The Layer 2 ecosystem of Ethereum is vast and fiercely competitive. Recent updates to the Ethereum mainnet, such as account abstraction and protodanksharding, have significantly improved its efficiency. These advancements have massively increased the throughput capabilities of Layer 2 solutions, creating a fertile ground for innovation and competition.
Layer 2 chains are also evolving rapidly. They leverage cutting-edge technologies such as zero-knowledge (zk) proofs, advanced data availability techniques, and improved hardware, including more efficient sequencers and provers. These innovations are driving substantial gains in efficiency and scalability, further intensifying the competitive landscape of Layer 2 solutions.
In a previous Coin Bureau article about the top new cryptocurrencies, we highlighted a promising Layer 2 project called the Mantle Network. Since then, Mantle has made impressive strides, climbing to the 20th spot in total value locked (TVL), surpassing legacy networks like Near, Algorand, Cardano and StarkNet, according to DefiLlama.
This Mantle Network review aims to provide a comprehensive overview, exploring the various components of its ecosystem, including its governance framework, liquid staking tokens and the second-largest treasury in Web3. As a unique and modular Layer 2 network, Mantle offers a novel approach to addressing the scalability trilemma. By examining these aspects, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of what sets Mantle apart in the highly competitive Layer 2 landscape.
What is the Mantle Network?
The Mantle Network originated from BitDAO, a prominent decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) established in 2021. BitDAO quickly became a significant player in the crypto space, thanks to substantial backing from high-profile investors such as Peter Thiel and venture capital firm Pantera Capital. Its mission was to support and invest in various decentralized projects and protocols.
In June 2022, BitDAO proposed the incubation of Mantle, marking the beginning of its journey as a specialized Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. This proposal set the stage for Mantle to leverage BitDAO's vast resources and strategic vision. By January 2023, Mantle launched its first testnet, a significant milestone in its development.
 The BitDAO-Mantle Merger Created the Second-Largest Treasury in Web3 | Image via CryptoSlate
The BitDAO-Mantle Merger Created the Second-Largest Treasury in Web3 | Image via CryptoSlateThe merger between BitDAO and Mantle was finalized in May 2023, a strategic move aimed at consolidating efforts and focusing solely on Layer 2 scaling solutions. This merger was approved through BitDAO's governance proposals, specifically BIP-21 and MIP-22, which received overwhelming support from the community. The integration allowed Mantle to inherit BitDAO's sizable treasury, providing substantial financial backing to fuel its growth and development.
As of June 2024, Mantle's treasury is valued at approximately $3.01 billion, comprising a mix of MNT, mETH, wETH, and USDe tokens. This robust financial foundation positions Mantle as a well-resourced network capable of driving significant innovation in the Layer 2 space.
A key milestone in Mantle's development was the Tectonic Upgrade (V2), completed in March 2024. This upgrade introduced several critical improvements, including fixed block schedules and removing Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) nodes. Additionally, the upgrade marked a pivotal change in Mantle's tokenomics. Post-upgrade, MNT became the native token of the Mantle Network, replacing its previous status as a bridged version of the Ethereum ERC-20 token. This transition enhanced the network's efficiency and aligned the token's functionality with Mantle's long-term vision.
How Mantle Network Works
The Mantle Network began its journey by developing Mantle V1 Alpha in late 2022, officially launching in July 2023. This initial version utilized Optimism's Optimistic Virtual Machine (OVM) codebase. The OVM is a key component of Optimism's Layer 2 solution, designed to execute transactions faster and cheaper by assuming transactions are valid and only verifying them if fraud is suspected.
However, the landscape of Layer 2 solutions saw a significant shift in October 2022 with the introduction of Optimism's OP Stack. The OP Stack is a modular, open-source, and forkable technology stack that enables the creation of new Layer 2 chains, known as OP Chains. These chains are interoperable, providing a flexible and scalable framework for developers.
The OP Stack brought several advantages over the OVM. Notably, it included support for Ethereum's EIP-1559, which streamlined gas management by introducing a base fee that adjusts dynamically based on network demand, thus eliminating the uncertainty of the previous auction-based system.
In March 2024, Mantle launched its V2 Tectonic upgrade, transitioning from the OVM to Optimism Bedrock, which is built on the OP Stack. This upgrade marked Mantle's transformation into an OP Stack Layer 2 chain, incorporating critical data management changes and significantly enhancing its performance and scalability.
 Bedrock is a Technology Stack for Creating OP Chains | Image via Optimism
Bedrock is a Technology Stack for Creating OP Chains | Image via OptimismMantle V2 Tectonic also introduced a new data availability solution, Mantle DA, powered by EigenLayer's EigenDA. This solution improves data availability and security, ensuring the network can efficiently handle higher transaction volumes. While Mantle DA currently enhances the network's capabilities, there are plans to entirely switch to EigenDA at an undisclosed future date.
The OP Stack
Optimism Bedrock is a collection of technological components that can create new interoperable layer 2 chains called OP Chains. Bedrock consists of the OP Stack, the tech stack Mantle leverages to build its infrastructure. The OP Stack consists of the following components:
- op-geth: The op-geth component implements the Layer 2 execution layer. It is based on the popular Ethereum client, Geth (Go Ethereum), but has been modified minimally to ensure a secure, Ethereum-equivalent environment for applications running on Layer 2. These minimal changes ensure that the op-geth remains closely aligned with the Ethereum mainnet, providing a consistent and secure execution environment for decentralized applications (Dapps).
- op-batcher: The op-batcher service is crucial in submitting Layer 2 sequencer data to Layer 1. Its primary function is to make this data available for verifiers. To optimize costs, the op-batcher only posts the minimal data necessary to reconstruct Layer 2 blocks on Layer 1. This minimalistic approach reduces the expense of writing data to the Ethereum mainnet while ensuring sufficient information is available to verify the integrity and sequence of transactions processed on Layer 2.
- op-proposer: The op-proposer service submits output roots to Layer 1. Output roots are essential for enabling the trustless execution of Layer 2-to-Layer 1 messaging. By submitting these roots, the op-proposer creates a view of the Layer 2 state from the perspective of Layer 1. This process ensures that Layer 1 has a verifiable and accurate representation of the Layer 2 state, which is critical for maintaining the integrity and trustlessness of cross-layer interactions.
- Sequencer Nodes (op-geth + op-node): Sequencer nodes combine op-geth and op-node, working together to manage the ordering and execution of transactions on Layer 2. The op-geth executes transactions, maintaining the Ethereum-equivalent environment, while the op-node manages the network-specific functionalities, such as transaction ordering and block production. Sequencer nodes play a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of the Layer 2 chain, as they are responsible for processing and sequencing transactions before they are submitted to Layer 1 via the op-batcher and op-proposer services.
These components collectively enable the Mantle Network and other OP Stack-based Layer 2 solutions to provide scalable, secure, and efficient execution environments that align closely with Ethereum's mainnet, ensuring compatibility and ease of use for developers and users alike.
Mantle DA
The Mantle Network differentiates from other layer 2s in how it handles the storage of its blockchain data. While other networks store their block data on the Ethereum network, incurring significant storage costs due to scarce storage capacity in Ethereum, Mantle leverages EigenLayer for Data Availability:
- MantleDA, consisting of permissioned EigenDA nodes staking MNT stores Mantle block data. This data will be crucial for constructing fault proofs in case disputes arise after the optimistic acceptance of transaction data.
- Mantle DA employs an erasure rate system, which stores block data in multiple fragments across multiple nodes. Validators reconstruct data by accessing numerous fragments as required. Fragmentation protects data integrity.
In summary, using Mantle DA reduces the load implied in Ethereum, which means layer 2 can pack more transactions into each block, drastically improving throughput and reducing the gas cost of Mantle transactions. However, third-party data availability makes Mantle theoretically less secure than full Ethereum rollups, as the Mantle Network depends on EigenLayer instead of Ethereum.
Mantle Transaction Life Cycle
A Mantle Transaction Life Cycle interacts with several modular layers that perform specific tasks. A Mantle transaction involves interaction between the Mantle execution layer, a modular data availability layer, and the Ethereum mainnet. Here are the three main stages of the transaction life cycle:
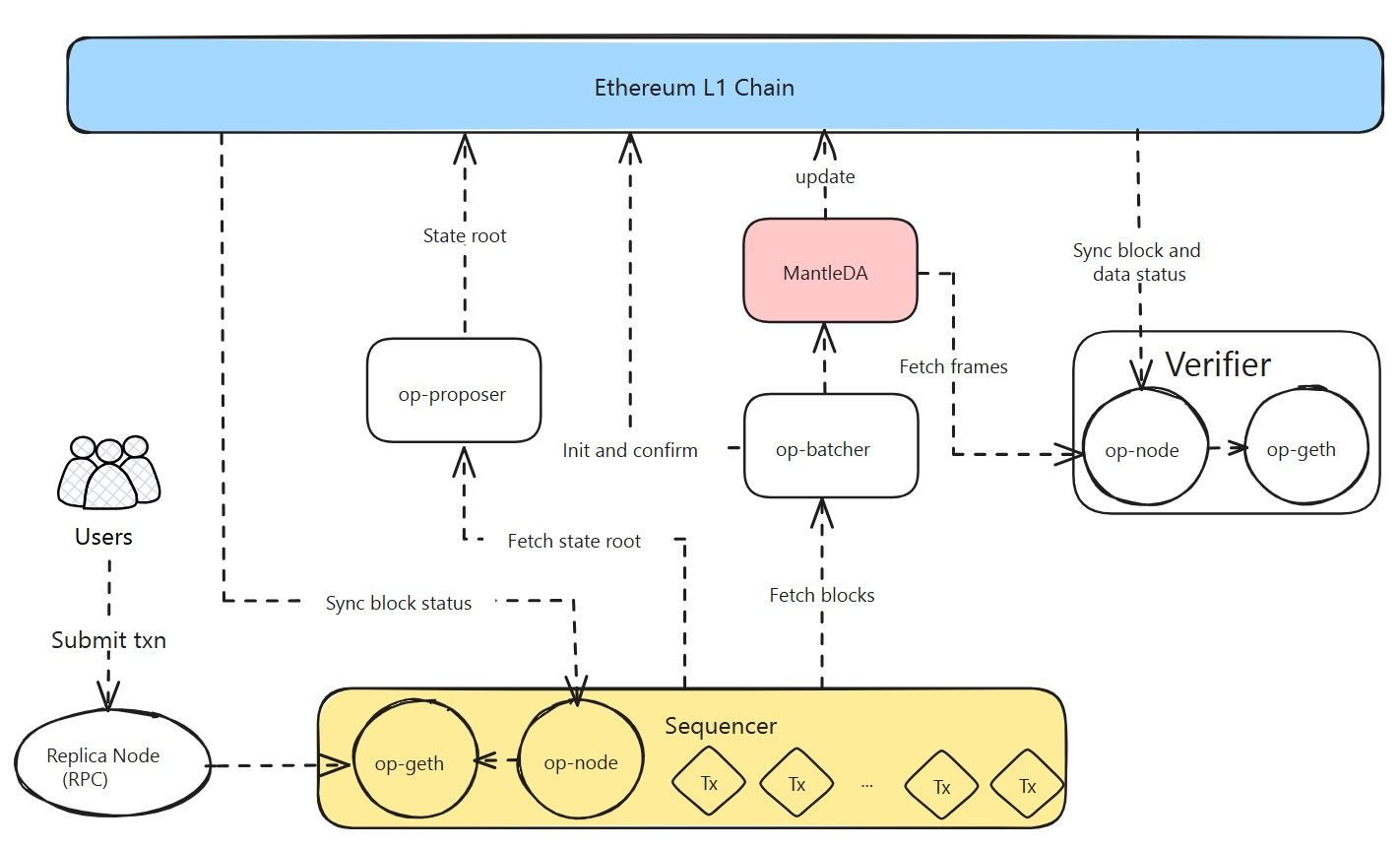 The Mantle Transaction Life Cycle | Image via Mantle
The Mantle Transaction Life Cycle | Image via MantleInitiating the Transaction
Users initiate transactions on the Mantle Network by sending signed transactions through available RPC nodes. On the other hand, decentralized applications (Dapps) leverage the integrated Mantle SDK, allowing them to connect seamlessly to the network. This integration ensures that both individual users and Dapps can interact with the Mantle Network efficiently.
Handling the Transaction
Once a transaction is initiated, the sequencer receives the transaction data from users and Dapps. The sequencer's primary responsibility is to package these transactions into blocks. Before constructing a block, the sequencer must ensure the following:
- Transaction Validity: The transactions must be fundamentally valid, adhering to the network's rules and protocols.
- Fee Payment: The transactions must have paid the necessary fees.
- Standard Execution Procedure: The transactions must follow the standard procedure for execution.
The sequencer performs this state verification process using the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) software op-geth. After calculating the new state, the op-proposer shares the new state's root with the Mantle Layer 1 (L1) smart contract on Ethereum. This process ensures that the state transitions are accurately recorded and can be verified on Ethereum's mainnet.
After creating several pending blocks, the op-batcher encodes and compresses these blocks into batches. These batches contain essential transaction data required for transaction settlement. Typically, a rollup would send these batches to Ethereum for storage, spreading the storage costs across individual transactions. These batches help solve disputes via fault proofs or create zk validity proofs, ensuring data availability.
Storing Transactions
The Mantle Network outsources data availability guarantees by storing batched transaction data with a third-party data availability (DA) provider called Mantle DA, powered by EigenLayer. The op-batcher submits the compressed transaction data to Mantle DA.
As an optimistic rollup, the Mantle Network does not need this data immediately. In case of disputes, verifiers can fetch the necessary transaction data from Mantle DA to create fault proofs and resolve discrepancies. This approach ensures that the Mantle Network remains efficient and scalable while maintaining the integrity and security of transaction data.
This transaction life cycle highlights Mantle's intricate processes to ensure efficient, secure, and scalable transaction handling on its Layer 2 network.
MNT Token
The Mantle Network token, officially known as MNT, is the native token of the Mantle ecosystem. In the Mantle V1 Alpha version, MNT functioned as an ERC20 token smart contract in the Ethereum network, while all the MNT tokens in layer 2 were bridged versions of the ERC20 tokens.
The Mantle V2 Tectonic upgrade changed MNT token status, MNT migrated to layer 2 and became the canonical token of the Mantle Network and not the bridged version of an Ethereum token. The MNT token has the following utilities:
- The Mantle crypto serves dual roles as a governance and utility token within the Mantle Ecosystem, providing holders voting rights and practical functionality.
- In terms of governance, each Mantle crypto carries an equal vote weight, enabling token holders to participate in DAO voting and influence the decision-making process actively. This ensures a decentralized and community-driven approach to shaping the future of the Mantle Ecosystem.
- As a utility token, MNT is utilized for gas fees on Mantle Network. Additionally, MNT tokens can serve as collateral assets for Mantle Network nodes, further incentivizing participation and contributing to the security and stability of the network.
MNT Distribution
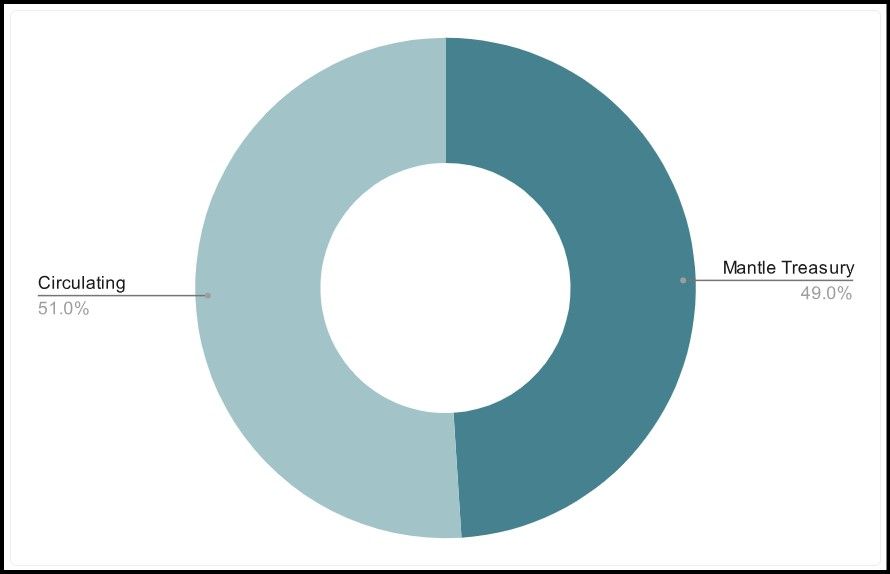 Initial MNT Distribution | Image via Mantle
Initial MNT Distribution | Image via MantleThe MNT token is unique in that its holders are not subject to any vesting or token lock period. It has a maximum supply of 6.2 billion tokens. In August 2024, the circulating supply of MNT sits at 3.2 billion tokens. The MNT token is distributed between the circulating supply and the Mantle treasury, which holds about 3 billion (~48%) MNT tokens.
The distribution of MNT tokens from the Mantle Treasury follows the Mantle Governance process, adhering to strict procedures exemplified by the BIP-19 Mantle Network Budget. As of June 2023, there are no formal macro targets or restrictions for MNT distribution. However, the primary categories for distribution include:
- User Incentives: Strategies to drive user adoption, such as multi-season achievements and quests, aim to increase daily active users, total transactions, protocol fees, and total value locked (TVL).
- Technology Partner Incentives: Incentives for Dapps, infrastructure service providers, and core protocol technology partners to foster collaborations and enhance the ecosystem.
- Core Contributor Team and Advisors: Resource allocation to the team and advisors through a transparent budget proposal process.
- Other Opportunities: Potential acquisitions, token swaps, treasury sales, and other deals evaluated on a case-by-case basis for their benefits to the Mantle Ecosystem.
Where To Buy MNT?
MNT can be bought via Bybit, Kraken, Gate.io and KuCoin, among other centralized exchanges. Also, check out our top picks for the best crypto exchanges.
Among decentralized exchanges, your options include Uniswap and PankcakeSwap. We also have an article highlighting the best decentralized exchanges.
Mantle Liquid Staking Protocol
Liquid staking is a technology where users mint a liquid representation of their staked ETH, which can participate in DeFi while also earning staking rewards. The liquid staking industry is one of the fastest-growing sectors in DeFi, attracting billions in value and generating significant capital that can fuel other activities in Web3.
Mantle Staked Ether
 mETH Market Values via CoinGecko
mETH Market Values via CoinGeckoThe Mantle Liquid Staking Protocol (LSP) integrates native liquid staking into the network. Users can stake ETH on Mantle LSP, which gives them mETH in return, representing their deposit and earning rewards over time. mETH is a value-accumulating token, meaning it rewards holders by increasing in value with time. As of August 2024, the price of 1 mETH is 1.0408 ETH. In August 2024, mETH market cap is at about $1.2 billion, which adds up to roughly 470,000 ETH staked in Mantle LSP.
mETH is indeed accessible on various DeFi platforms. Users can leverage mETH in liquidity pools and yield farming across many decentralized applications.
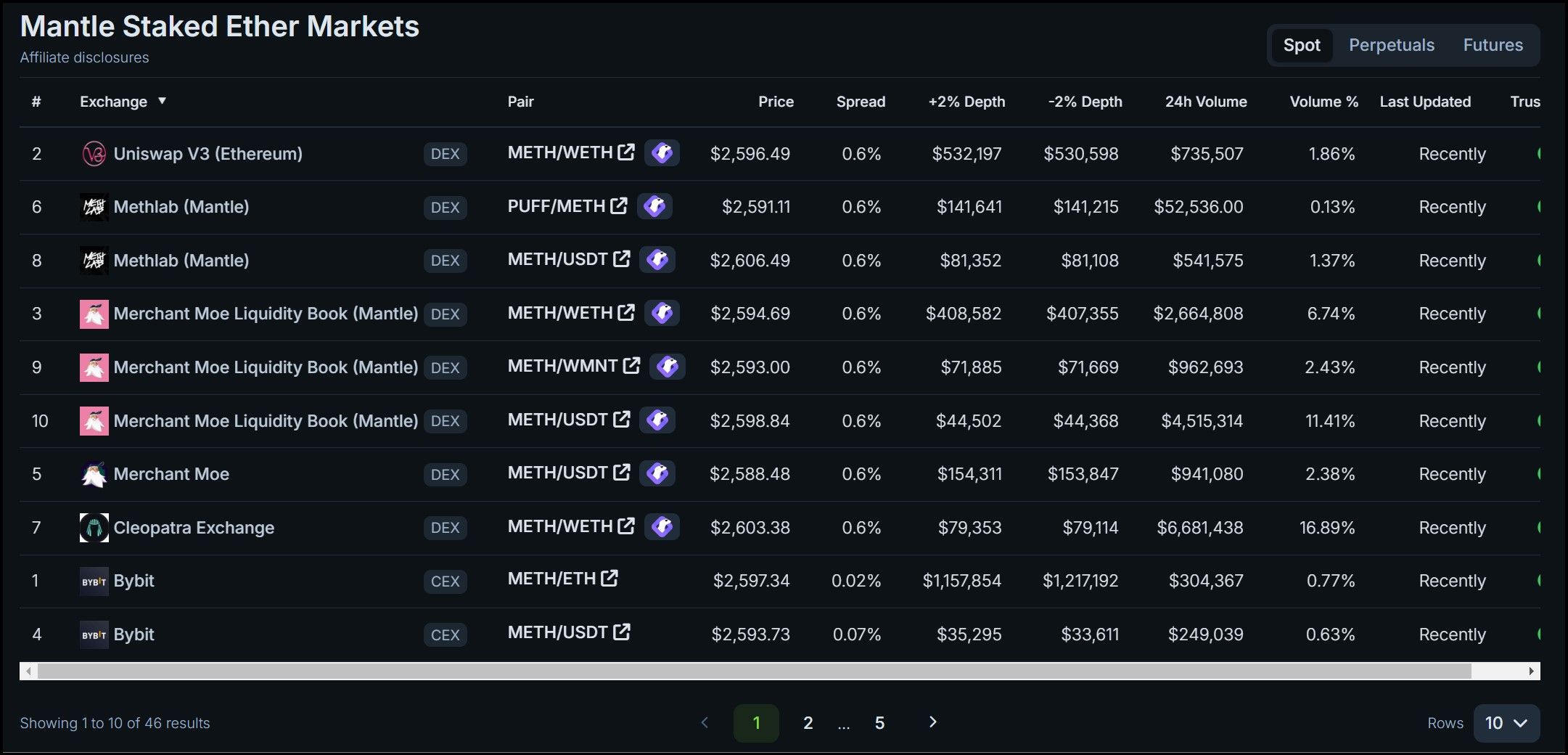 mETH Markets | Image via CoinGecko
mETH Markets | Image via CoinGecko$cMETH Restaking Token and $COOK
There are many applications of LSTs in decentralized finance. One interesting application involves reusing staked ETH to secure new networks by assuming additional slashing conditions called restaking.
The Mantle governance passed the MIP-30 upgrade and introduced the $cMETH liquid staking token. This token allows mETH holders to restake their tokens within the Mantle ecosystem. With cMETH, Mantle hopes to bring high composability in its ecosystem and reduce liquidity fragmentation. COOK is the governance token for cMETH.
The Mantle Ecosystem
The Mantle Network has rapidly evolved into a vibrant and diverse ecosystem, encompassing various decentralized applications (DApps) across multiple categories. Significant milestones, diverse DApp categories, and impressive performance metrics mark its growth.
Key Characteristics and Metrics
- The Mantle ecosystem witnessed two major periods of increased trading and adoption, driven by strategic initiatives and token rollouts.
- First Period (Late 2023 - January 2024):
- Launch of mETH and USDY in November 2023.
- mETH's market yield doubled to 7.2% in December 2023, with the cap increased from 250,000 mETH to 333,333 mETH in January 2024.
- The mETH and mUSD Holiday Raffle in December 2023 attracted significant participation, boosting daily active transactions to a peak of 2.2 million and 96,700 daily active addresses.
- Second Period (May 2024 - June 2024):
- Introduction of restaking initiatives such as mETH Eigen Points and the launch of cmETH and COOK.
- Mantle committed $5 million to SocialFi and gaming innovation, resulting in new dApps like Catizen, xMetaCene, and BladeGamesHQ.
- In May 2024, MNT on-chain holders increased by 9%, with DEX trading volume reaching $93.8 million and daily transactions hitting 790,900. Active addresses peaked at 194,200, and TVL reached its highest value at $437.4 million on June 6, 2024.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Mantle's ecosystem features a wide range of dApps across various categories, including DeFi, NFTs, and gaming.
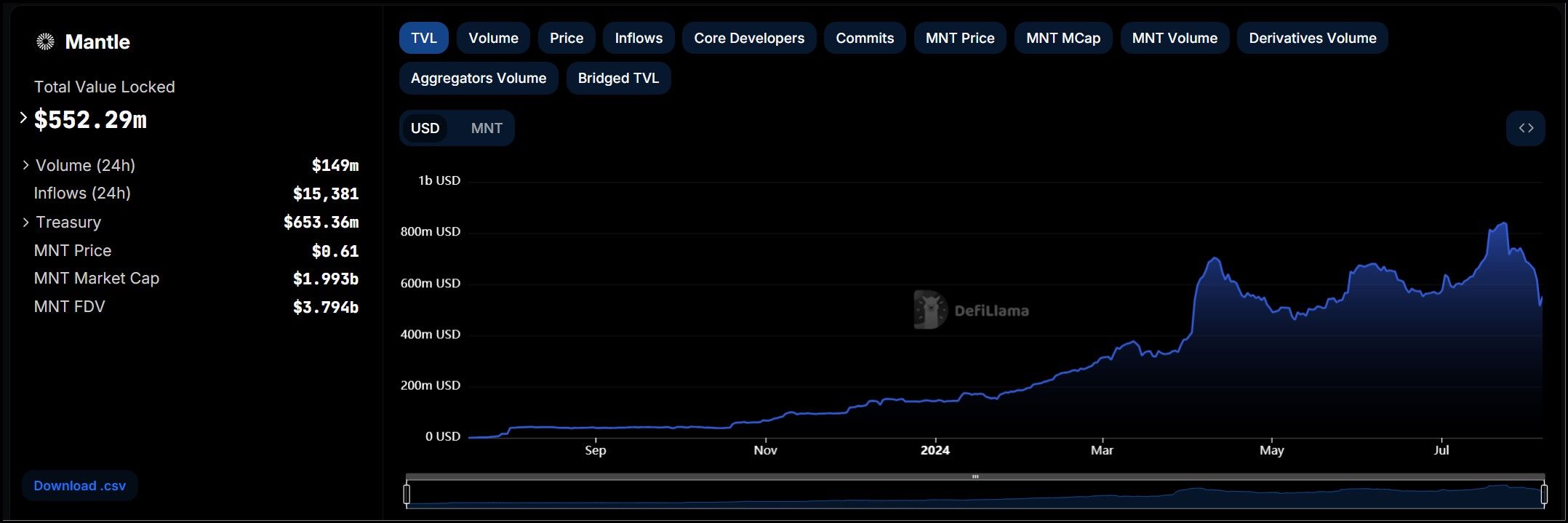 Mantle TVL. Image via DefiLlama
Mantle TVL. Image via DefiLlamaDeFi Applications:
- Agni Finance: An automated market maker-based decentralized exchange and launchpad. It leads Mantle's protocols with a TVL of $117.3 million.
- INIT Capital: A platform democratizing access to liquidity, with a TVL of $146.9 million and significant involvement in Mantle's Catalyzed Capital Pool.
- Merchant Moe: The largest DEX on Mantle, with a TVL of $78.4 million, part of the Trader Joe ecosystem, and featuring a Liquidity Book protocol.
- Agni Finance: An AMM-based DEX specializing in spot trading and concentrated liquidity, with a TVL of $55 million and notable trading pairs like mETH/wETH.
- Puff's Penthouse: A gamified staking platform where users bond mETH or USDT into PUFF tokens, boasting a TVL of $25.66 million.
NFT Projects:
- Mintle: A secondary NFT marketplace developed in partnership with Rarible, hosting the Citizens of Mantle collection and facilitating cost-effective NFT trading.
- Co-Museum: An NFT community platform for communally owned digital art, participating in events like Art Basel Miami and Singapore's Proof of Concept.
Gaming Initiatives:
- Catizen: A Web3 gaming network created by Pluto Studio, with 2.3 million addresses and 2.6 million transactions within a month of its beta launch.
- MetaCene: A gaming project connecting MMORPG players and Web3 enthusiasts, featuring a world divided into three chapters and several NFT series.
Key Performance Metrics and Milestones
- Daily Active Users and Transactions: Significant spikes in daily active transactions and addresses during key periods.
- Total Value Locked (TVL): Reached a peak of $437.4 million in June 2024.
- Trading Volume: DEX trading volume reached $93.8 million in May 2024.
- User Incentives: Mantle's initiatives like the Holiday Raffle and restaking programs, have driven user engagement and ecosystem growth.
Mantle Network Review: Closing Thoughts
The Mantle Network has strategically positioned itself as a leading contender in the Ethereum Layer 2 landscape by leveraging its robust financial backing, innovative technological advancements, and a diverse, rapidly expanding ecosystem. From its early development using Optimism's OVM to adopting the OP Stack and introducing advanced data availability solutions like Mantle DA, Mantle has consistently pushed the boundaries of scalability and efficiency.
The network's strategic focus on DeFi, NFTs, and gaming, coupled with significant user incentives and partnerships, has driven impressive growth in total value locked (TVL) and user engagement. As Mantle continues to evolve and integrate cutting-edge technologies, it stands poised to play a pivotal role in the future of decentralized applications and blockchain scalability, solidifying its position as a formidable player in the competitive Layer 2 arena.





