMask or Trust Wallet. Add BNB Chain RPC manually if needed, confirm chain ID 56, and fund the wallet with BNB and USDT.
- Gas token: Hold a small amount of BNB for transaction fees.
- Verify token contract: Confirm the official ASTER contract address from docs.asterdex.com. Cross-check ownership and renounce status on BscScan.
- Swap: Use PancakeSwap on BNB Chain or Uniswap on Ethereum. Swap USDT or BNB for ASTER. Keep slippage under 1% and test with around $100 before scaling.
- Confirm: Review the transaction on BscScan or Etherscan and add ASTER to the wallet token list.
- Post-swap hygiene: Start small, confirm receipt, and revoke token approvals afterward using tools like revoke.cash.
Compare leading DEXs and how they differ, check out the best decentralized exchanges analysis.
Storage Options
Once purchased, storage choice depends on usage and risk tolerance.
- Hot wallet (MetaMask or Trust): Convenient for trading or staking. Suitable for daily use, but exposed to browser and phishing risk. Hardware signing is recommended if supported.
- Hardware wallet (Ledger or Trezor): Best for long-term storage. Transactions are signed offline, making this ideal for holdings above $1,000. BNB Chain support is available.
- Exchange wallet: Convenient but custodial. Suitable only for small balances or short-term trading. Avoid storing more than a minimal portion of your portfolio.
- Trade-offs: Hot wallets are fast but riskier. Hardware wallets are secure but slower. Exchanges are easy but attractive targets. For India-based users, a hardware wallet combined with multisig offers a balanced approach.
To explore leading wallet options and features, read our best crypto wallets analysis.
Aster vs Hyperliquid
 Comparing Aster And Hyperliquid Across Key Metrics
Comparing Aster And Hyperliquid Across Key MetricsAt the top of the perp DEX stack, Aster and Hyperliquid dominate volume and mindshare, but they are solving very different problems. Both regularly sit inside a combined $13B+ daily volume bracket, yet their design choices pull traders in opposite directions: Aster leans wide, flexible, and multi-chain, while Hyperliquid goes narrow, deep, and sovereign.
Think of this less as “which is better” and more as what kind of trader each platform is built to serve.
High-Level Positioning
Aster operates like a multi-chain kitchen sink for active retail and semi-pro traders. It blends crypto perps, stock perps, extreme leverage, hidden orders, and yield-bearing margin into one interface, prioritizing flexibility and optionality.
Hyperliquid, by contrast, is an L1 purist. Everything lives on its own chain, optimized for raw order book depth, ultra-low latency, and institutional-grade consistency. Fewer features, fewer chains, fewer distractions — but exceptional execution stability.
Head-to-Head Snapshot
| Dimension | Aster | Hyperliquid |
|---|---|---|
| 24h Perp Volume | $4.27 billion | $9.26 billion |
| Open Interest | $1.2B avg ($2B peaks, volatile) | $3.2B stable (ATH $4B) |
| Max Leverage | 1001x Simple BTC/ETH (0.1% liq sensitivity); 50x Pro / stocks | 50x max with multi-tier ADL backstop |
| Fees (BTC Perp) | Pro: maker 0.01%, taker 0.035%; Simple: 0.08% + 0.03% PnL close | Maker rebates up to -0.003%; taker 0.025% (HYPE-tiered) |
| Capital Efficiency | Yield collateral (asBNB 6% APY offsets funding) | Tight spreads + cross-margin depth |
| Chains/Markets | 4 chains; crypto + stocks (AAPL/TSLA/NVDA 20–50x) | Sovereign L1; crypto-only |
Data current as of Jan. 29, 2026.
Cost Reality Example
A $10k 20x BTC long illustrates the divergence clearly.
- On Aster Simple, you pay an $8 open fee, $3 close if profitable, plus per-block funding creep. It favors rapid scalps and short holds.
- On Hyperliquid, the same position pays roughly $2.50 taker with predictable 8-hour funding resets. Holds age better here.
The takeaway is simple: Hyperliquid wins on duration; Aster wins on velocity.
Architecture & UX
Aster’s multi-chain infrastructure deploys Pro CLOB and Simple one-click flows across BNB (≈70% of volume), ETH, Solana, and Arbitrum. Hidden orders and optional email login add privacy and flexibility, but native gas fees and chain quirks remain part of the experience.
Hyperliquid’s custom L1 (HyperCore) pushes sub-second latency and 200k TPS with a native CLOB. It feels closer to a CEX than any DEX today, but at the cost of ecosystem lock-in — HYPE staking becomes mandatory for meaningful fee advantages.
Markets & Leverage (Risk Reality Check)
Aster deliberately expands the scope. Stock perps (TSLA 50x Pro, Pyth-pegged 24/7) and 1001x Simple modes push the risk envelope hard. A 0.1% adverse move at max leverage wipes capital instantly. Tail risk is real, but choice is the product.
Hyperliquid stays crypto-focused, and caps leverage at 50x, backed by aggressive ADL mechanics. It survives black swans better, and its $3B+ OI reflects sustained conviction rather than episodic hype.
Fees & Funding
Both platforms are elite, but incentives differ.
Aster Pro rewards makers aggressively, while per-block funding makes it hostile to lazy holds. Hyperliquid’s HYPE-staked rebates and scheduled funding resets favor positional discipline and larger accounts.
Capital Efficiency
Aster’s yield-bearing margin is its most unconventional edge. USDf rebases (7%–12%) can offset negative funding and even flip carry positive under certain conditions, but that yield introduces strategy, custody, and stress risk.
Hyperliquid keeps things simpler. Cross-margin plus deep books deliver implicit efficiency without yield complexity.
Which Should You Pick?
At this level, the choice comes down to what kind of edge you’re trying to extract.
Choose Aster if you:
- Want stock perps, multi-chain access, or hidden orders.
- Chase extreme leverage with yield offsets.
- Operate natively inside the BNB ecosystem.
- Prefer flexibility and speed over structural conservatism.
Choose Hyperliquid if you:
- Prioritize L1 speed and consistent order book depth.
- Trade size and hold positions longer than minutes.
- Prefer conservative 50x caps with ADL protection.
- Stake HYPE for sustained fee advantages.
Neither replaces the other. Many serious traders use both Hyperliquid as the core execution venue and Aster as the tactical edge layer.
Check out out in-depth comparison of Aster and Hyperliquid.
How to Sign Up on Aster
Before trading comes setup, and Aster deliberately keeps this part lean. The platform skips KYC entirely and offers two entry paths depending on how much control you want on day one: a traditional wallet connection for self-custody purists, and an email-based magic link for fast onboarding. Both routes land you in the same Pro/Simple dashboard once complete.
If you’re curious how trading works without identity checks, read the no-KYC crypto exchange guide.
There are no passwords to manage initially, no forced seed phrases mid-flow, and no approval delays. Setup usually takes 2–5 minutes, with gas costs in the $1–5 range depending on the chain. A short first-trade checklist at the end helps prevent the most common early mistakes.
Login With Wallet
If you already run a self-custody stack, this is the cleanest and safest way in. Nothing new is created unless you choose to — Aster simply reads from your existing wallet.
Here’s how the flow works in practice:
1. Navigate: Visit asterdex.com → top-right “Connect” → select the “Wallet” tab.
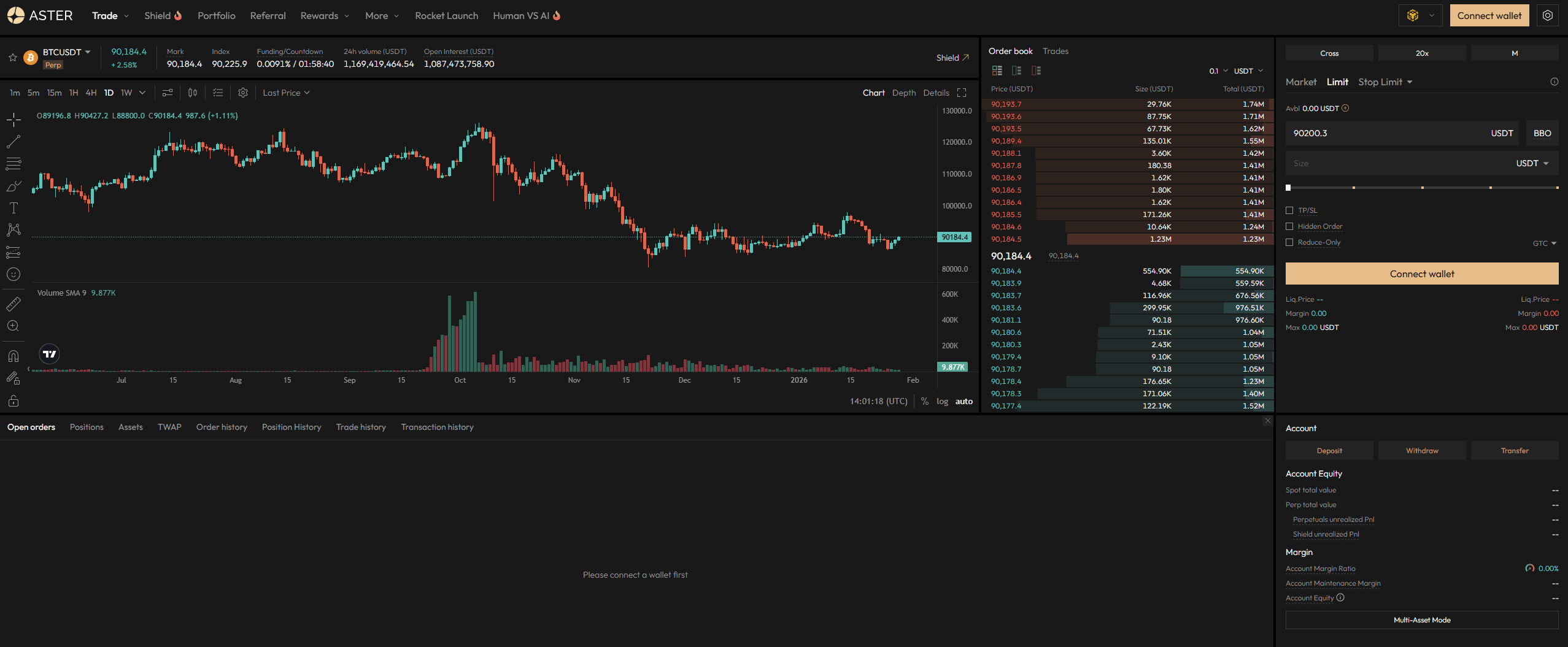
2. Pick provider: MetaMask (EVM), Phantom (Solana), or Rabby (multi-chain recommended).
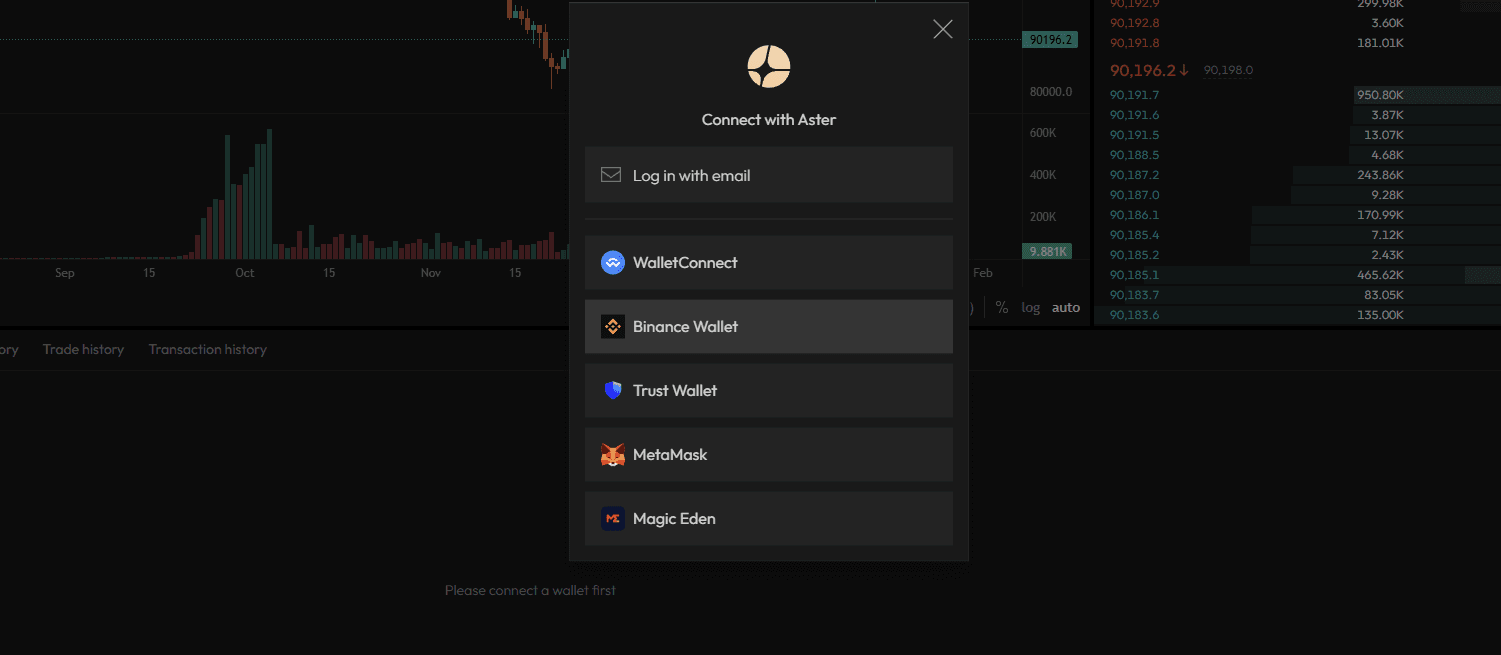
3. Approve: Choose a chain (BNB Chain by default for low gas) and sign the message. No funds move.
4. Fund gas: Keep $2–5 worth of native gas (BNB/ETH/SOL/ARB). Bridge via debridge or Synapse only if needed.
5. Visual check: You should see MetaMask/Phantom connected, BNB selected, and a green “Connected” banner after signing.
- Gas note: BNB Chain averages $0.50 per tx. Avoid ETH during congestion. Start with a $10 USDT test deposit.
Congrats, you're in now and can begin trading!
From the first click, everything remains self-custodial. No keys are generated, rotated, or abstracted away.
Login With Email
The email path exists for speed, not permanence. Aster generates a temporary burner wallet behind the scenes, which you fully control once you export the keys.
This route comes with clear warnings, and you should treat it as a stepping stone rather than a final setup.
1. Start: asterdex.com → “Continue with Email.”
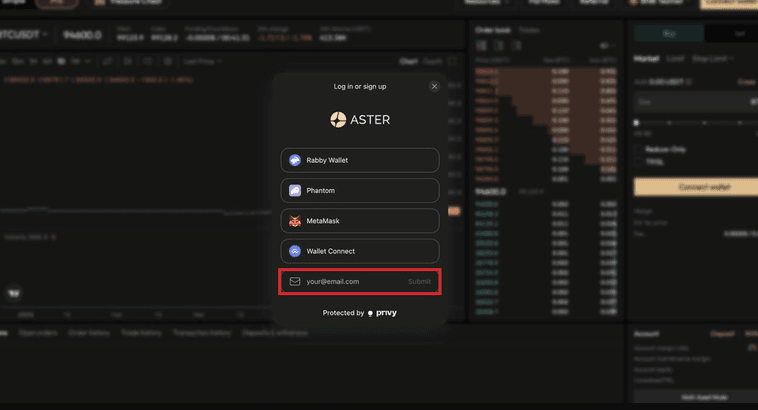
2. Enter email: [email protected] → click “Send Confirmation Code” (expires in 5 minutes).
3. Set Password: Set up a strong password.
4. Deposit warning: A prominent banner reminds you that only Arbitrum One USDT is supported. Sending on the wrong chain means permanent loss.
5. Click the link: You’re auto-logged in, and a self-custodial wallet is generated. Export the seed phrase immediately via settings.
6. Fund: Bridge USDT to Arbitrum and verify on arbiscan.io before trading
- After your wallet address linked to your email receives USDT on Arbitrum, you can begin using this asset as collateral for trading on Aster Pro.
Pro tip: Email login is the fastest fiat ramp (P2P USDT → Arbitrum), but always export and back up the seed to a hardware wallet if you plan to stay.
First Trade Checklist
Before placing your first position, pause here. These checks take under a minute and prevent most early blowups, especially in Simple mode.
- Mandatory pre-size checks:
- Market specs: Confirm leverage caps (1001x BTC?), tick size ($0.5?), and funding cadence (per-block in Simple).
- Risk preview: Check liquidation price (+5% buffer?), projected 1h funding, and max notional ($1M).
- Brackets: Add TP/SL (mark price reference preferred), trailing stops if trending.
- Position sizing: Cap at 1–2% of portfolio. Run a $50 Simple test trade first.
- Double-check: Confirm chain, wallet balance, and oracle status (no visible desyncs).
Both login paths are tested and reliable. Email onboarding removes “no BNB” friction for newcomers, while Wallet Connect keeps full control in experienced hands.
Risks You Must Understand
 Critical Risks Users Should Evaluate Before Participation
Critical Risks Users Should Evaluate Before ParticipationAster’s appeal comes from its extremes: 1001x leverage, fast-moving contracts, and a token model still early in its lifecycle. Those same qualities create tail risks that have wiped out disciplined traders on other venues before. This section keeps things practical by mapping each risk to what to watch and a playbook you can act on, grounded in actual mechanics rather than theory.
No perp protocol is permanently hardened. Treat size as a variable until OI, liquidity, and governance behavior stabilize over time.
Ultra-High Leverage Risk (1001x)
At 1001x, math stops being forgiving. In Simple mode, a 0.10% adverse move in mark price equals full liquidation. A $10k BTC position goes to zero on a 0.1% dip, before funding is even considered. Per-block funding drift compounds this further, with roughly 0.02% per 100 BNB blocks quietly shifting liquidation thresholds.
A concrete example makes this real. A 1001x ETH long entered at $2,500 that ticks to $2,497.50 is instantly wiped. There is no room for manual intervention, and stops are not available.
What to watch:
Funding rate spikes (+0.1% hourly), thin book windows (roughly 02:00–05:00 UTC), and sudden oracle wicks.
Playbook / Rule of thumb:
- Cap leverage at 20–50x max, never trade news, FOMC, or earnings events.
- Bracket every entry using TP/SL with mark-price reference and reduce-only.
- Keep size under 1% of portfolio; preview liquidation with a +5% buffer.
- Treat Simple as ≤15-minute holds only. Use Pro for anything resembling a swing.
Smart Contract & Oracle Risks
Aster runs upgradeable contracts, which means admin keys can modify parameters like leverage caps and oracle routing. Under stress, oracle desync between Pyth, Chainlink, and Binance feeds becomes the real danger. Gaps above 0.5% during volatility can trigger poor fills or unexpected liquidations.
There have been no major exploits so far, but a late-2025 launch still means the system is untested across deep drawdowns.
What to watch:
Governance proposals touching upgrades, oracle divergence alerts around 0.3%, and incident trackers such as DeFiLlama.
Playbook:
- Scale position size based on audit freshness (PeckShield, Salus reports).
- Avoid max leverage between 22:00–06:00 UTC when feeds thin out.
- Set alerts for Oracle gaps above 0.3% and de-risk immediately.
- Monitor admin keys via explorers. No multisig remains a red flag.
Token Concentration & Liquidity Risk
Post-airdrop, the top 10 holders control roughly 20–30% of ASTER. Layered on top are ecosystem unlocks from the 30% pool over 20 months and a team allocation with a 12-month cliff followed by 40-month vesting. These supply events create predictable slippage windows.
Governance adds another vector. If the treasury’s 7% allocation redirects unclaimed airdrops, concentration risk increases further.
What to watch:
Unlock calendars (Dropstab), large holder movements (Arkham), governance votes, and DEX liquidity depth in the $10–20M range.
Playbook:
- Stagger entries and exits around vesting dates with a ±7-day buffer.
- Assume 10–20% slippage on $1M+ ASTER trades.
- Track unlocks against perp volume; decoupling is bearish.
- Diversify beyond ASTER if governance trends toward centralization.
Looking Ahead
 What Aster’s Roadmap Signals Going Forward
What Aster’s Roadmap Signals Going ForwardAster’s roadmap clearly shows its shift in ambition. What began as a multi-chain perp DEX is now positioning toward a foundational L1 ecosystem, anchored around three pillars: core infrastructure, token utility, and ecosystem expansion. The messaging is deliberate. Perps remain the wedge, but the long-term goal is consolidation.
Most 2025 deliveries, including hidden orders and RWA-linked stock perps, are framed as groundwork for a larger push in H1–H2 2026. The L1 is presented as the centerpiece, with timelines labeled “scheduling only” and updates routed through official @Aster_DEX channels.
Full H1 2026 slate
What’s been communicated so far clusters around execution quality, privacy, and composability:
- Continuous UI/UX refinement.
- Shield Mode combines privacy controls with high leverage.
- Strategy orders, including TWAP, to reduce slippage on size.
- RWA expansion with more stock coverage and deeper liquidity (mid-Dec 2025 delivered).
Beyond features, two structural components move into view:
- Aster Chain testnet is already live for community testing.
- Aster Code, a developer toolkit meant to externalize infra beyond the core app.
Mainnet is targeted for Q1 2026, followed by third-party fiat ramps and, in Q2, ASTER staking, governance activation, and Smart Money features like copy trading.
Aster Chain L1
The L1 is designed as a sovereign execution layer rather than a general-purpose chain. The stated goal is to collapse today’s fragmented multi-chain perp liquidity into a single venue optimized for speed, privacy, and depth.
As outlined, Aster Chain mainnet is scheduled for Q1 2026, with testnet already active as of December 2025. The technical focus areas are clear: sub-second latency for CLOB perps, native orderbook infrastructure supporting TWAP and Shield Mode, and ZK-enhanced privacy that extends hidden order mechanics down to the chain layer.
Known wins so far include native fiat integration plans, early dev tooling via Aster Code, and the potential to pull BNB- and Arbitrum-split perp volume into one unified book. This directly challenges Hyperliquid’s L1 advantage by reducing fragmentation rather than outpacing it on raw speed alone.
What could change is equally important. Validator economics, decentralization targets, and the exact migration path away from bridge-dependent liquidity are still undefined. TPS benchmarks remain uncommitted, and bridgeless onboarding is aspirational rather than finalized.
Status and timeline snapshot:
- Testnet: Live and accessible.
- Mainnet: Q1 2026 target, no slips announced as of Jan 26.
- Q2: Staking and governance activation planned.
- Unknowns: Validator count, economic security model, final throughput metrics.
A practical way to think about impact: today’s $5B BNB-centric volume could become a $10B+ unified orderbook. With TWAP slicing, $1M orders could clear without breaching 1% slippage under ideal conditions.
What Would Make It a Real Upgrade
Ambition alone doesn’t make an L1 credible. Whether Aster Chain elevates the platform or adds drag comes down to execution against a short list of hard benchmarks.
Here’s what actually matters post-testnet:
- Security model: At least three independent audits, $2M+ in bounties, and a non-upgradeable genesis state.
- Decentralization: 200+ validators, with the top 10 controlling under 20% of stake.
- Censorship resistance: Fair transaction ordering with MEV capture below 5%.
- Bridge risk: Zero reliance on native bridges, with audited TVL limits enforced.
- Oracle design: Hybrid Pyth/Chainlink feeds sustaining 99.99% uptime in high-volatility simulations.
- Uptime under stress: Ability to handle a 50% BTC flash crash while sustaining 100k TPS.
Watchlist signals:
Testnet TPS and OI simulations, confirmation of the mainnet date, and early governance votes on tokenomics or validator incentives. If delivered cleanly, the L1 turns Aster into a direct Hyperliquid challenger rather than a complementary venue. If delayed or diluted, multi-chain drag persists, and the edge narrows. Roadmap ambition sets expectations. Price will fluctuate regardless. The real signal will be whether infrastructure delivery matches the narrative, without shortcuts or opacity.
Final Verdict
Aster is not a passive trading app or a simplified on-ramp. It is a perps infrastructure, deliberately opinionated and optimized for traders who care about execution, leverage control, and capital efficiency more than comfort. The platform’s real edge comes from how its pieces fit together: dual trading modes, hidden orders with MEV resistance, yield-bearing collateral, and expanding market scope that now includes stocks alongside crypto. Used correctly, it offers tools most perp DEXs still lack. Used casually, it punishes mistakes quickly.
The risks are real and non-negotiable. Extreme leverage, evolving contracts, and token concentration demand discipline and sizing awareness. That said, Aster is unusually transparent about these mechanics, and its roadmap — especially the proposed L1 — directly targets the fragmentation and liquidity leakage that limit current perp rails. If execution matches intent, Aster graduates from “feature-rich DEX” to a serious venue contender.
Bottom line: Aster rewards traders who show up prepared. It favors speed, structure, and strategy over intuition. For disciplined perps traders who understand funding, liquidity, and risk math, it’s one of the more interesting stacks in the market today. For everyone else, it’s better watched than rushed.





