At first glance, Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets sound overly technical. However, they represent one of the most significant innovations in Bitcoin key management, making the network more user-friendly.
Much of what makes HD wallets effective happens behind the scenes. While they automate address generation and security complexities, the user experience remains as simple as any other crypto wallet. You still send and receive Bitcoin the same way—but in the background, HD wallets enhance privacy, security, and backup efficiency.
This article demystifies those essential processes, explaining how HD wallets work, why they matter, and whether they should be part of your Bitcoin journey. Even if you don’t realize it, you’re probably already using an HD wallet—and by the end of this guide, you’ll understand precisely why.
What are Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets?
Introduced through Bitcoin Improvement Proposal 32 (BIP-32), HD wallets simplify handling Bitcoin transactions and fund management for individuals and businesses. They generate many addresses from a single master seed, organized in a tree-like structure. This approach streamlines fund management and makes the backup process more efficient.
How HD Wallets Differ from Traditional Crypto Wallets
To appreciate the innovation behind HD wallets, let's contrast them with traditional crypto wallets:
- Traditional Bitcoin Wallets: In the early days, Bitcoin wallets were non-deterministic, meaning they generated random, unrelated key pairs for each transaction. So users had to back up each private key individually—a cumbersome and error-prone process.
- Traditional Ethereum Wallets: While Ethereum wallets can generate multiple key pairs from a single seed, each key pair often functions as a separate account. Users typically reuse these accounts for numerous transactions, which can lead to privacy concerns and more complex key management.
In contrast, HD wallets generate a hierarchical structure of keys from a single seed, allowing for the creation of new addresses for each transaction without the need for multiple backups. HD Wallets enhance privacy and simplify the user experience by reducing the number of assets users need to secure to keep their on-chain funds safe.
Key Components of HD Wallets
Understanding the core components of HD wallets is crucial:
- Seed Phrase: Often presented as a 12 or 24-word mnemonic, the seed phrase is the root of the HD wallet's security. It's a human-readable representation of the master seed and is needed to back up and restore the entire wallet. Losing this phrase means losing access to all derived keys and addresses.
- Master Private and Public Keys: Derived from the seed phrase, the master private key is the starting point for generating all child private keys. The corresponding master public key allows for creating public addresses without exposing private keys, facilitating secure transaction monitoring.
- Extended Keys include the Extended Private Key (xprv) and Extended Public Key (xpub). The xprv can generate both child private and public keys, while the xpub can only generate child public keys. This distinction is vital for applications like watch-only wallets, where monitoring without spending capabilities is desired.
How They Work Together
- Seed Phrase → Generates Master Private Key (m) and Master Public Key (M).
- Master Private Key (m) → Generates the Extended Private Key (xprv).
- Master Public Key (M) → Generates the Extended Public Key (xpub).
- Extended Keys (xprv, xpub) → Used for hierarchical key derivation to generate multiple child keys and addresses.
Master keys (m, M) are the root keys of an HD wallet, while extended keys (xprv, xpub) are derivative keys that introduce hierarchical key derivation. Extended keys include additional functionality, such as the chain code, enabling structured and scalable key generation.
By leveraging these components, HD wallets offer enhanced security, improved privacy, and streamlined fund management, making them an indispensable tool for modern cryptocurrency users.
 HD Wallets are a Bitcoin Wallet Management Feature. Image via Shutterstock
HD Wallets are a Bitcoin Wallet Management Feature. Image via ShutterstockHow Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets Work?
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets optimize how cryptocurrency users generate, organize, and manage multiple Bitcoin keys from a single seed phrase. Introduced in Bitcoin Improvement Proposal 32 (BIP-32), HD wallets provide a structured method for efficiently handling numerous addresses. Subsequent proposals, BIP-39 and BIP-44, further enhanced their functionality, making them more user-friendly and versatile.
Let’s learn more about the operational stages of HD wallets to understand their inner workings.
Stage 1: Seed-Based Key Generation
- The seed phrase is the core of an HD wallet. A sequence of words is the root of all key generation.
- Seed Phrase Generation:
- Random Number Generation: The wallet generates a random number, typically 128 or 256 bits in length.
- Mnemonic Encoding: This number is then mapped to a set of words to create the seed phrase, making it more human-readable and easier to back up.
- Master Seed and Master Private Key:
- Master Seed: The seed phrase is converted into a binary format called the master seed.
- Master Private Key: The master seed is then used to generate the master private key, which is the starting point for all subsequent key derivations.
This process ensures that all keys and addresses can be traced back to a single, easily manageable seed phrase, simplifying backup and recovery.
Stage 2: Key Derivation and Hierarchical Structure
HD wallets utilize the master private key to generate a hierarchical, tree-like structure of keys and addresses.
- Extended Keys:
- Extended Private Key (xprv): Combines the master private key with additional data, deriving child private keys.
- Extended Public Key (xpub): Derived from the extended private key, it enables the generation of child public keys without exposing private keys.
- Hierarchical Structure:
- Tree-Like Organization: The wallet creates a branching structure where each node can have its own child nodes, representing different accounts or addresses.
- Practical Example:
- Receiving Funds: Alice uses her HD wallet to generate a new address for each transaction, enhancing privacy.
- Sending Funds: When Alice sends Bitcoin to Bob, her wallet automatically generates a change address for any leftover funds, ensuring efficient fund management.
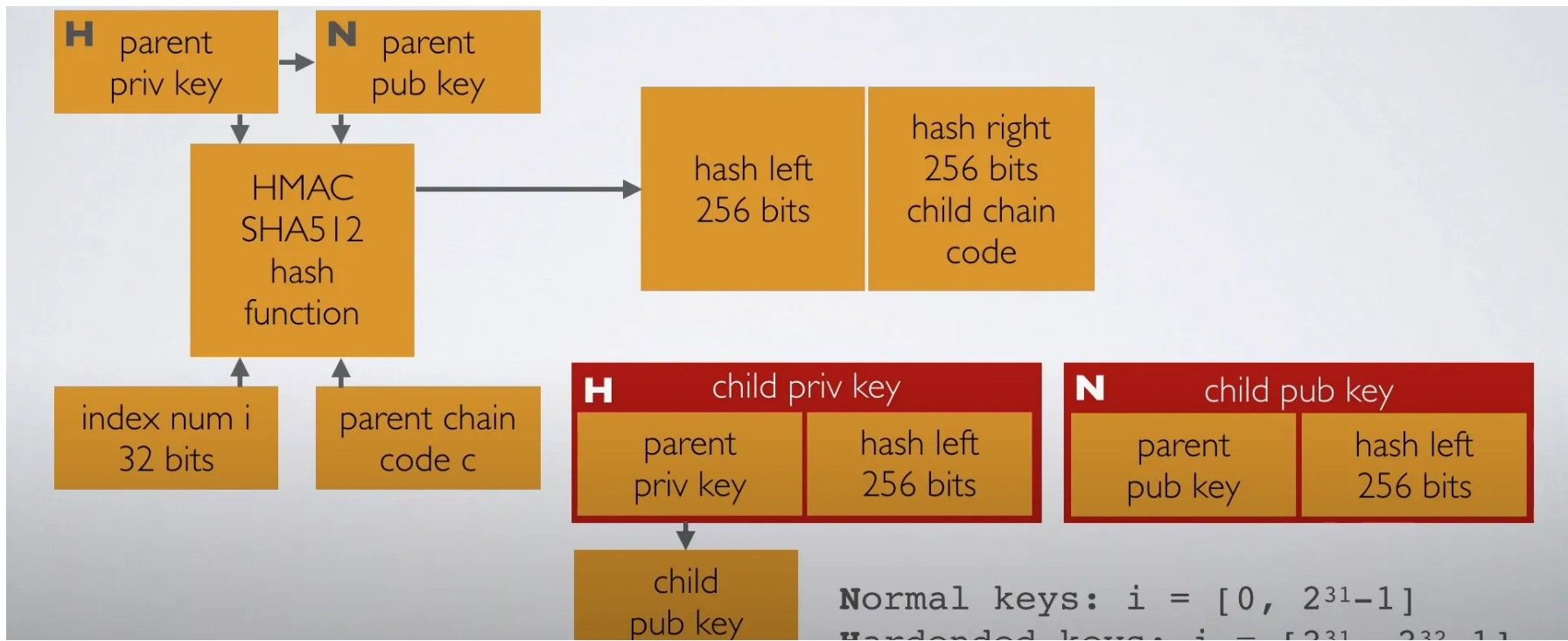 This Illustration Explains The Tree-Like Structure of HD Wallets in Bitcoin. Image via Medium
This Illustration Explains The Tree-Like Structure of HD Wallets in Bitcoin. Image via MediumThis hierarchical approach allows users to manage multiple addresses and accounts seamlessly derived from a single master key.
Enhancements: BIP-39 and BIP-44
While BIP-32 laid the foundation for HD wallets, subsequent proposals introduced significant improvements:
- BIP-39:
- Mnemonic Phrases: Standardized using mnemonic phrases for seed generation, making backups more user-friendly.
- Improved Security: Enhanced the entropy and randomness of seed generation, bolstering wallet security.
- BIP-44:
- Multi-Account Hierarchy: Defined a standard path structure, allowing users to manage multiple cryptocurrencies (like ETH, or LTC) and accounts within the same wallet.
- Interoperability: Ensured compatibility across different wallet implementations, facilitating smoother user experiences.
These enhancements have made HD wallets more versatile, secure, and user-friendly.
Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets User Experience
For users, interacting with an HD wallet is designed to be intuitive and straightforward:
- Seed Phrase Generation: Upon creating a new wallet, users are given a seed phrase, which they are prompted to write down and store securely.
- Address Generation for Receiving Funds: The wallet automatically generates a new address for each incoming transaction, enhancing privacy without requiring user intervention.
- Sending Funds: When sending funds, the wallet selects appropriate addresses and generates change addresses, ensuring efficient fund utilization.
- Backup and Recovery: In case of device loss or damage, users can restore their entire wallet, including all addresses and transaction history, using the previously saved seed phrase.
While the underlying processes involve complex cryptographic operations and hierarchical key derivations, the user experience is streamlined to ensure ease of use, security, and privacy.
Benefits of Using Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets have transformed the cryptocurrency experience, offering users enhanced security, privacy, and convenience. Let's explore these benefits through the lens of a typical user's journey.
Simplified Key Management
- Single Seed Phrase Backup: Imagine setting up your crypto wallet and being provided with a 12 or 24-word seed phrase. This single phrase is all you need to back up your entire wallet. In the event of device loss or failure, you can restore your wallet with all associated addresses and funds by simply inputting this seed into a new wallet. The HD wallet seed eliminates the need to manage and store multiple private keys, significantly simplifying the backup process.
- No Need to Store Multiple Private Keys: In traditional non-HD wallets, each new address corresponds to a unique private key, requiring individual backups. HD wallets, however, generate all addresses from a single master seed. You only need to secure one seed phrase; the wallet generates and manages the myriad of private keys internally. This approach reduces the risk of losing access to funds due to misplaced or unbacked-up keys.
Enhanced Privacy & Security
- Hierarchical Key Derivation Protects User Privacy: HD wallets derive keys using a hierarchical structure, allowing users to generate a new public address for each transaction, making it significantly more challenging for external observers to link multiple transactions to a single user, thereby enhancing privacy. This method ensures that financial activities remain discreet and less susceptible to tracking.
- Reducing Risks of Key Reuse in Transactions: Reusing the same address for multiple transactions can expose patterns that malicious actors might exploit. HD wallets mitigate this risk by automatically generating new addresses for each transaction. This practice enhances privacy and reduces the chances of certain types of attacks that rely on address reuse. By continually using fresh addresses, HD wallets help maintain the confidentiality and security of your cryptocurrency dealings.
 Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets Have Transformed The Cryptocurrency Experience. Image via Shutterstock
Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets Have Transformed The Cryptocurrency Experience. Image via ShutterstockEfficient UTXO Management
In Bitcoin's UTXO model, each transaction output can become an input for future transactions. Managing these outputs manually can be intricate, but HD wallets simplify this by:
- Automated Selection: When initiating a transaction, the wallet automatically selects appropriate UTXOs to fund it, optimizing for transaction fees and privacy.
- Consolidation: HD wallets can consolidate smaller UTXOs into a single output during low-fee periods, reducing future transaction costs and minimizing the number of UTXOs to manage.
Seamless Change Address Handling
In transactions where the input exceeds the output amount, the remainder (change) must be returned to an address controlled by the sender. HD wallets handle this by:
- Automatic Generation: The wallet generates a new change address for each transaction, enhancing privacy by making linking transactions to a single address difficult.
- Transparent Management: Users are not required to track these change addresses manually; the wallet manages them internally, ensuring that all funds remain accessible without additional user intervention.
User Experience
For the user, these complex processes are entirely abstracted. When sending or receiving Bitcoin:
- Sending: The user specifies the recipient and amount; the wallet selects the necessary UTXOs, calculates change, generates a new change address, and finalizes the transaction—all behind the scenes.
- Receiving: The wallet provides a new receiving address for each transaction to maintain privacy, but the user interacts with the wallet in the same straightforward manner each time.
In summary, HD wallets offer a user-friendly experience by simplifying key management and bolstering privacy and security. With a single seed phrase, users can manage multiple addresses effortlessly, ensuring ease of use and robust protection for their digital assets.
Risks of Using HD Wallets
While Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets offer enhanced security and convenience, it's important to be aware of potential risks associated with their use:
- Centralized Value: The master seed or private key is the single point of origin for all derived keys and addresses in an HD wallet. If this master key is lost or compromised, it can lead to the loss of access to all associated funds.
- Reliance on Third-Party Services: Many users depend on third-party wallet providers to manage their HD wallets. If these providers experience security breaches, vulnerabilities, or malicious activities, users' private keys and funds could be at risk.
- Privacy Concerns: Although HD wallets enhance privacy by generating new transaction addresses, improper management—such as reusing addresses or exposing the extended public key (xPub)—can compromise user anonymity. Sharing the xPub can allow others to view all associated addresses and transaction histories.
- Backup Complexity: While a single seed phrase simplifies backups, the responsibility of securely storing this phrase is critical. Loss, theft, or destruction of the seed phrase can result in irreversible loss of access to the wallet and its funds.
HD Wallet Security Best Practices
To mitigate these risks, consider the following best practices:
- Secure Seed Phrase Storage: Write down your seed phrase and store it in a secure, offline location. Avoid digital storage methods that are susceptible to hacking or data loss.
- Use Reputable Wallet Providers: Choose HD wallets from well-established and trusted providers known for their security measures and regular updates.
- Protect Extended Public Keys (xPubs): Keep your xPubs confidential to prevent unauthorized access to your transaction history and addresses.
- Regularly Update Backups: After significant wallet activities, such as generating new addresses or receiving funds, ensure your backups are up-to-date.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Where possible, enable 2FA to add an extra layer of security to your wallet access.
- Stay Vigilant Against Phishing: Be cautious of unsolicited communications and verify the authenticity of wallet-related messages to avoid phishing attacks.
 Always Secure a Tangible Copy of Your Seed Phrase. Image via Shutterstock
Always Secure a Tangible Copy of Your Seed Phrase. Image via ShutterstockBy adhering to these practices, you can enhance the security of your HD wallet and safeguard your digital assets.
Choosing the Right HD Wallet
Choosing the right Hierarchical Deterministic wallet is crucial for securely managing your cryptocurrencies. Here's a concise guide to help you make an informed decision.
Software vs. Hardware HD Wallets
- Software Wallets:
- Available as mobile or desktop applications.
- Offer quick access to funds and are user-friendly.
- Internet connection makes them more susceptible to cyber threats.
- Hardware Wallets:
- Physical devices resembling USB drives.
- Store private keys offline, providing enhanced protection against online attacks.
- Require connection to a computer or mobile device to access funds, which can be less convenient for frequent transactions.
Check out our extensive coverage of crypto wallets:
- Top Hot Wallets
- Best Mobile Wallets
- Top Anonymous Crypto Wallets
- Top DeFi Crypto Wallets
- Best Crypto Hardware Wallets
- Best Desktop Wallets
- Best Cold Storage Wallets
Differences Between Mobile, Desktop, and Hardware HD Wallets
- Mobile Wallets:
- Pros: Portable and convenient for daily transactions.
- Cons: Vulnerable to mobile malware and device theft.
- Desktop Wallets:
- Pros: Generally offer robust security features and a comprehensive interface.
- Cons: Limited to the device they're installed on; susceptible to malware if the computer is compromised.
- Hardware Wallets:
- Pros: Provide the highest level of security by keeping private keys offline.
- Cons: Less convenient for quick transactions; come at a monetary cost.
Security Trade-offs Between Different Wallet Types
- Software Wallets:
- Advantage: Ease of access and use.
- Disadvantage: Higher risk of exposure to online threats.
- Hardware Wallets:
- Advantage: Superior security due to offline storage.
- Disadvantage: Less convenient for frequent use; requires physical possession of the device.
Popular HD Wallet Providers
- Ledger
- Type: Hardware wallet.
- Features: Supports over 5,500 cryptocurrencies; integrates with the Ledger Live app for portfolio management.
- Security: Known for robust security measures, it faced a data breach in 2020 that affected customer information.
- Trezor
- Type: Hardware wallet.
- Features: User-friendly interface; supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies.
- Security: Emphasizes open-source firmware, allowing for community audits.
- Samourai Wallet
- Type: Mobile software wallet.
- Features: Focuses on privacy; offers features like coin mixing and stealth modes.
- Security: Implements advanced privacy tools to enhance transaction anonymity.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an HD Wallet
- Security Features: Look for wallets with strong encryption, two-factor authentication, and a solid reputation for security.
- Compatibility with Different Cryptocurrencies: Ensure the wallet supports all the cryptocurrencies you intend to store.
- User Experience and Recovery Options:
- A user-friendly interface simplifies management.
- Robust recovery options, like seed phrases, are essential for regaining access in case of device loss or failure.
You can choose an HD wallet that meets your security needs and usage preferences by carefully evaluating these aspects. To learn more about protecting digital assets, read the Coin Bureau Crypto Safety Guide.
Closing Thoughts
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets are a fundamental innovation in Bitcoin. They offer a structured and secure way to manage private keys. By generating multiple addresses from a single seed phrase, HD wallets simplify backups, enhance privacy, and make transactions more secure—all while keeping the user experience intuitive.
However, secure key management remains crucial. While HD wallets reduce the complexity of handling multiple keys, losing access to the seed phrase can result in permanent fund loss. Users must take responsibility for adequately storing backups and be mindful of potential security risks.
Exploring HD wallets is a step in the right direction for those looking to improve their privacy and security in Bitcoin. Whether using software or hardware wallets, understanding how these wallets function empowers users to make informed decisions about their Bitcoin custody. Ultimately, the wallet choice should align with personal security needs and risk tolerance, so always research and choose wisely.




