Imagine traditional urban development where some cities adopt a rapid urbanization model — quickly erecting structures, embracing innovation at an accelerated pace, and occasionally witnessing infrastructure challenges.
On the outskirts of this bustling crypto metropolis lies Cardano, approaching development more like a city planner than a hasty developer. In this scenario, before breaking ground and constructing new structures, the Cardano team engages in a thorough urban planning process. They pose essential questions, evaluating the purpose of their blockchain city, aligning different solutions with overarching objectives, and carefully considering the potential risks and rewards associated with each decision.
Some critics dub Cardano a "ghost chain," pointing to its deliberate pace in releasing updates. However, the city planners of Cardano see this as a strategic advantage, similar to a meticulous urban development plan. While other crypto neighbourhoods might rush into construction, Cardano focuses on getting the fundamentals right through academic peer reviews, in-depth research, and a careful examination of distributed systems design.

This Cardano review will explore how this cryptocurrency city is designed with intention, adopting a measured pace that prioritizes resilience over speed, ensuring it is fortified against the challenges faced by some of its counterparts. We'll also touch on Cardano's foray into privacy protocols, assess its status as an Ethereum killer, give you the lowdown on its scalability measures and evaluate whether it is indeed a ghost chain.
A History of Cardano
In April 2013, Charles Hoskinson made a bold move, leaving his consulting role to establish the Bitcoin Education Project. Recalling the initial reactions, he shares with Forbes, “My parents thought I was crazy. Everybody thought I was crazy. But I said, no, no, I got it all figured out.”
Fate played its part, leading Hoskinson to an encounter with Vitalik Buterin at the online school. This connection led him to become one of the eight original co-founders of Ethereum. However, the honeymoon phase was short-lived as disagreements surfaced on how to structure the Ethereum project. Describing it as a "boardroom brawl," Hoskinson advocated for accepting venture capital and establishing a for-profit entity with a formal governing structure. In contrast, Buterin envisioned Ethereum as a nonprofit organization with open-source, decentralized governance.
Frustrated with the differences, Hoskinson parted ways with Ethereum in June 2014. After a reflective six-month sabbatical contemplating a return to mathematics, Hoskinson was beckoned by former Ethereum colleague Jeremy Wood to embark on a new venture named IOHK. This company specializes in building cryptocurrencies and blockchains for corporations, government entities, and academic institutions.
The duo put in a few hundred thousand dollars and started getting contracts to build cryptocurrencies. With all revenue coming in Bitcoin, IOHK experienced substantial returns as the cryptocurrency surged in value. Once the crypto market exploded, they decided to liquidate. However, he remains tight-lipped about the specifics of the sale, emphasizing, “Relative to our burn rate, though, IOHK can now stay open for decades.”
IOHK's flagship project is Cardano, a public blockchain that hosts the ADA coin. The platform takes its name from the Italian mathematician Gerolamo Cardano, while the cryptocurrency is named after English mathematician Ada Lovelace.
The Cardano Project
Cardano is made up of four entities, each with a distinct role in the project.
- Cardano Foundation: A Swiss non-profit for the Cardano ecosystem and community. It is proactively working with governments and regulatory bodies and forming strategic partnerships with enterprises and other relevant open-source projects.
- IOHK: An engineering company dedicated to instrumentalizing peer-to-peer technologies. It is also determined to provide financial services to over three billion people who don’t have access to them. The group is contracted to design, build, and maintain the Cardano platform.
- Emurgo: A company formed to integrate, develop and support companies, businesses and industries that want to make use of Cardano’s decentralized blockchain and computation platform.
- Input Output Global: IOG is a US-based technology company that engineers and researches blockchain structures.
 Cardano's Charles Hoskinson Helped Co-Found Ethereum. Image via Cardano
Cardano's Charles Hoskinson Helped Co-Found Ethereum. Image via CardanoCardano's Development Process
Most start-ups follow the “move fast and break things” model characterized by a work ethos that prioritizes speed and experimentation in approaching tasks and innovation. Not Cardano though!
Academic Research
In contrast to numerous other blockchains, Cardano diverges from relying on technical principles derived from Bitcoin or other cryptocurrency systems. IOHK adopts a distinctive approach by collaborating with globally renowned academics for foundational research.
The majority of this research undergoes rigorous academic peer review, with papers subsequently presented at prestigious international conferences. The development process for all key components and functional aspects initiates with this research, aiming to ascertain the realm of possibilities and identify optimal approaches to achieve objectives.
The research and technical specifications forming the foundation of Cardano are openly published and accessible to the community.
 Cardano's Research Papers Are Available to the Public. Image via IOHK
Cardano's Research Papers Are Available to the Public. Image via IOHKPrototyping
Working alongside the research team, a technical prototyping team engages in experimenting with the implementations of functions and approaches outlined in the research. The goal is to translate theoretical possibilities into practical realities, gaining insights into real-world technical and functional implementation challenges. This process facilitates the development of technical specifications essential for developing the final product.
Technical Specifications
Through collaboration with the prototyping team, technical specifications are formulated and made public, drawing from the findings of research and prototyping efforts. These documents outline the anticipated functionality and behaviour, serving as a guide to guaranteeing that the final code implementation aligns with the initial research vision, achieves the necessary functionality, and remains technically viable.
Formal Development
IOHK engineers extensively leverage formal development methods — a stringent set of mathematical techniques for testing software to ensure it operates precisely as intended. While traditionally reserved for critical applications like avionics software, space flight systems, or high-volume banking software, IOHK pioneers the application of this rigorous approach in Cardano development, marking a first in the blockchain industry.
Functional Programming
IOHK adopts functional programming languages, with Haskell being a prominent choice. Functional programming languages, such as Haskell, exhibit reduced susceptibility to ambiguity and human error compared to other languages. Their inherent characteristics also facilitate easier testing and verification from a mathematical perspective.
The Cardano Architecture
The Cardano architecture is highly modular and includes the following components with different deployment use cases using different combinations of components.
- Node
- Command line interface (CLI)
- Daedalus wallet
- Cardano db-sync
- GraphQL API server (Apollo)
- SMASH server
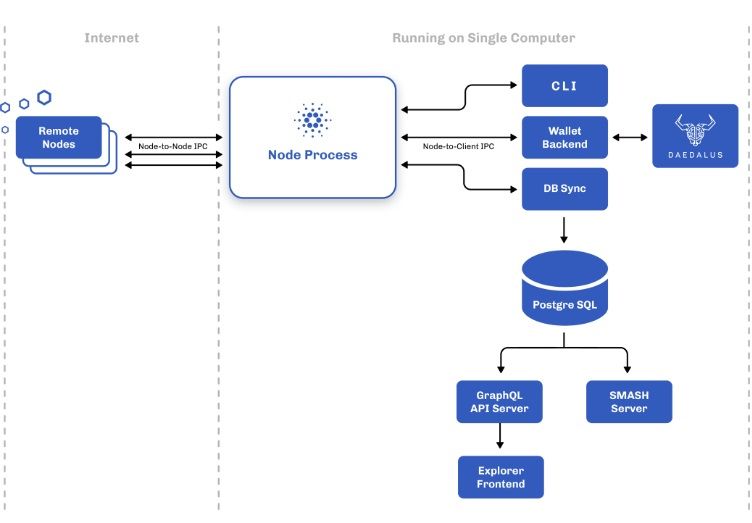 The Cardano Architecture is Highly Modular. Image via Cardano
The Cardano Architecture is Highly Modular. Image via CardanoNodes and Remote Nodes
In a blockchain system, nodes distributed across a network communicate to achieve consensus on the system's state. Nodes play a crucial role in:
- Executing the Ouroboros protocol
- Validating and relaying blocks
- Producing blocks (in some cases)
- Providing information about the blockchain state to local clients.
The Cardano-node, as the top-level node, encompasses subsystems like consensus, ledger, and networking, along with configuration, CLI, logging, and monitoring.
The node-to-node Inter-Process Communication (IPC) protocol facilitates block and transaction exchange among nodes as part of the Ouroboros consensus algorithm. It comprises three mini-protocols:
- Chain-sync for following the chain
- Block-fetch for obtaining block bodies
- Tx-submission for forwarding transactions
These mini protocols run on a single long-running Transmission Control Protocol connection between nodes, ensuring a modular and evolvable design with version negotiation for compatibility.
Node-to-Client IPC protocol serves local applications interacting with the blockchain through the node, enabling access to raw chain data, querying the ledger state, and submitting transactions. It utilizes similar design principles as node-to-node IPC but with different mini-protocols and local pipes instead of TCP connections. The mini-protocols include:
- Chain-sync for following the chain and obtaining blocks
- Local-tx-submission for submitting transactions
- Local-state-query for querying the ledger state
This protocol allows applications to interact with the node at a low level, with dedicated clients handling higher-level functionalities and APIs.
Command Line Interface
The CLI (Command Line Interface) tool for the node serves as a versatile Swiss army knife for the system, offering a wide range of functionalities. While it can perform almost any task, it operates at a low level and lacks the convenience of a graphical user interface (GUI) as it is text-based.
Key functionalities of the CLI tool include:
- Querying the node for information
- Submitting transactions
- Building and signing transactions
- Managing cryptographic keys
Daedalus Wallet
Daedalus serves as a comprehensive full-node wallet designed to assist users in managing their ADA, facilitating the sending and receiving of payments on the Cardano blockchain. The Daedalus system comprises both a wallet frontend, the graphical interface users interact with, and a backend, a service process responsible for essential tasks such as coin selection, transaction construction, and submission.
The backend communicates with a local node through the node-to-client IPC protocol and interfaces with the front end through an HTTP API. Additionally, it provides a CLI for direct wallet interaction and can operate independently of Daedalus, offering an API for seamless integration with other applications and systems. This standalone functionality is particularly convenient for software developers looking to integrate Cardano into diverse environments.
While the wallet backend can be utilized independently, it is recommended that most advanced users initiate their Cardano experience with Daedalus.
While you're here, check out our Daedalus Wallet review. If you don't have the software or hardware requirements needed to run a full-node wallet like Daedalus, our Top Cardano Wallets article provides some great alternatives.
Cardano db-sync
The Cardano node exclusively stores the blockchain and essential information required for blockchain validation. This design philosophy prioritizes minimizing code complexity, lowering computational costs, and optimizing resource usage. The objective is to keep the node's local interfaces streamlined, leveraging external clients to offer a range of user-friendly interfaces and additional functionalities.
The node abstains from providing a user-friendly query interface for historical blockchain information. Instead, this data service is delegated to a distinct component utilizing a Structured Query Language (SQL) database.
SMASH Server
SMASH (Stake Metadata Aggregation Server) serves as a metadata aggregation server for stake pools within the Cardano ecosystem. Its primary function is to manage metadata for stake pools, supporting their operations and the delegation ecosystem. SMASH offers a standardized framework, ensuring the listing of valid stake pools with verified metadata.
How Decentralized is Cardano?
Cardano is one of the most decentralized proof-of-stake networks out there with over 2,500 stake pool operators. However, in a September ranking of blockchains by their degree of decentralization, Cardano was noticeably absent.
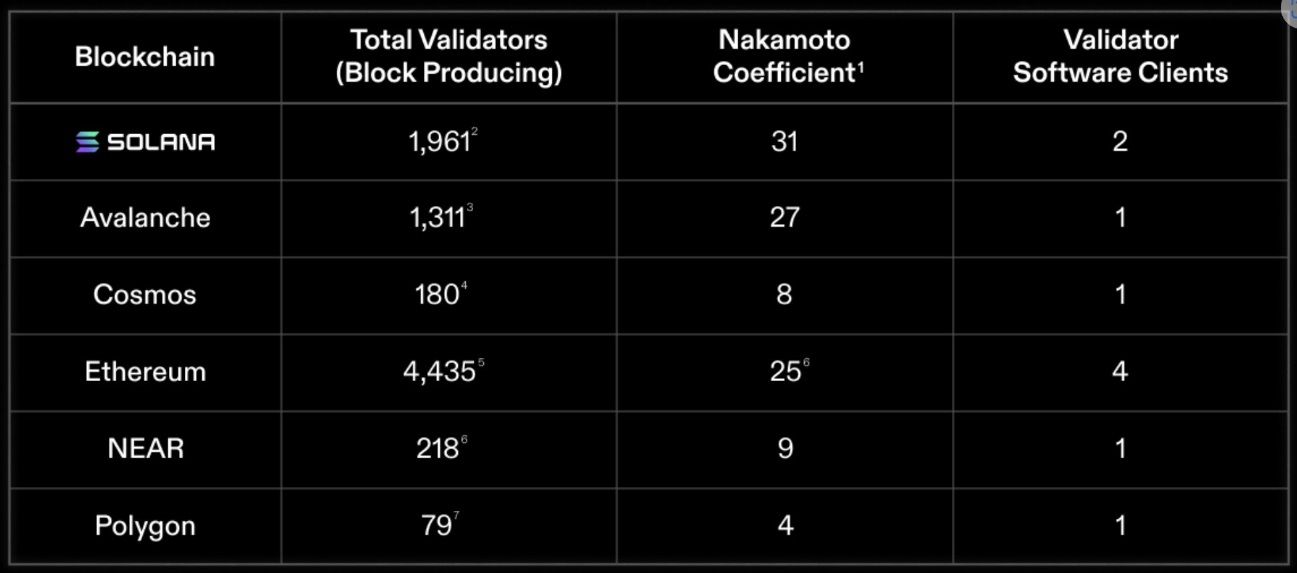 The Ranking is Based on the Nakamoto Coefficient Model. Image via X
The Ranking is Based on the Nakamoto Coefficient Model. Image via XThere could be a few reasons for this.
Ouroboros, while classified as a PoS consensus, distinguishes itself from conventional PoS mechanisms. Its design is tailored to attain consensus in a manner that is not only energy-efficient but also scalable. This commitment to a scientific philosophy in protocol development serves as a distinguishing factor for Cardano, often setting it apart from other chains compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Also, Cardano's architecture stands out with its layered structure. The independent operation of the settlement layer (Cardano SL) and the computation layer (Cardano CL) adds a unique dimension, setting it apart from other blockchains where these layers are commonly interwoven.
Regardless, the Cardano Foundation has recently taken steps towards achieving a fully decentralized on-chain governance structure. Enter CIP-1694.
CIP 1694
This is a proposal to revise Cardano's on-chain governance system to align with the requirements for Cardano's final Voltaire phase. This involves the removal of existing specialized governance support for protocol parameter updates and MIR certificates. Instead, two new fields will be introduced in normal transaction bodies for governance actions and votes.
Under this revamped governance framework, any Cardano user is empowered to submit a governance action. Additionally, three distinct governance bodies are introduced:
- A constitutional committee
- A group of delegate representatives, referred to as DReps
- Stake pool operators, henceforth called SPOs
For a governance action to be ratified, it must receive the endorsement of at least two out of these three governance bodies through their on-chain votes. The specific type of action and the governance system's state determine which bodies are required for ratification.
Once ratified, the actions are executed on-chain in adherence to a set of clearly defined rules. Similar to stake pools, ADA holders can register as a DRep, representing themselves and/or others. Additionally, ADA holders can choose to delegate their voting rights to any other DRep.
Cardano Security
Cardano revolutionized the Unspent Transaction Output (UTxO) model, prevalent in Bitcoin, by introducing the Extended UTxO (EUTxO) model. In this model, Cardano's blockchain consists of a list of unspent transactions that users can only consume, with each transaction representing a change in existing UTxOs. These UTxOs are governed by rules, such as the requirement of a signature, ensuring they are spent appropriately.
The uniqueness of Cardano's EUTxO model lies in its ability to support smart contracts. Unlike traditional transactions, smart contracts on Cardano can be signed by a smart contract address, introducing rules encoded in languages like PlutusTx, Aiken, and Plutarch.
Validators incorporate inputs like Context (checking transaction details), Datum (additional data attached to UTxOs), and Redeemer (data attached by the spender). This design allows for the processing of custom logic or smart contracts. The EUTxO model makes transactions deterministic, providing predictability in outcomes compared to non-deterministic transactions in other networks.
Cardano's security is further enhanced by its use of native tokens. Unlike other blockchains relying on smart contracts for token generation, Cardano treats all assets as native, avoiding complex permission hierarchies. Native tokens can be transferred with the regular user wallet signature, and smart contracts only require logic in the validator, eliminating the need for token control surrender.
Hydra and Cardano's Scalability
Hydra is Cardano's Layer 2 scalability solution, designed to enhance transaction speed with low latency and high throughput while minimizing transaction costs. The Hydra Head protocol version 0.10.0 or newer is now compatible with the Cardano mainnet, enabling the testing of Hydra nodes on the mainnet.
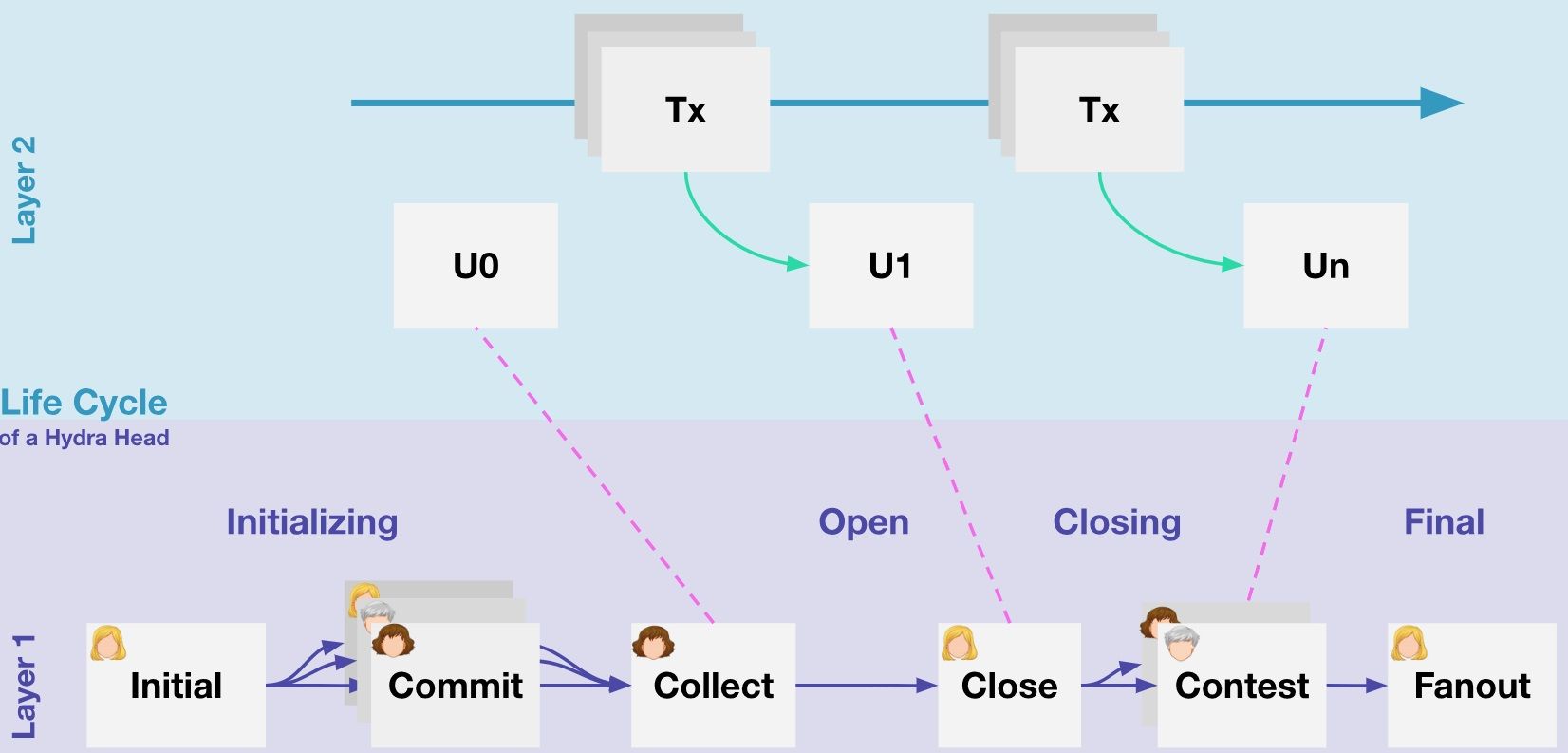 Hydra is Cardano's Layer 2 Scalability Solution. Image via Hydra
Hydra is Cardano's Layer 2 Scalability Solution. Image via HydraHail Hydra
Drawing inspiration from Bitcoin's Lightning Network, Hydra introduces a state channel framework that allows developers to execute scripts and complex transactions off-chain while maintaining security and functionality comparable to the Cardano main chain.
Hydra's isomorphism, replicating the functionality and security of the main chain, provides a cost-effective, secure, and computationally efficient solution for scaling decentralized protocols. This enables the development of optimized and scalable DApps within the Web3 ecosystem, supporting instant micropayments, subscription-based content, in-app purchases, and more without clogging the main chain or increasing network fees.
The protocol's customizability allows developers to run independent Hydra Heads tailored to their DApps' requirements. For example, decentralized exchanges can operate independently on Hydra Heads, managing millions of transactions, and implementing complex consensus and governance models while ensuring user security and network performance.
The Hydra Head is the first in the Hydra family of protocols that are designed to scale Cardano, and it establishes the groundwork for subsequent scalability enhancements. Operating as an off-chain mini-ledger, Hydra Head involves a relatively compact participant group and functions similarly to the primary on-chain ledger but with increased speed.
Hydra has the potential to make Cardano the fastest payment network globally, according to Hoskinson.
How Hydra Works
To explain how Hydra works, Cardano uses a poker game as an example of a multi-party state channel within the context of Hydra Heads. According to the network, this analogy captures the underlying principles of the Hydra Head protocol. Decentralized randomness or multi-party computation is assumed for this use case, allowing for the implementation of a decentralized poker game. The focus here is on the state channel aspect, and Hydra Heads offer a solution to facilitate this.
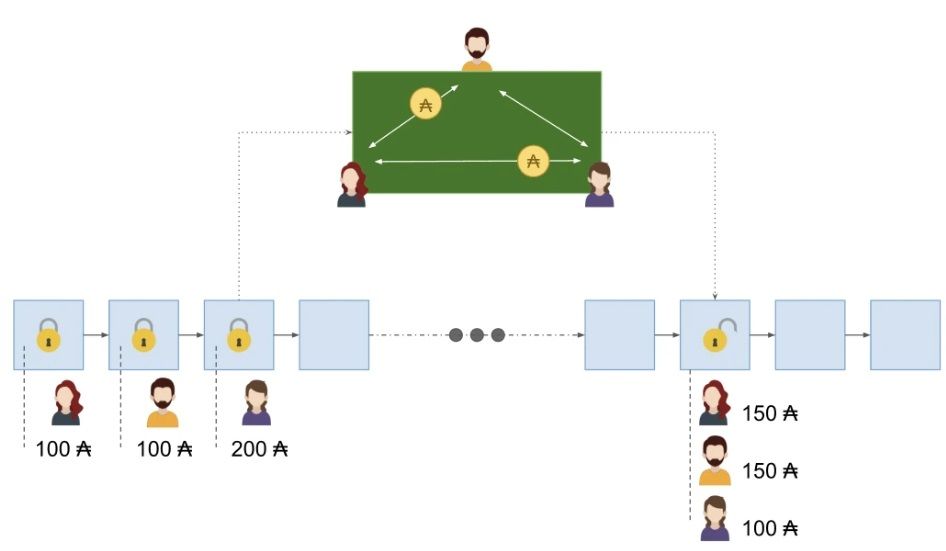 Cardano Uses a Poker Game as an Example of How Hydra Works. Image via Hydra
Cardano Uses a Poker Game as an Example of How Hydra Works. Image via HydraIn a poker game, participants engage in a structured activity with a defined beginning and end, governed by agreed-upon rules. The central element is the monetary aspect, involving bids, exchanges, and collaboration among players, each with individual goals and a level of mutual distrust.
In the Hydra Head model, each player in the poker game corresponds to a Hydra Head member, running its own Hydra node. Participants initiate a Head by committing funds, analogous to poker chips. Once established, the Head enables participants to seamlessly conduct transactions using on-head Plutus contracts. Funds are instantly transferred within the Head, with a script acting as the game dealer and ensuring adherence to the rules.
The game progresses until a well-defined distribution of funds is achieved, marking the end of the game. Participants can choose to engage in additional rounds or conclude the Head, recording the final UTxO distribution on Layer 1. Importantly, the entire game remains unknown on Layer 1, with only the conclusive UTxO distribution being recorded.
While this poker game scenario could be executed on Layer 1 alone, leveraging a Hydra Head offers advantages such as rapid transactions throughout the game and minimal or zero fees, aside from the costs associated with establishing the Hydra Head.
Hydra Use Cases
Hydra is currently exploring potential applications in areas such as payments, digital asset auctions, decentralized voting, and decentralized finance.
Payments
Hydra for Payments is an ongoing collaborative effort with Obsidian Systems, aiming to enhance the evolving Hydra Head Protocol with specialized tools tailored for payment-related scenarios.
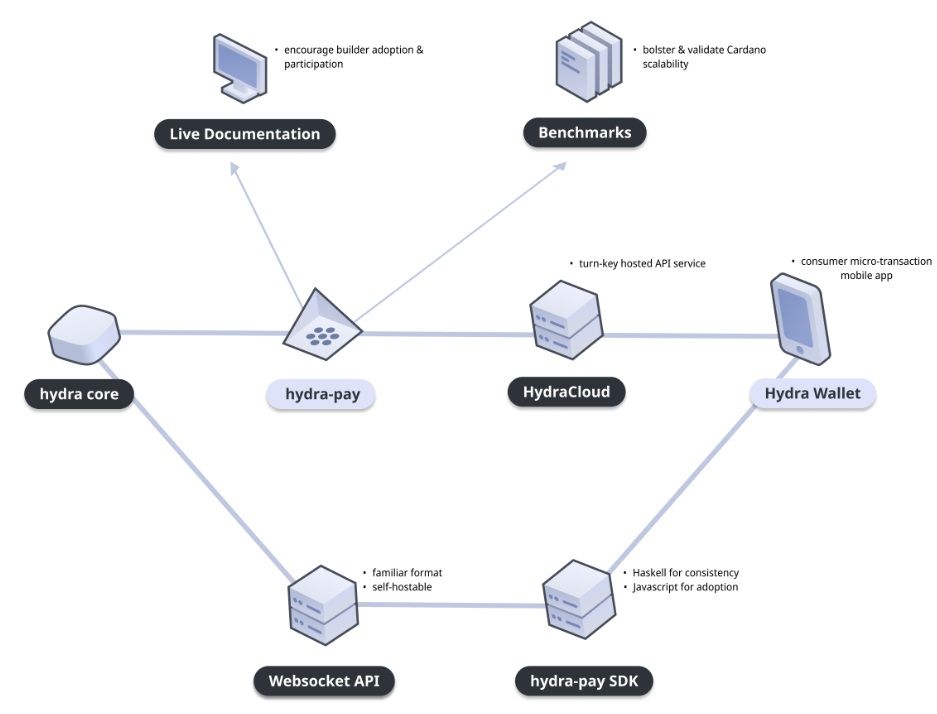 How Payments on Hydra Look Like. Image via Hydra
How Payments on Hydra Look Like. Image via HydraThe current development phase focuses on expanding the existing open-source Hydra for Payments library by incorporating the following features:
- An enhanced payment channel API with added convenience features, streamlining the onboarding process and reducing the time-to-market for project builders.
- Implementation of high-assurance mechanisms, which is particularly crucial for developers working on commercial projects entrusted with user assets.
- Adoption of flexible configurations with sensible defaults, empowering builders to dynamically scale their products and implement engaging user experiences.
- The plan is to consolidate these advancements and release them as the mainnet-compatible Hydra for Payments SDK.
To validate these objectives, a mobile reference application is set to be launched. This application will directly leverage the Hydra for Payments SDK, incorporating all critical payment channel functionalities.
Auctions
Hydra for Auctions on Cardano aims to enhance the NFT ecosystem by introducing efficient auction mechanisms to facilitate price discovery for various digital and non-digital assets. While Cardano has established itself as a platform for NFT marketplaces, the current challenge lies in price discovery due to the novelty of tokenized assets and the relatively small market size.
The proposed solution involves leveraging Hydra to address the constraints of conducting auctions on the main network. Hydra's short confirmation delays and immediate finality within Hydra Heads make it an ideal choice for creating an efficient auction experience.
The envisioned milestones for implementing Hydra-based auctions include:
- Delegated Voucher Invitational: Creating a prototype for auctions hosted on L2, allowing for invitation-based bidding.
- Delegated Voucher Open: Extending the auction model to include open auctions, where participants can freely join without seller permission, requiring fully collateralized bids.
- SDK for Delegated Voucher Auctions: Developing a modular Software Development Kit (SDK) for application developers to integrate delegated voucher auctions into their products.
- Auctions-as-a-service Single: Establishing a persistent service for decentralized applications (DApps) to run multiple auctions on L2, utilizing a single Hydra head and introducing an as-a-service business model.
- Auctions-as-a-service Multi: Expanding the service to support multiple auctions concurrently, further enhancing the scalability and functionality of auction services on Cardano.
This approach not only addresses the challenges of price discovery in the NFT sector but also lays the groundwork for a new business ecosystem where scalability providers can offer L2 hosting services to applications, fostering growth and innovation within the Cardano network.
Has Cardano Solved the Blockchain Trilemma?
So far, we've touched on Cardano's security, scalability and decentralization. The Blockchain Trilemma, popularized by Ethereum's Buterin, is a concept that highlights the inherent trade-off between the three.
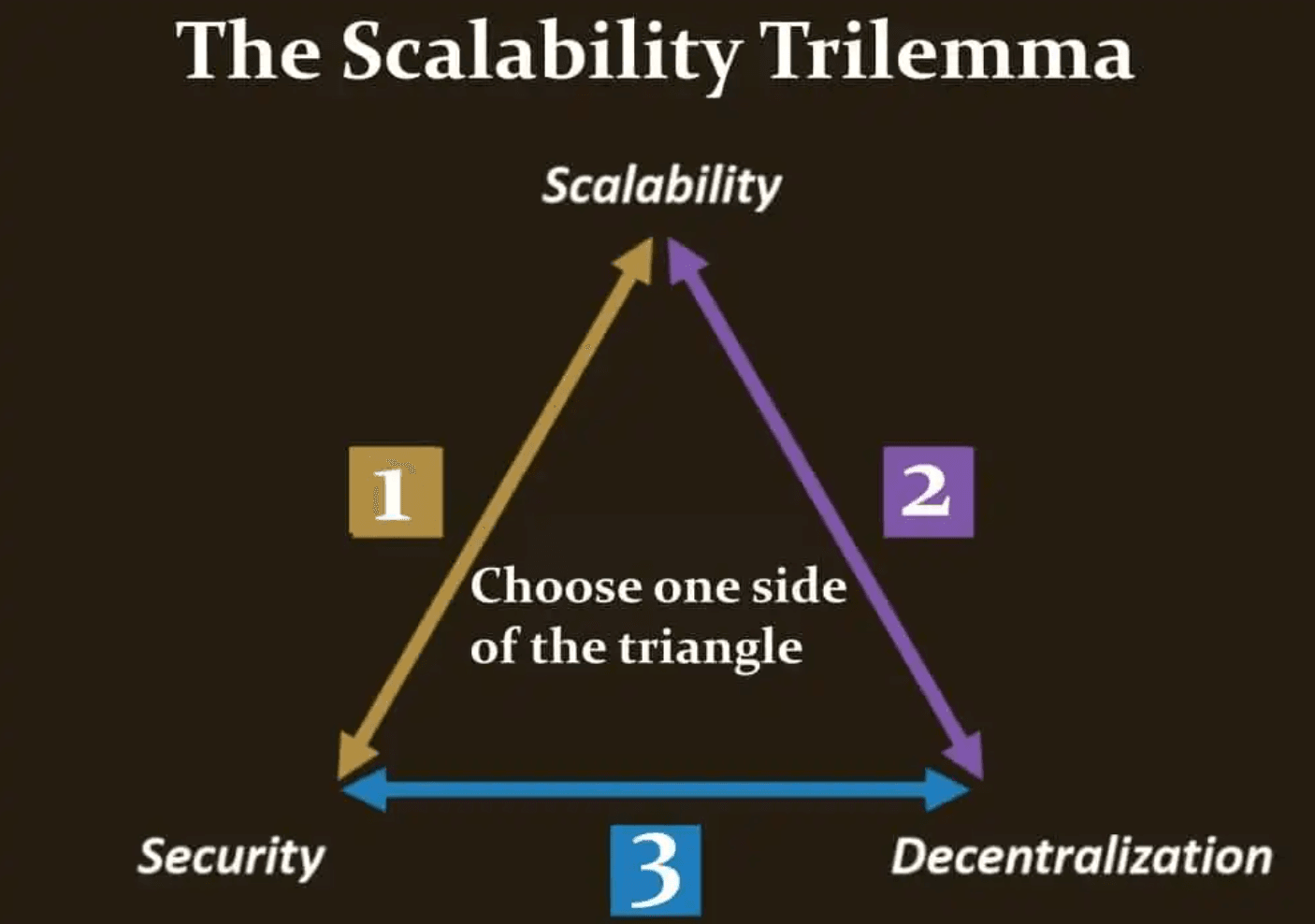
With regard to Cardano, the answer to that question is no. At least, not yet!
While Cardano is decentralized and has impenetrable security, its efforts towards scalability have yet to yield any solid results. Of course, Hydra is a main piece in the Cardano scalability puzzle, and a recent development report showed that work continues on that front.
In addition to Hydra, there are two more components that are expected to contribute to Cardano's scalability aspirations: The consensus upgrade and Mithril. The blockchain Trilemma has proven to be quite the obstacle to overcome and plagues nearly all blockchain networks. One interesting project that has claimed to overcome this hurdle is Algorand.
What Is Ouroboros Leios?
Imagine you have a highway (blockchain) where cars (transactions) need to move smoothly. However, the highway's limitations mean only a certain number of cars can pass through, which results in clogged traffic, or network congestion in blockchain parlance. This means an upgrade is due so the highway can handle more cars at a faster pace. Another consideration: the revamped highway should remain secure, just as it was before.
That's the crux of Ouroboros Leios, a planned upgrade to the Cardano proof-of-stake consensus.
With Ouroboros Leios, Cardano's goal is to increase the number of transactions that can use the blockchain highway and make the overall journey quicker. Keeping the above example in mind, it's like adding more lanes to the highway, which would not only mean it can handle rush hour traffic, ensuring that each car can reach its destination faster.
The introduction of a new design opens avenues for integrating various features. These include tiered transaction fees, aligning with varying levels of service priority, and expediting chain synchronization by eliminating the necessity to execute every smart contract.
These advancements, however, come with trade-offs in the form of an uptick in resource utilization and transaction latency.
It's important to note that the Ouroboros Leios design represents more than a modest or incremental extension. Instead, it stands as a significant expansion beyond the Ouroboros Praos and Genesis designs, with consequential adjustments required for practical implementation.
Supercharging Scalability With Leios
The Ouroboros Leios design emphasizes vertical scalability, indicating that increasing the computational and network resources of individual nodes can proportionally enhance throughput. This is comparable to the concept of vertically scalable databases or web servers, where greater computational capabilities lead to increased performance.
However, the design does not inherently offer horizontal scalability, which would involve boosting throughput by adding more computers to the system. Future research may explore variations or extensions to the Leios design to introduce a degree of horizontal scalability. One potential approach involves having block producers validate only the input blocks they report on, distributing the validation process across different reporters. This could increase the overall number of input blocks and align the validation workload with the stake held by participants, promoting fairness.
Achieving horizontal scalability would require revisions to various aspects of the design, including finding mechanisms to handle transactions on the submission side so that not all nodes are obligated to validate every transaction.
Mithril
Participating in the Cardano ecosystem traditionally involves either running a full node, which demands substantial resources or using a lightweight client with third-party APIs. Mithril, live on Cardano, aims to change this.
Mithril bootstraps a full Cardano node, reducing synchronization time and maintaining robust security. The process of synchronizing a full node typically takes a few hours, but it can be achieved in under 23 minutes with Mithril. This not only benefits node operators but also opens doors for DApp developers to create lightweight applications, streamline sidechain operations, and facilitate stake-based voting and governance solutions.
Cardano says Mithril's evolution promises to simplify decentralized decision-making through secure and lightweight tally verification, marking a significant advancement for the network.
Cardano Partner Chains
At the Cardano Summit 2023, Charles Hoskinson, CEO of Input Output Global, introduced a new framework for developing partner chains on the Cardano blockchain.
 Cardano Recently Introduced a New Framework For Developing Partner Chains. Image via IOHK
Cardano Recently Introduced a New Framework For Developing Partner Chains. Image via IOHKThese partner chains leverage Cardano's core strengths, modular blockchain technology, and security to transform the launch and operation of new blockchains. This framework allows for the creation of partner chains without being tied to any specific network or technology stack.
Cardano's design, separating the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) from the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL), enables the development of a robust cross-chain settlement layer. Partner chains utilize a modular framework, with Parity Technologies' (Polkadot) Substrate stack as a foundation. IOG extends Substrate with trustless integration to Cardano and contributes composable Substrate components, known as “pallets,” fostering interoperability and collaboration.
The new partner chain framework addresses key challenges in existing modular blockchain solutions, such as interoperability, security, tokenomics, and lock-in. Cardano serves as the ultimate settlement layer, offering security through stake pool operators (SPOs) and the Minotaur multi-resource consensus protocol allows validators from other ecosystems to contribute. Babel fees resolve tokenomics concerns for new networks, ensuring compensation for SPOs in ADA. Trustless bridges connect partner chains to Cardano and beyond, facilitating risk-free interoperability.
The first partner chain to implement this framework is Midnight.
Cardano's Midnight
Blockchain technology, for all its transparent and decentralized strengths, has a complicated relationship with privacy, especially for those who value anonymity.
Transparency ensures that all participants within a network can access and verify the transaction history. However, when it comes to personal identities, blockchain operates on a pseudonymous model. Instead of revealing actual names or addresses, participants are identified by cryptographic addresses or public keys. This pseudonymity can be a double-edged sword, particularly for individuals who prioritize privacy. While blockchain transactions are traceable and verifiable, the true identities behind these cryptographic addresses remain obscured.
For privacy-minded individuals, the pseudonymous nature of blockchain may not provide the level of confidentiality they desire. Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash have emerged in response to this concern. These projects integrate advanced cryptographic techniques to enhance privacy by obfuscating transaction details and offering enhanced anonymity features.
Cardano's Midnight is the latest entrant in this vertical.
What is Cardano's Midnight?
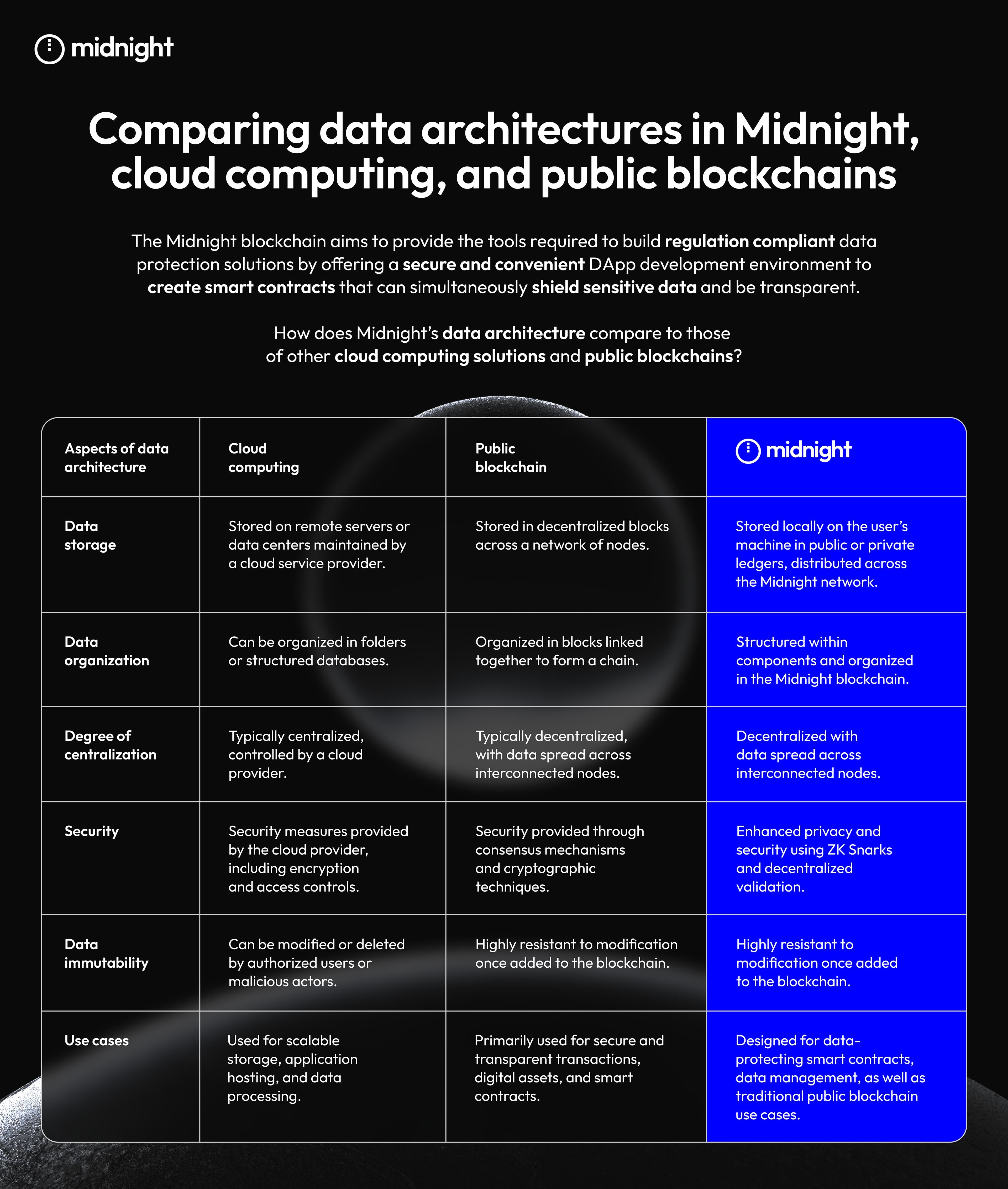
Developed by Input Output Global (IOG), Midnight is a blockchain designed to comply with regulations while prioritizing data protection.
 Midnight is a Privacy-Focused Sidechain by Cardano. Image via Midnight
Midnight is a Privacy-Focused Sidechain by Cardano. Image via MidnightMidnight gives individuals the essential tools to develop data protection solutions that adhere to regulatory standards. It introduces a secure and user-friendly environment for developing DApps, facilitating the creation of smart contracts that not only safeguard sensitive data but also maintain transparency.
Midnight divides a smart contract's state into two components — a public state housed on the blockchain that can be viewed by everyone, and a private, off-chain, local state dedicated to each party.
The Cardano sidechain utilizes succinct non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs (ZK Snarks), which enable one party to prove to another that a certain statement or claim is true, without revealing the contents behind that statement.
 Trustless Verification and Lower Fees Are Among ZK Snarks' Benefits. Image via Midnight
Trustless Verification and Lower Fees Are Among ZK Snarks' Benefits. Image via MidnightMidnight Features
Midnight is currently in the development phase. As a result, some features are still being explored and there's a chance features listed here may not be accessible in pre-production releases.
Data Protection
Midnight's primary focus revolves around addressing the issue of data protection. A significant portion of data in decentralized finance (DeFi) is not suitable for public ledger exposure. Midnight presents developers with the capability to develop DApps that exercise control over which data is disclosed publicly and which remains private, allowing for selective disclosure.
These measures are extended to metadata — information about the data itself. Traditional blockchains often expose transaction metadata to anyone with a suitable application, which can include both trustworthy and untrustworthy entities. Midnight introduces features such as shielded tokens, ensuring interactions occur without the leakage of metadata (e.g., keeping wallet addresses and transaction specifics confidential). As a result, DApps utilizing Midnight can afford the same level of safeguarding of sensitive metadata as they do to other classified information.
Midnight's smart contract protocol makes four key contributions to data-protecting systems:
- Creation of data-protecting smart contracts
- Realization of a large class of such contracts
- Enablement of concurrent interactions with smart contracts, without compromising on data confidentiality
- Demonstration of a general methodology to efficiently and composably build smart contract systems.
Meeting regulatory requirements
Every industry has to meet regulatory requirements and the crypto industry is no exception, finding itself squarely within the regulators' purview. The onus of meeting these requirements falls on application builders who must ensure that their solutions align with the relevant regulations. To achieve this, they must take into account factors such as the nature of their operations, the jurisdiction they function in and their target audiences.
Midnight's adaptable framework, allowing the creation of DApps that span the entire spectrum from fully public to entirely private, provides developers with the flexibility to make data-protecting applications while meeting regulatory requirements. The robust data protection capabilities of Midnight not only bolster DApps' compliance with privacy laws but also align with customers' expectations for safeguarding their data.
Tools to Build Regulation-Compliant DApps
Midnight equips developers with the essential tools to develop DApps that not only harness innovative features but also adhere to regulatory standards. Here is a look at some of its capabilities:
- Midnight Programming Model: Based on the principles outlined in the Kachina research paper, the Midnight programming model incorporates a domain-specific language and the midnight.js client library, providing a tangible realization of innovative concepts.
- Dual-State Management: Smart contracts within Midnight can efficiently handle two states simultaneously — an individual's private state on a local machine and a public state existing on the blockchain.
- Domain-Specific Language with TypeScript: Critical components of smart contracts are written in a domain-specific language seamlessly integrated with TypeScript.
- Microsoft Visual Studio Code Plugin: Developers benefit from the familiarity and power of the Microsoft Visual Studio Code IDE through a dedicated plugin.
- ZK Snarks: Midnight employs Zero-Knowledge proofs using ZK Snarks, offering advantages such as a constant proof size and minimal communication between the prover and verifier.
- Selective Disclosure: Midnight's ZK proofs enable selective disclosure of information, safeguarding against potential information leakage that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Theoretical Foundation: Midnight's ZK proofs are grounded in a robust theoretical foundation — the Universally Composable (UC) Framework — ensuring universally composable privacy and security.
Midnight Benefits and Use Cases
Traditional blockchains grapple with limitations that hinder broader adoption. However, Midnight aims to be a groundbreaking solution.
 Midnight Aims to Blow the Competition Out of the Park. Image via Midnight
Midnight Aims to Blow the Competition Out of the Park. Image via MidnightThe platform facilitates the creation of DApps with a myriad of benefits, including:
- Data Protection: Midnight ensures robust data protection, a crucial element for fostering trust and compliance with privacy standards.
- Assurance of Data Integrity: The platform provides a secure environment for transactions and information.
- Scalability: Midnight prioritizes scalability, ensuring seamless user experiences and accommodating growth without compromising performance.
- Verifiable and Decentralized Web3 Environment: It contributes to the creation of a verifiable and decentralized Web3 environment.
- Self-Sovereign Identity Management: Midnight empowers users with self-sovereign identity management, offering individuals greater control over their personal information.
- Enhanced Developer Experience: The integration of ZK Snarks is made simple and accessible, enhancing the overall developer experience.
- Potential Reduction of Compliance Costs: Organizations leveraging Midnight may experience a potential reduction in compliance costs and system maintenance. The platform's design minimizes the need to capture and store extensive customer data.
Noteworthy potential DApp use cases encompass:
- Shareable Know Your Customer (KYC) Credentials: Enabling individuals or institutions to validate themselves without the need for extensive documentation.
- Decentralized Credit Scoring: Assigning credit scores to decentralized identifiers, preventing data leakage to malicious actors.
- Decentralized Anonymous Voting: Allowing voters to prove their eligibility and the absence of fraudulent voting without revealing additional information.
- Medical History Systems: Safeguarding patient confidentiality in the management of medical histories.
Midnight's DUST Token
Powering Midnight's ecosystem will be DUST, its native shielded token that will allow participants to transact with privacy, Midnight CEO Eran Barak said at the Cardano Summit in November.
Shielded tokens tend to have liquidity issues. Midnight's solution? A second unshielded token that will provide network liquidity and security. Barak didn't expand further on the dual-token system or the tokenomics likely because the project is still in the development phase.
Cardano Developer Ecosystem
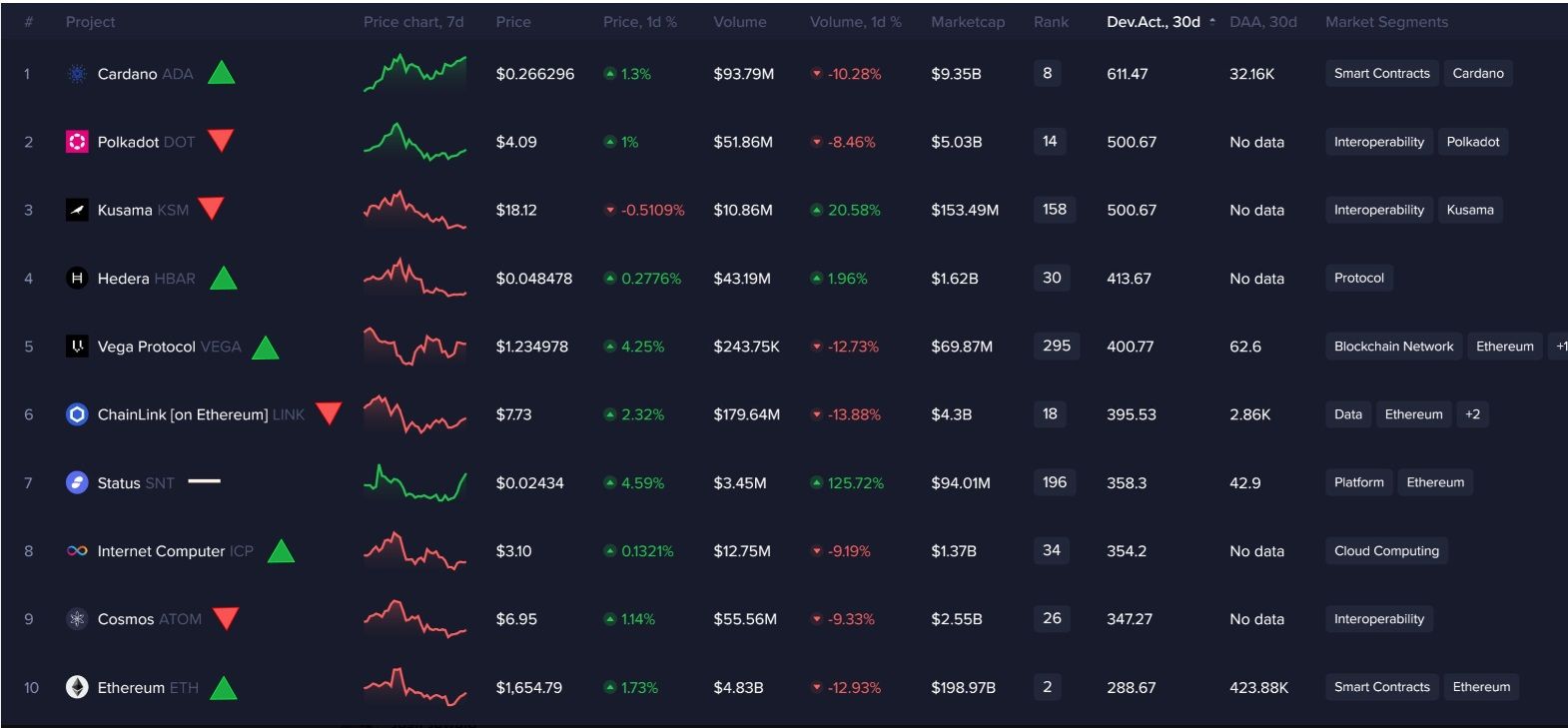
Cardano has emerged as the blockchain with the highest development activity for a period in Q4 of 2023, surpassing other prominent projects in the cryptocurrency space. Cardano outshined competitors like Polkadot, Kusama, Cosmos, and even Ethereum, securing the top position in terms of notable GitHub commits.
 Cardano Emerged as the Blockchain with the Highest Development Activity. Image via X
Cardano Emerged as the Blockchain with the Highest Development Activity. Image via XAccording to data from Santiment, Cardano recorded 611.47 GitHub commits in the last 30 days, showcasing a substantial lead over Polkadot and Kusama, both of which tied for second place with 500.67 GitHub commits each.
This significant surge in development activity is a positive indicator of the confidence developers place in Cardano's potential.
In 2022, Cardano conducted a survey to assess the state of its developer ecosystem. Here are some of the findings.
- While software engineers formed the majority of those participating in the survey, there was also a significant number of students, potentially signalling interest from younger audiences and younger academic audiences.
- The vast majority of the Cardano developer ecosystem has either over 10 years of experience writing software or between 3 and 10 years of experience.
- In response to a question on the Cardano developer ecosystem's greatest asset, respondents emphasized the “impressive community,” which they described as goal-oriented and helpful.
- Survey participants said the onboarding process was the most painful point in Cardano's developer ecosystem.
The survey for the 2023 edition is still open.
In addition, Cardano publishes developer reports every week, which contain behind-the-scenes updates.
 Cardano Publishes Weekly Developer Reports. Image via Essential Cardano
Cardano Publishes Weekly Developer Reports. Image via Essential CardanoADA Token
Cardano's native ADA coin powers its whole ecosystem. Each transaction done using ADA is immutably and transparently recorded on the Cardano blockchain.
Every ADA holder possesses a stake in the Cardano network. ADA held in a wallet can be delegated to a stake pool, enabling users to earn rewards and actively contribute to the network's successful operation. While we're on the topic, head over to our guide on how to choose a Cardano staking pool.
Users can also discover the opportunity to run their own stake pool, enhancing their chances of receiving rewards.
ADA Tokenomics
Cardano has undergone several public funding rounds that have fetched the network over $79 million.
- Tranche 1 (November 2015) raised $2.7 million at an average price of $0.0024.
- Tranche 2 (April 2016) raised $16.5 million at an average price of $0.0025.
- Tranche 3 (September 2016) raised $14.3 million at an average price of $0.0026.
- Tranche 3.5 (September 2016) raised $19.4 million at an average price of $0.0027.
- Tranche 4 (February 2017) raised $26.4 million at an average price of $0.0028.
 The Initial Token Distribution of ADA. Image via CoinGecko
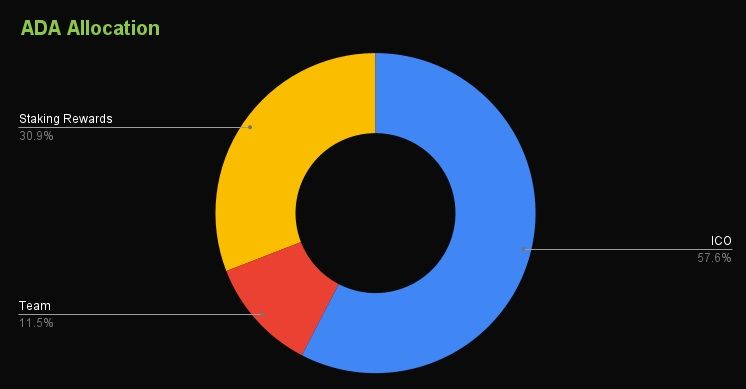
The Initial Token Distribution of ADA. Image via CoinGeckoAs for the initial token distribution of ADA, this is what it looks like:
- 57.60% was allocated to ICO
- 11.50% is allocated to the team
- 30.90% is allocated to staking rewards
ADA's max supply is capped at 45 billion with an inflationary emission rate.
Cardano's Monetary Policy
Cardano's monetary policy serves two main purposes:
- Incentivizing community participation in network development
- Funding the treasury
In terms of rewards, participants, including delegators and stake pool operators, receive staking rewards from transaction fees and monetary expansion. Transaction fees contribute to a reward pool, and a portion of it is allocated to the treasury, with the rest distributed as epoch rewards. This approach encourages early adopters by offering higher initial rewards, gradually transitioning to smaller rewards compensated by increasing transaction fees over time.
The treasury plays a vital role in financing Cardano's development activities through a voting process. Regular contributions are made to the treasury to ensure a consistent availability of funds. This monetary system aims for predictability in rewards, avoiding drastic variations and facilitating a smooth decline over time.
Where to Buy ADA
If you're looking to get your hands on ADA, you can check out centralized exchanges like Binance, Bybit, Kraken and Coinbase. If you're more into decentralized exchanges, you can buy ADA through Sundaeswap, SushiSwap and Minswap.
Also, check out our top picks for the best crypto exchanges and the best decentralized exchanges.
Where to Store ADA
When it comes to storing your ADA tokens, a variety of wallet options cater to different needs and preferences. Among the popular choices known for their user-friendly interfaces and accessibility are hot wallets like Exodus, and Trust Wallet. These wallets provide a convenient solution for users who engage in frequent transactions and prefer instant access to their funds.
If you fancy yourself a HODler, opting for cold wallets, also known as hardware wallets, would be your best bet. Cold wallets offer enhanced security by keeping your private keys offline, protecting your assets from potential online threats. Among the reputable cold wallet options for ADA storage, Ledger, Trezor, and Ellipal stand out, providing robust security features and a reliable means of safeguarding your ADA tokens.
However, before you choose a wallet, it's essential to weigh the features and benefits to make sure they align with your preferences and risk tolerance.
Is Cardano a Ghost Chain?
A "ghost chain" refers to a cryptocurrency project characterized by a lack of notable activities within its ecosystem.
Cardano cannot be characterized as a ghost chain, and here's why.
DeFi is Thriving
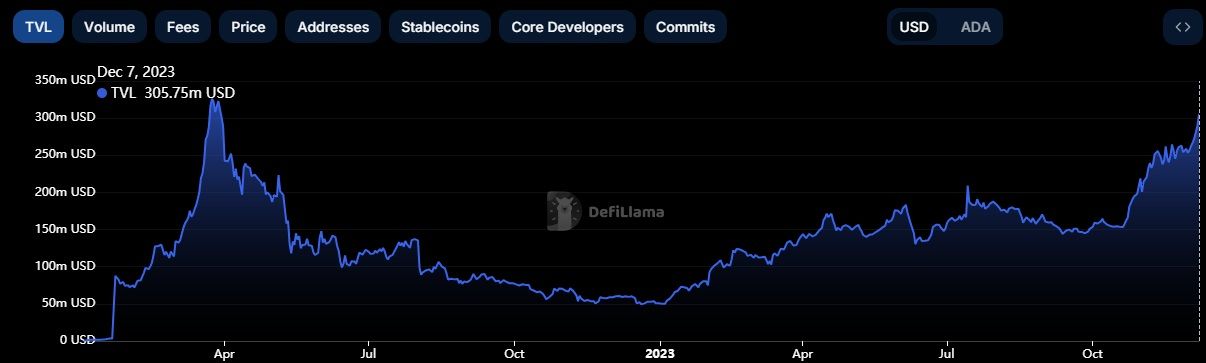
Data compiled by DeFi Llama shows that Cardano’s TVL stood at $305.8 million as of Dec. 7, growing a whopping 6,146% year to date. In ADA terms, TVL has reached an all-time high of 691.7 million.
 Cardano's TVL Has Grown Over 6,000% Thus Far in 2023. Image via DefiLlama
Cardano's TVL Has Grown Over 6,000% Thus Far in 2023. Image via DefiLlamaBut perhaps the most significant DeFi project is the one that is set to launch later this month.
USDM Stablecoin
Mehen Finance is set to introduce the fiat-backed USDM stablecoin on Dec. 19, marking a significant advancement in Cardano's DeFi landscape.
The news comes after the launch of USDA, a stablecoin by Cardano's commercial arm Emurgo, was delayed amid regulatory uncertainty.
Registered with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network and currently seeking US licensing, Mehen is prioritizing a robust regulatory framework to ensure user security. Mehen's services have limited access depending on user jurisdiction, allowing only eligible users to connect their Cardano wallet to the Mehen DApp. Mehen has also implemented Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures.
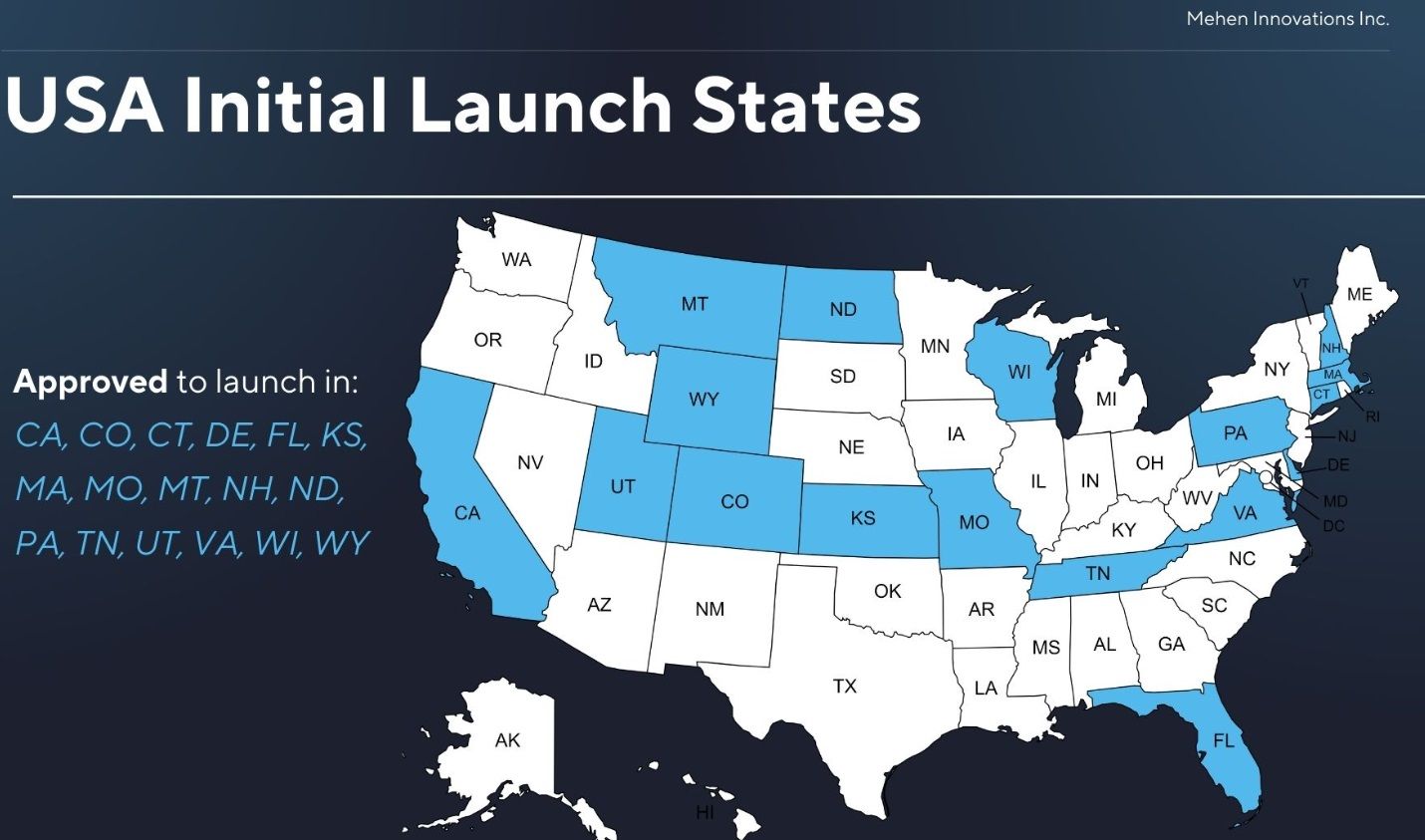 The USDM Stablecoin Will Launch in 17 US States. Image via X
The USDM Stablecoin Will Launch in 17 US States. Image via XMehen is gearing up for its initial launch with “Wave 0” on Dec. 19, having obtained licenses in California, Colorado, Delaware, Kansas, Montana, Missouri, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming. The company hopes to reach an agreement with Texas before launch, and it aims to launch the stablecoin across the pond in Europe sometime in 2024.
How Cardano Benefits From This
The introduction of a USD-backed stablecoin into Cardano's DeFi ecosystem should bring stability, capital efficiency, and robust security and compliance to the network. USDM provides users with a dependable store of value, mitigating the inherent volatility seen in many cryptocurrencies.
In addition, Mehen's commitment to a rigorous regulatory framework ensures a secure and compliant operational environment, which positions Cardano as a reliable hub for decentralized finance.
User Base
Ghost chains do not have thousands of users. As of Dec. 7, there were over 55,000 returning Cardano addresses, according to Defi Llama. DappRadar pegs the network's unique active wallets at 24,790.
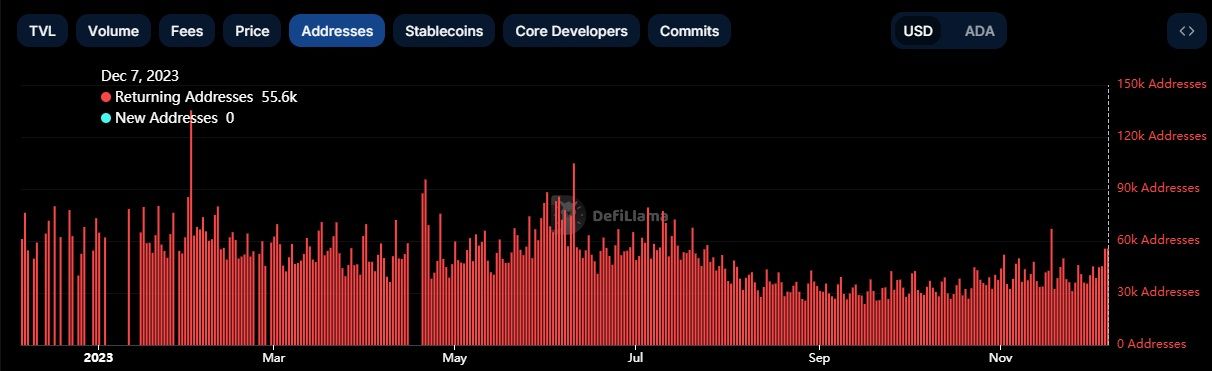 There Are Over 55,000 Returning Cardano Addresses. Image via DefiLlama
There Are Over 55,000 Returning Cardano Addresses. Image via DefiLlamaNFTs Are Alive and Well
Data by CryptoSlam shows that the total sales of Cardano NFTs in the past seven days totalled $1.2 million, making it the 10th-largest blockchain by NFT sales volume.
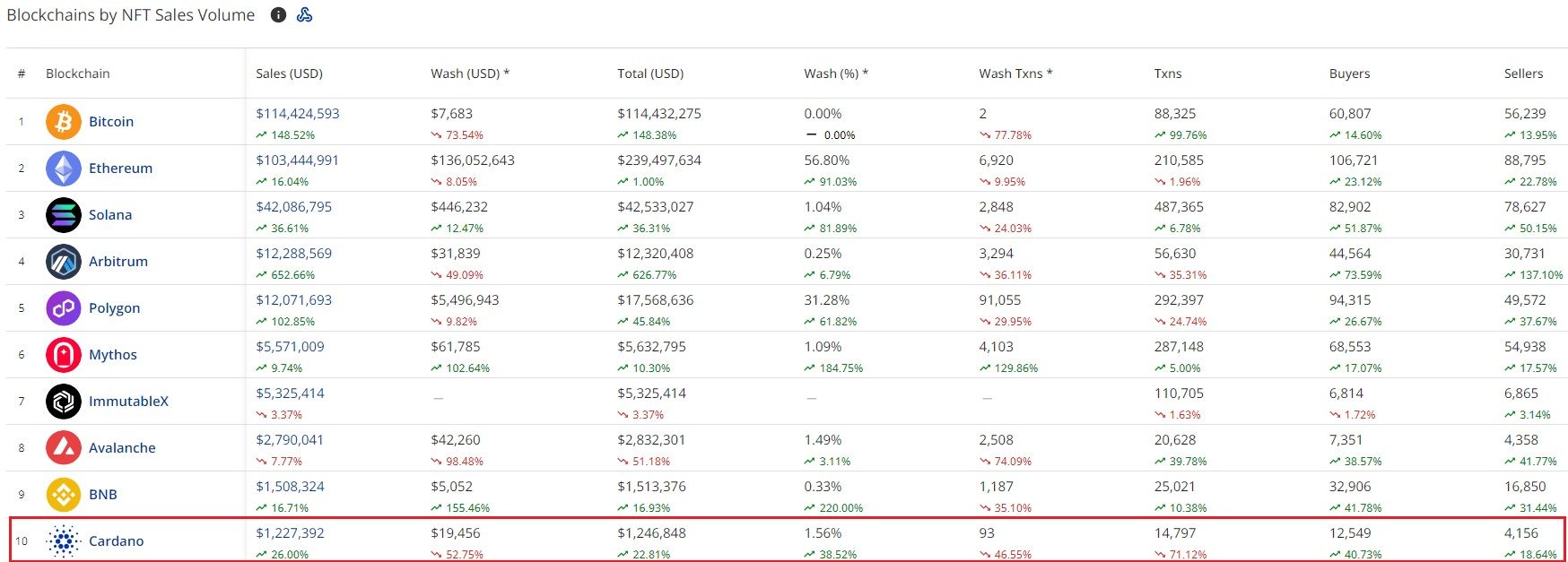 Cardano Ranks in the Top 10 in Terms of NFT Sales. Image via CryptoSlam
Cardano Ranks in the Top 10 in Terms of NFT Sales. Image via CryptoSlamTop Projects on Cardano
When compared with other third-generator blockchains like Solana and Avalanche, Cardano's total DApp count is minuscule. This is one of the largest criticisms against Cardano is the lack of a thriving DApp and DeFi ecosystem. But, just as Rome was not built in a day, Cardano enthusiasts are patient and feel that it is only a matter of time before the floodgates open.
The former two have 210 and 529 DApps with a total value of $339.9 million and $474.9 million, respectively, according to DappRadar. Cardano only has 43 DApps. At $2.1 billion, however, the value blows past the other two. When ranked by the number of DApps, Cardano is ranked 19th. Filter it by DApps' value and Cardano rounds out the Top 3 with Ethereum first (duh!) and BNB Chain coming in second.
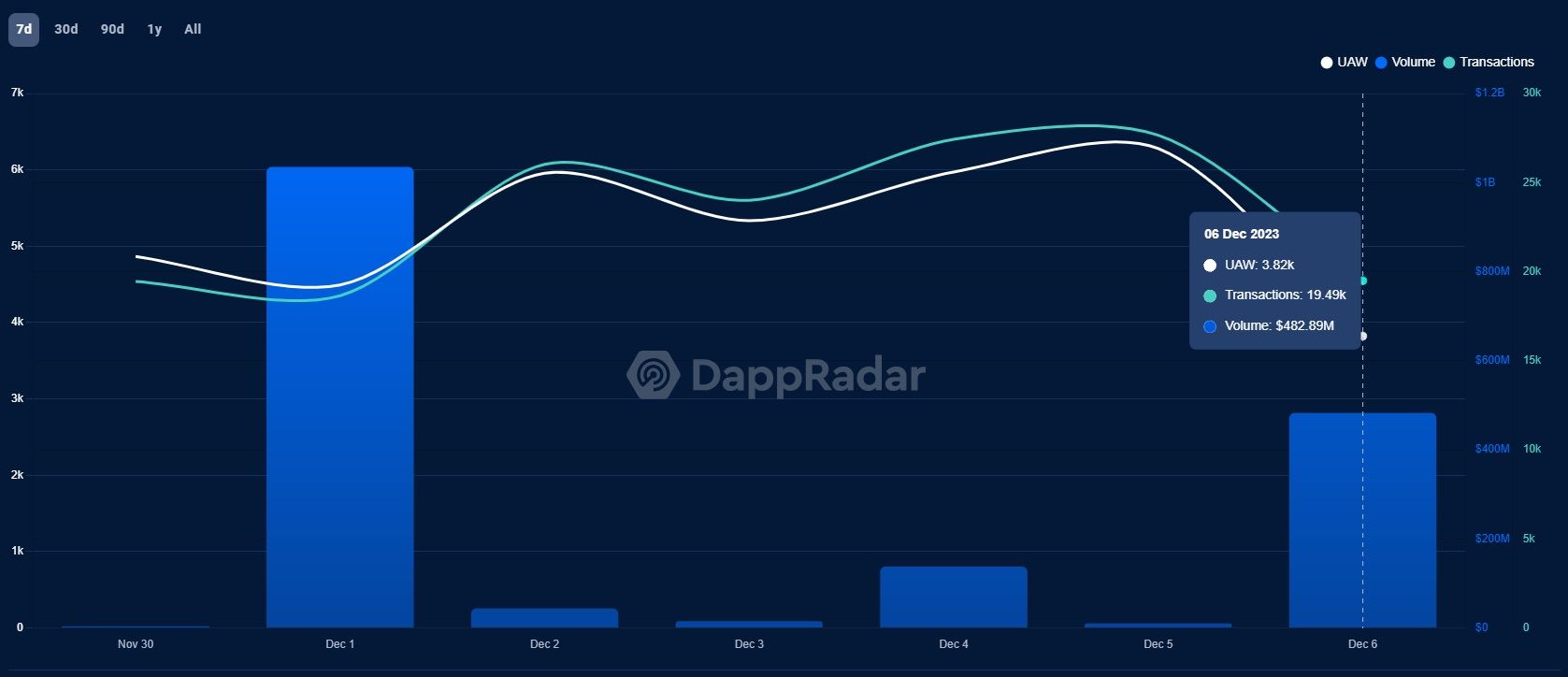 Cardano's DApps' Value Blows Past Solana and Avalanche. Image via DappRadar
Cardano's DApps' Value Blows Past Solana and Avalanche. Image via DappRadarHere are some of the top projects on Cardano.
- Minswap: Minswap is the largest decentralized exchange on Cardano. Its 24-hour volume was $259.9 million at press time.
- JPG Store: JPG Store is the largest NFT marketplace on Cardano. For creators, JPG Store has a Launchpad to support artists in the Cardano community as well as a minting feature that enables artists to turn their artwork into an NFT.
- Wingriders: WingRiders is an automated market maker and DEX built on Cardano. Its 24-hour volume was $492.0 million at press time.
- SundaeSwap: This is another DEX.
While you're here, check out our article on the best Cardano DApps.
Cardano As An “Ethereum Killer”
Ethereum's dominance has led to the rise of so-called "Ethereum killers," blockchains that aim to improve Ethereum's shortcomings just as it did with Bitcoin. Cardano is among the networks that have earned the “Ethereum killer” moniker.
Ethereum pioneered smart contracts, had a first-mover advantage, boasts a robust ecosystem and enjoys market recognition and network effect. Cardano, on the other hand, takes a slow, measured approach to development and has solid science backing. Cardano's TVL is a fraction of Ethereum's $29.7 billion. In simple words, Cardano has a long way to go before it can be seen as a credible threat to Ethereum. However, with Hydra and a planned upgrade to its Ouroboros consensus addressing scalability issues that have long plagued Ethereum, the network certainly appears to be on the right track.
If this piques your interest, head over to our article where we dive deep into Ethereum's dominance and shine a spotlight on the challengers who seek to dethrone Ethereum from its high perch.
Cardano's Africa Focus
EMURGO Africa is the regional arm of EMURGO, dedicated to driving the adoption of Cardano and Web3 technologies across the Middle East and Africa.
The division is directing efforts toward advancing Web3 technology, with a particular emphasis on nurturing local communities, investing in, and accelerating the growth of Web3 entrepreneurs and startups that leverage Cardano's capabilities.
- Addressing Local Challenges: Web3 solutions built on Cardano aim to address regional and local challenges, offering impactful solutions to economic inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and accountability issues faced by local populations.
- Investment and Acceleration: A key aspect of this strategy involves actively investing in and accelerating the development of promising regional Web3 startups. By supporting these ventures, the goal is to drive the adoption of Cardano and Web3 technologies while contributing to positive social change.
- Raising Awareness: Efforts are underway to raise awareness of Cardano and Web3 technologies at the local level. This involves promoting the economic benefits that these innovative solutions can bring to businesses and users within the region.
- Community Building: The initiative seeks to foster the growth of local blockchain communities. By creating a platform for dialogue and collaboration, the aim is to connect regional and local stakeholders, including policymakers, to explore the societal benefits that can be achieved through the adoption of Web3 solutions.
EMURGO plans to invest over $200 million to support Africa's ecosystem growth over the next three years. Thus far, it has invested in 29 African start-ups across the GameFi, crypto fintech, SocialFi and SaaS marketplace verticals, among other industries.

Cardano Review: Closing Thoughts
Cardano's development approach, characterized by a meticulous and research-driven strategy, contrasts sharply with the rapid expansion tactics of many other cryptocurrencies. This deliberate pace, grounded in academic research and formal methods, aims to balance the blockchain trilemma of security, decentralization, and scalability. While this method may slow down development, it is designed to ensure a robust and scalable platform.
Despite criticisms of being a "ghost chain," Cardano's ecosystem demonstrates healthy growth, particularly in its DeFi sector and NFT marketplace. The platform is actively working on scalability solutions, notably through initiatives like Hydra and Mithril, to enhance transaction speed and throughput. Furthermore, Cardano's global impact, especially its focus on real-world applications in regions like Africa, and its efforts in privacy and regulatory compliance with projects like Midnight, showcase its commitment to practical and impactful blockchain applications.
Cardano's approach, while slower, may lead to a more resilient and versatile platform in the long run. Its growing ecosystem, active developer community, and focus on real-world utility position it as a significant player in the blockchain space. As the technology continues to evolve, Cardano's methodical approach could prove advantageous in the rapidly changing landscape of decentralized technologies.





