The financial landscape has undergone several transformative shifts over the past few decades, each marked by technological advancements that redefine how financial transactions are conducted. One of the most significant shifts was the digitization of finance, spurred by the advent of computers and the internet. This revolution simplified traditional financial operations and introduced entirely new paradigms.
For example, the rapid communication and processing capabilities of digital technology made day trading and real-time stock market monitoring feasible, activities that were nearly impossible in the pre-digital, paper-based era. These innovations have paved the way for more efficient, transparent, and accessible financial processes, setting the stage for the next evolutionary financial step: Tokenizing Real-World Assets (RWAs).
Digitization to Tokenization
Tokenization represents a groundbreaking development in modern finance, echoing the seismic changes brought about by digitization. Just as the internet expanded the financial markets' reach and improved efficiency, tokenization is set to democratize access to investment opportunities and asset liquidity. RWAs, or tokenized real-world assets, refer to converting physical and traditional financial assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. This process imbues these assets with inherent advantages of digital operations, such as fractional ownership, global accessibility, and streamlined executions, which were once restricted to digital currencies and assets alone.
This piece aims to explore the top RWA projects in 2024, highlighting how these initiatives harness blockchain technology's power to integrate tangible assets into the digital domain. By examining the leaders in this burgeoning field, we will delve into how they are not only expanding the scope of what can be tokenized — from real estate and art to corporate debt and beyond — but also how they are setting new standards for financial security, efficiency, and inclusivity. Through this exploration, the article will shed light on the revolutionary potential of RWAs to reshape the financial landscape, much like digitization did before.
What Are RWAs in Crypto?
Real-world assets (RWAs) are tangible and traditional assets such as stocks, bonds, fiat currencies, debt instruments, properties, and others that originate outside the blockchain technology realm. The term "real world" highlights their conventional origins, contrasting with the digital genesis of typical blockchain-based assets. In the context of cryptocurrency and blockchain, RWAs refer to digital tokens that represent a tokenized version of these physical or traditional assets.
Tokenization of a real-world asset involves using distributed networks and blockchain technology to manage these assets by maintaining an accurate and secure digital representation on the blockchain. This technological approach allows for enhanced liquidity, transparency, and global tradeability of assets that were once confined to more rigid and localized markets.
Types of RWAs
Tokenized RWAs come in two broad categories:
- Physical RWAs: These are digital assets that are tokenized versions of assets originating outside of blockchain technology. A well-known example within this category is stablecoins. Stablecoins are digital tokens that represent a specific unit of fiat currency, making them a direct digital counterpart of real-world money. While stablecoins have rapidly gained mainstream adoption, the scope of physical RWA tokenization has broadened significantly. Today, innovative RWA projects are extending their reach to include tokenizing stocks, bonds, credit, real estate, artwork, and many other assets previously digitized for Web3 infrastructure.
- Digital RWAs: These assets are inherently digital and were created as digital assets on the blockchain without a prior physical form. Unlike physical RWAs, which are tokenized as a secondary measure to meet market demand, digital RWAs were conceived and born in the digital realm. Examples of digital RWAs include the digital yuan and various forms of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). The adoption of digital RWAs might lag behind that of physical RWAs due to the current higher demand and familiarity with tokenizing existing physical assets.
Market Dynamics and Regulatory Challenges
The market for RWAs has seen explosive growth recently, evolving from a niche area in 2022 to a burgeoning industry valued at over $6 billion by 2024. This remarkable growth underscores an unparalleled demand for RWAs as investors and businesses seek to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology for traditional assets. Despite this significant demand, the long-term success of the RWA sector critically depends on regulatory and governmental acceptance.
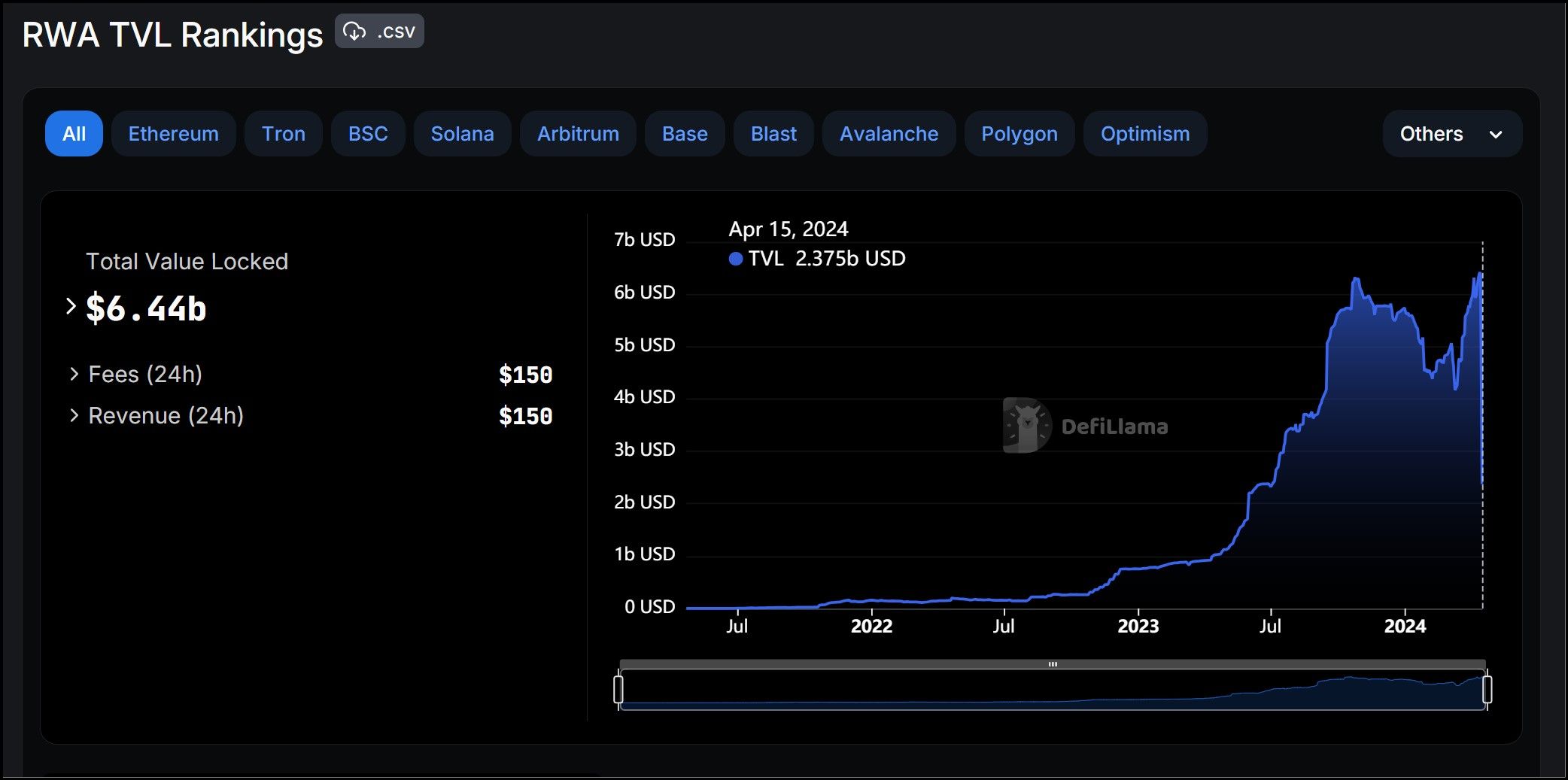 The RWA Sector Has Been Growing Steadily Since 2023 | Image via DeFiLlama
The RWA Sector Has Been Growing Steadily Since 2023 | Image via DeFiLlamaAuthorities' willingness to transition from established record-keeping infrastructures to a speculative and still-emerging blockchain framework is crucial. Regulatory compliance and integrating traditional legal frameworks with innovative blockchain models remain fundamental challenges that could shape the future landscape of RWAs in the global economy.
The Significance of RWA in DeFi
By integrating RWAs with decentralized finance (DeFi), the financial landscape is set to transform, making it more inclusive, functional, transparent, and globally cohesive. The following benefits highlight why RWAs are not just a novelty but a necessary evolution in the democratization and efficient functioning of financial markets:
Enhancing Financial Inclusion
One of the most transformative impacts of RWAs in DeFi is the promotion of financial inclusion. By tokenizing physical and traditional assets, RWAs become accessible to a broader audience. This democratization of access means that people from various economic backgrounds, who might not have had the opportunity to invest in these assets through conventional channels, can now participate in their ownership and benefits. Tokenization breaks down large asset barriers, allowing for fractional ownership and significantly lowering the entry cost for investors.
Improved Composability
Tokenizing RWAs also enhances composability within the DeFi ecosystem. Composability seamlessly integrates and combines different services and assets on a single platform. With RWAs integrated into DeFi, these assets can be used as the base for various DeFi protocols, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending platforms. This integration allows for greater functionality and utility of the assets, as they can be easily swapped, collateralized, or used in yield farming strategies, expanding their use cases beyond traditional confines.
Unified Liquidity
Another significant benefit of RWAs in DeFi is the concept of unified liquidity. When a diverse array of tokenized assets exists on the same blockchain network and is valued under a common currency like Ethereum (ETH), they achieve greater liquidity. This unified liquidity facilitates easier and more efficient cross-asset exchanges, operations that would require considerably more resources and time in traditional financial systems. Such fluidity in asset exchange enhances market efficiency and opens new opportunities for portfolio diversification and risk management.
Enhanced Transparency
The blockchain's pseudonymous and immutable nature ensures that transactions involving RWAs are auditable and transparent to the public. This level of transparency is often unachievable in traditional asset markets, where layers of brokers and regulatory complexity can obscure transactions. In DeFi, however, every transaction is recorded on a public ledger, accessible to anyone for verification, significantly reducing the possibility of fraud and increasing trust among participants.
Global Cohesion
Blockchain technology standardizes how RWAs are stored, recorded, traded, and valued globally. This standardization promotes greater cross-border interest and participation, producing more liquid markets and fostering economic cohesion. Investors worldwide can engage with the same asset classes without the usual bureaucratic and regulatory hurdles, paving the way for a truly global financial marketplace.
Reduced Transaction Costs
Finally, the ongoing advancements in blockchain technology are continuously reducing on-chain transaction fees. These costs are projected to become cheaper than those in traditional financial systems very soon, if not already. Lower transaction costs make it feasible for more frequent and smaller transactions to occur, which is particularly beneficial for individuals and small businesses seeking to maximize their operational efficiency.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Managing RWAs
Smart contracts are fundamental to the process of tokenizing RWAs, mainly because the very concept of "tokens" in the blockchain context is rooted in smart contracts. These self-executing contracts, with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, enable the creation, sale, and exchange of tokens on a blockchain.
Key Roles of Smart Contracts in Enabling RWAs:
- Token Creation: At their core, tokens are a set of smart contracts. RWAs require a digital representation on the blockchain, and smart contracts generate these tokens. This process includes defining the rules for the token’s behaviour, its interactions with other tokens, and how it can be traded or transferred.
- Operational Framework: RWAs run on application-layer technologies built on programmable layers like the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Smart contracts provide the necessary infrastructure to ensure that these assets can operate seamlessly within the existing blockchain ecosystems.
- Security and Compliance: Utilizing established platforms like Ethereum helps leverage their robust security mechanisms, which are crucial for managing assets that have real-world value. Building a new blockchain to avoid using smart contracts could introduce security risks, as newer networks might not offer the same level of security guarantees as established ones like Ethereum.
- Integration with DeFi Protocols: Smart contracts allow RWAs to be easily integrated into various DeFi protocols. This integration enhances RWAs' utility by enabling them to be used as collateral for loans, for example, or as part of more complex financial instruments.
In summary, developing RWAs without smart contracts would require creating a new blockchain infrastructure from scratch—a risky and less secure approach. Smart contracts make it possible to tokenize RWAs efficiently on platforms like Ethereum and ensure that these tokens can operate safely and interactively within the broader DeFi ecosystem. Now that we have a little background on how RWAs are created and what makes them significant let's go over some promising projects building innovative RWA products in Web3.
Top RWA Projects
Before we explore the top RWA projects, users must understand that the RWA sector is extremely sensitive to regulatory oversight, making many RWA projects incredibly speculative. Therefore, I have limited this curation to projects that have established some regulatory acceptance and shown signs of a sustainable ecosystem.
Ethena
 Ethena is Pioneering a New Approach to Stablecoins With its Synthetic Dollar. Image via Ethena
Ethena is Pioneering a New Approach to Stablecoins With its Synthetic Dollar. Image via EthenaStablecoins are the pioneers of Real-World Assets and were in the space before the concept of RWAs was even a thing. Reaching a peak market cap of about $180 billion, stablecoins underscore a critical role in Web3 adoption. Stablecoins typically fall into two categories: Custodial and Non-custodial.
Custodial stablecoins are backed by government-issued securities such as cash or commercial papers. All mainstream stablecoins like USD Circle (USDC), USD Tether (USDT), and First Digital USD (FDUSD) are custodial. Non-custodial stablecoins maintain the dollar peg with other digital currency assets like ETH. Maker’s DAI is a classic non-custodial stablecoin.
What Makes Ethena Unique?
Ethena (USDe) is a non-custodial stablecoin backed by Ether-equivalent assets like ETH and stETH. It uniquely uses age-old trading practices to absorb the volatility subject to USDe. Delta hedging is a well-known technique used by hedge funds to maintain portfolio stability. Ethena also deploys a delta-neutral strategy where the protocol opens equivalent short derivatives positions in ETH for every USDe unit. The gains in short positions offset any drop in the value of USDe, maintaining a stable price.
 Ethna Staggering Returns | Image via Ethena App
Ethna Staggering Returns | Image via Ethena AppChallenges and Criticisms:
- Some experts express concerns regarding the sustainability of its high-yield offers, particularly in bear market conditions. They worry that maintaining such high yields could be challenging without continuous market growth (Cointelegraph).
- There are also concerns about the potential for regulatory issues, given the complex and somewhat opaque nature of its derivatives operations and the lack of traditional collateral backing (Coinspeaker).
Learn more about stablecoins in a deep dive on the Coin Bureau.
Ondo Finance
In the burgeoning world of Web3, the financial narrative has often leaned heavily towards high-risk, high-yield products that boast potentially large returns but come with considerable risk. While these opportunities can be attractive to speculators, Web3's core mission extends beyond just offering speculative yields; it is fundamentally about promoting financial inclusion and ensuring fair access to financial products.
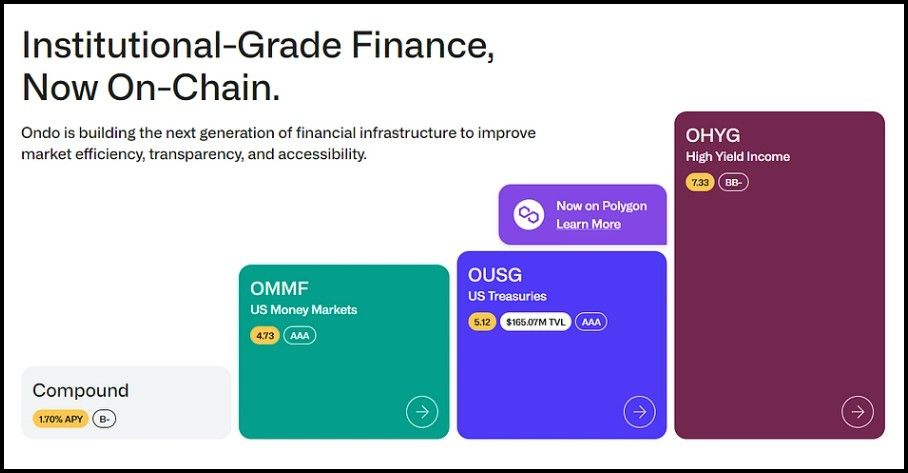 Ondo Finance Offers Tokenized Money Market Products | Image via CoinGecko
Ondo Finance Offers Tokenized Money Market Products | Image via CoinGeckoOndo Finance is leading the charge in shifting this paradigm by introducing a new script in the DeFi sector. Unlike traditional platforms focusing primarily on high-yield, speculative products, Ondo Finance is dedicated to integrating risk-averse investment strategies into the blockchain ecosystem. This innovative platform allows for the on-chain transaction of bond market products, making conservative investment strategies accessible to a broader audience.
Ondo Finance Products
 Ondo Finance USDY Product | Image via Ondo
Ondo Finance USDY Product | Image via OndoOndo's approach is built on the belief that blockchain should host a variety of trading activities, not just those seeking dramatic yields. By tokenizing institutional-grade investment products, Ondo Finance enhances financial inclusivity. This tokenization process democratizes access to traditional financial markets, previously the domain of select investor classes typically within specific geographic confines.
An exemplary aspect of Ondo's offerings is its facilitation of access to the U.S. bond market for non-U.S. nationals. This is particularly revolutionary as it overcomes geographical and regulatory barriers that typically limit such access. Ondo manages compliance issues, ensuring that these traditionally illiquid assets are seamlessly integrated into the digital asset space. Through products like USDY and OUSG Flux Finance, Ondo is making it possible for investors around the world to engage with and benefit from U.S. bond markets without the usual bureaucratic encumbrances.
Compliance is key
Another cornerstone of Ondo Finance is its commitment to regulatory compliance, particularly through its Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols. These measures are crucial in aligning Ondo’s operations with global financial regulations, further ensuring the security and legitimacy of the investments on its platform.
Mantra
Mantra is a layer 1 chain designed for deploying tokenized Real World Assets. It is built using the Tendermint consensus engine and Cosmos SDK, making it interoperable with the Cosmos ecosystem and compatible with Cosmos Hubs.
 Mantra Offers a Regulatory Compliant Infrastructure | Image via Mantra
Mantra Offers a Regulatory Compliant Infrastructure | Image via MantraMantra seeks to become the leading asset tokenization platform in the Cosmos ecosystem. It offers the following features:
- MANTRA Compliance: It is a module that offers tools and services to automate meeting regulatory compliance obligations for issuing RWAs so that Web3 projects can easily establish a blockchain economy. The compliance modules offer frameworks for services like KYC (Know Your Customer), KYB (Know Your Business), AML (Anti Money Laundering), transaction screening, address verification, and more. It also features a Decentralized Identification system and Soulbound NFTs.
- MANTRA Token Service (MTS): It is an SDK that enables the creation, issuing, and management of digital tokens on the Mantra network. Key offerings include:
- Create, issue and manage tokens and NFTs.
- Access control mechanism with the ability to freeze, seize, destroy or transfer tokens.
- Yield and royalty configuration.
- Predictable and low fees
- MANTRA Assets: It is a Dapp that uses the MTS SDK to allow users to issue security tokens on Mantra. It offers customization and management tools for security tokens, that can represent real world assets like stocks.
- MANTRA DEX: As the name suggests, it is a platform for trading RWAs on the Mantra network. It offers low latency trading of RWAs using Automated Market Makers (AMMs). Users can also farm tokens and interoperate within the Cosmos ecosystem.
MANTRA OM Token
The OM token within the MANTRA Chain ecosystem plays a central role in governance, staking, and access to various services. OM token utility:
- Governance: OM token holders can participate in governance decisions, including proposing and voting on network upgrades and changes within the MANTRA ecosystem (Binance Academy).
- Staking: Tokens can be staked to earn rewards, secure the network, and participate in the governance process. Staking also incentivizes token holders by allowing them to earn a passive yield (Binance Academy).
- Access to Services: Holding OM tokens provides access to various services on the MANTRA platform, including special features in the MANTRA DEX and other decentralized finance (DeFi) applications developed on the MANTRA Chain (Binance Academy).
Pendle
Pendle is a decentralized finance application where users can tokenize and trade future yields. Pendle is a testament to the limitless capability of composability in blockchain technology.
 Pendle Introduces Novel Market Speculation Techniques | Image via Pendle
Pendle Introduces Novel Market Speculation Techniques | Image via PendleYield-bearing tokens are digital assets that accrue interest over time. Yield varies based on several factors, including the cost of capital – how much lenders are charging for loans and demand for credit. Yield is another variable that influences the performance of an investor’s portfolio. There are situations where:
- The asset prices increase, but yield plummets due to less demand.
- The asset price doesn’t change or drop, but demand for credit increases yield.
- Yield and the asset price may fall together in bear markets.
- Yield and asset prices rise together in bull markets.
How Pendle Works
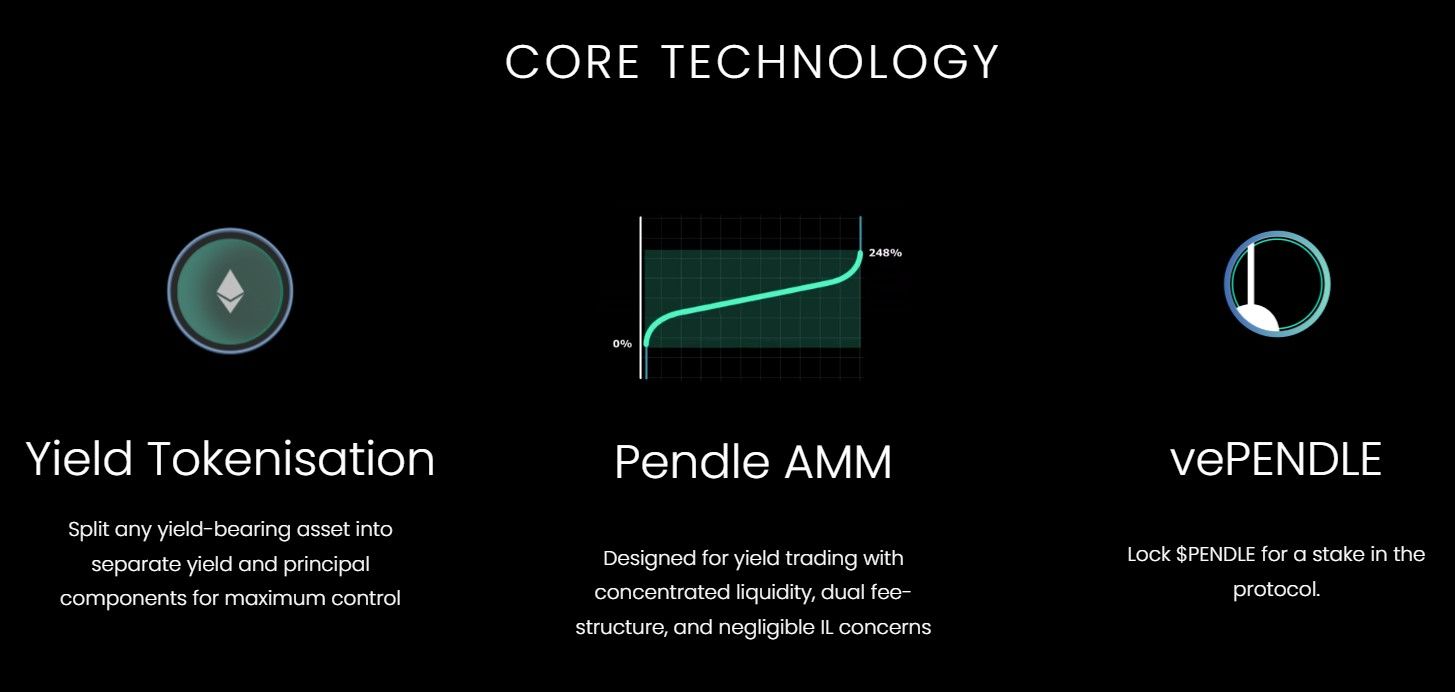 Pendle Architecture | Image via Pendle
Pendle Architecture | Image via PendleThere are three major parts of the Pendle Protocol:
- Yield Tokenization: Yield is traditionally an intrinsic property of a yield-bearing token. The yield protocol automatically issues rewards to any address holding yield tokens. Pendle allows users to abstract away yield and tokenize it as a separate tradable token. Pendle wraps the yield tokens into SY (Standardized Yield) tokens. It then splits SY tokens into two components – PT (Principal Token) and YT (Yield Token), effectively tokenizing yield on the blockchain.
- Pendle AMM: An on-chain platform for trading Principal and Yield tokens
- vePENDLE: Vote-escrowed PENDLE is the governance token of the Pendle ecosystem. PENDLE token holders must stake their tokens on the platform to earn vote-escrowed tokens, which are used in governance decisions. Vote-escrowing ensures only participants with a genuine interest in the growth of the platform participate in Pendle governance.
Traders can formulate crafty investing strategies on Pendle. Consider a scenario where you anticipate a correction in the price of a token. You believe that the price drop will cause a short-term surge in demand for the token, which could lead to an improved yield. You can capitalize on your analysis by shorting the corresponding Principal token, which goes long in its Yield Tokens on Pendle, leading to a better return than only shorting the token in spot or lending it in the capital market.
OriginTrail
OriginTrail is an innovative platform designed to enhance transparency and integrity across various supply chains and other data-dependent sectors using blockchain technology and decentralized knowledge graphs (DKGs). At its core, OriginTrail addresses crucial issues such as data silos, lack of transparency, and inefficiency in data exchange across different stakeholders. Particularly in the realm of RWA, OriginTrail facilitates the tokenization and traceability of assets ranging from agricultural products to manufacturing goods, ensuring their authenticity and origin are verifiable in a tamper-proof system.
OriginTrail Architecture
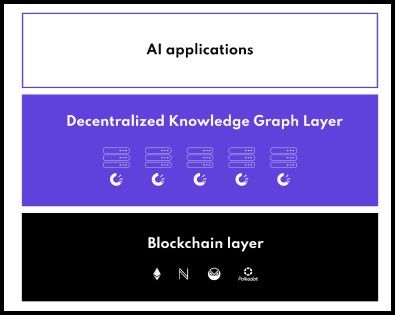 OriginTrail Architecture | Image via OriginTrail Whitepaper
OriginTrail Architecture | Image via OriginTrail WhitepaperThe architecture of OriginTrail is built on a multi-layered framework that ensures wide applicability and robust data integrity:
- Decentralized Knowledge Graph (DKG): This is the backbone of the OriginTrail ecosystem, allowing for the connection and verification of data across multiple sources with high security and reliability. The DKG integrates data into a unified graph database, which is structured to support semantic queries and complex data relationships, making information readily accessible and verifiable across the network.
- OriginTrail Blockchain: While the DKG handles data connections and integrity, the OriginTrail blockchain secures the transactions and interactions within the ecosystem. It operates across multiple chains (including Ethereum, Polkadot, and others) to leverage the strengths of each while ensuring high scalability and interoperability.
- TRAC Token Utility and Tokenomics: The TRAC token underpins the economic model of the OriginTrail network. It is used to compensate node operators for their services in data processing and storage, to facilitate transactions within the marketplace, and as a stake in governance processes ensuring security and compliance with the network’s protocols. The tokenomics are designed to incentivize participation and investment in the network, balancing supply and demand effectively to maintain operational efficiency and network growth.
OriginTrail Use Cases
OriginTrail's versatile architecture supports a wide range of applications, particularly in areas where data authenticity and traceability are paramount:
- Supply Chain Transparency: One of the most significant applications of OriginTrail is in enhancing transparency in global supply chains. Providing a verifiable trail of product journeys from manufacturer to consumer helps prevent fraud, ensure compliance with regulations, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
- Data Marketplace: The OriginTrail ecosystem includes a decentralized marketplace for data where companies can buy and sell authenticated data securely. This not only helps to improve the quality of data available to businesses but also opens up new revenue streams for data providers.
- Compliance and Standards Enforcement: Through its DKG and blockchain layers, OriginTrail can help organizations adhere to various international standards and regulatory requirements by providing an immutable record of compliance and operational data.
These applications demonstrate the flexibility and potential of OriginTrail to fundamentally change how data is handled across different sectors, making operations more transparent, secure, and efficient. Learn more about OriginTrail in its review on the Coin Bureau.
Potential Challenges RWAs Could Face
Here are some challenges RWAs could face as the tech and the sector evolve with time:
Regulation
Regulatory challenges are perhaps the most significant hurdles for the integration of RWAs into Web3. Although the technology and demand exist, effective migration of real-world assets into the blockchain ecosystem is contingent upon comprehensive regulatory frameworks. The complexity of regulation in this context is exacerbated by the fact that each country has distinct laws and attitudes towards Web3 technologies. This disparity can hinder the provision of uniform RWA services globally, as adoption may be confined to countries that are more receptive to such innovations.
Adoption
Beyond regulatory issues, adoption presents another major challenge. For RWAs to truly mainstream, there needs to be a broader willingness among users from all demographics to embrace the tokenization of real-world assets. This includes being open to using cryptocurrencies as a mode of payment and overcoming the steep learning curve associated with new technologies. While current RWA projects are adept at bridging access gaps for users facing geographical or regulatory barriers, such as non-Americans purchasing US stocks or real estate, incentivizing users who already have access to these assets through traditional channels could require significant efforts.
Sustainability
The long-term sustainability of the RWA paradigm is also under scrutiny. While tokenization can enhance accessibility and liquidity, it may also fuel excessive speculation, leading to volatility in assets that are typically stable. This speculative activity could cause unsustainable price surges, potentially destabilizing the market for certain assets. The challenge lies in balancing increased accessibility with the risk of creating overly speculative markets that could detract from the foundational goals of stability and reliability in asset investment.
Each of these challenges—regulation, adoption, and sustainability—plays a crucial role in shaping the future of RWAs in the DeFi landscape. Addressing these issues effectively will be key to ensuring that the integration of real-world assets into the blockchain does not just create new opportunities but also promotes a stable, inclusive, and regulated financial environment.
Top RWA Projects: Closing Thoughts
In our exploration of the top RWA projects in 2024, we've seen how RWAs represent the next evolutionary phase in finance, mirroring past shifts brought about by digital technologies. RWAs facilitate broader financial inclusion, enhanced market liquidity, and increased transparency through the tokenization of traditional assets such as real estate, stocks, and bonds. However, the successful integration of RWAs into decentralized finance hinges on overcoming significant regulatory, adoption, and sustainability challenges. Addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining market stability and ensuring that the growth of RWAs contributes positively to the global financial ecosystem.





