The Ethereum Merge represents one of the most significant upgrades to the Ethereum network since its inception. This transition from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism marked a revolutionary shift for Ethereum and the broader blockchain landscape. The Merge effectively eliminated Ethereum's reliance on energy-intensive mining. The Merge has also catalyzed the development of various niche industries and utilities within the Ethereum ecosystem. In the brief period since its implementation, many of these use cases have become defining characteristics of Ethereum.
One notable outcome of the Merge is the rise of Staking-as-a-Service (SaaS), a concept that differs from the traditional Software-as-a-Service model. Staking-as-a-Service allows users to stake their Ethereum without having to manage the technical complexities involved in running a validator node. This service has quickly gained popularity as it lowers the barriers to entry for participating in Ethereum staking, enabling more users to contribute to network security and earn staking rewards.
This review focuses on Lido Protocol, a leading project in the Staking-as-a-Service domain. Lido has rapidly ascended to become the largest protocol by Total Value Locked (TVL) in Ethereum, boasting over $25 billion in TVL as of September 2024, according to DefiLlama. Lido's success can be attributed to its user-friendly approach to staking, allowing users to participate in staking without needing the technical knowledge or the full amount of 32 ETH required to run a personal validator.
In this Lido Finance review, we will explore every aspect of the Lido Protocol, including its unique features, its impact on the Ethereum ecosystem, and its potential future developments. We'll also assess the pros and cons of using Lido for staking, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of its role within the rapidly evolving Ethereum landscape.
What is Liquid Staking?
Liquid staking is an innovative approach to staking on proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains. Unlike traditional staking, where tokens are locked up and inaccessible for a set period, liquid staking allows users to stake their assets while still retaining liquidity. Users receive a derivative token representing their staked assets, which can be used in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, enabling them to earn additional yields or trade their positions without waiting for the staking period to end.
Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs)
Liquid staking derivatives (LSDs) are tokens issued to users when they stake their assets through liquid staking platforms. These tokens, such as stETH for Ethereum or stMATIC for Polygon, represent the staked asset and accrue staking rewards over time. They allow users to maintain flexibility and liquidity, utilizing their staked assets across various DeFi protocols while still participating in staking. They are more commonly known as Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs).
For more, you can read our complete guide to liquid staking.
What is Lido Finance?
Lido Protocol was launched in December 2020 as a liquid staking solution for proof-of-stake (PoS) cryptocurrencies. The protocol was co-founded by a group of investors and developers, including Semantic Ventures, ParaFi Capital, Terra, MakerDAO creator Rune Christensen, Aave CEO Stani Kulechov, and Synthetix founder Kain Warwick. Early support also came from node operators like Stakefish and Staking Facilities.
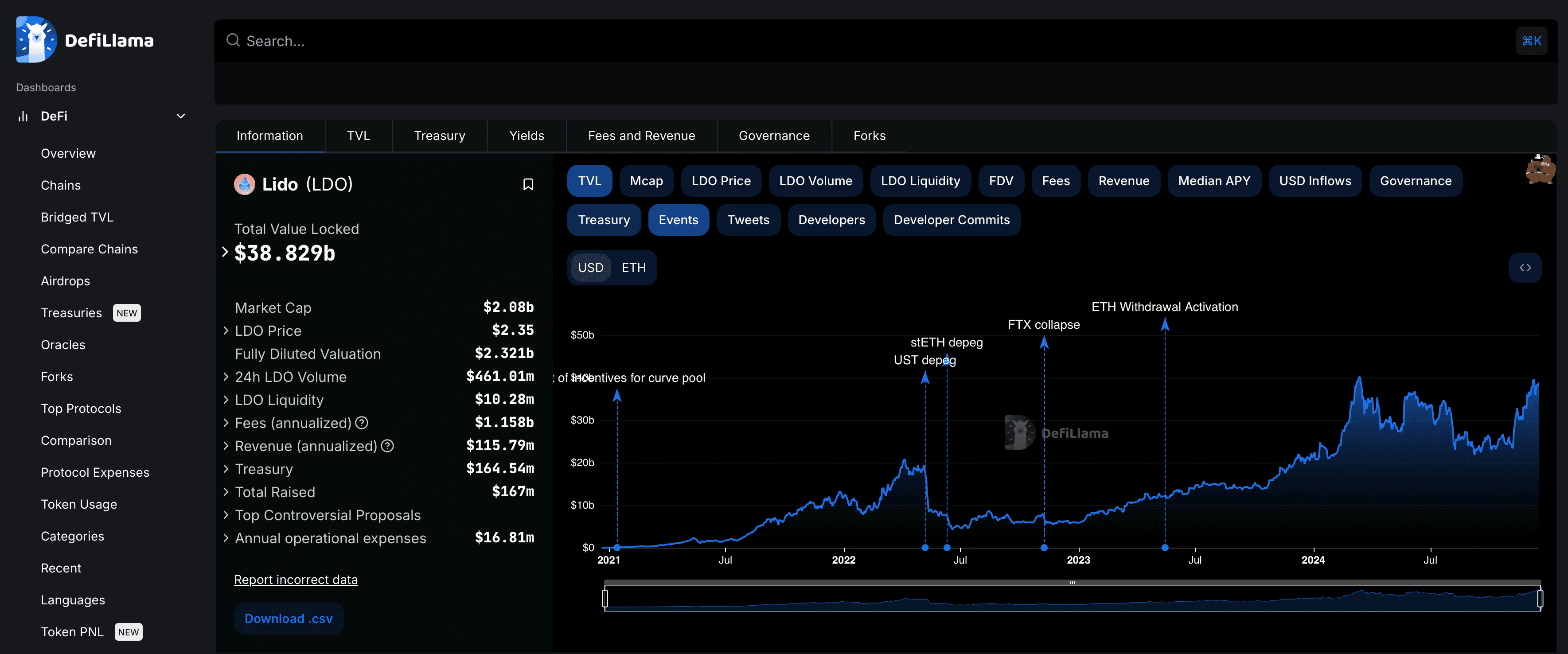 Lido On-Chain Metrics from DefiLlama
Lido On-Chain Metrics from DefiLlamaLido initially launched its staking service on Ethereum and soon expanded to include support for other networks, such as Solana, Polkadot, Kusama, and Polygon, each offering a similar liquid staking model.
The Lido Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) was established to oversee the protocol's governance and ensure its decentralized operation. The DAO is responsible for key decisions, such as protocol upgrades and the allocation of staking rewards. The governance of Lido is conducted using the LDO token, which allows holders to participate in the decision-making processes of the protocol).
Lido Protocol Economics
The ethos of liquid staking revolves around maximizing the utility of staked tokens while enhancing accessibility for users interested in Ethereum staking. Traditional staking requires users to lock up their tokens, making them inaccessible for a specific period, which limits their utility. Liquid staking, however, allows users to stake any amount of tokens and retain liquidity, providing them with flexibility and the potential for additional yield from DeFi applications.
How Does Lido Work?
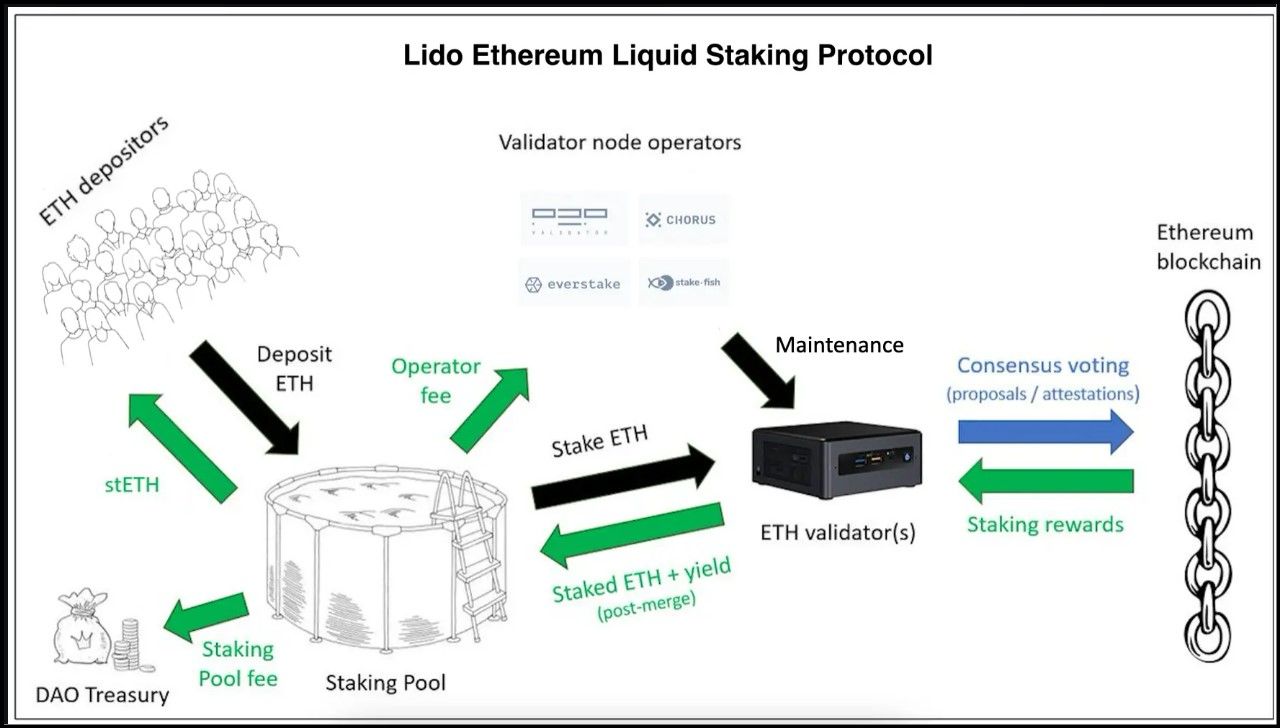 Lido Protocol Architecture. Image via Messari
Lido Protocol Architecture. Image via MessariLido is a liquid staking protocol designed to enable users to participate in Ethereum staking without dealing with the technical complexities or financial burdens traditionally associated with it. Users can deposit any amount of ETH into the Lido protocol, regardless of size, which Lido then stakes through a network of trusted validators.
- Staking and Minting stETH: When users stake their ETH with Lido, the protocol mints stETH tokens equivalent to the amount staked. These stETH tokens represent the user's staked ETH in the Lido contract and accrue staking rewards proportionally.
- Utility of stETH: stETH tokens are liquid and are useful in various Web3 use cases, including DeFi protocols, trading, or even restaking to generate additional yields. This versatility makes stETH valuable within the broader Ethereum ecosystem.
Governance
Lido's governance is managed by the Lido DAO, which oversees the protocol's core principles, including setting fees, assigning node operators, and managing oracles. The DAO operates on the LDO token, allowing token holders to participate in decision-making processes.
Lido Fees
Lido charges a 10% fee on all staking rewards earned through the protocol. This fee is divided equally, with 5% allocated to the DAO treasury and 5% rewarded to node operators for their services. The remaining 90% of the staking rewards are distributed among Lido stakers in proportion to the amount of stETH held in their wallets.
Strategic Implications
Combining DeFi strategies with liquid staking tokens (LSTs) like stETH can significantly enhance returns, as users can leverage their staked assets across multiple financial products and protocols. However, this also comes with increased risk, particularly the possibility of losing the initially deposited ETH if the stETH tokens are lost or mismanaged.
The next section will explore the nuances of the Lido protocol's components in greater detail, shedding light on the mechanics and intricacies that underlie this staking solution.
Lido Structural Components
The Lido protocol comprises the following essential components:
Node Operators
Node operators are a crucial component of the Lido Protocol. They are responsible for staking users' ETH and ensuring the security and efficiency of the staking process. Here's an overview of how node operators function within the Lido ecosystem:
- Role and Whitelisting: Lido currently has a group of 36 whitelisted Ethereum validator nodes. These nodes are selected and managed by the Lido Node Operator Sub-Governance Group (LNOSG), which oversees the whitelisting process to ensure that only reliable and trustworthy validators participate in the network.
- Importance of Honest and Efficient Operations: The role of node operators is critical for maintaining the security and integrity of the funds staked within the Lido Protocol. Honest and efficient node operators help minimize slashing penalties, which can occur if validators behave maliciously or fail to maintain proper node operations.
According to Lido's documentation, their node operators have maintained a solid track record with no slashing penalties to date, demonstrating their reliability and efficiency. - Non-Custodial Structure: Lido operates on a non-custodial basis, meaning that node operators do not have direct control over the users' funds. Instead, they use a public validation key to validate transactions using the staked assets. This structure enhances the security of the protocol by ensuring that node operators cannot access or mismanage the staked funds directly.
By leveraging a network of trusted and diversified node operators, Lido ensures that the staking process is secure and efficient, aligning with the broader goals of decentralization and user fund security.
Lido Smart Contracts
The Lido Protocol relies on several smart contracts to manage its operations and maintain the integrity of its liquid staking services. Two primary smart contracts form the core of Lido's architecture: the Lido Staking Pool Contract and the Lido Oracle Contracts. Here's an overview of their functions and significance within the protocol.
Lido Staking Pool Contract
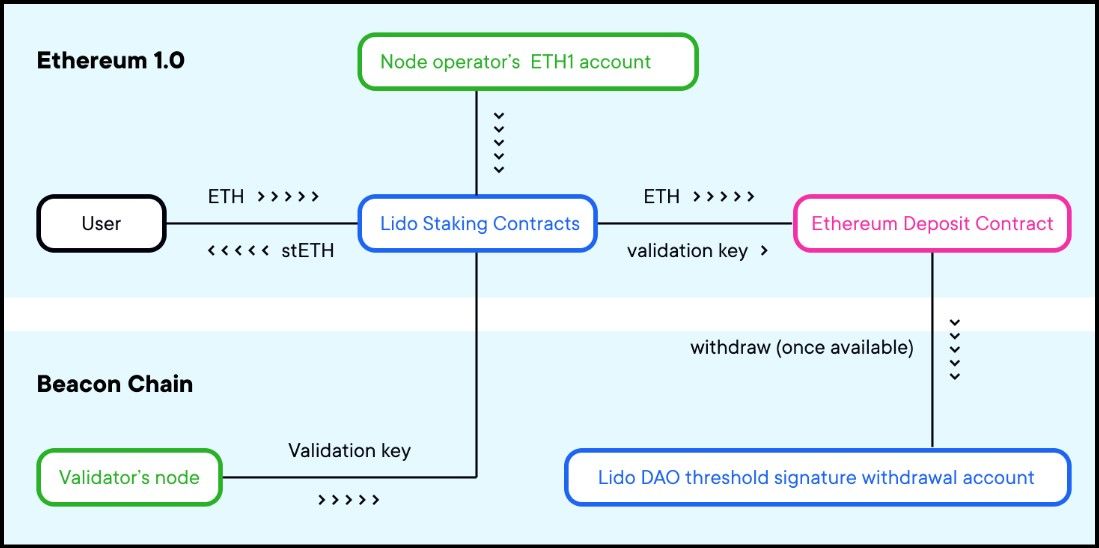 The image by Lido Blog illustrates the architecture of Lido Staking contracts. Note that the diagram describes pre-merge architecture, post which, the Ethereum 1.0 components became a part of the Beacon chain.
The image by Lido Blog illustrates the architecture of Lido Staking contracts. Note that the diagram describes pre-merge architecture, post which, the Ethereum 1.0 components became a part of the Beacon chain.The Lido Staking Pool Contract is the central smart contract responsible for handling the core functionalities of the Lido Protocol. Its primary responsibilities include:
- Managing User ETH Deposits and Withdrawals: The contract accepts ETH deposits from users and processes their withdrawal requests. This ensures users can participate in staking without the need to run their own validator nodes.
- Minting and Burning stETH Tokens: Upon receiving ETH deposits, the staking pool contract mints stETH tokens equivalent to the amount of ETH deposited. These tokens represent the staked ETH and accrue staking rewards over time. Conversely, when users withdraw their staked ETH, the corresponding stETH tokens are burned.
- Managing the Node Operators Registry: The contract maintains a registry of node operators through the NodeOperatorsRegistry contract. It distributes ETH to node operators in a round-robin fashion, ensuring a fair and balanced allocation of staking duties.
- Delegating Funds to Node Operators for Staking: The staking pool contract delegates the pooled ETH to a network of trusted node operators who perform the actual staking operations on the Ethereum network. This delegation process is crucial for maintaining the protocol's non-custodial nature.
- Applying Fees and Distributing Rewards: Lido charges a 10% fee on staking rewards, which is divided equally between the DAO treasury and node operators. The remaining 90% of the rewards are distributed to stETH holders in proportion to their holdings. This fee structure ensures sustainability while rewarding both the DAO and the operators.
Lido Oracle Contracts
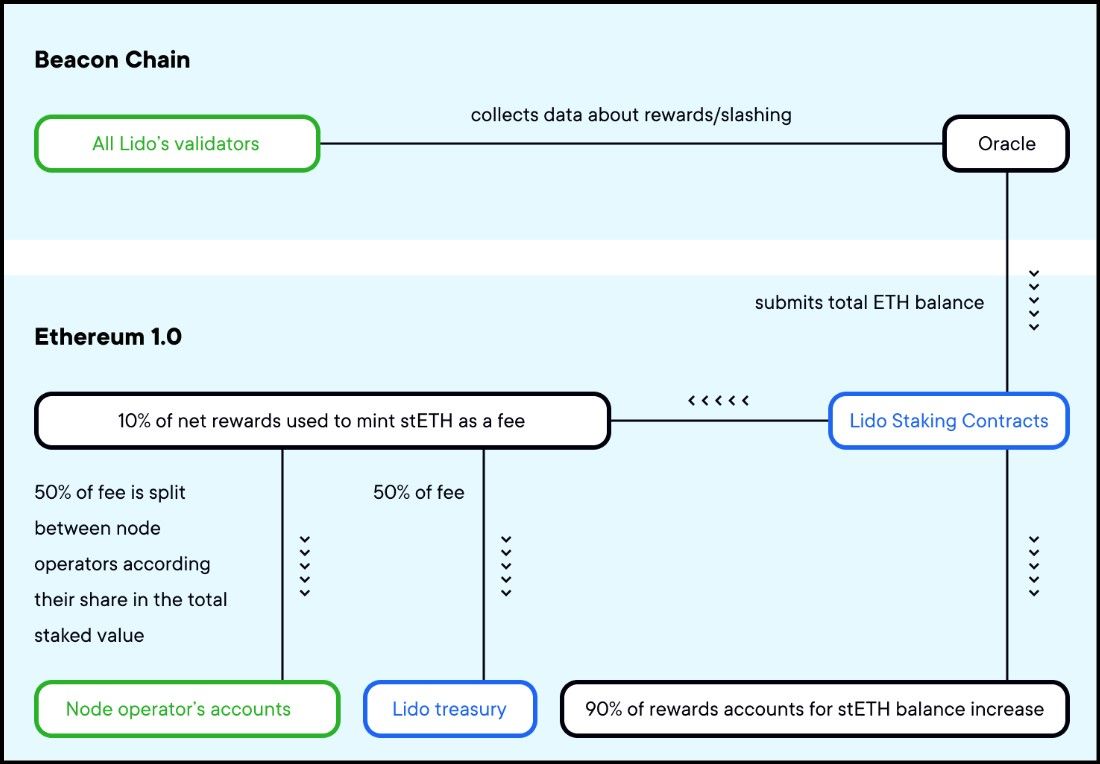 The image by Lido Blog illustrates the Lido reward distribution by its oracles. Note that the diagram describes pre-merge architecture, post which, the Ethereum 1.0 components became a part of the Beacon chain.
The image by Lido Blog illustrates the Lido reward distribution by its oracles. Note that the diagram describes pre-merge architecture, post which, the Ethereum 1.0 components became a part of the Beacon chain.The Lido Oracle Contracts play a vital role in maintaining the accuracy and security of the protocol by providing up-to-date data on the state of the network and validators. Key functions of the Oracle contracts include:
- Tracking Validator Balances: The oracles monitor the staked ETH balance of each validator, reporting any changes due to block rewards or slashing penalties. This ensures the staking pool contract is always aware of the accurate staking state.
- Updating the Staking Pool with Rewards and Penalties: On days when validators generate net positive rewards, the oracles report the additional ETH to the staking pool, which mints equivalent stETH tokens. These tokens are then distributed: 90% to stETH holders, 5% to the DAO treasury, and 5% to the node operators. This process keeps the rewards distribution transparent and fair.
- Ensuring Accurate stETH Rebase: The oracles also play a critical role in the rebase mechanism of stETH. They ensure the stETH token supply reflects the current value of the underlying staked ETH, maintaining a 1:1 peg with ETH.
By combining the functionalities of the staking pool contract and the oracle contracts, Lido ensures a secure, efficient, and decentralized staking solution that offers liquidity to staked assets, enhancing their utility across various DeFi applications.
Lido LSTs: stETH and wstETH
Lido's liquid staking ecosystem relies on two main tokens, stETH and wstETH, which serve distinct roles to enhance flexibility and compatibility in the staking and DeFi landscape.
stETH: The Core Liquid Staking Token
- stETH is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum network that represents ETH staked through the Lido protocol. It serves as a receipt for users who stake their ETH, allowing them to maintain liquidity while earning staking rewards.
- Representation of Staked ETH: When users deposit ETH into Lido, the protocol stakes this ETH through its network of validators. In return, users receive stETH tokens in an equivalent amount, representing their staked ETH. This tokenization allows users to retain exposure to ETH and participate in staking rewards.
- Distribution of Staking Rewards: stETH holders earn rewards derived from two sources:
- Consensus Layer Rewards: These are rewards from Ethereum's Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism, reflecting the inflationary issuance of ETH.
- Execution Layer Rewards: These include transaction fees and Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) rewards earned by validators.
As these rewards accumulate, they are converted into additional stETH tokens, which are proportionately distributed to all stETH holders, allowing them to benefit from the staking returns.
- Rebasable Token Maintaining a 1:1 Ratio with ETH: stETH is a rebasable token that adjusts its supply to reflect the rewards earned, maintaining a 1:1 ratio with the ETH staked in the Lido pool. This rebasing ensures that the value of stETH stays aligned with the underlying ETH, making it an attractive option for users seeking liquidity alongside staking rewards.
- Daily Balances Calculated by Oracles: Lido employs a system of oracles to calculate and update stETH balances daily. These oracles track validator performance, including earned rewards and slashing penalties, ensuring that the stETH supply accurately reflects the total staked ETH and accrued rewards. After deducting a 10% fee (5% for the DAO treasury and 5% for node operators), the remaining rewards are distributed to stETH holders.
wstETH: The Wrapped Version of stETH
- wstETH is a wrapped version of stETH designed to provide compatibility with DeFi protocols that do not support the rebasing feature of stETH.
- Token Wrapper Mechanism: Unlike stETH, which rebases periodically to distribute staking rewards directly to token holders, wstETH maintains a fixed balance. This feature makes it compatible with DeFi protocols that cannot handle rebasing tokens. For example, if MakerDAO does not support stETH's rebasing mechanism, a user with stETH locked in MakerDAO might miss out on the rebasing rewards. To solve this issue, Lido offers wstETH, which does not rebase but instead accumulates staking rewards.
- Accumulating Token: wstETH acts as an accumulating token. When users convert stETH to wstETH, they lock in the value of their stETH at the current rate. The wstETH contract accumulates rewards by increasing the intrinsic value of each wstETH token over time. Thus, while stETH adjusts its supply to distribute rewards, wstETH grows in value, reflecting the accrued staking rewards. This accumulation allows wstETH to be worth more than 1 ETH as the staking rewards increase, whereas stETH maintains a close 1:1 peg with ETH.
- Conversion and Redemption: The conversion process between stETH and wstETH is straightforward. Users can mint wstETH by depositing their stETH, and conversely, they can burn wstETH to redeem stETH. This flexibility allows users to choose the token that best fits their strategy, whether they need compatibility with non-rebasing-friendly DeFi platforms or prefer the liquidity of stETH.
The Role of stETH and wstETH in Lido's Ecosystem
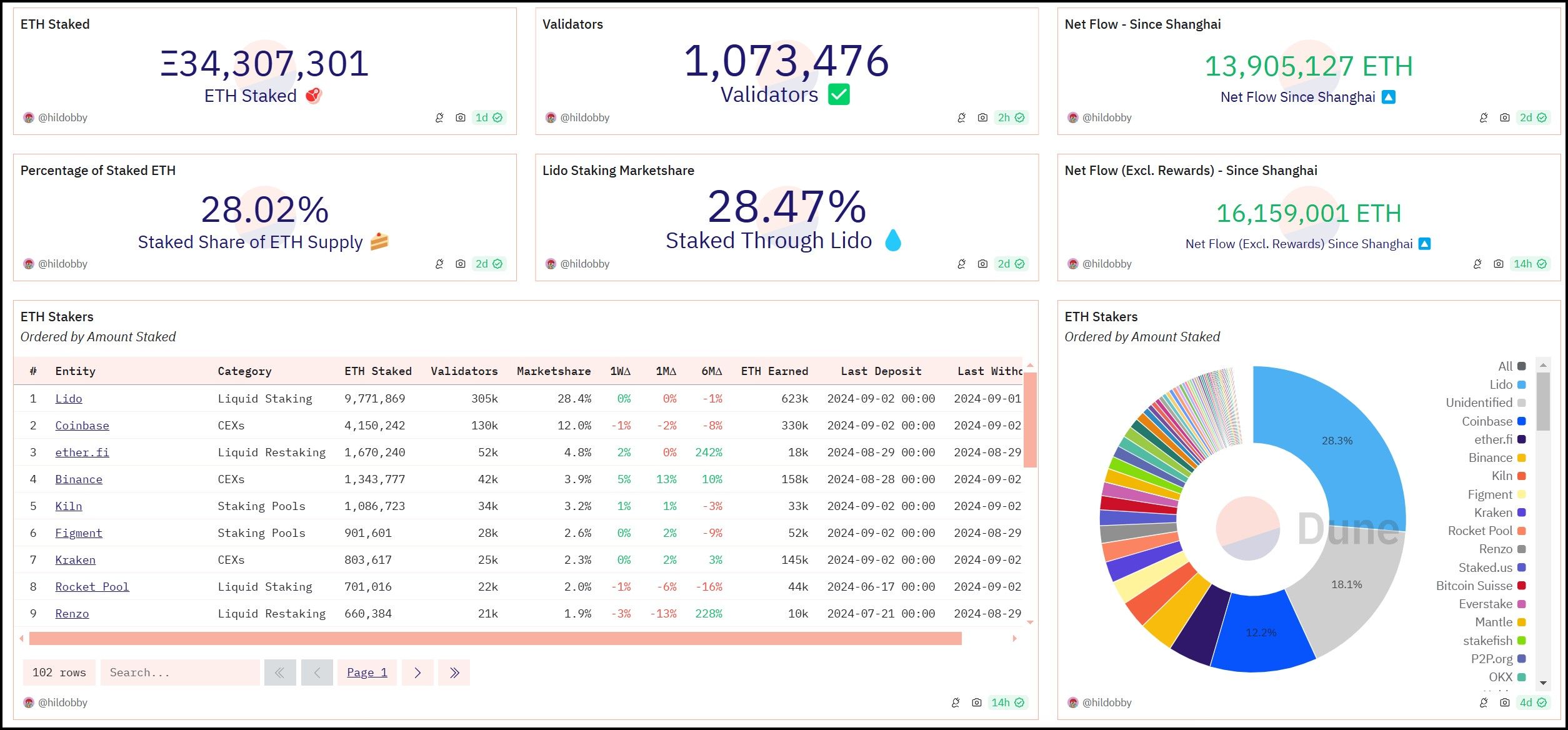 Lido Market Share. Image via Dune Analytics
Lido Market Share. Image via Dune AnalyticsTogether, stETH and wstETH underpin Lido's liquid staking model, providing users with options that cater to various DeFi strategies and risk appetites. As of September 2024, Lido holds a significant position in the Ethereum staking ecosystem, controlling 28.3% of the total staked ETH, making it the largest staker on Ethereum, according to Dune Analytics. This dominant position highlights the protocol's ability to offer scalable and flexible staking solutions that meet the diverse needs of the Ethereum community.
Lido expanded its liquid staking ecosystem to many chains after Ethereum. Here's a complete list of networks Lido supports:
- Ethereum (stETH)
- Polygon (stMATIC)
- Solana (stSOL)
- Polkadot (stDOT)
- Kusama (stKSM)
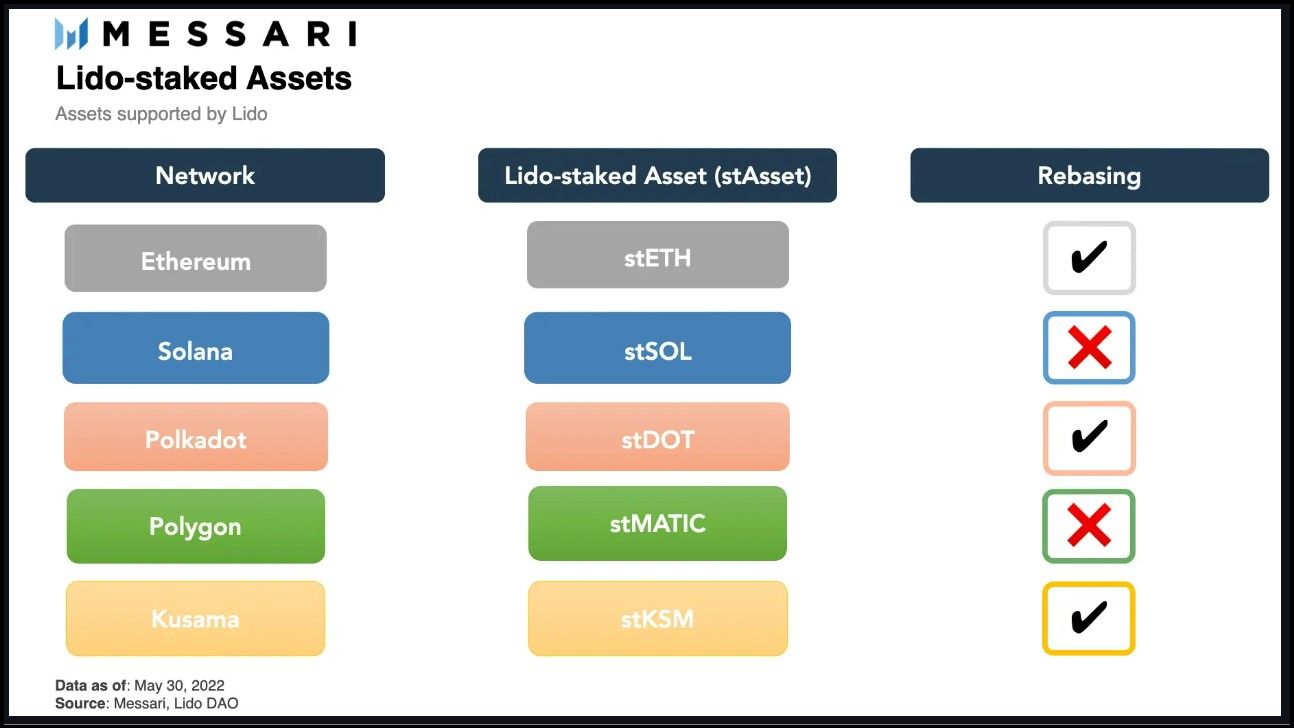 Lido LST Tokens. Image via Messari
Lido LST Tokens. Image via MessariMoreover, currently, wstETH token is present on the following networks:
LDO Token and the Lido DAO
The Lido DAO manages the liquid staking protocol and votes to decide key system parameters. The primary functions of the DAO are:
- Decide key parameters of the liquid staking protocol, like fees, oracles and node operators.
- Scouting, assessing and qualifying node operators to ensure efficient protocol operations.
- Approve grants to support research initiatives.
- Bug bounty program.
- Conducting other operational duties.
The LDO token facilitates the DAO's governance decisions. LDO is the Lido protocol's ERC-20 token. The tokenomics of the LDO token are designed to support the Lido ecosystem's growth and sustainability by strategically distributing tokens among various stakeholders and maintaining a fixed supply. Here are the key aspects:
- Circulating and Total Supply:
LDO has a total supply of 1,000,000,000 tokens, with a circulating supply of 892,898,290 tokens. This capped supply structure helps maintain the token's value by preventing inflation from an unlimited supply. - Token Distribution:
The allocation of LDO tokens is planned to ensure long-term sustainability and incentivize participation in the Lido ecosystem:- DAO Treasury: A significant portion of the LDO tokens is reserved for the DAO treasury, which funds development, community initiatives, and other activities approved by LDO holders.
- Founders and Team: Tokens are allocated to the founders, team members, and early contributors as an incentive for their ongoing support and development efforts.
- Validators and Advisors: A portion of the LDO tokens is allocated to validators operating staking nodes and advisors contributing to the platform's strategic direction.
- Investors: Early investors who provided capital for Lido's initial development are allocated a share of the tokens, aligning their interests with the platform's growth.
Where to Buy LDO?
LDO tokens can be purchased on both centralized and decentralized exchanges.
- Centralized Exchanges: Major centralized exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken offer LDO trading pairs, allowing users to buy LDO using fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies. These platforms provide a user-friendly interface and additional features like fiat on-ramps, making it easier for new users to acquire LDO.
- Decentralized Exchanges: LDO can also be purchased on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and SushiSwap. These platforms allow users to trade directly from their wallets, providing greater privacy and control over their funds. Users can swap ETH or other ERC-20 tokens for LDO without needing to create an account or undergo KYC verification.
Lido DeFi Integrations
stETH, Lido's liquid staking token, has become a vital asset in the Ethereum DeFi ecosystem, providing various utilities across different categories. These utilities enhance the yield potential of ETH holders and contribute to Ethereum's security and resilience. Here is a categorized overview of stETH's integrations and their roles:
1. Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
- Curve Finance (stETH/ETH Liquidity Pool): Curve offers a stETH/ETH liquidity pool that allows users to earn trading fees and liquidity mining rewards with low slippage. This pool is designed to maintain a stable peg between stETH and ETH, minimizing impermanent loss for liquidity providers. The APR for providing liquidity here is approximately 3-5%.
- Uniswap V3 (wstETH/ETH Pool): Uniswap supports a wstETH/ETH liquidity pool. This pool is particularly suitable for wstETH due to its non-rebasing nature, which avoids the complexities associated with rebasing tokens like stETH. The estimated APR for this pool ranges from 2-5%, depending on market conditions.
- Balancer v2 (wstETH/ETH Composable Stable Pool): Balancer v2 provides a customizable and dynamic stable pool for wstETH/ETH. This pool offers dynamic swap fees and the flexibility of Balancer's unique liquidity management features, providing an APR of 2-5%. This pool allows users to earn trading fees while benefiting from Balancer's features like dynamic asset weights.
2. Lending Protocols
- Aave v2 Ethereum Mainnet Market: stETH is listed as an accepted collateral asset on Aave, allowing users to borrow other assets while retaining their exposure to staking rewards. The APR for stETH on Aave ranges from 3-8%, making it an attractive option for users looking to leverage their stETH without unstaking it.
- Other Lending Platforms (Cream Finance, Compound): Similar to Aave, platforms like Cream Finance and Compound accept stETH as collateral, enabling users to borrow other assets while still earning staking rewards. The yield on these platforms aligns with the rates on Aave, generally ranging from 3-8%.
3. Restaking Platforms
- EigenLayer: EigenLayer allows users to restake stETH, enhancing their yields while contributing to Ethereum's extended security framework. With a massive $2.19 billion in stETH restaked (898,555.15 stETH tokens), EigenLayer represents approximately 75% of the Ether staked in the protocol. This substantial figure highlights the growing importance of liquid staking tokens (LSTs) in securing Ethereum and its extended ecosystem.
- Blast Layer 2 Chain: Blast offers a native yield mechanism utilizing LST tokens, with approximately $946.72 million in stETH (388,634.68 tokens) locked in its contracts to earn yield for the layer 2 protocol. This integration showcases how LSTs are not just for yield farming but also for providing security to other blockchain layers.
4. Yield Aggregators and Other DeFi Opportunities
- Providing Liquidity on DEX Protocols: Beyond Curve and Uniswap, other DEXs such as SushiSwap also offer stETH liquidity pools. These pools enable users to earn trading fees, liquidity mining rewards, and the underlying staking rewards from stETH. The combined APR for providing stETH liquidity can range from 3% to 8%, depending on the specific DEX and market conditions.
- Yield Optimization Platforms (Yearn Finance, Convex, Idle Finance): Platforms like Yearn Finance and Convex offer advanced yield optimization strategies involving stETH. These strategies can include auto-compounding and leveraged positions, potentially increasing yields up to 5-10% APR. Idle Finance offers risk-adjusted tranches that provide yields between 1.5% and 8.5% APR, depending on the user's risk appetite.
Impact of stETH in the Ethereum Ecosystem
- The widespread integration of stETH across multiple DeFi platforms demonstrates its critical role in the Ethereum ecosystem. These integrations allow ETH holders to earn additional yields through various DeFi strategies while maintaining liquidity. Moreover, by staking ETH through Lido, users contribute to Ethereum's security and resilience, incentivizing more ETH to be staked in the protocol. This increased staking activity helps to secure the Ethereum network and its associated layers, enhancing the overall robustness of the blockchain.
Enhanced Yield on ETH Through Liquid Staking
- Combining the base staking rewards from Lido with the additional yields earned through DeFi integrations significantly enhances the potential returns on ETH. For example, staking ETH via Lido provides a base reward of approximately 4.8% annually. By further integrating stETH into DeFi platforms—whether through liquidity pools, lending, or yield optimization strategies—users can potentially achieve combined yields ranging from 8% to 10% or higher. This multi-layered yield strategy leverages the flexibility of liquid staking while optimizing returns across various DeFi protocols, albeit with the added risks associated with smart contracts, market volatility, and impermanent loss.
- By using Lido's stETH, ETH holders can maximize their returns, contributing to the broader DeFi ecosystem and reinforcing the security of Ethereum and its extended networks.
Lido Finance Review: Closing Thoughts
Lido's liquid staking protocol has established itself as a pivotal component in the Ethereum ecosystem, offering ETH holders a flexible and rewarding way to participate in staking. The diverse integration of stETH across various DeFi platforms underscores its utility, enabling users to maximize their returns while contributing to the security and stability of the Ethereum network. With opportunities ranging from liquidity provision on DEXs to lending and restaking on innovative platforms like EigenLayer and Blast, Lido provides multiple avenues for ETH holders to enhance their yields.
However, the landscape of liquid staking is competitive, and Lido faces significant competition, most notably from RocketPool. RocketPool, like Lido, is a prominent liquid staking solution on Ethereum but differs fundamentally in its design and approach:
- Validator Set Design: One of the primary differences between Lido and RocketPool lies in their approach to validator set participation. Lido emphasizes an efficient and experienced validator set, which involves selecting a curated group of validators to ensure high performance and minimal risk. While this approach provides a reliable and secure staking environment, it introduces a degree of centralization, as only whitelisted validators can participate. In contrast, RocketPool adopts a permissionless model, allowing any user with the necessary technical skills and capital to become a validator. This open approach promotes decentralization but may come with increased risks associated with less experienced validators.
- Liquidity Incentives: Another notable distinction is the way these protocols handle liquidity incentives. Lido allocates a significant amount of funds to LDO-induced rewards, encouraging liquidity provision and participation through various incentive programs. This strategy helps maintain high liquidity levels for stETH and enhances its utility in the DeFi ecosystem. RocketPool, on the other hand, does not have a built-in incentive mechanism like Lido's extensive LDO rewards. While this might limit RocketPool's immediate liquidity, it aligns with its ethos of fostering organic growth and reducing reliance on external incentives.
These differences reflect broader philosophical divergences between the two protocols: Lido prioritizes efficient, centralized control for security and high liquidity, while RocketPool leans towards a more decentralized and permissionless approach. As both protocols continue to evolve, these distinctions will shape their roles and influence within the Ethereum ecosystem.
In conclusion, liquid staking is becoming increasingly integral to Ethereum's future, providing new opportunities for yield and enhancing network security. As protocols like Lido and RocketPool advance and adapt to changing market dynamics, they will continue to play crucial roles in shaping the landscape of Ethereum staking and DeFi. For ETH holders, understanding these nuances is key to making informed decisions on how to maximize their participation and returns in the rapidly expanding world of liquid staking.





