Crypto lending allows individuals to borrow funds or earn interest using cryptocurrency. Borrowers provide their crypto assets as collateral and receive cash or stablecoins, while lenders earn returns by making their assets available to others. Although the structure is similar to traditional lending, the process is facilitated by blockchain-based protocols or centralized crypto platforms rather than banks, with interest typically paid in cryptocurrency or, in some cases, fiat currency.
This guide is for borrowers seeking liquidity without selling their crypto and yield seekers comparing platforms for interest income. We deliver a data-driven comparison of top platforms, explain real risks like liquidation and custody, clarify how crypto loans are taxed, and provide practical use-case recommendations.
Before moving ahead, keep in mind that crypto lending can lead to forced liquidation and total loss, especially at high LTV. You also face counterparty/custody risk when using CeFi platforms. The UK FCA has warned that crypto-linked products are high risk and you should be prepared to lose all your money.
Disclaimer
- Not financial advice. This article is educational and not a recommendation to invest, lend, borrow, or take any action.
- Affiliate disclosure. Coin Bureau may earn commissions from some platform links at no extra cost to you.
- Jurisdictional variability. Legal, tax, and regulatory treatment of crypto lending varies by country and can materially affect your rights and obligations. Always consult local laws and appropriate professionals.
Quick Verdict
Best Platforms by Use Case
Best for Beginners
Crypto.com (Loans)
If you want the most “normal app” experience, Crypto.com is the least intimidating option. Everything happens inside a familiar dashboard with clear in-app quoting before you commit.
Why it wins for beginners
- Guided flow from collateral → quote → borrow → repay
- No wallet approvals, gas fees, or on-chain mistakes
- Borrowing integrated into everyday app features
Beginner watch-outs
Best for Bitcoin Holders
Unchained Capital
If you are BTC-only and custody risk matters, Unchained’s 2-of-3 multisig collaborative custody is purpose-built for that concern.
Why it wins for Bitcoin holders
- Bitcoin-only focus with no asset sprawl
- Collaborative custody reduces single-party control risk
- Fixed-term structure with predictable repayment
Trade-offs
- $150,000 minimum loan size
- Still exposed to BTC drawdowns and margin requirements
Best for High LTV Loans
YouHodler
YouHodler is explicit about very high plan-based LTVs, making it the most aggressive option for maximum borrowing power.
Why it wins for high LTV
- High LTV options published by plan tier
- Clear visibility into fees, term, and price-down limits
Reality check
Best for DeFi Power Users
Aave
Aave offers non-custodial borrowing with live, transparent risk parameters enforced by smart contracts.
Why it wins for power users
- Self-custody via wallet interaction
- Asset-specific LTV and liquidation thresholds
- Composable with on-chain DeFi strategies
Power user hazards
- Liquidations are fast and automatic
- Smart contract and oracle risk applies
Best for Lowest Rates
Binance Loans
Binance often shows the lowest snapshot borrowing costs thanks to tight exchange integration and dynamic rate tables.
Why it wins on cost
- Live in-product rate comparisons
- Instant execution for existing users
- Extremely low minimum loan sizes
Important caveat
How We Ranked the Best Crypto Lending Platforms (Our Methodology)
Most “best crypto lending” lists rank platforms by headline APRs or promotional yields. That approach ignores the risks that actually determine outcomes for borrowers and lenders. Our methodology is designed to surface risk-adjusted quality, not marketing claims, and to make trade-offs explicit.
Our Evaluation Criteria (Weighted Scoring)
Each platform was scored using a weighted framework that prioritizes capital safety, clarity of terms, and real-world usability.
- Maximum LTV ratios (20%)
Higher LTV = higher liquidation probability during drawdowns. - APRs, fees, and rate transparency (20%)
Variable rates can change quickly; disclosure quality matters. - Custody model and rehypothecation risk (15%)
Who controls collateral, and can it be reused? - Term flexibility and liquidation controls (10%)
Grace periods, margin call mechanics, partial liquidation options. - Speed to funding (10%)
On-chain settlement vs KYC/fiat processing. - Geographic availability and compliance (10%)
Platform access and regulatory posture matter, particularly as availability can change by jurisdiction - Track record and incident history (10%)
Past freezes, insolvencies, hacks, or emergency restructurings were treated as material risk signals rather than isolated events. - Transparency and documentation (5%)
Clear terms of service, liquidation explanations, and publicly available documentation were scored higher than opaque or incomplete disclosures.
What We Tested
This is what we actually did for platforms in this guide, so readers can understand how “real” the comparisons are.
For CeFi Lending Platforms
- Quote testing: Checked borrow quotes across common collateral (BTC/ETH) and common loan assets (stablecoins) on the same day
- LTV and liquidation math: Captured max LTV, margin-call level, liquidation level (if disclosed), and any penalties
- Fee inspection: Reviewed interest schedules, fixed fees, early repayment language, hidden spreads where applicable
- Custody review: Mapped where collateral sits, who controls it, and whether rehypothecation is stated or implied
- Workflow checks: Steps from “start loan” to “funds received,” plus repayment and collateral release flow
- Documentation quality: Looked for clear terms, risk disclosures, and loan mechanics explanations
For DeFi Lending Protocols
- On-chain parameter verification: Pulled live collateral factors, max LTV, liquidation thresholds, and liquidation penalties per reserve
- Position simulation: Modeled example borrows to see how health factor behaves with price drops
- Oracle dependency review: Documented oracle sources and liquidation triggers conceptually (protocol-level)
- Contract and audit review (high-level): Confirmed whether audits exist and whether parameters are transparent in official interfaces
- UX reality check: Gas costs, steps required, risk of user error (approval, collateral enablement, borrow, repay)
What We Didn’t Test
- Every jurisdiction and state-level eligibility edge case
- Institutional OTC lending desks and bespoke credit lines
- Full bankruptcy outcome modeling for CeFi lenders
- Stress testing under live crisis conditions
- Long-duration performance of variable rates
- All token-incentive yield loops and leverage looping strategies
- Cross-chain bridge risk and wallet compromise scenarios
- Every asset on every platform
The Best Crypto Lending Platforms Compared (2026)
This section puts the leading crypto lending platforms side by side so you can compare terms, risk models, and suitability at a glance rather than jumping between individual reviews.
Comparison Table
Below is the comparison framework we use across all platforms reviewed in this guide. Each row in the final table is populated using the same data sources and methodology outlined earlier.
| Platform | Minimum loan / debt | Geographic availability | Custody model | Rehypothecation policy | Best for (1-line) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance Loans | $1 equivalent (varies by asset) | Region-restricted by Binance account eligibility | CeFi custodial (Binance holds collateral) | Yes. Collateral is auto-subscribed to Simple Earn while pledged | Very small, short-term loans for active Binance users |
| Crypto.com | Not applicable (no native crypto-backed borrowing product) | Available in 100+ markets; DeFi features subject to regional restrictions | Hybrid. Users access DeFi lending via integrated smart-contract protocols (e.g., Aave) | Not applicable. Funds are lent via DeFi protocols, not rehypothecated on a CeFi balance sheet | Users who want DeFi lending exposure through a familiar app interface |
| YouHodler Loans | $100 | Country restrictions apply (published lists) | CeFi custodial | Not explicitly disclosed in public loan docs | Small borrowers who want a simple, structured UI |
| CoinRabbit | $100 | Broad availability, jurisdiction limits apply | CeFi custodial (cold multisig wallets) | No rehypothecation stated | Fast liquidity with no fixed repayment schedule |
| Unchained Capital | $150,000 | US only (state list published) | 2-of-3 multisig collaborative custody | No rehypothecation | High-net-worth BTC holders prioritizing custody control |
| Nexo Borrow | $50 (stablecoins) / $500 (bank transfer) | Jurisdiction-dependent | CeFi custodial (credit line model) | Not clearly disclosed on borrow pages | Flexible credit-line style borrowing |
| Ledn | $1,000 loan minimum (BTC-backed) | Country and state restrictions apply | CeFi custodial (specialist BTC lender) | No rehypothecation (stated policy) | Bitcoin-only borrowers seeking simple structure |
| Figure (Crypto-Backed Loan) | $5,000 | US, state-by-state availability. Crypto loans are offered through Figure Markets Credit globally. | CeFi custodial (fintech loan structure) | Not disclosed on product page | Borrowers wanting a traditional fintech loan flow |
| SALT Lending | $5,000 | Jurisdiction-dependent | CeFi custodial, contract-based lending | Not clearly disclosed | Longer-term, structured crypto loans |
| Aave | No protocol minimum; constrained by gas + market parameters | Global, permissionless | DeFi, non-custodial smart contracts | Not applicable (on-chain liquidity pools) | On-chain borrowing with transparent parameters |
| Compound (Compound III) | Market-level minimum borrow (e.g. baseBorrowMin) | Global, permissionless | DeFi, non-custodial | Not applicable | Money-market style DeFi borrowing |
| Alchemix | Borrow capped by collateralization (≈50% LTV) | Global, permissionless | DeFi, self-repaying vault model | Not applicable | Users trading capital efficiency for auto-repayment |
Top Crypto Lending Platforms Reviewed (In-Depth)
Every platform below follows the same structure, so you can compare like-for-like
CeFi Platforms
1. Binance Loans | Best for small, flexible loans if you already use Binance
Binance Loans is best if you already use Binance and want a small, fast loan with flexible repayment. The trade-off is simple: your collateral is held custodially and rates are variable, so you must watch LTV thresholds and the live interest table.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Pledge supported crypto as collateral.
- Select borrow asset and loan size.
- Monitor LTV against margin-call and liquidation thresholds.
- Repay principal and interest to release collateral.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: Binance holds collateral for the loan’s duration.
- Counterparty risk: Platform risk applies in addition to market risk.
Pros
- Extremely low minimum loan size.
- Fast issuance for existing users.
- Transparent in-product LTV and pricing mechanics.
Cons
- Custodial exposure.
- Rates can change quickly.
- Jurisdiction-dependent availability.
Pledged collateral is subscribed to Binance Simple Earn Flexible Products while locked. This is a structural detail to understand before treating collateral as inert.
Reference: Binance Loans documentation.
Who it’s best for
- Existing Binance users.
- Borrowers seeking small, flexible loans.
- Users comfortable with custodial risk.
2. Crypto.com Loans | Best for app-based borrowing and CRO users
Crypto.com borrowing is best for users already embedded in the Crypto.com app or exchange who want integrated, exchange-style loans. The trade-off is custodial exposure and variable terms that must be actively monitored.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Users select eligible assets as collateral within the Crypto.com app or exchange.
- Borrow amounts are quoted based on the collateral and chosen LTV.
- Interest accrues hourly on outstanding balances.
- Positions must maintain collateral thresholds to avoid forced closure.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: Crypto.com holds collateral on-platform.
- Counterparty risk: Platform operations and policies affect your position.
Pros
- Borrowing integrated into the Crypto.com app and exchange.
- Flexible tiers and CRO-based benefits for loyal users.
- No external wallets or complex DeFi steps required.
Cons
- Custodial exposure on all loans.
- LTV and APR figures must be confirmed during loan setup.
- Region-dependent access and eligibility.
Loans can be margin-called or liquidated if collateral prices fall or if maintenance requirements aren’t met. Close monitoring is needed during volatile markets.
Who it’s best for
- Active Crypto.com app or exchange users.
- Borrowers who want a seamless integrated experience.
- Users comfortable with custodial risk and monitoring their positions.
3. YouHodler | Best for smaller borrowers who want a fintech-style interface
YouHodler is a strong pick for smaller, everyday borrowers who want a simple, fintech-style “get cash without selling” flow. The trade-off is that terms are plan-based (LTV, fees, and liquidation buffers vary by plan) and availability is country-restricted, so you must verify eligibility before relying on it.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Deposit crypto or stablecoins as collateral and receive the loan amount in fiat (USD, EUR, GBP, CHF) or in BTC or stablecoins (depending on options shown).
- Select a loan plan (plan defines LTV, term, daily fee, and price down limit).
- Repay the loan to receive the collateral back, even if the collateral increased in value.
Sources: How loans work and Loan plans.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: Collateral is held on-platform for the life of the loan (typical for centralized, fintech-style lending).
- Counterparty risk: Your outcome depends on platform operations and custody, not only market price movements.
Pros
- Fintech-style “get cash” UX, designed for smaller borrowers who want simple execution.
- High LTV options are publicly shown (up to 97% value ratio).
- Transparent loan plan table shows LTV, term, daily fee, and price down limit.
Cons
- Custodial counterparty exposure (your collateral is held on-platform).
- High LTV plans usually mean tighter liquidation buffers (price down limit varies by plan).
- Country restrictions are explicit and include major jurisdictions.
Loan plans can run at very high LTV (up to 97% value ratio). High LTV generally leaves less room for price drops before hitting limits, and the “price down limit” varies by plan, so liquidation risk is highly plan-dependent.
Reference:
Who it’s best for
- Smaller borrowers who want a clean fintech interface and quick “borrow against crypto” flow.
- Users comfortable with custodial risk in exchange for convenience and plan-based clarity.
4. CoinRabbit | Best for fast loans with low friction
CoinRabbit is designed for speed and simplicity. It strips borrowing down to the basics: deposit collateral, receive funds, repay to unlock. That makes it useful for fast liquidity, but the custodial model and fixed-fee structure mean you should understand liquidation thresholds before borrowing.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Select a supported crypto asset as collateral.
- Send collateral to the provided address.
- Receive the loan amount shortly after confirmation.
- Repay the loan plus fixed fee to unlock collateral.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: CoinRabbit holds your collateral for the duration of the loan.
- Counterparty risk: Repayment and collateral return depend on platform operations.
Pros
- Very fast loan setup with minimal friction.
- No variable interest rates; costs are disclosed upfront.
- Lower onboarding friction compared to large exchanges.
Cons
- Fully custodial model.
- Limited transparency around liquidation mechanics beyond in-app quotes.
- Fewer advanced controls compared to exchange-based platforms.
Loans are issued at relatively high LTV compared to conservative platforms, which can reduce the buffer before liquidation during sharp market moves. Borrowers should treat CoinRabbit as a short-term liquidity tool rather than a long-duration credit line.
Who it’s best for
- Borrowers who need fast liquidity with minimal setup.
- Users comfortable with custodial lending for short-term needs.
- People prioritizing speed and simplicity over advanced risk controls.
5. Unchained Capital | Best for high-ticket Bitcoin-backed loans with shared custody controls
Unchained Capital is built for borrowers taking large Bitcoin-backed loans who care deeply about custody risk. Its collaborative custody model reduces single-party control over collateral, but minimums are high and flexibility is lower than exchange-based lenders.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Borrower sets up a 2-of-3 multisig wallet with Unchained.
- Bitcoin collateral is deposited into the collaborative custody vault.
- Loan funds are issued after collateral confirmation.
- Repayment releases collateral at loan maturity.
Security & custody model
- Collaborative custody: 2-of-3 multisig shared between borrower, Unchained, and a third-party key agent.
- No unilateral control: Unchained cannot move collateral alone. Custody model.
Pros
- Reduced custody risk versus fully custodial lenders.
- Bitcoin-only focus aligns with long-term BTC holders.
- Fixed-rate terms provide predictability.
Cons
- High minimum loan sizes.
- Less flexible than exchange-style borrowing.
- Bitcoin-only collateral.
While collaborative custody reduces single-party risk, loans still carry market risk. A sharp BTC drawdown can trigger margin requirements or collateral liquidation.
Reference: Rehypothecation policy context.
Who it’s best for
- High-net-worth Bitcoin holders.
- Borrowers seeking large, long-term BTC-backed loans.
- Users prioritizing custody control over convenience.
6. Nexo | Best for flexible credit-line style borrowing (where available)
Nexo’s Crypto Credit Line is designed for borrowers who want ongoing access to liquidity rather than a fixed-term loan. Interest accrues only on the amount drawn, but the product is fully custodial and availability depends on jurisdiction.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Deposit supported crypto into your Nexo account.
- Your credit line activates automatically based on collateral value.
- Withdraw funds up to your available limit.
- Interest accrues only on withdrawn balances.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: Nexo holds collateral while the credit line is active.
- Counterparty risk: Platform solvency and operational risk apply.
Pros
- Flexible, revolving access to liquidity.
- Interest charged only on funds used.
- Low minimum draw amounts.
Cons
- Fully custodial structure.
- Rates and LTVs must be checked in-app.
- Availability varies by jurisdiction.
- Rehypothecation policy is not clearly disclosed.
If collateral values fall and LTV thresholds are breached, Nexo may require additional collateral or initiate automatic adjustments.
Reference: Nexo lending terms.
Who it’s best for
- Users who want flexible, ongoing borrowing.
- Borrowers who prefer credit-line style products.
- Those comfortable with custodial risk for convenience.
7. Ledn | Best for straightforward Bitcoin-backed loans with published base terms
Ledn offers simple, Bitcoin-backed term loans with clearly published base terms. There’s no revolving credit or asset complexity, but flexibility is lower than exchange-style lenders.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Deposit Bitcoin as collateral.
- Select loan amount and fixed term.
- Funds are issued once collateral is confirmed.
- Repay principal and interest to unlock BTC.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: Ledn holds BTC collateral during the loan.
- Platform risk: Borrowers are exposed to Ledn’s operational controls.
Pros
- Clearly published LTV and base pricing.
- Bitcoin-only focus avoids asset sprawl.
- Fixed-rate predictability.
Cons
- No revolving credit or repay-anytime flexibility.
- Bitcoin-only collateral.
- Custodial exposure.
A sharp Bitcoin drawdown can trigger margin calls or liquidation if LTV thresholds are breached during the loan term.
Who it’s best for
- Bitcoin holders seeking simple, fixed-term loans.
- Borrowers who value transparent base terms.
- Users comfortable with custodial BTC collateral.
8. Figure | Best for borrowers who want a “traditional loan” style crypto-backed product (US/state dependent)
Figure’s crypto-backed loans are structured like traditional installment loans, with fixed APRs and scheduled repayments. This appeals to borrowers who want clarity and predictability, but availability is limited to supported U.S. states.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Apply for a crypto-backed loan through Figure’s platform.
- Pledge supported crypto as collateral.
- Receive a fixed-rate, fixed-term loan offer.
- Repay in scheduled installments over the loan term.
Security & custody model
- Custodial: Figure holds crypto collateral for the duration of the loan.
- Regulated structure: Loans are issued under U.S. lending frameworks.
Pros
- Fixed APR and predictable repayment schedule.
- Traditional loan structure familiar to non-crypto users.
- Clear upfront disclosures.
Cons
- U.S.-only with state-level restrictions.
- Less flexible than credit-line products.
- Custodial collateral model.
- Rehypothecation policy is not disclosed on the product page.
Declines in collateral value can trigger margin requirements or liquidation. State-level lending rules may also affect loan availability and terms.
Who it’s best for
- Borrowers wanting a traditional fintech loan flow.
- U.S.-based users in supported states.
- People who value fixed APRs and repayment certainty.
9. SALT Lending | Best for term-based crypto-backed loans with published LTV ceilings
SALT is a strong fit if you want a traditional, term-based crypto-backed loan with explicitly published LTV tiers and an official rates/fees schedule. The trade-off is that terms can vary by jurisdiction and loan length, and higher LTV tiers narrow your liquidation buffer.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Choose a loan term (typically 12, 36, or 60 months) and an LTV tier.
- Deposit supported crypto as collateral into SALT’s custodial setup.
- Review the disclosed APR, fees, and loan terms before acceptance.
- Receive loan proceeds and make payments for the duration of the term.
- Collateral is released after the loan is repaid (subject to the agreement and jurisdictional rules).
Security & custody model
- Custodial: SALT holds the pledged collateral while the loan is active.
- Contract-first approach: Terms, LTV tiers, and fees are published, but can still vary by state and loan duration.
- Key risk lever: Higher LTV tiers reduce the buffer before margin action or liquidation.
Pros
- Published LTV tiers and a clear rates/fees schedule.
- Term-based structure suits borrowers who want a “set it and repay it” loan.
- Multi-term options (shorter and longer durations).
- Minimum loan size is accessible for many borrowers.
Cons
- Custodial collateral model (you rely on the platform’s custody and operational controls).
- Availability and terms vary by jurisdiction, with many U.S. states excluded.
- Higher LTV tiers can compress your liquidation buffer.
- Supported collateral list is narrower than “big exchange” lending menus.
The main trade-off is buffer. At higher LTV tiers, smaller drawdowns can force margin action sooner. Also, state-level availability and product terms can change, so borrowers should confirm eligibility and disclosures for their jurisdiction before committing.
Who it’s best for
- Borrowers who want published LTV tiers and a straightforward term-based loan structure.
- Users who prefer upfront APR/fee schedules rather than “rates on request.”
- People comfortable with custodial collateral and jurisdiction-dependent availability.
DeFi Platforms
10. Aave | Best for on-chain borrowing with transparent, live risk parameters
Aave is best if you want non-custodial, on-chain borrowing with transparent collateral rules. Risk parameters like Max LTV, liquidation threshold, and liquidation penalty are visible per-asset and update via governance and market configuration.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Connect a wallet to Aave and supply collateral assets to a market.
- Enable collateral, then borrow supported assets up to your limit.
- Monitor your Health Factor and per-asset liquidation thresholds.
- Repay to reduce risk and unlock collateral.
Security & custody model
- Non-custodial: Your wallet interacts with smart contracts; there is no centralized custodian holding your funds.
- Smart contract risk: Borrowing relies on protocol code and oracle-driven pricing.
Core concepts: Reserve parameters and Health Factor explanation.
Pros
- Non-custodial borrowing with transparent, per-asset risk parameters.
- Live, public Max LTV and liquidation settings visible per reserve.
- Composability with on-chain strategies and DeFi tooling.
Cons
- Variable rates can rise quickly with utilization.
- Liquidation risk requires active monitoring in volatile markets.
- Smart contract and oracle risks still apply.
Liquidations can occur when your Health Factor drops below 1, typically after collateral price declines or borrow rates increase. Because parameters are asset-specific, you must track both your position and the reserve settings of your collateral.
Reference: Aave FAQ (Health Factor).
Who it’s best for
- DeFi-native users who want non-custodial borrowing.
- Borrowers who value transparent, live risk parameters per asset.
- Users comfortable monitoring Health Factor and liquidation mechanics.
11. Compound | Best for money-market style lending/borrowing with explicit liquidation mechanics
Compound is best if you want a classic DeFi money-market: supply assets, earn yield, and borrow against collateral with clearly defined collateral factors and liquidation rules. The trade-off is that rates and risk parameters are dynamic, liquidations are mechanical (not negotiable), and smart contract/oracle risk comes with the territory.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Supply assets to a Compound market (or supply the base asset to earn interest).
- Enable collateral (market rules apply) to unlock borrowing power.
- Borrow up to your limit based on collateral factors.
- If your borrowing exceeds your allowed capacity, your position becomes liquidatable.
Security & custody model
- Non-custodial: Users interact via smart contracts from their wallet.
- Explicit liquidation mechanics: Liquidation is determined by liquidation collateral factors (separate from borrow collateral factors). Liquidation docs.
Pros
- Non-custodial lending/borrowing with transparent rules.
- Explicit collateral factors and liquidation parameters per market.
- Live, algorithmic interest rates visible per market.
Cons
- Rates can spike quickly when utilization rises.
- Liquidations are automatic when thresholds are breached.
- Smart contract and oracle risk apply, even with audits and governance.
Liquidation triggers are parameter-driven. Compound III specifically uses a liquidation collateral factor that is separate from the borrow collateral factor to maintain a price buffer, and positions become liquidatable when borrowing exceeds the liquidation threshold for their collateral set.
Who it’s best for
- DeFi users who want money-market style lending/borrowing with explicit liquidation rules.
- Borrowers who value transparent collateral factors and protocol-defined risk parameters.
- Users comfortable monitoring collateral health during volatility.
12. Alchemix | Best for “self-repaying” loan design via yield-backed vaults
Alchemix is best if you want liquidity today without scheduled repayments, using yield from your collateral to amortize debt over time. The trade-off is that outcomes depend on yield performance and alAsset liquidity, not fixed interest rates.
Key stats
Data current as of Jan. 8, 2026.
How it works
- Deposit supported collateral into an Alchemist vault.
- Collateral is routed into yield strategies.
- Mint alUSD or alETH up to 50% of collateral value.
- Yield harvests gradually reduce outstanding debt.
Security & custody model
- Non-custodial: Collateral is locked in smart contracts; you control your wallet.
- Strategy risk: Outcomes depend on integrated yield strategies and contract safety.
Pros
- 0% interest on debt.
- Clear, fixed 50% borrowing limit.
- No liquidation mechanics in the traditional sense.
Cons
- Debt repayment speed depends on yield conditions.
- alAsset liquidity and discount can affect exit price.
- Higher smart contract and integration complexity.
Yield compression, strategy underperformance, or smart contract failures can slow or impair debt amortization. While there is no forced liquidation, liquidity and peg risk can become the binding constraint.
References: Alchemist docs and Protocol overview.
Who it’s best for
- Borrowers who can wait and prefer yield-driven amortization.
- Users comfortable with DeFi contract and strategy risk.
- People who want liquidity without selling collateral.
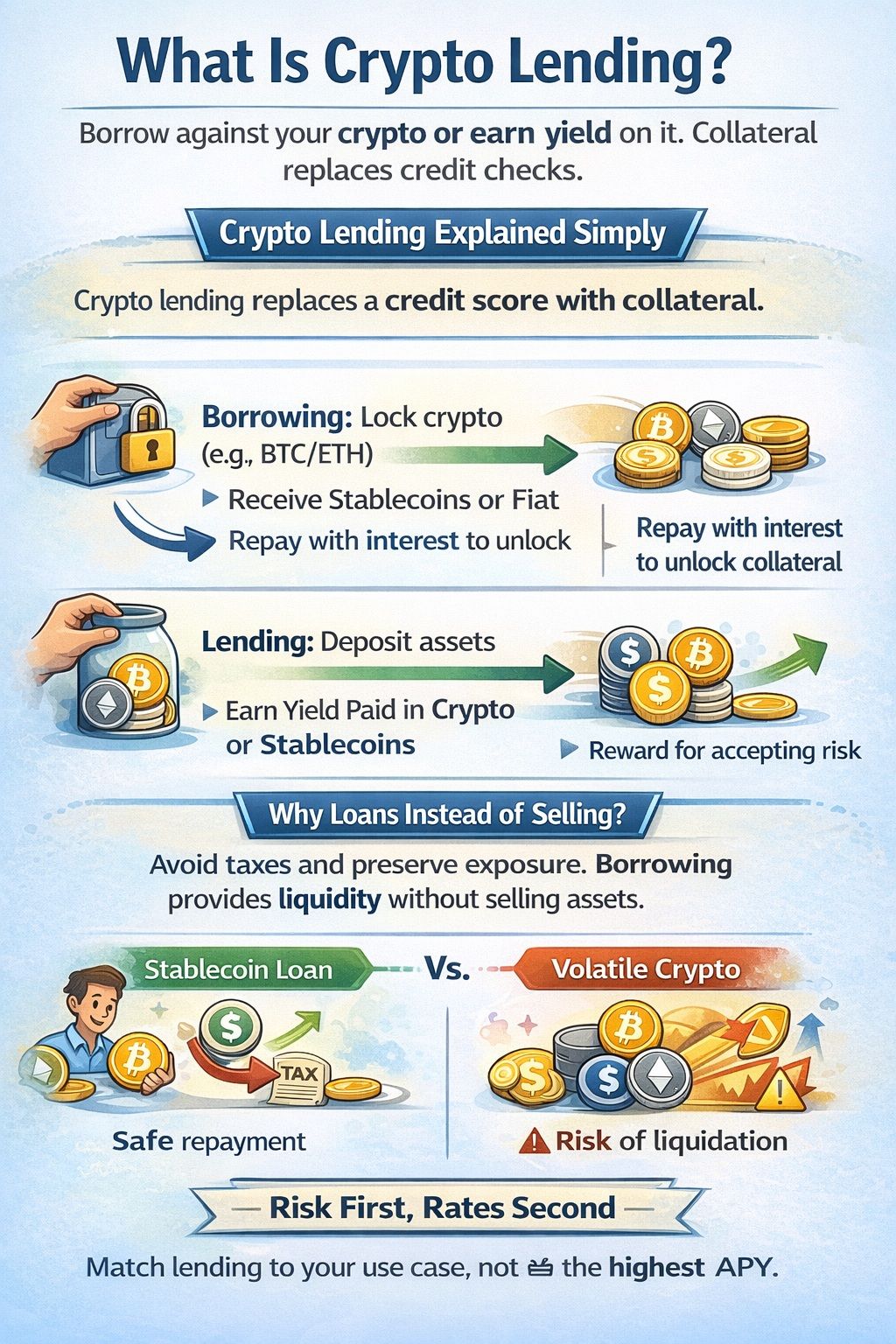
What Is Crypto Lending?
Crypto lending allows users to borrow against their crypto holdings or earn yield on them, using collateral rather than credit checks as the primary risk control.
Crypto Lending Explained Simply
In simplest words, crypto lending replaces a credit score with collateral.
- Borrowing: You lock crypto (e.g., BTC/ETH) and receive stablecoins. You repay principal + interest to unlock collateral.
- Lending: You deposit assets and earn yield, paid in crypto or stablecoins, while accepting platform/protocol risks.
Why people use loans instead of selling crypto
Many users borrow against crypto to access liquidity without selling their assets. Selling can trigger capital gains taxes and permanently reduce exposure if prices rise later. Borrowing preserves upside exposure while unlocking capital.
Stablecoins vs volatile collateral
Loans are commonly issued in stablecoins to reduce repayment volatility, while collateral is often volatile crypto such as BTC or ETH. This mismatch increases liquidation risk during sharp market moves, a risk highlighted in consumer guidance on crypto lending products published by the UK Financial Conduct Authority.
 Crypto Lending Explained
Crypto Lending ExplainedWho Crypto Lending Is For (and Who Should Avoid It)
Crypto lending can be useful in specific situations, but it carries risks that make it unsuitable for many users.
Who can it make sense for
- Long-term holders who want liquidity without exiting positions
- Traders avoiding taxable events by borrowing instead of selling
- Businesses and institutions using crypto balance sheets for short-term liquidity or capital efficiency
Avoid if…
- You cannot actively monitor collateral and loan health
- You rely on high LTV ratios with little margin for volatility
- You do not understand liquidation mechanics or margin call triggers
- You would be financially harmed by sudden forced liquidation
How Crypto Lending Works (Step-by-Step)
This section explains what actually happens when you take out a crypto-backed loan, from the first click to the moment liquidation becomes a risk.
Step-by-Step: How to Get a Crypto Loan
- Choose platform (CeFi vs DeFi)
Pick a centralized lender (custodial, managed internally) or a DeFi protocol (smart contracts on-chain). They handle custody, risk, and liquidations very differently. - Deposit collateral
Lock crypto as collateral for the loan’s duration. You cannot move or sell it until the loan is repaid. - LTV calculation
Your loan size depends on the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. Higher LTV means more borrowing power but faster liquidation if prices drop. - Loan issuance timeline
DeFi loans are issued minutes after on-chain confirmation. CeFi loans may take longer due to checks or fiat processing. - Monitoring & repayment
You must monitor collateral and LTV. If prices fall, add collateral or repay. If thresholds are breached, liquidation is automatic.
Key Terms You Must Understand
- LTV
Loan-to-value ratio. It measures how much you borrow relative to your collateral. Lower LTVs give you more protection during volatility. - Liquidation price
The price level at which your collateral will be sold or seized to repay the loan. This is set by platform or protocol rules and should be calculated before borrowing. - Health factor
A risk metric used mainly in DeFi. It combines collateral value, loan size, and liquidation thresholds into a single number. When it drops too low, liquidation is triggered automatically. - Rehypothecation
When a platform reuses deposited collateral for its own purposes, such as lending it out again. Rehypothecation increases systemic risk and played a major role in past CeFi lending failures. - Margin call
A warning that your loan is approaching liquidation levels. Some platforms offer a grace period to add collateral. Others liquidate immediately without notice. - APY vs APR
APR shows the simple annual cost of borrowing. APY includes compounding. In crypto lending, rates are often variable, which means headline numbers can change quickly and may not reflect the true cost over time.
CeFi vs DeFi Crypto Lending (Decision Guide)
If you want a more familiar “app + support team” borrowing experience, CeFi lending usually fits best — but you’re accepting custody and platform solvency risk. If you want self-custody and rules enforced by code, DeFi lending is usually the better match — but you’re taking on smart contract/oracle risk and zero hand-holding during liquidations.
Crypto loans (CeFi or DeFi) are not the same as bank credit. Regulators in the UK have repeatedly emphasized that most cryptoasset activity comes with limited protections, and consumers should be prepared to lose money if things go wrong.
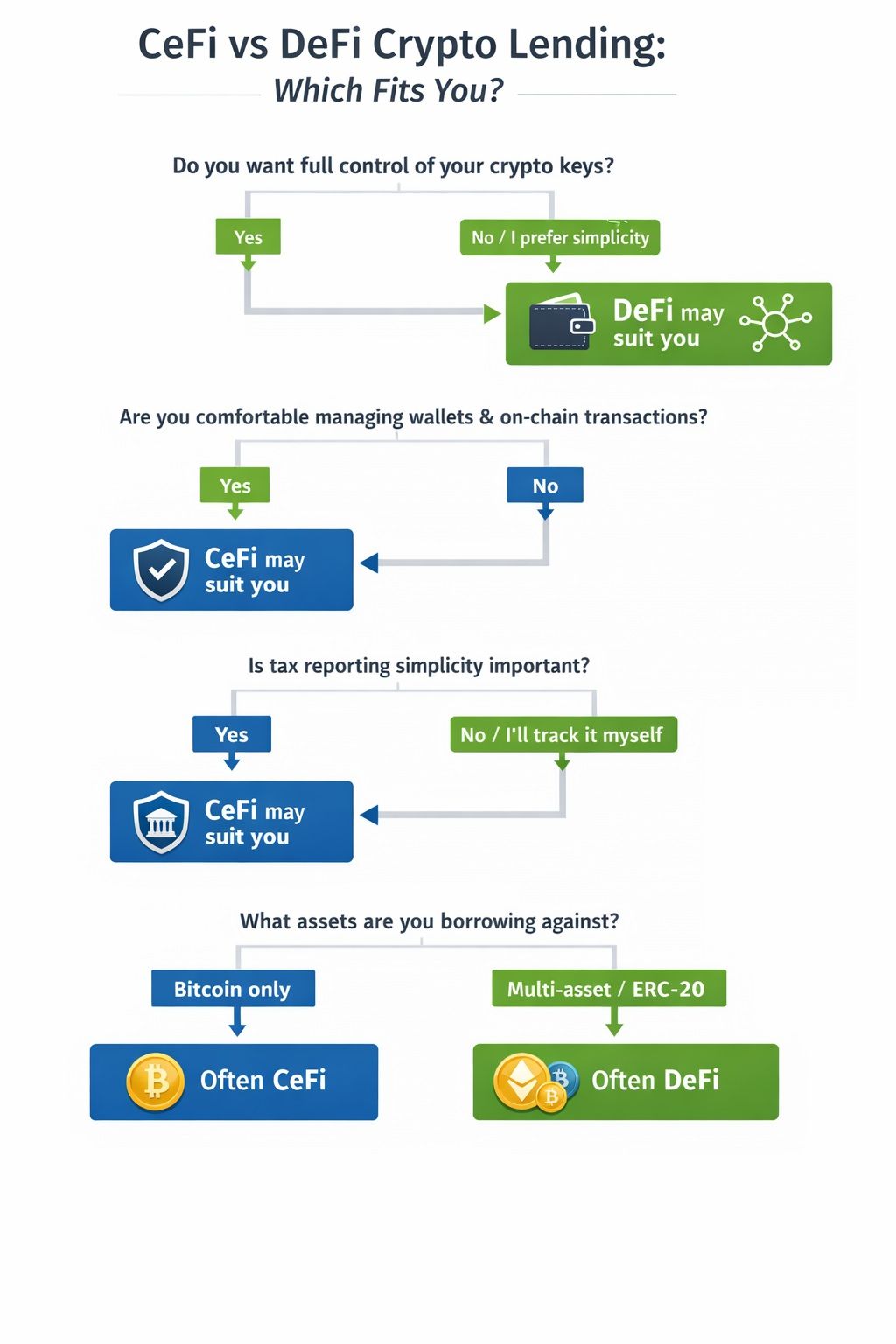 A Comparison of CeFi and DeFi Ecosystems
A Comparison of CeFi and DeFi EcosystemsCentralized Lending Platforms (CeFi)
With CeFi lending, you typically deposit collateral into a platform-controlled wallet for the life of the loan. That means, with CeFi lending, the platform takes custody of your collateral for the duration of the loan. You no longer control the private keys, and access depends on the platform remaining solvent and operational.
Most CeFi lenders require identity verification. While this simplifies compliance and fiat access, accounts can face freezing or restrictions. Regulators repeatedly point out the lack of protection in crypto lending.
CeFi platforms typically offer customer support, account dashboards, and manual intervention options. This can be helpful during onboarding or repayment, but it does not eliminate counterparty risk if the platform itself runs into trouble.
Your primary risk in CeFi lending is the platform. If it mismanages funds, rehypothecates collateral aggressively, or becomes insolvent, users may lose access to assets regardless of loan performance. This risk has been central to multiple past failures in the centralized lending sector.
Decentralized Lending Platforms (DeFi)
With DeFi lending, you connect a wallet and interact with smart contracts directly. Your collateral is locked in a contract, not held by a company.
DeFi lending runs entirely on smart contracts deployed on public blockchains. Loan terms, interest rates, and liquidation rules are enforced by code rather than a company. This removes reliance on a central intermediary but introduces technical risk.
In DeFi, users retain control of their wallets and interact directly with protocols. Collateral is locked in smart contracts, not held by a company. This reduces counterparty risk but places full responsibility on the user for wallet security and transaction accuracy.
Furthermore, liquidations in DeFi are automatic. When collateral value falls below protocol thresholds, smart contracts allow third-party liquidators to repay debt and seize collateral. There are usually no grace periods or manual overrides.
Lastly, instead of trusting a company, DeFi users trust code. Bugs, oracle failures, or governance exploits can cause losses even if markets behave normally. Regulators and financial institutions routinely highlight smart contract risk as a key vulnerability in decentralized finance systems.
CeFi vs DeFi Decision Tree
Use this simple framework to narrow your choice:
- Beginner vs advanced
Beginners often prefer CeFi for its familiar interfaces and support. Advanced users who understand wallets, gas fees, and liquidation mechanics may prefer DeFi. - Bitcoin-only vs multi-asset
Bitcoin-focused borrowers often lean toward CeFi lenders that specialize in BTC-backed loans. DeFi protocols typically support a wider range of assets, especially Ethereum-based tokens. - Tax simplicity vs autonomy
CeFi platforms usually provide account statements and transaction records, which can simplify tax reporting. DeFi offers greater autonomy and self-custody, but users must track transactions and taxable events themselves.
Defunct Platforms & Lessons Learned
The collapse of several high-profile crypto lenders between 2022 and 2023 wasn’t a black swan. It was a stress test. These failures exposed structural weaknesses that still matter today.
What Happened to BlockFi
- What failed: BlockFi had major exposure to FTX/Alameda, then paused withdrawals and filed for bankruptcy after FTX’s collapse. BlockFi’s interest product also allowed broad rehypothecation of customer assets.
What users lost: Users were pulled into bankruptcy, with slow, process-driven distributions tracked via the Kroll distributions portal. - Lesson: If a lender depends on a single major counterparty or opaque credit backstops, users inherit that risk.
What Happened to Celsius Network
What failed: Celsius paused withdrawals (June 12, 2022) during market stress. It later filed for Chapter 11 with a reported $1.19B balance-sheet deficit.
What users lost: Funds were locked into a long restructuring, and a court examiner said Celsius’s actual business differed from what it advertised.
Lesson: High yields without transparent, stress-tested sources are a warning sign.
What Happened to Hodlnaut
What failed: Hodlnaut attributed its distress to losses during the TerraUSD crash plus heavy withdrawals.
What users lost: Hodlnaut suspended withdrawals (Aug 2022) and users entered Singapore’s interim judicial management process.
Lesson: A reputable jurisdiction isn’t protection if asset concentration and correlated risk aren’t controlled and disclosed.
Crypto Loan Taxes Explained
Crypto loan taxes are usually triggered around the loan: interest, liquidation, and reporting.
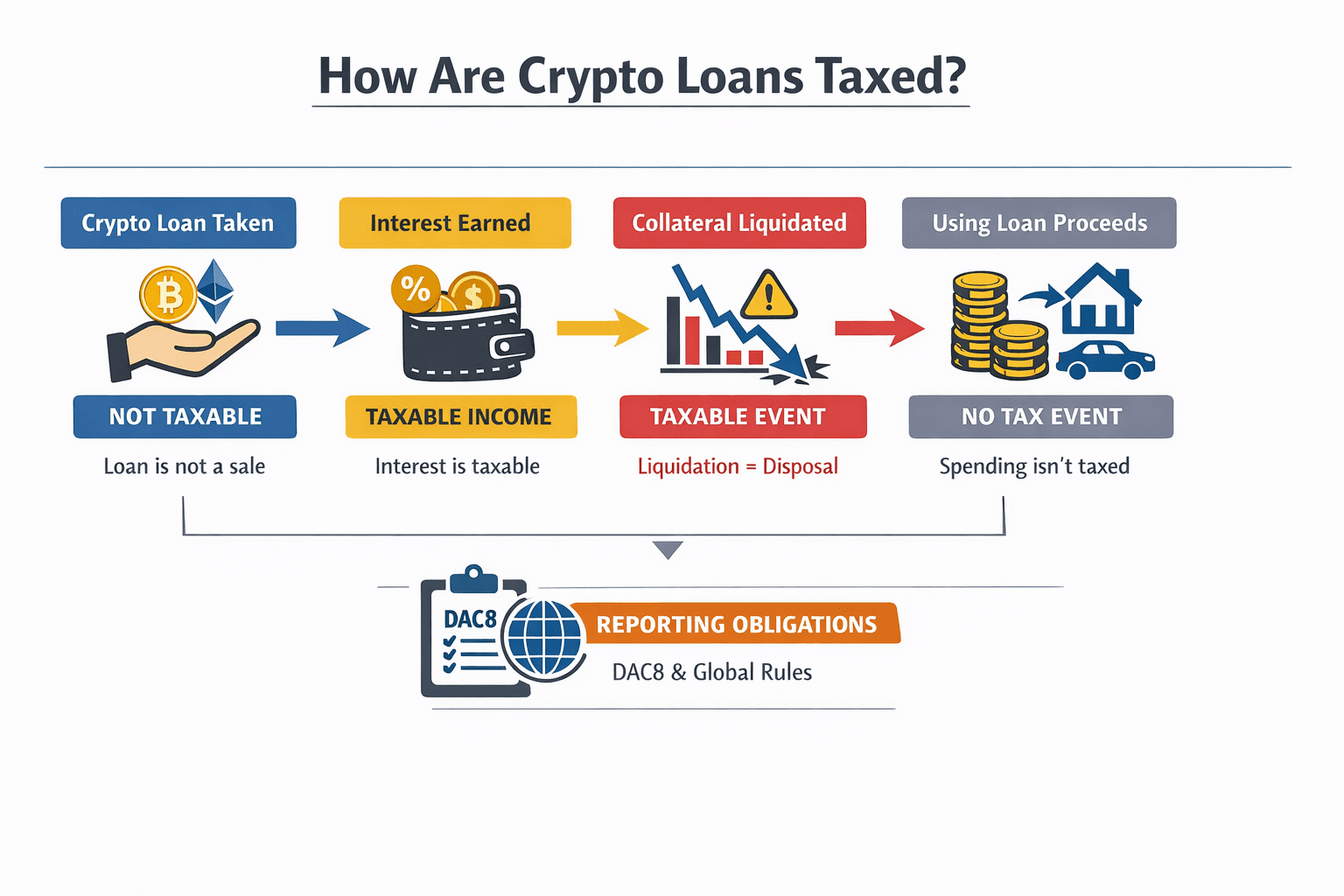 A Looks At How Crypto Loans Are Taxed
A Looks At How Crypto Loans Are TaxedAre Crypto Loans Taxable?
Loans vs sales
A loan isn’t a sale. In the U.S., the IRS says virtual currency is treated as property (see Notice 2014-21), and gains/losses generally show up when you sell, exchange, or otherwise dispose of an asset (see IRS digital asset transactions FAQ).
Why loans are often non-taxable events
Borrowing typically isn’t income because you’re taking funds with an obligation to repay. Where it can get messy is if the contract effectively transfers beneficial ownership/control of your collateral (jurisdiction + terms matter more than marketing language).
A useful “boundary marker” from an official source: the IRS repeatedly frames taxable outcomes around dispositions.
When Taxes Do Apply
Interest earned
If you earn yield, it’s generally taxable interest income.
If paid in crypto, the taxable amount is typically based on fair market value in local currency at receipt/accrual, and the IRS emphasizes reporting digital asset amounts in U.S. dollars when calculating tax items.
- Earn $800 interest: The $800 is the taxable piece.
- Earn 0.05 ETH interest: Tax is typically based on ETH’s USD value when received/accrued.
Forced liquidation
Liquidation is a big trap because it can be treated like an involuntary disposal of your collateral. HMRC’s Cryptoassets Manual gives a clear worked example where collateral is liquidated (10 tokens transferred + 1 token penalty at £6 each) and shows how to compute the chargeable gain.
Using loan proceeds
Spending borrowed funds usually isn’t a tax event. But knock-on effects can be:
- Buying another asset creates a new cost basis for that asset.
- If you’re liquidated later, the tax bite is often at the collateral disposal, not when you borrowed.
Jurisdictional Caveat
U.S., UK, EU differences
U.S.: Digital assets are treated as property, and the IRS focuses on dispositions as the key trigger.
UK: HMRC provides detailed DeFi/lending examples, including liquidation math.
EU: DAC8 says in-scope providers must start collecting reportable data from Jan. 1, 2026, with first reporting due within 9 months after the first fiscal year covered (see the Commission’s DAC8 overview).
Reporting obligations
Even if your loan isn’t taxable at origination, activity may still become reportable under emerging regimes like DAC8 and the OECD’s Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework.
Why professional advice matters
Two “similar” loans can produce different outcomes depending on:
- Whether your contract implies control/ownership transfer of collateral
- How and when interest is recognized
- Whether liquidation occurs and at what valuation
Real-World Crypto Loan Use Cases
Crypto loans are used for liquidity and capital management, not as a general-purpose leverage tool.
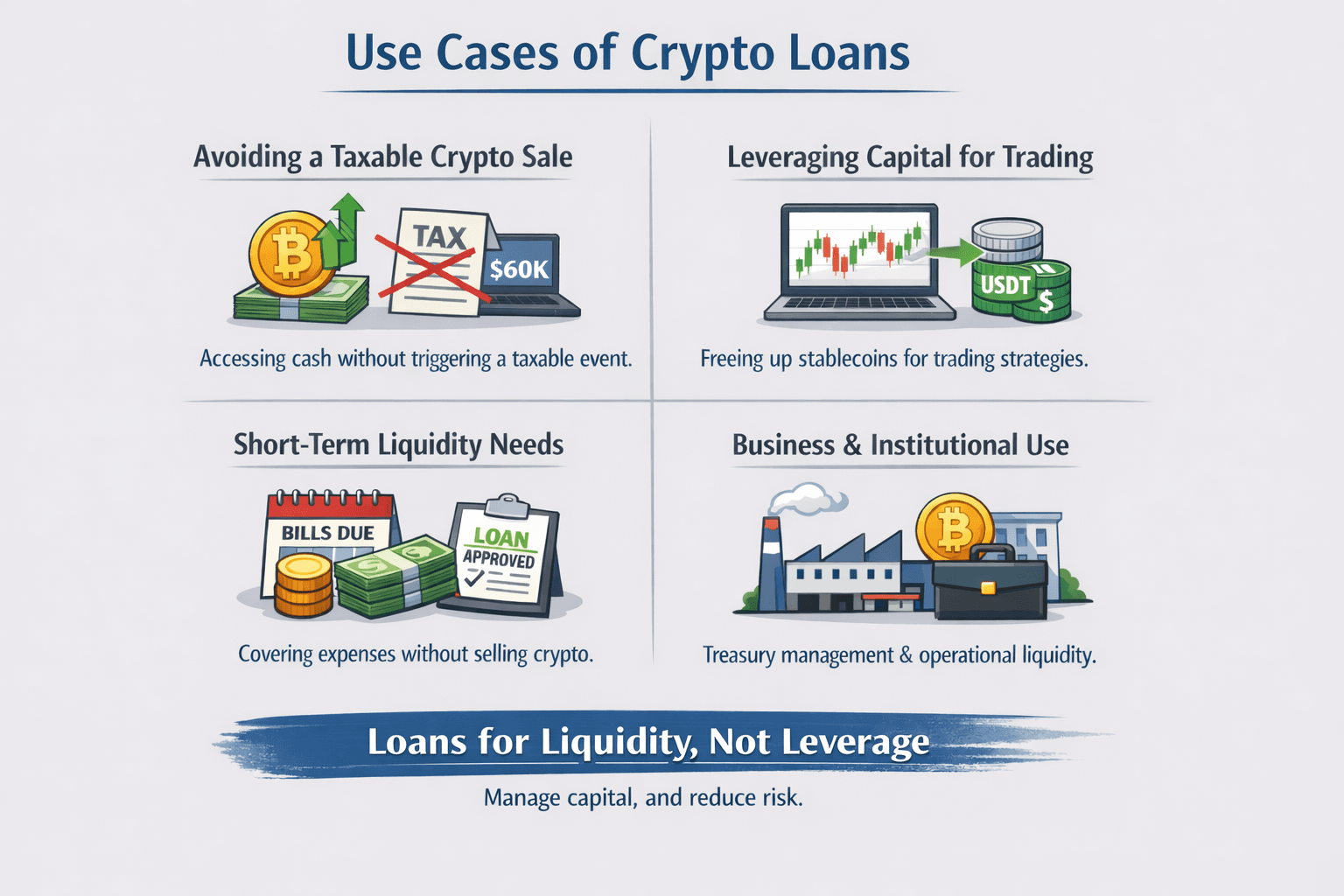 A Look At
A Look At Avoiding a Taxable Crypto Sale
The most common use case is accessing cash without triggering a disposal.
In jurisdictions like the U.S. and UK, capital gains tax is typically tied to selling or disposing of crypto, not pledging it as collateral. Borrowing against BTC or ETH does not involve a sale at loan origination, which is why long-term holders often choose loans over spot sales. Tax authorities such as the IRS and HMRC focus on disposal events when assessing capital gains.
A holder who bought 1 BTC at $10,000 and sees it trading at $60,000 faces a $50,000 gain on sale. At a 20% capital gains rate, that is roughly $10,000 due immediately. Borrowing $30,000–$40,000 at a 40–60% LTV avoids crystallizing that gain upfront, assuming no liquidation occurs.
Leveraging Capital for Trading
Traders often borrow against long-term holdings instead of selling them. This frees stablecoin liquidity for separate strategies while keeping core exposure intact.
Functionally, this mirrors securities-backed lending in traditional finance. The difference is volatility. Because crypto moves faster than equities, lenders cap LTVs lower, typically 40–70% during peak cycles.
The key point is intent. Loans are used to free capital, not to blindly increase exposure.
Short-Term Liquidity Without Exiting Positions
Loans are also used for short-term cash needs: paying taxes, covering expenses, bridging business cash flow, or managing liquidity during drawdowns.
Selling into a falling market locks in losses. The risk is simple: if prices keep falling and liquidation triggers, losses are realized anyway, often with tax consequences. Conservative LTVs and clear exit plans matter most here.
Business & Institutional Use
Businesses use crypto loans for treasury management and operational liquidity. Mining firms have borrowed against BTC to fund operations without immediately selling production. Crypto-native companies use loans to smooth working capital while keeping reserves intact.
Institutional loans are typically lower leverage, tighter margining, and more conservative. The goal is predictability and balance-sheet management, not yield chasing.
Across all user types, crypto loans are a liquidity tool, not free leverage. Used conservatively, they can delay tax events and improve capital efficiency. Used aggressively, they fail for the same reason leveraged strategies always do: markets move faster than margin allows.
Risks of Crypto Lending
Crypto lending concentrates several risks into a single structure: volatile collateral, leverage, custody, and regulation. These risks do not show up evenly. They tend to surface under stress, and when they do, outcomes move fast.
 These Are The Crypto Lending Risks You Should Be Aware Of
These Are The Crypto Lending Risks You Should Be Aware OfMarket Volatility & Liquidation Risk
Liquidation risk is the most immediate and mechanical danger.
Example: A user deposits $100,000 worth of BTC and borrows $50,000 at a 50% loan-to-value (LTV). The platform sets liquidation at 70% LTV.
If BTC falls 30%, the collateral value drops to $70,000. The loan is now at ~71% LTV. At that point, liquidation triggers.
This is not hypothetical. During the 2022 drawdown, BTC fell more than 75% peak-to-trough. High-LTV loans were liquidated long before the bottom. The key lesson is simple: liquidation thresholds, not long-term conviction, determine outcomes once leverage is involved.
Platform Insolvency & Custody Risk
When lending through centralized platforms, users are exposed to platform balance sheets, not just market prices.
CeFi failures
The collapses of BlockFi, Celsius Network, and Hodlnaut showed a consistent pattern: rehypothecation, opaque risk-taking, and liquidity mismatches. When markets turned, withdrawals were frozen and users became unsecured creditors.
Custodian dependencies
Even when a lending platform appears solvent, it may rely on third-party custodians, prime brokers, or trading firms. If any link in that chain fails, access to funds can be disrupted. Users rarely have visibility into these dependencies until something breaks.
The core risk is structural. In CeFi lending, “your collateral” usually means a contractual claim, not segregated ownership.
Smart Contract & DeFi Risks
DeFi lending removes human discretion but introduces technical fragility.
Oracle failures
Most DeFi lending protocols rely on price oracles. If an oracle feeds incorrect or delayed prices, positions can be liquidated unfairly or exploited. Several major incidents have involved temporary price distortions rather than real market moves.
Exploits
Smart contracts are immutable once deployed. Bugs, faulty assumptions, or unexpected interactions can be exploited at machine speed. When this happens, losses are often irreversible. There is no bankruptcy court or customer support queue in DeFi.
Audits reduce risk, but they do not eliminate it. Exploits have occurred in audited protocols.
Regulatory Risk by Region
Regulatory risk is uneven and often sudden.
Sudden platform shutdowns
In some jurisdictions, regulators have ordered platforms to halt lending products with little notice. This can freeze new loans, restrict withdrawals, or force rapid unwinds of positions, regardless of market conditions.
Account freezes
Compliance actions can also lead to account freezes while reviews are conducted. Even if funds are eventually returned, access during critical market periods may be lost. For leveraged positions, timing matters as much as legality.
Crypto Loan Alternatives
Crypto loans are not always the best tool. In many cases, simpler or less risky alternatives achieve the same goal with fewer moving parts.
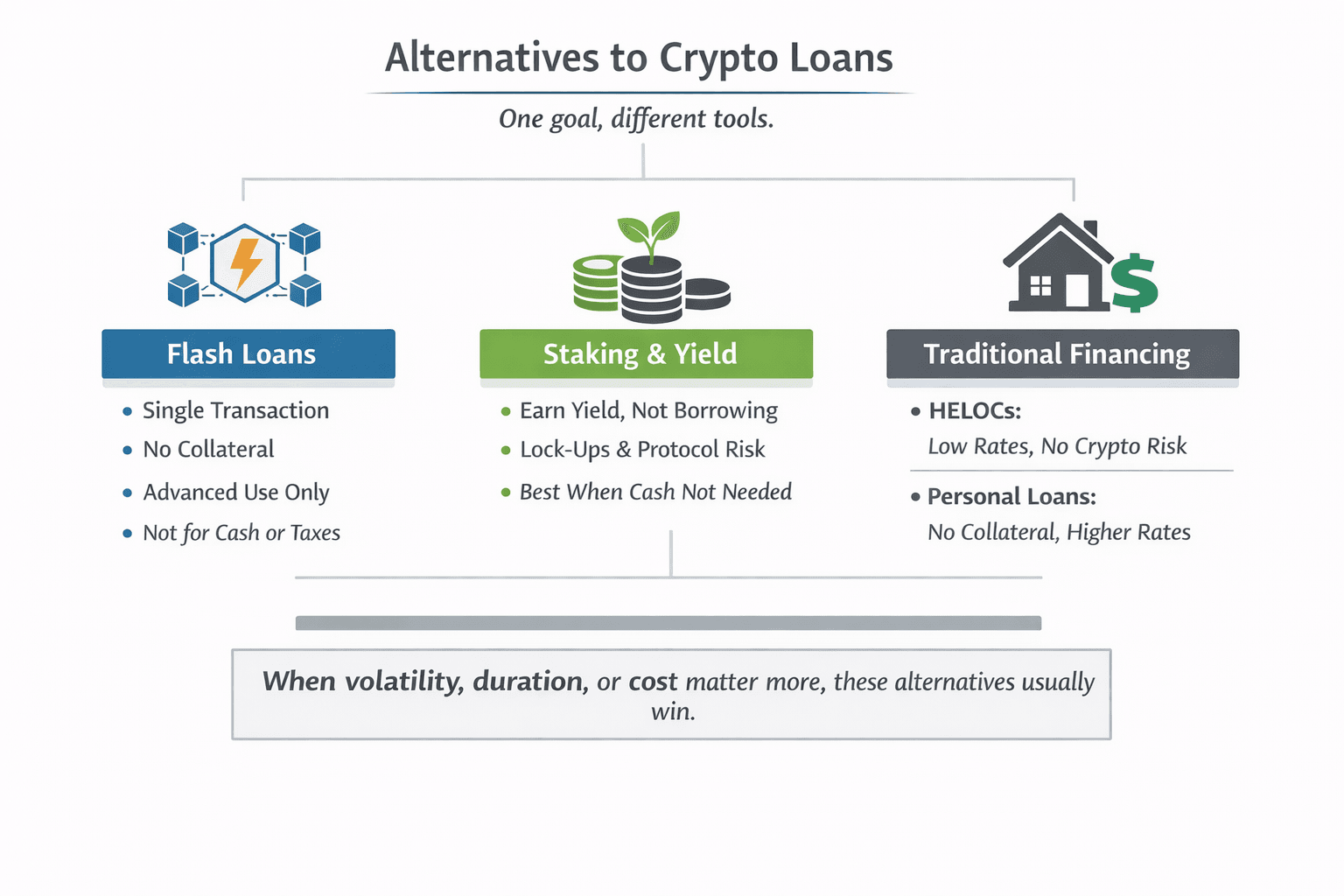 Sometimes, An Alterantive To Crypto Loans Might Be a Better Choice
Sometimes, An Alterantive To Crypto Loans Might Be a Better ChoiceFlash Loans
- Flash loans are uncollateralized loans that exist within a single blockchain transaction. The loan is borrowed and repaid instantly, or the transaction fails entirely.
- They are designed for advanced users and developers executing arbitrage, liquidations, or protocol-level strategies. Flash loans are not suitable for personal liquidity, tax management, or cash-flow needs.
Staking & Yield Farming
If the objective is income rather than liquidity, staking or yield farming may be more appropriate. Earning 4–10 percent annually on assets through staking can be lower risk than borrowing against them, depending on lock-up terms and protocol risk.
The trade-off is access. Staked assets may be locked or subject to slashing, and yields are not guaranteed. But when no cash is needed upfront, yield strategies often dominate loans on a risk-adjusted basis.
Traditional Financing Options
- HELOCs
Home equity lines of credit typically offer lower interest rates than crypto loans and do not carry liquidation risk tied to crypto volatility. They are slow, jurisdiction-dependent, and require strong credit, but they are structurally more stable. - Personal loans
Unsecured personal loans avoid collateral risk entirely. Rates are usually higher than HELOCs but can still undercut crypto loan APRs during volatile periods. - When crypto loans are not optimal
Crypto loans are a poor choice when volatility risk is unacceptable, funds are needed long-term, or cheaper traditional credit is available. They are best used for short-term liquidity with conservative leverage, not as a default financing solution.
How to Choose the Right Crypto Lending Platform
- Jurisdiction
Where the platform is legally registered and regulated matters. Jurisdiction determines consumer protections, reporting obligations, and how disputes or insolvencies are handled. - Custody model
Understand who actually controls the collateral. Is it held by the platform, a third-party custodian, or a smart contract? Custody structure defines whether you own assets outright or hold a contractual claim. - LTV buffer
Look beyond maximum LTVs. Check liquidation thresholds and margin call buffers. Wider buffers mean more room to react during sharp market moves. - Liquidation controls
Review how liquidations are triggered and executed. Partial liquidations, warning alerts, and gradual unwind mechanisms reduce downside risk compared to instant full liquidation. - Rate volatility
Variable rates can change quickly in stressed markets. Assess how often rates reset, historical spikes, and whether fixed-rate options exist. - Track record
Longevity matters. Platforms that have operated through multiple market cycles without freezing withdrawals or changing terms mid-crisis carry a stronger trust signal than new entrants.
Final Verdict: Is Crypto Lending Worth It?
Crypto lending sits in an interesting middle ground. It is neither a magic yield machine nor a financial booby trap by default. Used thoughtfully, it can be a practical tool. Used carelessly, it can turn volatility into a very expensive teacher.
The balanced take
Crypto lending can be worth it if you understand what you are trading off.
- It lets long-term holders access liquidity without selling their assets
- It can reduce taxable events compared to selling, depending on jurisdiction
- It offers faster access to capital than most traditional loans
- It works best for disciplined users with clear risk limits
But the benefits are conditional. You are exchanging price risk, platform risk, and liquidation risk for convenience and flexibility. That trade only makes sense when you know exactly why you are borrowing or lending.
The risk-aware reality check
Crypto lending in 2026 is more mature, but it is not risk-free.
- Market risk still dominates. Sharp price drops can trigger liquidations faster than many users expect.
- Platform risk has improved, but smart contracts, custodians, and CeFi operators remain points of failure.
- Rate risk cuts both ways. Attractive APYs can vanish quickly when demand shifts.
- Regulatory risk varies by region and can affect withdrawals, availability, or terms with little notice.
The safest outcomes tend to come from conservative loan-to-value ratios, overcollateralization, and constant monitoring. If you cannot watch your positions or top up collateral during volatility, lending and borrowing become much riskier.
Match the platform to the job
This is where many users go wrong.
- Short-term liquidity needs favor fast, transparent platforms with clear liquidation mechanics
- Passive yield seekers should prioritize audited protocols, simple strategies, and modest returns
- Active traders may benefit from flexible terms, but only with tight risk controls
- Long-term holders should treat loans as tools, not habits
Headline rates are marketing. Risk management is the product.
Bottom line: Crypto lending is worth it when it serves a specific purpose in your strategy, not when it is used because the numbers look good. Choose platforms based on transparency, risk controls, and fit for your use case, and treat every yield figure as a question, not a promise.





