Two fundamental principles exist in Web3: Bitcoin is the ultimate store of value, while Ethereum is the decentralized finance hub. These beliefs have led people to call Bitcoin "digital gold" and Ethereum the largest "decentralized computer" of the internet. These networks serve distinct purposes; the limitations of the Bitcoin network are designed to help it excel in preserving value, whereas Ethereum enables seamless value exchange and programmability with smart contracts.
However, users have always tried to get the best of worlds – leveraging Bitcoin's value within Ethereum's DeFi ecosystem. This demand inspired the Wrapped Bitcoin, a system that creates an ERC-20 token counterpart of Bitcoin so it is compatible with Ethereum-based decentralized applications (DApps). This interoperability between the two networks has made wrapped Bitcoin an essential tool for anyone looking to unlock the value of Bitcoin within Ethereum's DeFi landscape.
In this article, we will answer what is wrapped Bitcoin, including how it works, its benefits, and its role in the ever-evolving Web3 ecosystem.
What is Wrapped Bitcoin?
Web3 consists of a diverse and expanding collection of blockchain networks, each operating independently through its own unique set of nodes. These networks communicate and validate transactions internally but remain isolated from one another. This isolation ensures that no external interference can compromise the network's security, as each blockchain upholds its own rules and mechanisms.
However, this separation, while enhancing security, leads to a significant drawback: liquidity fragmentation. Blockchain assets like Bitcoin on the Bitcoin network cannot natively interact with applications or assets on networks like Ethereum. This means that despite Ethereum's growing decentralized finance (DeFi) sector, Bitcoin's liquidity remains locked within its own ecosystem, limiting its use to a single chain. Without bridging this divide, users cannot seamlessly move their assets across different blockchains, reducing the potential for enhanced utility and engagement.
Bridges and Connecting Interchain Liquidity
The need for cross-chain asset movement has led to the development of wrapped tokens. Wrapped tokens are synthetic versions of native assets designed to operate on blockchains other than their native networks. The process involves securely locking the original tokens—like Bitcoin—on their source blockchain. These tokens are typically locked within a smart contract, but since Bitcoin does not house an execution layer, the funds are held by a trusted custodian. Proof of this locked asset is then sent to the target blockchain, where an equivalent amount of wrapped tokens is minted to represent the original asset.
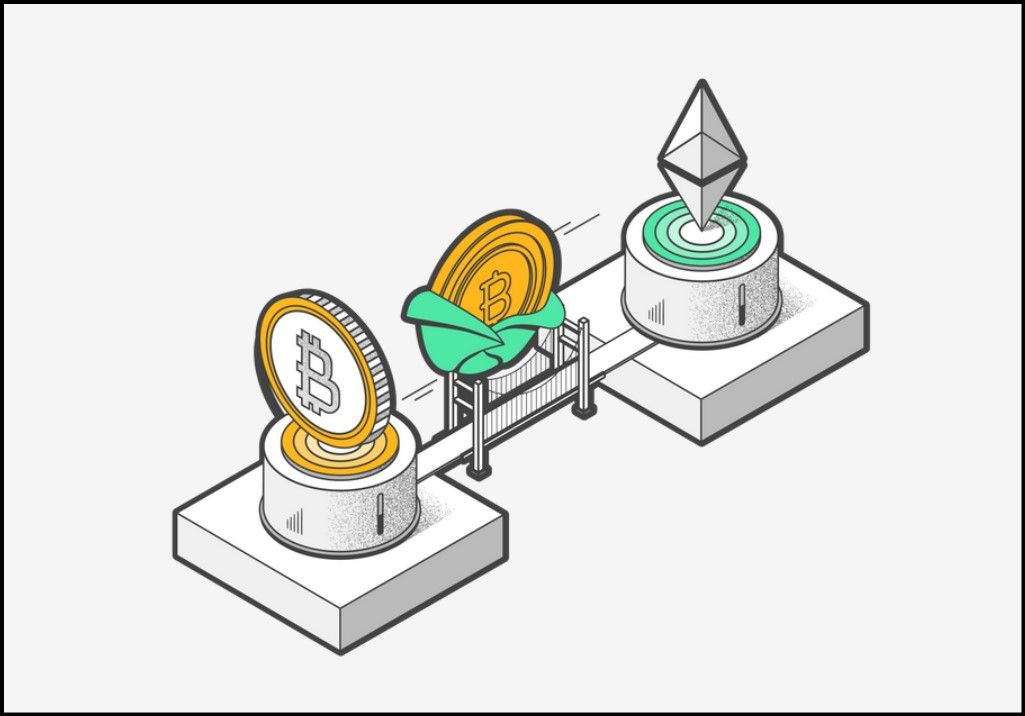 Wrapping tokens Involves Making Them Compatible With Other Networks | Image via Tangem
Wrapping tokens Involves Making Them Compatible With Other Networks | Image via TangemThis method allows the asset's value to be transferred across chains without losing integrity. In essence, wrapped tokens are pegged 1:1 to the value of the original token, ensuring the wrapped version can be redeemed for the actual asset at any time. The primary advantage of wrapped tokens is that they enable assets to interact with decentralized applications (DApps) on networks like Ethereum, which would otherwise be inaccessible. The process minimizes risks such as double spending, which can occur if assets are replicated across chains without proper safeguards.
Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapping Bitcoin allows the asset's use outside the Bitcoin network, allowing BTC holders to participate in DeFi activities like trading, lending, and yield farming while also benefiting from the price action of BTC. Several projects have created versions of wrapped Bitcoin. Here are some notable ones:
- Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC): Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is an ERC-20 token that brings Bitcoin into the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing BTC holders to participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) activities on Ethereum. By converting Bitcoin into WBTC, users can engage in trading, lending, yield farming, and more within Ethereum's vast network of decentralized applications, all while maintaining Bitcoin's value. WBTC holds a 1:1 peg with Bitcoin, ensuring that each WBTC token is backed by an equal amount of Bitcoin held in reserve.
- renBTC: Issued by the Ren Protocol, renBTC offers a decentralized approach to Bitcoin wrapping. Unlike WBTC, which relies on a custodial service, renBTC is managed through the RenVM, a decentralized network of nodes that facilitates cross-chain interoperability. This decentralization reduces reliance on a single custodian, offering enhanced security by avoiding central points of failure. However, renBTC's process has its own risks, particularly in terms of smart contract vulnerabilities.
- Stacks BTC (sBTC): A newer entry in the space, sBTC is part of the Stacks protocol, which aims to bring smart contract functionality to Bitcoin. Unlike custodial solutions, sBTC enables a trustless two-way peg system, where Bitcoin can move into and out of the Stacks network while being secured by the Bitcoin blockchain itself. This setup unlocks new possibilities, such as DeFi applications and smart contracts for Bitcoin, while maintaining Bitcoin's simplicity.
These different versions of wrapped Bitcoin serve the same purpose—unlocking the value of Bitcoin within other blockchain ecosystems—but each takes a different approach to security, decentralization, and use cases. Whether through custodial (WBTC), decentralized (renBTC), or trustless peg systems (sBTC), wrapped Bitcoin expands the utility of BTC across the broader Web3 ecosystem.
Through these innovations, Bitcoin's liquidity and utility can be extended far beyond its native blockchain, opening doors to a range of decentralized applications without sacrificing the core value and security that Bitcoin provides.
Is Wrapped Bitcoin Safe?
The safety of wrapped Bitcoin largely depends on the specific implementation of the wrapping process and the protocols used. Below is an analysis of the safety aspects of three prominent wrapped Bitcoin tokens: WBTC, renBTC, and sBTC.
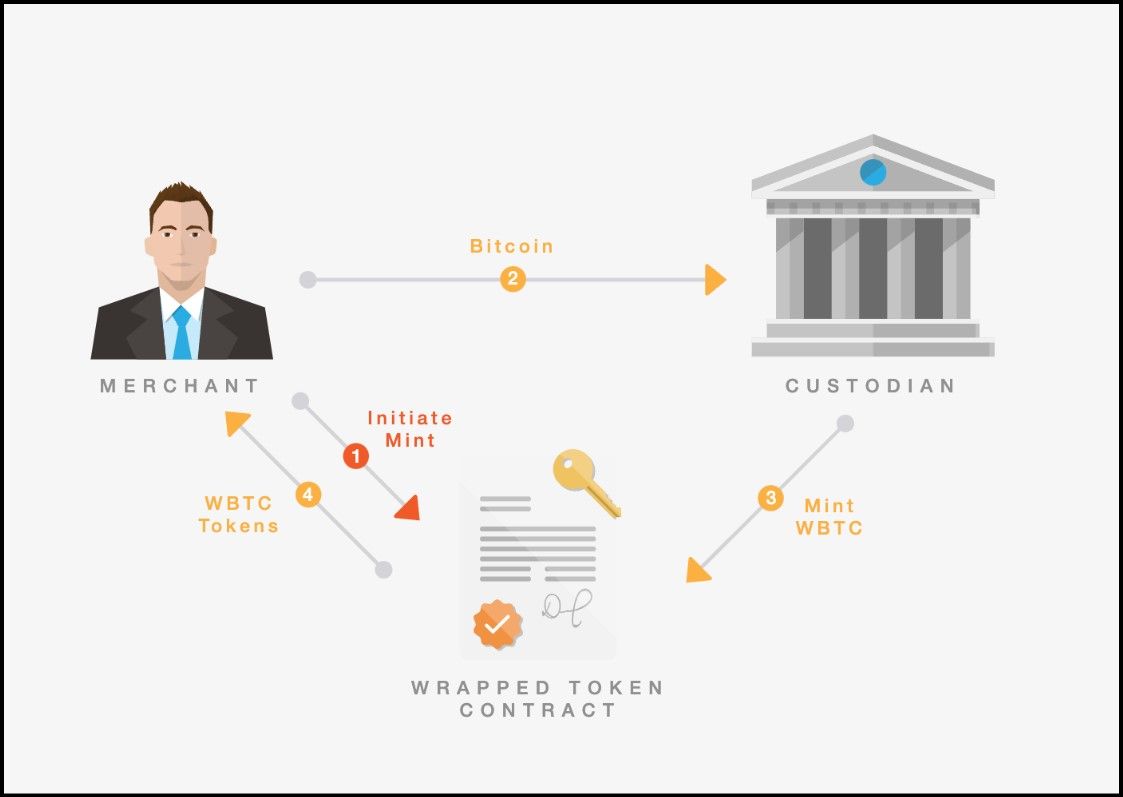 WBTC Architecture | Image via INX
WBTC Architecture | Image via INXWrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is a custodial-based wrapped asset, meaning its safety is tied to the trustworthiness of the custodians who hold the original Bitcoin in reserve. These custodians are responsible for locking Bitcoin in secure vaults and issuing an equivalent amount of WBTC on the Ethereum blockchain.
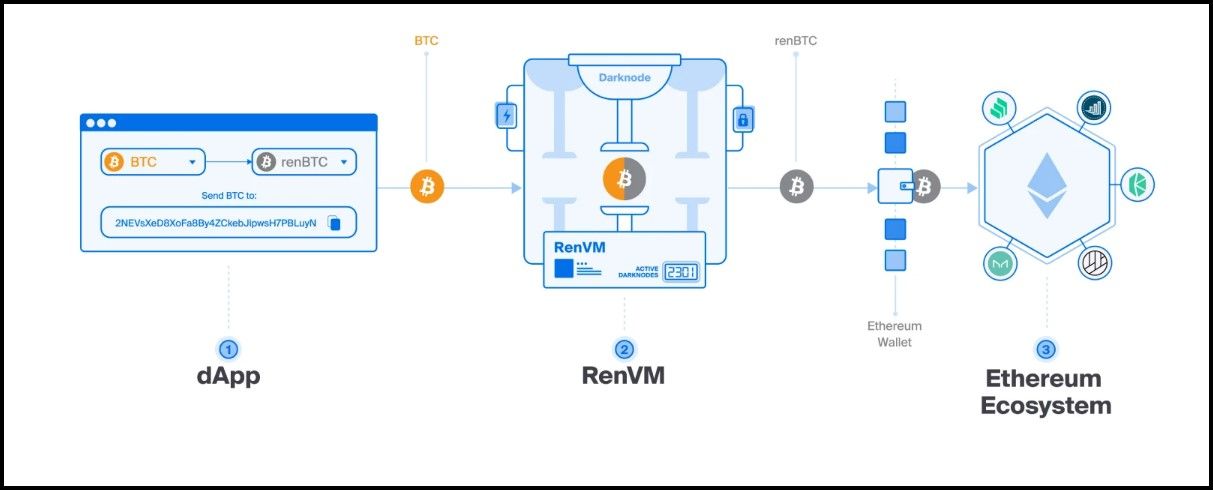 RenBTC Architecture | Image via CoinStats
RenBTC Architecture | Image via CoinStatsrenBTC uses RenVM protocol, a decentralized network of nodes called Darknodes. These nodes collectively manage the locking and minting of renBTC, reducing the reliance on a single entity. Therefore, safety hinges on smart contract vulnerabilities and node centralization of the Darknodes.
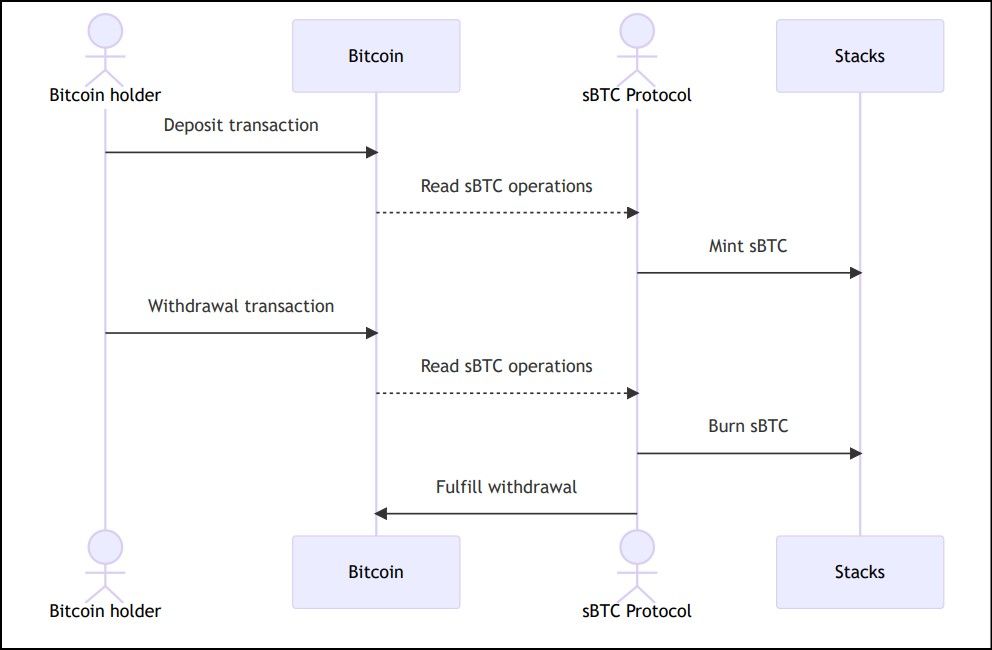 sBTC Flow Chart | Source: Github
sBTC Flow Chart | Source: GithubsBTC, from the Stacks protocol, is a newer form of wrapped Bitcoin that takes a trustless approach, offering decentralized custody without intermediaries. Using a two-way peg system, sBTC enables Bitcoin to move in and out of the Stacks network while being secured by Bitcoin's own blockchain. Stacks offers a trustless approach, but the scope of sBTC is limited to the Stacks protocol.
In summary, the safety of wrapped Bitcoin depends on the specific protocol being used:
- WBTC: Highly liquid and widely adopted, but centralized custodians introduce trust and counterparty risks.
- renBTC: Decentralized but susceptible to smart contract vulnerabilities and recent governance concerns.
- sBTC: Trustless and anchored to Bitcoin's security but limited to the Stacks network, which restricts its broader DeFi use.
Each wrapped Bitcoin option has trade-offs between security, decentralization, and usability. Understanding these risks is crucial for users seeking to interact with wrapped assets in DeFi.
Wrapped Bitcoin vs. Bitcoin
When considering whether to use Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) or original Bitcoin (BTC), the choice largely depends on your specific use case and goals within the blockchain ecosystem. Both forms of Bitcoin serve different purposes and have distinct advantages depending on your goal. Below is a comparison to help guide the best option for different scenarios.
Who Should Use Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)?
- Wrapped Bitcoin is ideal for those looking to utilize Bitcoin's liquidity in decentralized applications (DApps) and DeFi platforms on the Ethereum network. It allows users to take advantage of Bitcoin's value while enjoying the flexibility of Ethereum's ecosystem.
- DeFi participants: If you're looking to participate in yield farming, liquidity provision, or borrowing/lending on decentralized finance platforms like Aave, Curve, or Uniswap, WBTC is the better choice. You can use your Bitcoin in the Ethereum ecosystem without selling it for Ether or other tokens.
- Traders seeking liquidity: WBTC offers a faster and more efficient way to trade Bitcoin on Ethereum-based decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Transaction speeds on Ethereum are generally faster than on Bitcoin, and WBTC can seamlessly integrate with various DEXs and other DeFi protocols.
- Developers building on Ethereum: For developers creating decentralized applications or smart contracts on Ethereum that require Bitcoin's liquidity, WBTC is a natural fit since it behaves as an ERC-20 token, making integration smoother within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Who Should Stick with Original Bitcoin (BTC)?
- Original Bitcoin remains the better option for long-term holders and those who prioritize the core principles of Bitcoin: security, decentralization, and immutability. Bitcoin's value as a store of wealth is unmatched, and its robust security infrastructure makes it ideal for holding and transacting large amounts of value.
- Long-term HODLers: If your primary goal is to hold Bitcoin as a store of value or a hedge against inflation, there's no need to convert it to wrapped versions. Bitcoin's security and decentralized nature make it one of the safest assets to hold in the long term.
- Users looking for security: Since Bitcoin's blockchain has never been compromised, those prioritizing maximum security over other features should continue using the original Bitcoin. Its extensive hashrate and decentralized nature ensures it is the most secure blockchain network.
- Making transactions on Bitcoin's network: If you're using Bitcoin for peer-to-peer transactions or as a payment method, using BTC directly makes more sense. Wrapped versions like WBTC, while useful for DeFi, are designed for different purposes and require trust in custodians.
Summary of Use Cases:
| Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) | Original Bitcoin (BTC) |
| Participate in DeFi (lending, borrowing, yield farming) | Long-term holding as a store of value |
| Trade on Ethereum-based DEXs like Uniswap | Secure peer-to-peer transactions |
| Use in Ethereum DApps and smart contracts | High-security storage and transfers |
| Faster transaction speeds and lower fees compared to Bitcoin | Backed by Bitcoin's full hash power and network security |
In summary, Wrapped Bitcoin provides enhanced utility for DeFi users and traders who want to leverage Bitcoin's value in the Ethereum ecosystem. On the other hand, original Bitcoin remains the gold standard for security and long-term wealth preservation. Your specific needs and priorities should guide the choice between the two.
How to buy WBTC?
If you're looking to acquire Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), there are two primary methods:
1. Minting WBTC by Depositing Bitcoin
The first way to acquire WBTC is to deposit Bitcoin (BTC) with a custodian who mints an equivalent amount of WBTC on the Ethereum blockchain. This process involves working with merchants and custodians who manage the wrapping of Bitcoin:
- Custodian process: You deposit your BTC with a trusted custodian, such as BitGo, which then locks the BTC in reserve. In exchange, you receive WBTC on the Ethereum network.
- Minting WBTC: The custodian mints WBTC tokens, pegged 1:1 to the deposited BTC. This option is typically used by institutions or traders looking to convert significant amounts of BTC into WBTC for use in DeFi.
While this process guarantees a 1:1 backing of WBTC to BTC, it does require trust in the custodian and is more suitable for large-scale transactions.
2. Buying WBTC on Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
The second and more user-friendly option is to buy WBTC directly from decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or centralized exchanges (CEXs) where WBTC is listed. This option avoids depositing Bitcoin with a custodian and is faster for users looking to acquire WBTC instantly.
- Decentralized Exchanges on Ethereum:
- Uniswap: One of the largest DEXs on Ethereum, Uniswap offers liquidity pools where users can swap Ether (ETH) or other ERC-20 tokens for WBTC.
- SushiSwap: A popular alternative to Uniswap, SushiSwap provides WBTC trading pairs with other DeFi assets.
- Curve Finance: Known for stablecoin swaps, Curve also lists WBTC pools, often paired with stablecoins like USDC or DAI, for efficient swaps.
To buy WBTC on these platforms, connect your Ethereum-compatible wallet (e.g., MetaMask), select a trading pair (such as ETH/WBTC), and execute the swap.
Summary of Options
- Mint WBTC: Deposit BTC with a custodian (suitable for large amounts).
- Buy WBTC on DEXs: Use platforms like Uniswap, SushiSwap, or Curve Finance to swap tokens for WBTC.
Using either method, you can quickly and securely acquire WBTC for use in Ethereum's DeFi ecosystem.
What is Wrapped Bitcoin: Closing Thoughts
Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is an example of how blockchain technology continues to bridge the gap between different ecosystems to create a more interconnected and accessible financial system. By allowing Bitcoin to participate in Ethereum's decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, wrapped tokens like WBTC, renBTC, and sBTC unlock new opportunities for users to leverage their Bitcoin holdings in previously impossible ways.
The underlying technology that makes all of this possible is blockchain composability, which allows different networks to interact and communicate seamlessly. Wrapped tokens are among the many innovations driving blockchain's integration, making decentralized finance more accessible and efficient for users of all backgrounds.
As DeFi continues to grow, the innovations around wrapped assets will play a critical role in breaking down the silos between blockchains, offering users more flexibility and power over their financial activities.





