Technological innovations often take time before they achieve widespread acceptance. While breakthroughs can captivate the imagination, their true potential is unlocked only when they become accessible and user-friendly for everyone.
Take the internet, for example. The IP address of Google.com is 216.58.203.36, but when was the last time you used this number instead of just typing Google? It was probably never. The computers we use these days are another example; take a look at the first-generation computers and how people used them back in the day:
 First-Gen Computers Worked by Typing Lines of Commands | Image via Quora
First-Gen Computers Worked by Typing Lines of Commands | Image via QuoraThe introduction of Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) revolutionized computing, making it intuitive and approachable for all. These technologies are integral to our lives, not because they are revolutionary but because they are incredibly user-friendly.
Blockchain technology, a pioneering innovation, is grappling with a similar accessibility issue. Just like the command lines of initial computers or the IP addresses of the internet, alphanumeric public addresses (e.g., 0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045) across various networks are intimidating and prone to errors. Although niche, blockchain domain names like Ethereum Name Service or Unstoppable Domains are already a thing in Web3. These names are emerging as a solution to demystify crypto transactions by replacing cumbersome public addresses with easy-to-remember, human-readable names.
Enter FIO Protocol
The FIO Protocol is a decentralized service layer for the entire blockchain ecosystem. It abstracts the complexities of blockchain communication and value transfer using human-readable identifiers, encompassing many networks like Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Solana. With FIO, using blockchain feels less like operating a cryptic software system and more like communicating directly with another person. It's akin to how sending an email or invoicing an online order feels seamless without comprehending the intricate payment processes behind the scenes.
The protocol's unique features, such as FIO Requests, NFT Signatures, and FIO Data, extend its utility beyond simple naming systems, making it an attractive choice for individuals, businesses, organizations, and public figures. With ongoing integration efforts and economic cost structure, FIO Protocol is poised to enhance the blockchain experience for a wide range of users.
This FIO review will demystify the FIO Protocol and explain its features and benefits. We'll uncover how FIO maintains its commitment to decentralization, privacy, and security while ensuring compatibility across various networks in the Web3 ecosystem. By the end, you'll understand how FIO Protocol is poised to transform blockchain from a complex, niche technology into a user-friendly tool anyone can comfortably utilize.
FIO Review Summary
FIO Protocol offers a comprehensive and user-friendly solution for blockchain address management, perfectly aligned with the multi-chain evolution of the Web3 ecosystem. By replacing complex public addresses with easy-to-remember FIO Handles, transactions are simplified, and errors are reduced.
Key Features and Benefits of FIO
- Multi-Chain Compatibility: Integrates with various EVM and non-EVM blockchain networks.
- FIO Handles: Simplifies blockchain transactions with human-readable addresses.
- FIO Requests: Allows detailed and secure payment requests.
- Custom Domains: Offers branded, professional addresses for businesses and organizations.
- NFT Signatures: Enhances security and authenticity for NFTs.
- FIO Data: Adds metadata to transactions for better tracking and management.
- Economic Cost: Affordable use of the protocol with bundled transactions.
- Enhanced Security: Encrypted data ensures user privacy and security.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive and easy to use, reducing the complexity of blockchain interactions.
- Continuous Integration: Ongoing efforts to expand compatibility with more wallets, chains, and applications.
FIO Protocol Overview
The FIO Protocol, short for Foundation for Interwallet Operability, is a blockchain solution that simplifies cryptocurrency transactions and offers a uniform user experience while exchanging value and information across blockchain networks. It addresses one of the most significant barriers to widespread crypto adoption: The complexity of managing and using long, alphanumeric wallet addresses. FIO transforms these confusing strings into easy-to-remember, human-readable names that are homogeneous across all blockchain networks, wallets, decentralized applications, and social networks.
 FIO Handles Are Easy-to-Read Identifiers That Replace Public Keys. Image via FIO Website
FIO Handles Are Easy-to-Read Identifiers That Replace Public Keys. Image via FIO WebsiteKey Components of FIO Protocol:
- FIO Handles: Similar to ENS names (like vitalik.eth), FIO Handles are easy-to-read identifiers that replace public keys. One FIO Handle works across all EVM chains and all non-EVM networks like Bitcoin and Solana. By treating Handles like email addresses, FIO offers greater customizability than traditional ENS names. A Handle like sid@moon includes a name (sid) under the domain (@moon), where all the elements are customizable.
- FIO Requests: The Requests feature allows one FIO handle to request payment from another. The protocol encrypts the transaction credentials and shares them on-chain so only the involved parties can access them. This feature brings the on-chain payment experience closer to PayPal, Venmo, and Google Pay.
- FIO Data: It enables a Handle user to embed metadata to their transactions. The data may include:
- Invoicing information and additional information relevant to a particular transaction.
- Additional information relevant to specific blockchain networks when transacting across different blockchains (like memo information in Monero).
- Arbitrary data or messages users may want to include with transactions.
- NFT signatures: Owners can attach signatures with their NFTs using their FIO Handles as an additional proof of authenticity. The product protects against NFT forgery and simplifies signing NFTs on online galleries and marketplaces that integrate this feature.
Accessing any feature on FIO begins with creating a Handle — the FIO Protocol's applicability scopes beyond simplified transactions. With additional features like the ability to link your socials to your Handle, along with a dedicated directory to lookup registered Handles, FIO enables Web3 individuals and organizations to construct an elaborate and secure on-chain profile operable across all the blockchain networks and facilitated by the FIO protocol. The FIO protocol is a decentralized Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) network helping preserve self-sovereignty and privacy (more on later).
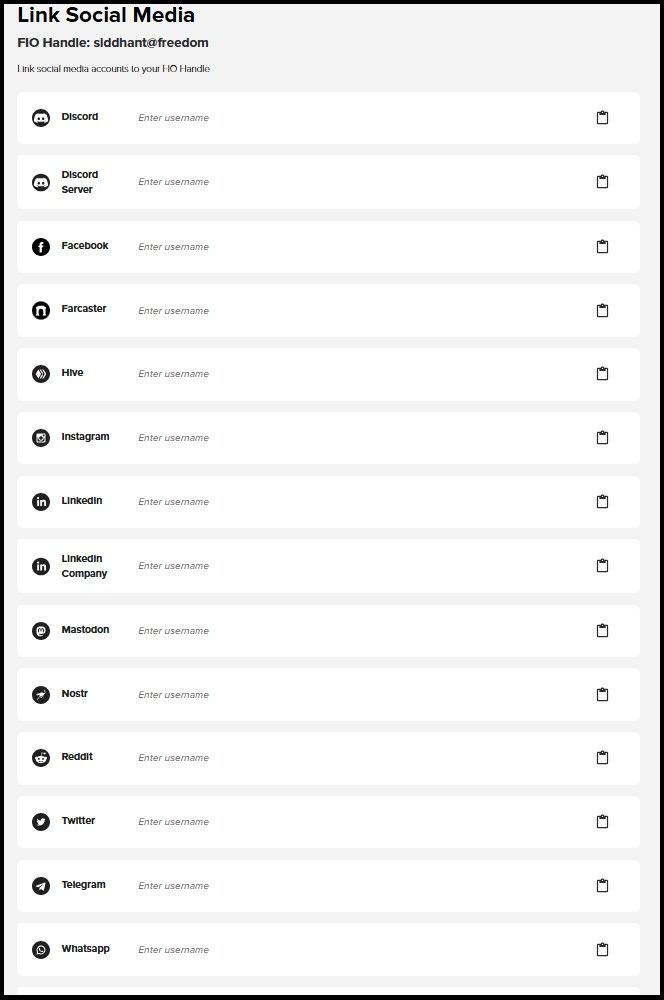 A FIO Handle Can Link All Your Social Accounts in One Place | Image via FIO App
A FIO Handle Can Link All Your Social Accounts in One Place | Image via FIO AppHow Does FIO Work?
Most wallet naming systems, like ENS, are limited to certain blockchain networks. They use smart contracts that help associate a public address on that chain with a unique identifier. The FIO Protocol is designed as a protocol-agnostic system that can work with any existing or upcoming chain or token.
Achieving the flexibility to work with any network requires FIO to run on a proprietary blockchain, the FIO Chain. The FIO Chain is a public decentralized DPoS network whose primary participants are wallets and exchanges integrating FIO.
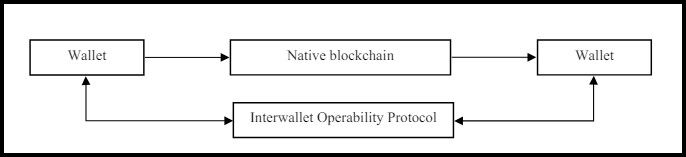 Image via FIO Whitepaper
Image via FIO WhitepaperThe FIO Chain is an iteration of the Interwallet Operability Protocol (IOP). It does not operate as an intermediary between the user and blockchain networks but as a service layer facilitating the communication of users and assets in different networks.
FIO Handles
FIO Handles do a lot more than a typical blockchain domain name. When an ENS domain essentially replaces an Ethereum public address with a name, a FIO Handle has to route information across any blockchain network, not just Ethereum. Security and privacy are critical to these Handles, as a viewer must not have the means to link a user's different public addresses.
Structure
FIO Handles have the structure username@domain. The Handles are nested NFTs. The Handle siddhant@moon is an NFT under the @moon domain, which is also an NFT. Akin to email addresses, domains may be public or private. For instance, my email address, [email protected], is under a public domain (@gmail) that Google has made public, while my official email, [email protected], is under a private domain created for me after seeking approval from Coin Bureau.
Similarly, when users are creating new Handles on FIO, they have the following customization options:
- Create a custom username under a public domain for a nominal price. FIO also provides some domains where you can create handles for free for a limited time.
- Join a private domain by having a domain owner create a handle for you.
- Create a custom domain for an additional price.
FIO Handles are permanent once created. One Handle can be a proxy for any blockchain you might transact on. Here is a sample handle I created on Edge Wallet on my phone:
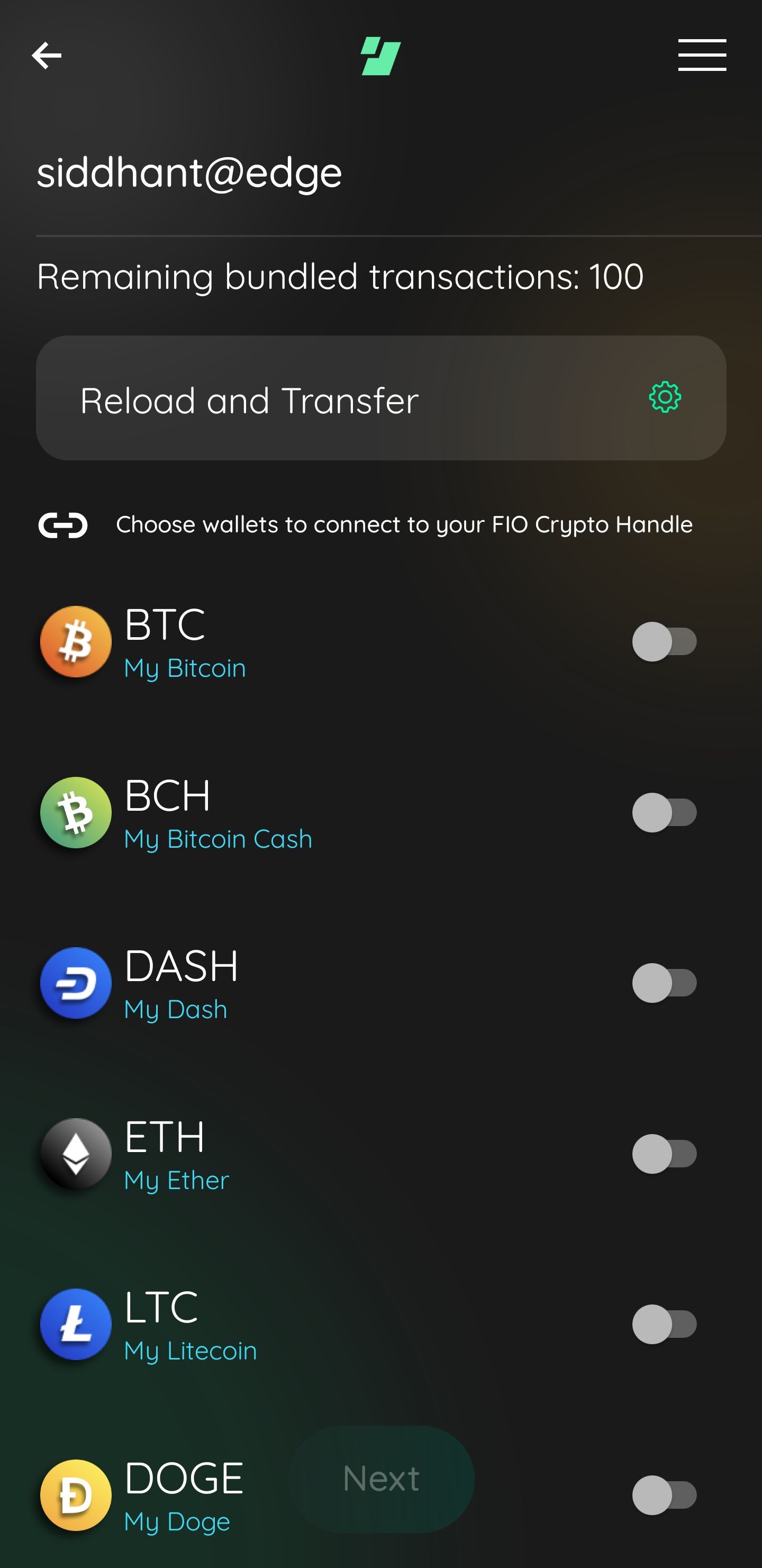 A Screenshot of Edge Wallet on My Phone
A Screenshot of Edge Wallet on My PhoneThe Edge wallet lets me manage public addresses on a variety of networks. With FIO Handles (siddhant@edge) integrated into my wallet, I can transact on all these chains without checking the respective public addresses. When you register a new Handle, the protocol creates a new FIO wallet whose private key controls the Handle and signs all the transactions on the FIO Chain, such as sending crypto or requesting from other Handles. All FIO Chain transactions get recorded in its decentralized ledger maintained by the FIO Chain consensus process, leaving no single central authority any control over it.
Security and Privacy
If you are reading this article, chances are you have addresses set up across multiple blockchain networks. You might own an NFT or two on Solana, while most of your crypto funds are in Ethereum and Bitcoin. If you begin using FIO Handles to manage your on-chain activity across all these networks, you surely wouldn't want anyone to be able to link your various addresses together. The FIO protocol is built with privacy by design, meaning it has measures to protect user privacy as an integral component of the protocol.
Registering a FIO Handle stores its name as a hash on the blockchain and does not link it to any public address from another blockchain by default. When the user initiates a FIO REquest Transaction from its FIO Handle to another, the protocol uses Diffie-Hellman encryption to create a shared secret between the involved parties.
Decryption is only possible by a receiver with their FIO key pairs, making it impossible for anyone to "look up" the public address of the sender using their FIO Handle and reveal the transaction particulars like tokens sent, transaction amount, and the receiver. If a user has intentionally made some of their connected addresses publicly available, there is a dedicated Profile Lookup feature where you can find information about the registered Handles.
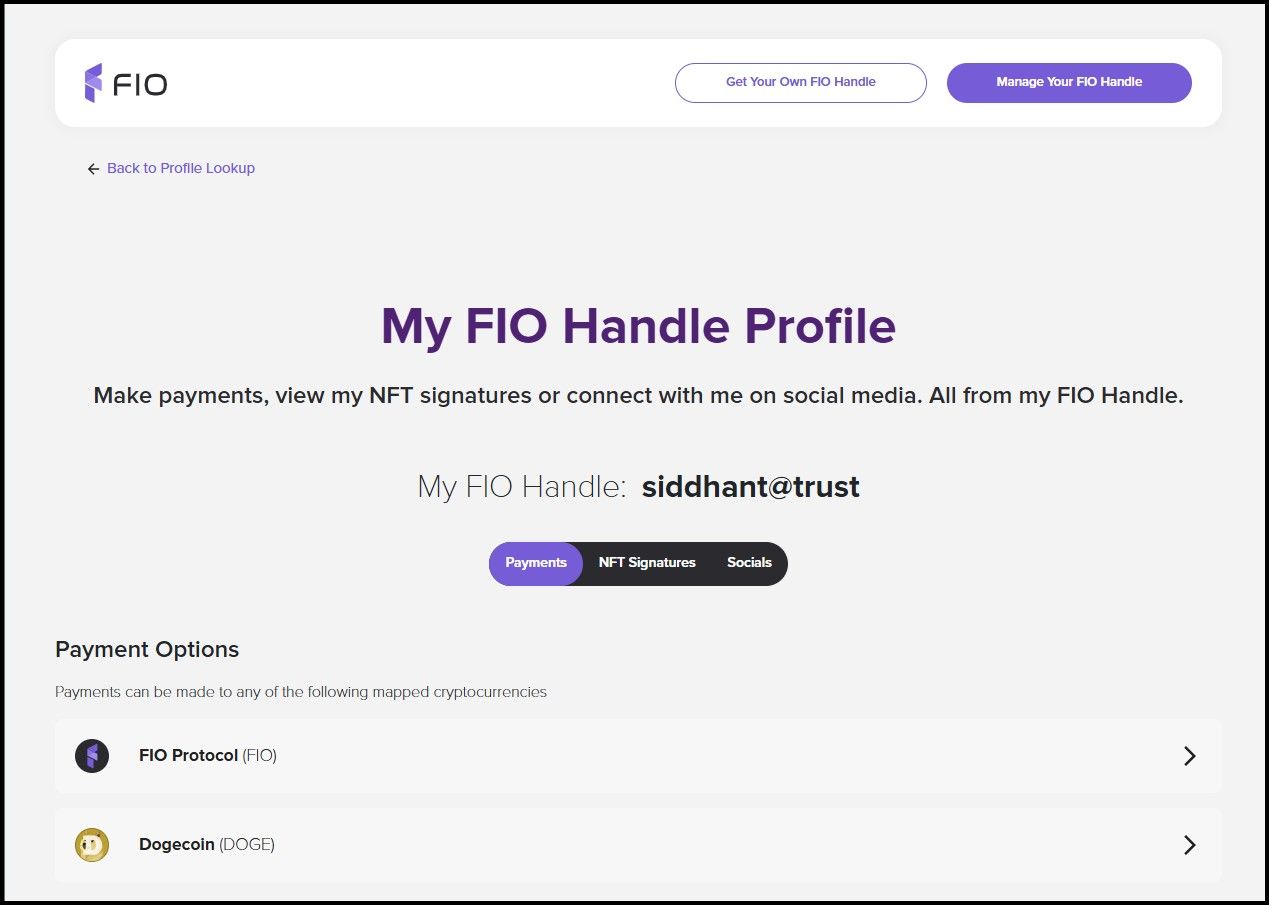 FIO Profile Lookup
FIO Profile LookupMapping Addresses
Privacy dictates that Handles obfuscate its link with the user's token addresses in different networks. However, there are certain cases where you'd want to make your token address public. Suppose you are an influencer who accepts donations from your followers, maybe you are running a fundraiser for your startup, or you're a public figure who wishes to make their holdings public. In all these scenarios, you might want to make a certain public key accessible to the public.
Mapping is a feature in FIO that allows you to make a specific token address visible to anyone who knows your Handle and will enable them to send you that token using your Handle name easily.
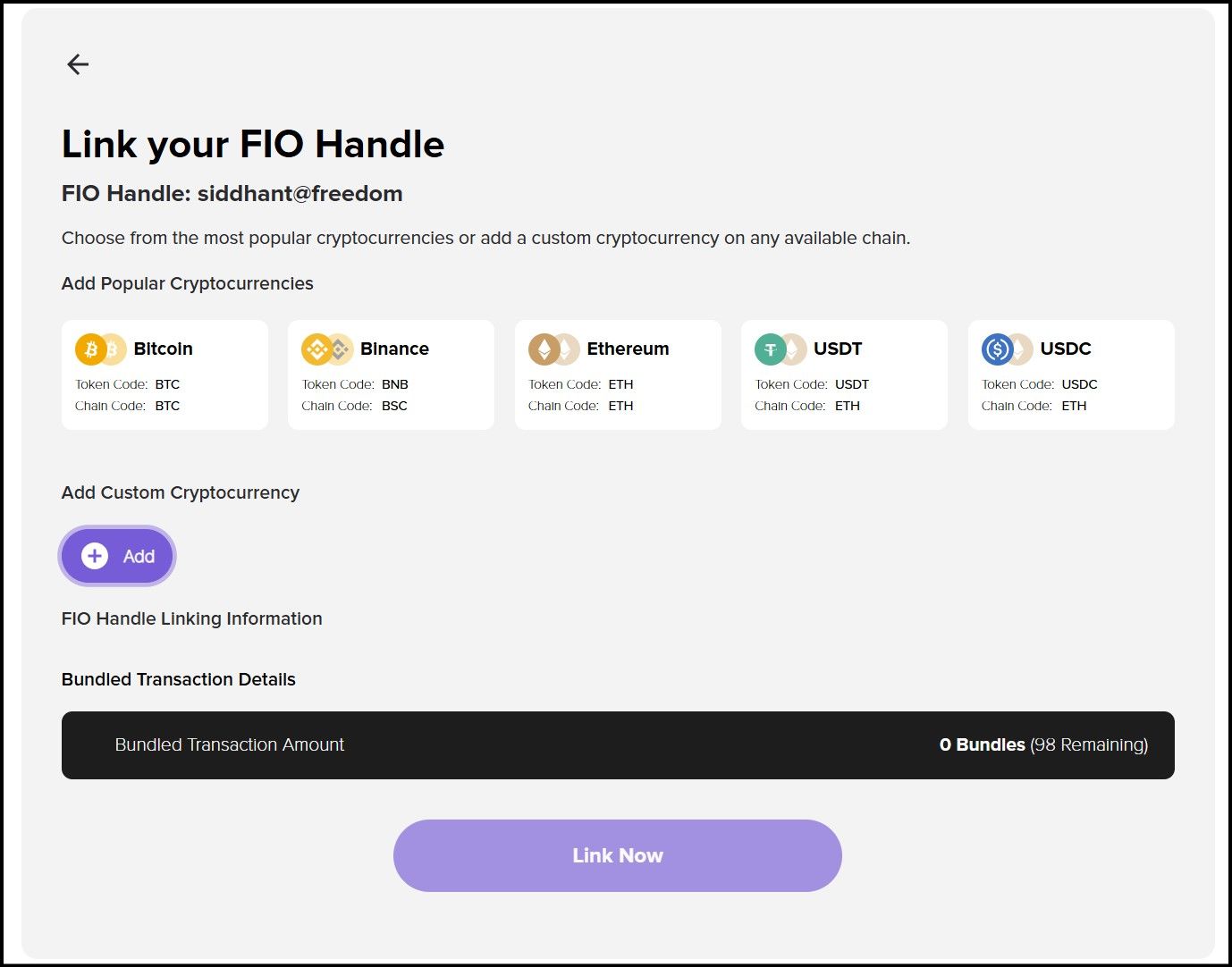 The Token Mapping Screen on the FIO App
The Token Mapping Screen on the FIO AppThe mapping process is straightforward. You sign in on the FIO App and find the 'Link' option, which will take you to the mapping screen. Now, you need to provide FIO the following information:
- The chain code where the token resides. It will help FIO reach the appropriate blockchain network.
- The token code, FIO will use the token code to find the token smart contract on the target blockchain.
- Finally, your token public address on the target blockchain.
The codes for commonly used tokens like ETH and USDT are accessible easily from the tiles on the screen. Enter these values and confirm the link, triggering an on-chain transaction on FIO to record the change on its ledger. Now, anyone can send you these tokens with just your FIO Handles, and there is no need to deal with alphanumeric public addresses.
It is noteworthy to mention that what's customizable on FIO is the default setting on other naming services like ENS. An ENS name is a simple replacement for the Ethereum public key. On the other hand, sharing your FIO Handles allows the user to decide which token addresses to make public with it. Users can also map several addresses from different networks to a common Handle. One of the key differentiators of FIO is that, unlike other naming systems, it is not a gatekeeper to which public addresses on which chains a user can map, which means that any chain is supported as soon as it is released.
Note: Mapping is only essential for receiving tokens. You don't need to map addresses to send or request crypto from other Handles.
FIO Requests
FIO requests are a vital element of the FIO Protocol. They are an easy and error-free way of requesting any crypto from one FIO user to another. When I need someone to send me some crypto, the typical process involves agreeing upon the token and amount on informal channels. Then, I share my public key associated with that token with the other party, who copies it to their wallet to send the transaction.
This process is cumbersome and involves copying and pasting addresses at multiple points, making it prone to mistakes. I have a habit of double-checking all the elements before sending the transaction. Although I am used to the process, it takes a lot of time and effort, and there is always a lingering fear of messing something up until the other party acknowledges receiving the funds.
Sending Requests
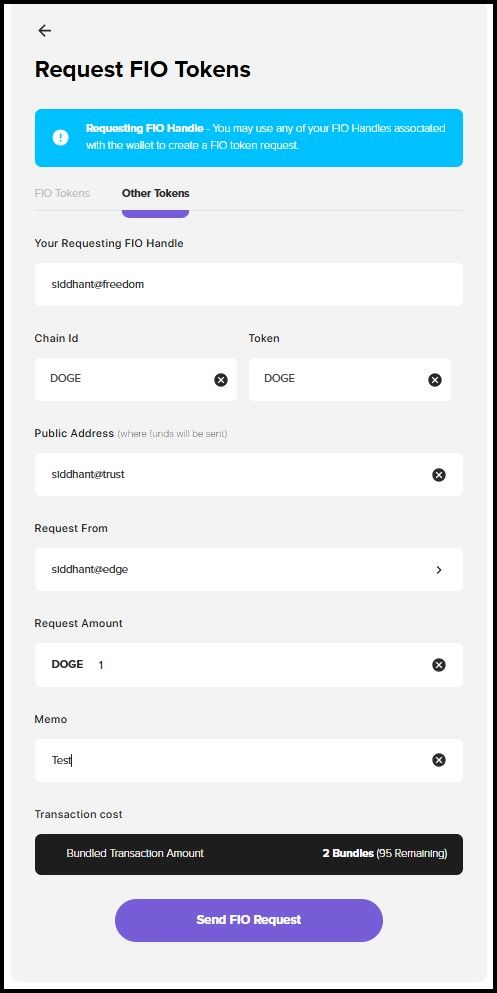 Requests Feature on the FIO App
Requests Feature on the FIO AppSending requests on FIO is more efficient. All you need is the payer's FIO Handle, and there is no need to deal with public addresses at any point during the whole process. Using the FIO App, users can send payment requests, where they fill in the payer and payee Handles and specify the token and the amount. The request is sent on the FIO Chain and will be visible as an alert on the payer's wallet app.
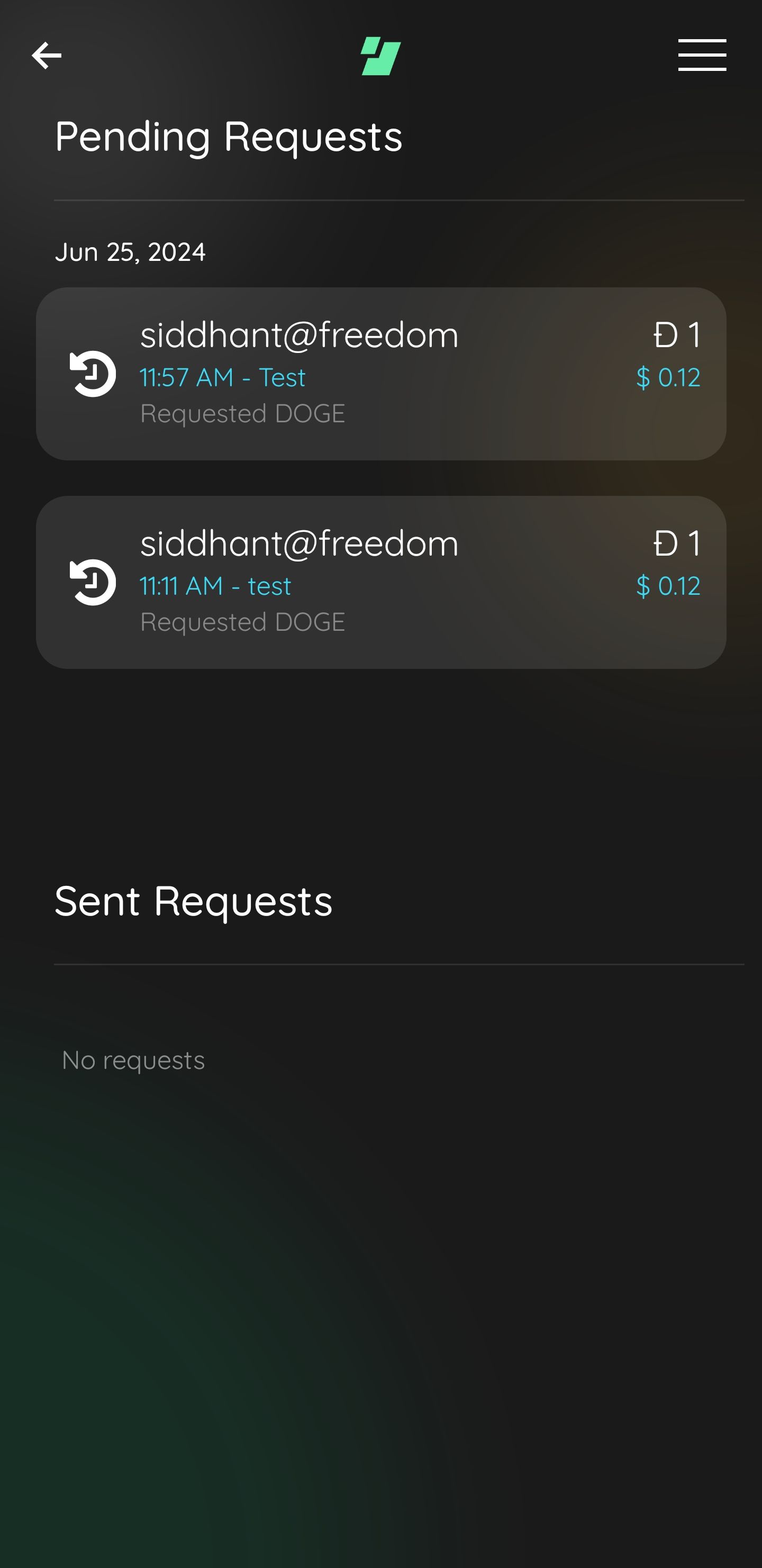 How Requests Are Received And Payers Can Either Approve or Deny Them.
How Requests Are Received And Payers Can Either Approve or Deny Them.Security
All the metadata embedded in the FIO request (involved addresses, tokens, memos) are encrypted using Diffie-Hellman encryption before publishing on the FIO Chain. The encryption can only be decrypted by the payer, so the transaction information is not available to anyone on the FIO Chain, maintaining the privacy and security of the involved parties.
Using the FIO Protocol
While working on this review, I used the FIO protocol extensively to get a feel of the user experience. I tried to understand the protocol from the eyes of someone uninitiated in blockchain technology. Before discussing my experience, here is a quick user guide on registering FIO Handles and Domains.
Registering a Standard FIO Handle
- Open a Partner Wallet: Use a wallet that supports FIO Protocol (e.g., Edge Wallet, Trust Wallet).
- Navigate to FIO Handle Registration: Look for the option to register a FIO Handle in the wallet's interface.
- Choose a FIO Handle: Enter your desired FIO Handle (e.g., yourname@wallet). The Handle must be unique.
- Confirm and Pay: Confirm your choice and pay the registration fee using FIO Tokens or the wallet's supported payment method. The wallet may even subsidize or make the registration free.
- Complete Registration: Once the payment is processed, your FIO Handle is registered and ready to use.
Registering a Custom Domain FIO Handle
- Open the FIO Portal: On the official FIO website, find the 'Get your FREE FIO Handle' tab and click on it.
- Create a Handle Name: Enter the desired Handle name on the next page and click the tab that says 'GET IT'.
- Review Available Options: On the next page, you will find many Handle options to choose from, along with their respective prices. Find the 'Add Custom Ending' option if you want a custom domain.
- Create the Domain: You can create a desired Domain name on the next page. The average charge of a custom domain revolves around $40.
- Free Domain: You can use this link to get the @crypto domain for free!
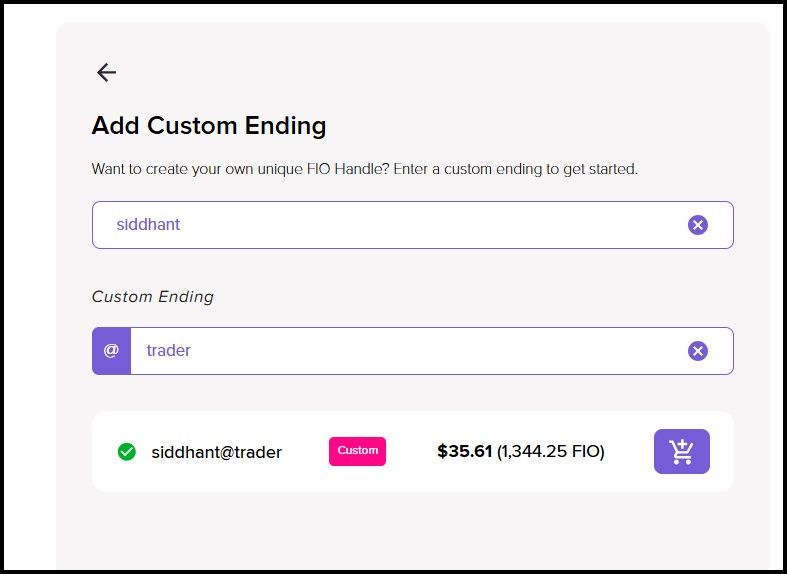 Domain Registration on The FIO App
Domain Registration on The FIO AppThe experience of using the FIO protocol is how it is supposed to be - easy and hassle-free. The registration process was straightforward; anyone with experience using crypto wallets will not face hiccups while navigating the FIO protocol. Sending tokens and requests was also quick and easy. The FIO Chain is responsive and only takes a few seconds to confirm transactions.
Practical Use Cases of the FIO Protocol
Simplifying Personal and Business Transactions with FIO:
- Ease of Use: FIO Handles make sending and receiving cryptocurrency easy without dealing with long, complex public addresses. Instead of entering an alphanumeric string, users can simply use a human-readable FIO Handle, like john@wallet, to facilitate transactions.
- Error Reduction: The risk of errors is significantly reduced since there's no need to copy and paste intricate addresses, making everyday transactions smoother and more reliable.
Businesses and E-Commerce Accepting Cryptocurrency:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Businesses can offer a more user-friendly payment process with FIO Handles, reducing friction for customers paying with cryptocurrency.
- Branding and Professionalism: Custom FIO Domains (e.g., businessname@areaname) allow businesses to maintain a professional appearance while making transactions more intuitive.
Examples of FIO Protocol in Action in Commercial Settings:
- E-Commerce Integration: Online stores using FIO can simplify customers' checkout process. For instance, a store might use FIO Requests to send payment details directly to a customer's FIO Handle, making the payment process straightforward and efficient.
- Service Payments: Businesses offering services can use FIO Handles to bill clients, ensuring that invoices are easy to understand and pay.
Donation and Crowdfunding Platforms:
- Simplified Donations: Non-profits can use FIO Handles to simplify the donation process. Donors can send contributions using easy-to-remember addresses rather than long wallet strings.
- Transparent Tracking: FIO Requests can include detailed metadata about the purpose of the donation, making it easier to track and manage contributions.
- Multiple Currencies: A platform may accept different cryptocurrencies and use a common Handle for all of them, making it easier to spread the word about the cause.
Influencers and Public Figures:
- Simplified Fan Contributions: Influencers can provide their FIO Handle to fans for contributions, tips, or support, making the process straightforward and secure.
- Brand Consistency: Public figures can maintain a consistent and professional image using custom FIO Domains (e.g., influencername@instagram), making it easy for fans to verify their identity and send support.
- Giveaways and Rewards: They can host giveaways that reward Handles under their domain name by leveraging FIO as a marketing tool.
Wallet and Address Management
- Unified Management: FIO Handles allow users to manage multiple wallet addresses under one simple, human-readable name, making organizing and keeping track of various cryptocurrency holdings easier.
- Cross-Chain Compatibility: FIO Protocol supports multiple blockchains, so users can manage addresses for different cryptocurrencies using a single FIO Handle, simplifying overall asset management.
The FIO Protocol offers versatile and practical solutions for various use cases, from everyday transactions to complex business operations. By simplifying the process of sending, receiving, and managing cryptocurrency, FIO enhances user experience, reduces errors, and promotes broader adoption of blockchain technology. Whether you are an individual, a business, a non-profit, or a public figure, FIO Protocol provides tools that make interacting with the blockchain easier, more secure, and more intuitive.
The FIO Token
FIO is the native token of the FIO Chain. It has a total supply of 1 billion tokens, of which 65% were minted at launch. Its utility lies in the incentive mechanism built for the participants of the FIO Chain.
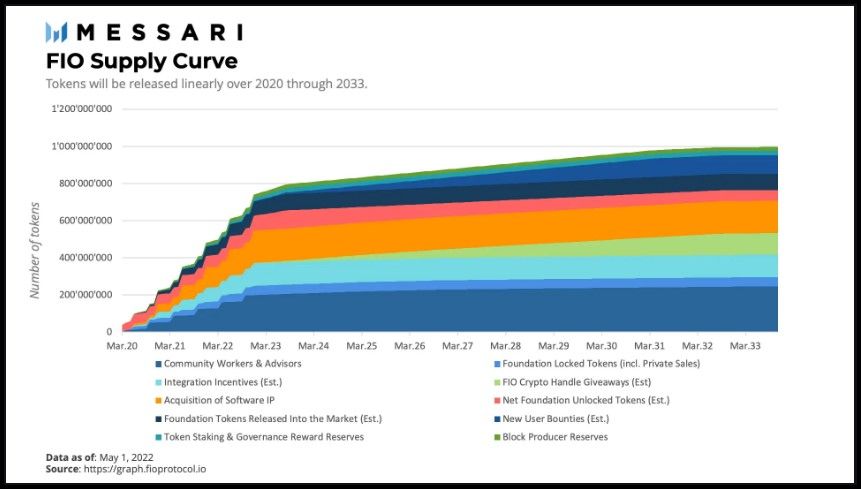 FIO Supply Schedule | Image via Messari
FIO Supply Schedule | Image via MessariKey utilities of the FIO token include:
- Pay transaction fees for using FIO Handles to send crypto or receive tokens through requests, mapping addresses, signing NFTs, and other FIO wallet management activities.
- Staking FIO in the network to earn a portion of protocol fees.
- Participating in FIO Protocol governance.
With every wallet registration, the FIO protocol offers 100 bundled transactions per year that can cover fees. Users need FIO tokens to pay for fees once they exhaust the provided bundles.
Fees
In the FIO Chain, 21 active block producers vote on the desired fee for each operation on FIO. The final fees are the medium of the proposed values.
Governance
Block Producers (BPs) and Voting
- Becoming a BP: Anyone can become a BP, but to produce blocks, set fees, and earn rewards, BPs must rank highly in voting power.
- Active and Standby Validators: 21 BPs are selected as active validators for block production in rounds of 126 blocks. Standby validators can earn rewards and set fees without producing blocks.
- Consensus and Protocol Changes: BPs modify system contracts and enact protocol changes. Proposals require approval from at least 15 of the 21 active BPs (greater than two-thirds) to pass.
FIO Foundation and DAO
- Funding and Role: The Foundation for Interwallet Operability (FIO) receives 5% of protocol fees to run a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) that coordinates protocol development with independent developers and contributors.
- Participation: Wallets and exchanges that join the FIO consortium participate in governance by signaling support for new protocol features, which BPs then vote on.
Voting Mechanism
- Eligibility: Token holders with a FIO Handle can vote for network BPs or delegate their voting power to proxies.
- Proxies: Wallets or exchanges can act as governance proxies for the FIO tokens held in their users' wallets, allowing prominent stakeholders to influence network decisions.
FIO Improvement Proposals (FIPs)
- Review and Approval: FIPs are available for public review on GitHub before BP voting. Foundation-funded proposals require review and consent to be prioritized.
- Community Involvement: Self-funded FIPs can also be brought to BP vote at the discretion of community members, reflecting the open-source and community-driven nature of the protocol.
This governance structure ensures that FIO remains decentralized, with significant input from various stakeholders, including BPs, the FIO Foundation, and the broader community, fostering an inclusive and collaborative environment for protocol development.
Staking FIO
Overview of FIO Token Staking
- Launch: FIO token staking began in January 2022 and is accessible through partner wallets.
- Eligibility: Users must have voted for at least one BP or proxied their vote to participate in staking.
Staking Rewards and Distribution
- Staking Rewards: Users who stake FIO tokens receive rewards. The staking rewards can be redeemed upon request, but the initially staked amount has a 7-day cool-down period.
- Partner Wallets: If staking is done through a registered integrated wallet, the organization behind the wallet receives 11% of the stakers' rewards.
Fee Mechanism and Reward Allocation
- Distribution of Protocol Fees:
- Stakers: Receive 25% of the protocol fees.
- BPs: Earn 60% of the protocol fees.
- FIO Foundation: Receives 5% of the fees for its operations.
- Integration Partners: Get 10% of the protocol fees.
- Subsidizing Rewards:
- If protocol fees are insufficient to reward participants, FIO tokens are drawn from reserves to subsidize BPs and stakers.
- BP Reserve: 20 million FIO (2% of total supply) is set aside. If less than 50,000 FIO is collected in fees for BPs in 24 hours, tokens from the reserve are used to reach this cap until the reserve is exhausted.
- Staking Reward Reserve: 25 million FIO (2.5% of total supply) is allocated. This allocation ensures that staking rewards total 25,000 FIO per day among stakers, until the reserve is depleted.
Incentive Mechanism
- Decentralized Benefits: FIO's incentive mechanism and decentralized business model ensure that rewards are distributed across all ecosystem participants, supporting a broad and inclusive participation framework.
This staking structure promotes active participation in the FIO network while providing consistent rewards to users, BPs, and integration partners, thus fostering a sustainable and incentivized ecosystem.
FIO partnerships and integrations are critical to the success of the protocol. Since its launch in 2020, FIO has partnered with numerous exchanges to list the FIO token and wallets to integrate FIO Handles and Requests. Wallet integration is essential for FIO as it allows users to send and receive crypto using Handles within their wallets.
 FIO Has Made 70+ Integrations Since Launch | Image via FIO
FIO Has Made 70+ Integrations Since Launch | Image via FIOThe Edge wallet provides the most integrated experience of using FIO right now. Edge has integrated Handles. You can simply type the Handle to which you want to send tokens, and the wallet will resolve the corresponding public address. The FIO governance has dedicated 125 million to reward and incentivize projects that integrate FIO into their services.
Additional FIO Features
Here are a few other features of FIO:
FIO Data
FIO Data refers to the ability to include metadata and additional contextual information within blockchain transactions. This feature enhances the usability and functionality of the FIO Protocol by providing a richer and more informative transaction experience.
Key Aspects of FIO Data:
- Metadata Inclusion:
- Transaction Details: Users can attach relevant information such as notes, invoices, or references to their transactions, making it easier to track, manage, and understand the purpose of each transaction.
- Enhanced Communication: By allowing the inclusion of descriptive data, FIO Data improves communication between transaction parties, which is particularly useful for businesses and individuals who need to keep detailed records of their blockchain activities.
- Organizational Benefits:
- Accounting and Reporting: Businesses can benefit from having detailed metadata attached to transactions, simplifying accounting, financial reporting, and auditing processes.
- Transaction Management: Users can organize and categorize their transactions more effectively, leading to better financial management.
- Privacy and Security:
- Encrypted Data: Metadata included with FIO Data is encrypted, ensuring that sensitive information remains private and secure.
- User Control: Users have control over what data is attached to their transactions, maintaining the principle of self-sovereignty and privacy.
FIO NFT Signatures
FIO NFT Signatures provide a way to sign Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) using the FIO Protocol. This feature enhances NFTs' security, authenticity, and usability by leveraging the FIO ecosystem's capabilities.
Key Aspects of FIO NFT Signatures:
- Authenticity and Provenance:
- Digital Signatures: FIO NFT Signatures allow users to sign NFTs digitally, verifying the authenticity and origin of the token. Signing helps establish the provenance of the NFT, ensuring that it is genuine and has not been tampered with.
- Creator Verification: Artists and creators can use FIO NFT Signatures to authenticate their work, providing collectors and buyers with confidence in the legitimacy of the NFT.
- Enhanced Security:
- Immutable Records: The signatures are recorded on the blockchain, providing an immutable and verifiable record of the NFT's authenticity, reducing the risk of fraud and forgery in the NFT market.
- Decentralized Validation: The decentralized nature of FIO Protocol ensures that the validation and verification processes are secure and trustworthy without relying on a central authority.
- Usability and Integration:
- Seamless Integration: FIO NFT Signatures can be integrated with existing NFT platforms and marketplaces, enhancing their functionality and security.
- User-Friendly Experience: By leveraging FIO's human-readable addresses, signing and verifying NFTs becomes more intuitive and user-friendly.
- Cross-Chain Compatibility:
- Interoperability: FIO NFT Signatures are designed to work across different blockchain networks, providing a unified NFT authentication and security solution.
- Wide Adoption: This cross-chain capability facilitates broader adoption and usage of FIO NFT Signatures within the diverse and growing NFT ecosystem.
FIO Data enhances transaction management by allowing users to include encrypted metadata, improving communication, organizational efficiency, and privacy. FIO NFT Signatures provide a robust mechanism for verifying the authenticity and provenance of NFTs, enhancing security and trust in the NFT market through digital signatures recorded on the blockchain. Both features leverage the strengths of the FIO Protocol to provide user-friendly, secure, and efficient solutions for the blockchain community.
FIO Competition and Challenges
Primary Value Proposition:
- Integration with Any Blockchain Network: FIO Protocol's standout feature is its compatibility with multiple blockchain networks, both EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) and non-EVM. This flexibility allows users to manage transactions across various blockchains using a unified interface. Users navigating through several blockchain networks will find this feature particularly beneficial, as it simplifies the complexity of dealing with different blockchain protocols.
- Complete On-Chain Token Management Toolkit: While other projects like Ethereum Name Service (ENS) primarily offer a simple naming system, FIO extends its functionality to a comprehensive on-chain token management toolkit. This includes features like FIO Requests, FIO Data, and custom domains, making it a more holistic solution for blockchain users.
Standout Features and Niche Markets
- FIO Requests: Appealing to Businesses and Public Figures: FIO Requests allow users to send detailed payment requests, including metadata and transaction details. This feature is highly attractive to businesses and public figures who need to manage payments and transactions efficiently and securely.
- Custom Domains: Utility for Organizations: Custom domains enable organizations to create branded, human-readable addresses. This feature enhances professionalism and ease of use, making it easier for clients and partners to interact with the organization's blockchain services.
- Expanding to Niche User Types: By catering to businesses, public figures, and organizations, FIO can tap into niche markets that require more sophisticated transaction management tools than what simple naming systems can offer. This strategy can help FIO expand its user base and market reach.
Challenges and Competitive Landscape
- Dependency on Wallets and Projects: Despite its compatibility with any network, FIO's success hinges on integration by wallets and projects operating within those networks. This dependence poses a significant challenge as wallets might prioritize naming systems more aligned with their primary networks. FIO is making progress towards integration, they have already established themselves as the default handle provider for Opera Wallet, Trust Wallet and EDGE Wallet.
- Competition from Established Naming Systems: Metamask, a widely used wallet in the Ethereum ecosystem, supports ENS resolution, making ENS the default choice for many users within the Ethereum+Metamask space, creating a strong competitive barrier for FIO. Metamask is currently working on letting third-party naming systems integrate with the app, after which it will become compatible with FIO.
- Market Entrenchment: Established naming systems like ENS have a first-mover advantage and deep integration within their respective ecosystems, making it challenging for FIO to displace them.
- Opportunity in Multi-Chain Ecosystems: As Web3 evolves, the blockchain landscape becomes increasingly multi-chain. This shift presents an opportunity for FIO to break the strongholds of single-chain naming systems by offering a versatile solution that seamlessly integrates with various blockchains.
- Solving the Integration Problem: To capitalize on this opportunity, FIO must efficiently solve the integration problem by forging partnerships with wallet providers and blockchain projects, emphasizing its value proposition of multi-chain compatibility and comprehensive transaction management.
FIO Protocol has a strong value proposition with its multi-chain compatibility and comprehensive transaction management features. However, it faces significant challenges in achieving widespread integration and competing against established naming systems like ENS. By focusing on strategic partnerships, targeted marketing, and continuous technological improvement, FIO can leverage the growing multi-chain landscape of Web3 to establish itself as a leading solution in the blockchain space.
FIO Review: Final Thoughts
FIO Protocol stands out as the most holistic naming solution in Web3, perfectly aligned with the industry's increasing shift towards a multi-chain future. The protocol is thoughtfully designed to enhance the experience of everyday users, offering economic costs and bundled transactions that many will find invaluable.
Beyond just a naming system, FIO's features like FIO Requests, NFT Signatures, and FIO Data position it uniquely in the blockchain DNS space. These capabilities make it an attractive option for businesses, organizations, and public figures, not just retail investors and general users. By providing tools that simplify and secure complex blockchain interactions, FIO can carve out a new niche and set itself apart from more limited solutions.
The FIO team's ongoing efforts to expand integration across more wallets, chains, and applications are commendable and critical for gaining a competitive edge. As they continue to build out these integrations, the protocol's utility and user base are likely to grow significantly.
Given its comprehensive feature set and focus on improving the user experience, I highly recommend readers try out FIO Protocol. It has the potential to significantly enhance your Web3 interactions and streamline your blockchain activities.
Disclaimer: This is a paid review, yet the opinions and viewpoints expressed by the writer are their own and were not influenced by the project team. The inclusion of this content on the Coin Bureau platform should not be interpreted as an endorsement or recommendation of the project or product being discussed. The Coin Bureau assumes no responsibility for any actions taken by readers based on the information provided within this article.





