If there’s one principle that defines crypto security, it’s don’t trust, verify. But what happens when verification isn’t possible? This is the issue of blind signing—a long-standing vulnerability in Web3 that has resulted in billions of dollars in stolen assets. Despite advancements in DeFi, NFTs, and smart contracts, many users still approve transactions without fully understanding what they’re signing.
Ledger, a leader in hardware wallet security, is addressing this problem head-on with Clear Signing—a technology designed to ensure that what you see is what you sign. But this initiative isn’t just about improving security for Ledger users—it’s about creating an industry-wide standard that protects everyone in crypto.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- Why blind signing is a critical security risk
- How Clear Signing eliminates uncertainty in transactions
- What it will take for this standard to be adopted across the crypto space
Let’s get into it.
Ledger’s Leadership and the Push for an Industry-Wide Standard
Blind signing is more than just a user-level risk—it’s a systemic problem affecting the entire Web3 ecosystem. While many security solutions focus on protecting private keys, the real issue lies in transaction transparency. A user can have their keys stored in a hardware wallet, but if they don’t understand what they’re signing, they’re still vulnerable.
Ledger is addressing this at its core. With over a decade of experience in hardware wallet security, they’ve built Clear Signing to eliminate uncertainty in transactions. By ensuring that every transaction is displayed in a human-readable format, Clear Signing allows users to verify exactly what they’re approving before signing.
 Ledger Blind Signing Meme. Image via Ledger
Ledger Blind Signing Meme. Image via LedgerBut Ledger isn’t just developing this technology for its own users—it’s working to make Clear Signing an open standard across the industry. This means collaborating with:
- Wallet providers to integrate Clear Signing into their transaction flows.
- DApp developers to encourage the use of standardized metadata that enables human-readable transaction details.
- The broader Web3 ecosystem to ensure that secure signing is accessible to as many users as possible.
A key step in this direction came in February 2025, when MetaMask partnered with Ledger to support Clear Signing. As one of the most widely used Web3 wallets, MetaMask’s adoption of Clear Signing sets an important precedent, helping bring this technology to millions of users. But this is just the beginning—Ledger is actively engaging with other wallet providers, DeFi platforms, and blockchain developers to expand adoption further.
At the heart of this initiative is ERC-7730, a standardized metadata format that allows any dApp or wallet to implement Clear Signing without complex technical hurdles. By making this open-source and accessible, Ledger is ensuring that security improvements are not limited to its own ecosystem—they’re designed to benefit everyone.
The goal is simple: no crypto user should have to blindly sign a transaction ever again. But for this vision to become reality, developers need to integrate Clear Signing into their platforms. Let’s take a look at their role in making this happen.
A Call to Action for DApp Developers
For Clear Signing to become a true industry standard, DApp developers play a crucial role. While Ledger has built the infrastructure to support human-readable transactions, the accuracy and clarity of transaction details depend on developers implementing the right metadata.
Without structured metadata, transactions remain unreadable, leaving users to rely on blind signing—a major security risk. To address this, Ledger has introduced ERC-7730, an open-source metadata standard that allows DApps to provide clear, structured transaction details that wallets can display in a human-readable format.
 An Example Of Blind Signing. Image via Ledger
An Example Of Blind Signing. Image via LedgerHow Developers Can Implement Clear Signing
- Adopt ERC-7730 Metadata – This format enables smart contracts to include structured transaction details, allowing wallets to display them properly.
- Use Ledger’s Developer Tools – Ledger offers plug-in architecture, open-source libraries, and technical documentation to simplify integration.
- Improve User Security – Clear Signing ensures that users can verify transactions before approval, reducing the risk of signing malicious contracts.
By integrating Clear Signing, developers improve transaction transparency, enhance user trust, and contribute to a safer Web3 environment. Ledger has also made integration resources publicly available through its developer portal.
While Clear Signing works well for standard transactions, some interactions—like multicalls—introduce additional challenges. Let’s take a look at how Ledger is working to extend Clear Signing to handle complex transactions more effectively.
Tackling Complex Transactions
While Clear Signing is a major step forward for transaction transparency, not all blockchain interactions are simple. Many DeFi protocols, NFT platforms, and automated smart contracts use multicalls—transactions that bundle multiple actions into a single approval. This can include swaps, staking, token approvals, and contract interactions, all executed at once.
The challenge? Multicalls obscure transaction details, making it harder for users to verify what they are approving. A single signature might grant permissions to multiple smart contracts, some of which could be malicious. Without a way to break down these transactions clearly, even experienced users face security risks.
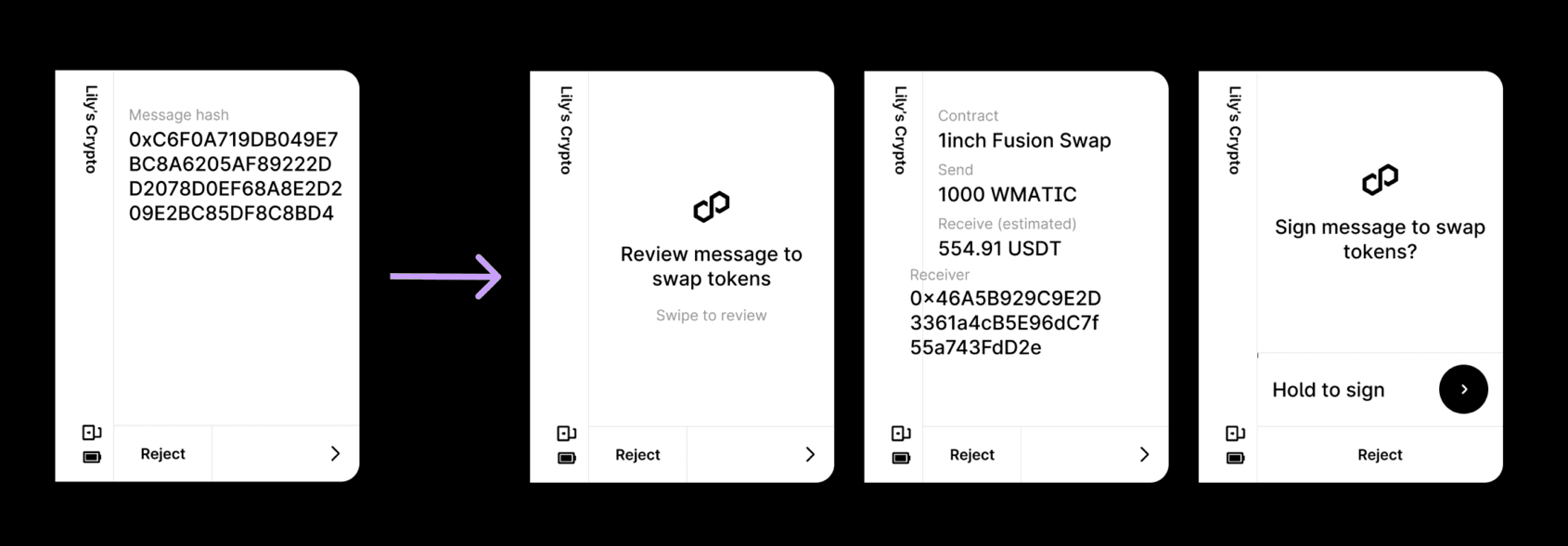 From Blind Signing to Clear Signing. Image via Ledger
From Blind Signing to Clear Signing. Image via LedgerLedger is addressing this by working on enhancements to ERC-7730 and developing new ways to interpret and display complex transactions. Their approach includes:
- Improving Metadata Structure – Refining how bundled transactions are processed, so users can see individual actions within a multicall before signing.
- Collaborating with Developers – Engaging with blockchain teams and DApp creators to ensure Clear Signing can adapt to different transaction types across ecosystems.
- Expanding Cross-Chain Compatibility – Since different blockchains handle multicalls differently, Ledger is working to ensure Clear Signing remains effective across networks.
These improvements will allow users to review and verify every step of a complex transaction, making it easier to spot potential risks. However, for Clear Signing to remain a trusted standard, it needs a governance model that ensures metadata integrity. In the next section, we’ll explore how Ledger is working toward decentralized governance to maintain transparency and trust.
Decentralized Governance
For Clear Signing to remain a trusted and scalable security standard, it must be governed in a way that ensures neutrality, transparency, and long-term reliability. If the metadata that powers Clear Signing were controlled by a single entity, it could introduce centralization risks, potential bias, or even censorship. Worse, if bad actors could manipulate this data, they could misrepresent transaction details, undermining the very security Clear Signing is meant to provide.
To prevent these risks, Ledger is exploring a decentralized approach to managing Clear Signing metadata. This would allow the community—wallet providers, developers, and security researchers—to contribute to, verify, and maintain the accuracy of transaction metadata.
Why Decentralized Governance Matters
- Maintaining Transparency – A decentralized system ensures that Clear Signing data remains openly auditable and resistant to manipulation.
- Preventing Censorship – No single party would have control over what transaction data gets displayed, ensuring fair and unbiased access to Clear Signing.
- Enhancing Security and Trust – By distributing verification across multiple stakeholders, metadata integrity is maintained without reliance on a central authority.
 Billions Of Dollars Get Stolen Every Year Due to Security Breaches in Crypto. Image via Ledger
Billions Of Dollars Get Stolen Every Year Due to Security Breaches in Crypto. Image via LedgerBy decentralizing governance, Clear Signing can evolve into a long-term, community-driven security standard, rather than being dependent on any single company or organization.
How to Enable Blind Signing (and When to Be Cautious)
While Clear Signing is designed to eliminate the risks of blind signing, some decentralized applications (DApps) still require it for certain interactions. This is particularly common in DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, and smart contract interactions that lack built-in metadata support.
If you need to enable blind signing on your Ledger device, follow these steps carefully:
- Unlock Your Ledger Device and open the relevant blockchain app (e.g., Ethereum, Solana, or another network you’re interacting with).
- Access App Settings – On Ledger Live, navigate to Settings within the blockchain app.
- Locate the Blind Signing Option – By default, blind signing is disabled for security reasons. Toggle it on to enable it.
- Confirm the Change – Once activated, your Ledger will allow transactions that do not display full human-readable details.
Important: Always disable blind signing after completing your transaction to minimize exposure to potential risks.
 Sometimes You Have No Other Option Than To Use Blind Signing. Image via Youtube
Sometimes You Have No Other Option Than To Use Blind Signing. Image via YoutubeWhen Blind Signing is Risky (What to Watch Out For)
Since blind signing means approving a transaction without fully understanding its contents, it’s essential to take extra precautions before signing anything. Here are key safety tips:
1. Verify the Website or DApp
- Always check that you are on the correct URL before signing any transaction.
- Avoid clicking links from social media, Discord, or unsolicited messages—phishing attacks often impersonate legitimate services.
2. Double-Check Smart Contract Permissions
- Some transactions grant unlimited access to your funds (infinite approvals).
- Use tools like Revoke.cash or Etherscan’s token approval checker to review and revoke unnecessary approvals.
3. Be Wary of Urgent or Time-Sensitive Requests
- Scammers often create fake "limited-time offers" or urgent warnings to pressure users into signing.
- If a transaction feels rushed, step back and verify it through official channels.
4. Never Blind Sign Transactions from Unknown Sources
- If you don’t fully understand the purpose of a transaction, do not sign it.
- Research the DApp’s official documentation or community discussions to confirm it’s legitimate.
5. Use Ledger’s Secure Screen to Cross-Check Addresses
- Even if blind signing is required, Ledger’s secure screen ensures that transaction details cannot be altered by malware on your computer.
- Compare the recipient address displayed on your Ledger device with the one shown in your DApp to detect potential tampering.
6. Keep Ledger Devices Updated
- Regular firmware updates provide new security enhancements.
Closing Thoughts
Blind signing has long been a weak point in crypto security, leaving users vulnerable to scams and unauthorized approvals. Clear Signing is a major step toward eliminating this risk, ensuring that transactions are fully transparent and verifiable before being approved.
Ledger’s approach goes beyond its own ecosystem. By working to make Clear Signing an industry-wide standard, Ledger is encouraging wallet providers, DApp developers, and the broader Web3 community to prioritize security and user protection. Initiatives like ERC-7730 and collaborations with major wallets like MetaMask mark an important shift toward making blind signing a thing of the past.
However, the responsibility doesn’t rest solely on technology providers. Security is a shared effort—developers must implement transaction metadata, wallet providers must support transparency, and users must remain vigilant in their interactions with smart contracts.
As the crypto ecosystem evolves, Clear Signing represents a significant step forward, but it’s only part of the solution. Continued education, security improvements, and collaboration across the industry will be necessary to create a safer, more transparent digital asset landscape.