Decentralized finance (DeFi) has opened up new opportunities for users to earn yield on their assets, but it still faces significant challenges.
Many platforms offer only variable yields, leaving users exposed to market volatility and interest rate fluctuations. Additionally, assets locked in yield-bearing protocols often reduce liquidity, limiting the ability to pursue other investment opportunities. DeFi also lacks advanced tools for managing risk, forcing users to accept uncertainty in their returns.
This is where Pendle Finance steps in, offering a solution that addresses these issues by allowing users to tokenize and trade future yields, unlock liquidity, and manage risk more effectively.
This Pendle Finance review will explore how the platform addresses key challenges in DeFi, such as yield volatility, limited liquidity, and the lack of risk management tools. We’ll dive into Pendle's solution of yield tokenization, the mechanics of how Pendle works, its core features, and the role of the PENDLE token in the ecosystem.
Pendle Finance Review Summary
Pendle Finance is an innovative DeFi protocol specializing in yield tokenization and trading. It introduces a novel framework allowing users to tokenize and trade future yields of yield-generating assets, effectively creating a market for interest rates in the DeFi space. By enabling the separation and trading of yield and principal components of an asset, Pendle unlocks new possibilities for yield optimization, risk management, and speculative opportunities within the DeFi ecosystem.
The Key Features of Pendle Finance Are:
- Yield Tokenization: Pendle allows users to tokenize yield-bearing assets, separating them into Principal Tokens (PT) and Yield Tokens (YT).
- Fixed and Variable Yields: By tokenizing future yields, Pendle allows users to lock in fixed yields, offering protection against market fluctuations. Traders can also speculate on yield changes by trading YT, benefiting from potential yield increases.
- Unlocking Liquidity: Pendle enables users to unlock liquidity from their locked assets by selling the future yield component (YT) while retaining ownership of the principal (PT).
- Automated Market Maker (AMM): Pendle's custom AMM is designed for time-decaying assets like Yield Tokens, offering optimized pricing and minimal slippage. Users can trade PT and YT, providing liquidity and earning fees while benefiting from Pendle's dynamic fee structure.
- Risk Management Tools: Pendle brings risk management to DeFi by enabling users to hedge against interest rate volatility. Users can sell their YT to lock in fixed returns or buy YT to speculate on future yield movements, offering greater control over their investments.
What is Pendle Finance?
In traditional finance, instruments like zero coupon bonds and interest rate swaps allow investors to manage interest rate exposure and trade future cash flows separately from the principal amount.
Let’s use a US Treasury Zero-Coupon Bond as a specific example.
 US Treasury Zero-Coupon Bond | Image via Wikipedia
US Treasury Zero-Coupon Bond | Image via WikipediaA US Treasury Zero-Coupon Bond is issued at a discount, meaning the buyer pays less than the bond’s face value. Suppose an investor buys a 10-year US Treasury Zero-Coupon Bond for $800, with a face value of $1,000. The bond does not pay periodic interest (coupons), but at maturity—10 years later—the bondholder receives the full $1,000.
The key idea is that the bond's interest (yield) is embedded in the difference between the purchase price ($800) and the face value ($1,000). In traditional finance, this separation allows investors to either hold the bond until maturity or sell it before maturity based on their interest rate or liquidity needs.
How Pendle Finance Parallels this Concept:
The DeFi landscape has historically lacked such sophisticated tools. Yield-bearing assets in DeFi—such as tokens representing stakes in lending protocols or liquidity pools—typically lock users into variable yields with limited flexibility. Pendle addresses this gap by introducing fixed-income concepts to DeFi, enabling users to take control over their yield exposure.
Pendle tokenizes yield-bearing DeFi assets in a similar way. For example, imagine you are holding an asset in a DeFi lending protocol that generates a variable yield. Pendle lets you tokenize this asset into two components:
- Ownership of the principal (similar to the bond's face value). The Principal Token (PT).
- Future yield or interest (similar to the difference between a zero-coupon bond's discounted price and face value).
 Pendle Yield Tokenization | Image via Pendle
Pendle Yield Tokenization | Image via PendleNow, just like an investor can sell their zero-coupon bond before maturity, you can sell your future yield on Pendle, locking in a fixed return. Meanwhile, another user may buy this future yield, betting that yields will rise, thus gaining more than they paid—just as someone might buy a zero-coupon bond in anticipation of future gains.
This structure provides yield control and flexibility, which DeFi users previously lacked. It is similar to how zero-coupon bonds give traditional investors control over future cash flows.
The Problems Pendle Solves
Pendle finance is an example of the extensive composability possible with smart contracts. Traditional financial instruments are matured. They allow investors to control their investments and expected returns granularly, and DeFi is building towards that control. Here are some limitations of DeFi that Pendle solves:
Lack of Yield Flexibility
In traditional finance, investors can access sophisticated tools such as fixed-rate bonds or swaps to manage their interest-rate exposure. However, in decentralized finance (DeFi), most platforms offer variable yields, which fluctuate based on market conditions, creating several issues:
Fixed vs. Variable Yields:
Variable Yields: Most DeFi lending platforms, like Aave or Compound, offer variable interest rates, which change based on supply and demand for the underlying assets. This exposes users to interest rate volatility—one day, they could earn 10%, but the next, it might drop to 2%.
Example: Imagine you're staking in a lending protocol that initially offers a 10% annual yield. As more people enter the market, the yield drops to 5%. If you relied on that 10% yield for future returns, you're now stuck with lower earnings. When market conditions are favorable, you cannot lock in that original 10% yield.
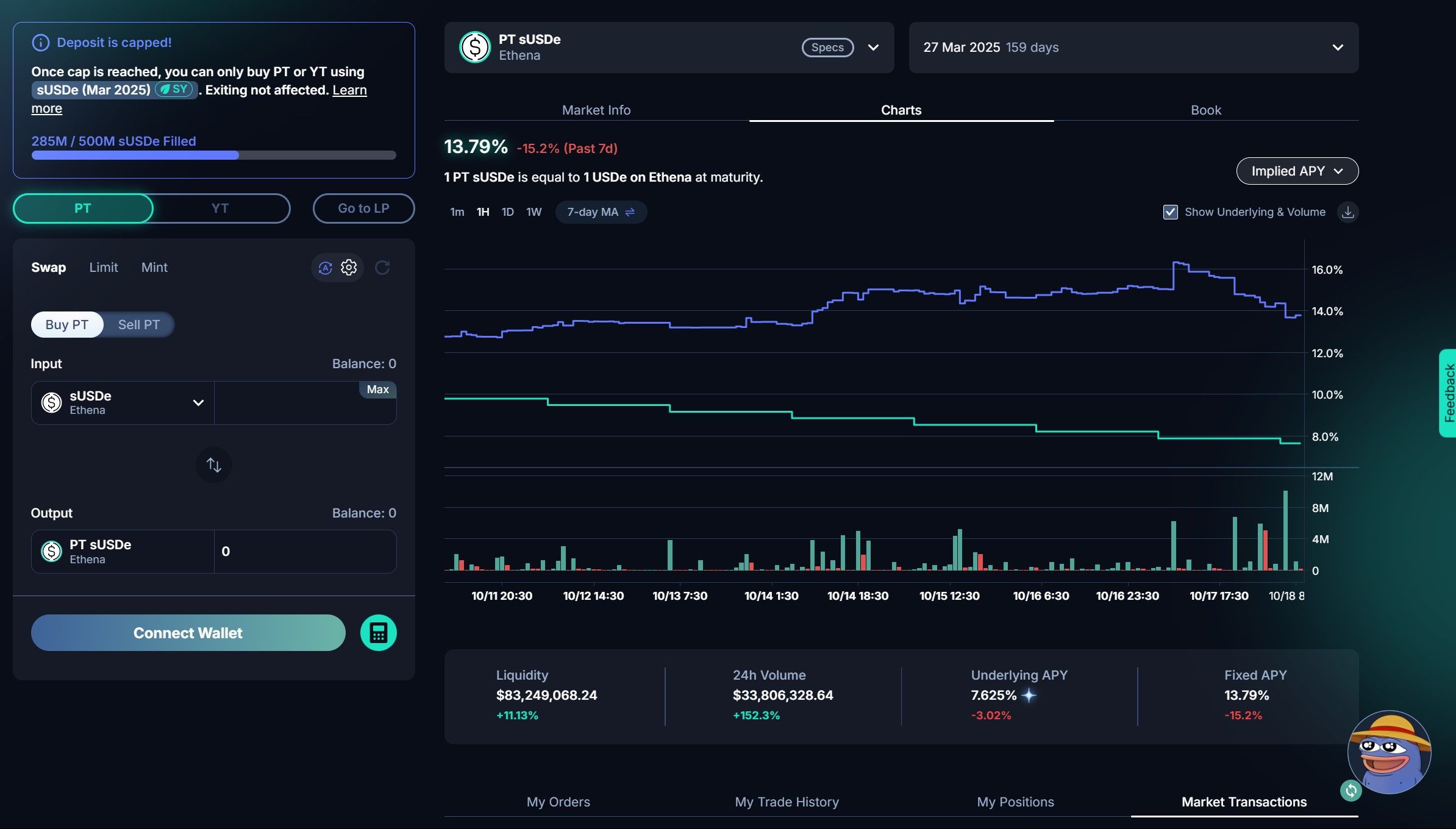 Pendle Displaying Variable Yield in USDe token | Image via Pendle DApp
Pendle Displaying Variable Yield in USDe token | Image via Pendle DAppFixed Yields with Pendle: Pendle allows users to lock in a fixed yield on their assets by separating the yield from the principal, effectively enabling them to hedge against this interest rate volatility. Users can sell their future yield to lock in their current rates, ensuring stable returns regardless of future market changes.
Inefficient Capital Utilization
In DeFi, yield-bearing assets such as tokens staked in lending protocols or liquidity pools are often locked within those protocols, reducing liquidity and the ability to use that capital elsewhere. If you lock your tokens in a liquidity pool, those tokens are unavailable to you for other investment opportunities. While you wait to collect yield, you may miss out on better opportunities elsewhere in the market.
Unlocking Liquidity with Pendle
Pendle solves this issue by allowing users to tokenize their yield-bearing assets, which can be traded on secondary markets. This means you can unlock liquidity from your locked assets by selling the future yield, freeing up capital for other investments.
Opportunity Cost: Because assets are often locked in protocols, users face opportunity costs—missing out on potentially better investments elsewhere. Pendle mitigates this by creating a market for yield, allowing users to gain liquidity without sacrificing their initial investment.
Limited Risk Management Tools
Traditional finance offers a range of tools to manage risk, such as interest rate swaps, options, and futures contracts. In DeFi, the lack of instruments to manage interest rate risk has been a significant limitation, forcing users to bear all the risk of volatile returns.
Interest Rate Risk
In traditional finance, instruments like interest rate swaps allow investors to hedge against future changes in interest rates. DeFi users face uncertainty in their investment returns without such tools, as yield rates fluctuate due to market conditions. In a DeFi protocol, if yield rates drop dramatically after you’ve committed your assets, you may face a sharp reduction in returns. Without tools to hedge against this, users are fully exposed to interest rate risk.
Mitigating Risk with Pendle
By separating yield from principal and creating a market for future yield trading, Pendle introduces risk management into DeFi. Users can lock in fixed yields and protect themselves from future fluctuations in interest rates, bringing much-needed stability to yield-bearing assets.
Speculative Limitations: Before Pendle, it was difficult for DeFi traders to speculate on yield movements. Pendle enables users to take long or short positions on future yield, adding a speculative component that didn’t previously exist in DeFi.
By addressing these three main problems—lack of yield flexibility, inefficient capital utilization, and limited risk management tools—Pendle brings a much-needed layer of financial sophistication to DeFi, enabling users to manage their yield exposure, unlock liquidity, and hedge against interest rate volatility.
Core Mechanism of Pendle Finance
Pendle’s core innovation lies in its ability to tokenize yield-bearing assets into two distinct, tradable tokens:
- Principal Token (PT): Represents the ownership of the principal amount of the underlying yield-generating asset. Key features:
- Non-Yield Bearing: Does not accrue any future yield.
- Maturity Date: Has a specified maturity date when it can be redeemed for the underlying asset.
- Yield Token (YT): Represents the right to receive the future yield generated by the underlying asset until maturity.
- Time-Decaying Asset: Its value diminishes as it approaches maturity since less future yield remains.
- Tradable: Can be bought or sold independently of the principal.
As of October 2024, Pendle is live on Ethereum, Optimism, Arbitrum and BNB Chain.
How Pendle Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Deposit Yield-Bearing Asset
Users start by depositing a yield-generating asset into the Pendle protocol. Supported assets might include:
- Liquidity Provider (LP) Tokens: From platforms like Uniswap or SushiSwap.
- Lending Protocol Tokens: Such as cTokens from Compound or aTokens from Aave.
- Staked Assets: Like stETH (staked Ether) from Lido.
Step 2: Tokenization into PT and YT
Upon deposit:
- Minting PT and YT: The protocol mints an equal amount of PT and YT tokens corresponding to the deposited asset.
- Maturity Date Assignment: Both tokens are assigned a specific maturity date.
Step 3: Trading and Liquidity Provision
Users have several options:
- Trading PT and YT: Users can trade these tokens on Pendle's specialized automated market maker (AMM) or other supported exchanges.
- Providing Liquidity: Users can provide PT and YT to liquidity pools to earn fees and incentives.
Step 4: Redemption at Maturity
At the maturity date:
- PT Redemption: Holders of PT can redeem them for the underlying principal asset.
- YT Expiry: YT tokens expire as all future yield has been realized.
Pendle's Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Pendle utilizes a custom AMM designed specifically for assets with time-decaying value, like YT tokens.
Key Features
- Time-Decaying Pricing Model: Adjusts asset pricing based on the decreasing time to maturity.
- Dynamic Fee Structure: Fees can be adjusted to incentivize liquidity provision during different market conditions.
- Dual Asset Support: Facilitates trading between PT, YT, and the underlying assets.
Benefits
- Efficient Trading: Optimizes for minimal slippage and efficient price discovery.
- Liquidity Incentives: Encourages users to supply liquidity through rewards and fee-sharing mechanisms.
Pendle Use Cases
Fixed Yield for Investors
- Objective: Secure a fixed yield by locking in current rates.
- Mechanism:
- Sell YT: Users deposit a yield-bearing asset, receive PT and YT, and sell the YT.
- Result: The sale of YT provides an upfront payment equivalent to the future yield, effectively fixing the yield rate.
Yield Speculation for Traders
- Objective: Profit from anticipated changes in future yield rates.
- Mechanism:
- Buy YT: Traders purchase YT if they expect yield rates to increase.
- Sell YT: Conversely, they can short YT if they anticipate a decrease in yields.
Yield Hedging for Risk Management
- Objective: Mitigate exposure to yield volatility.
- Mechanism:
- Sell YT: Users can sell YT to hedge against potential declines in future yields.
- Maintain OT: Retain ownership of the principal without yield exposure.
Enhanced Liquidity Provision
- Objective: Earn additional income through liquidity provision.
- Mechanism:
- Provide PT and YT to AMM Pools: Earn trading fees and potentially PENDLE token rewards.
- Benefit: Increased capital efficiency and income diversification.
 Here are ways you can use Pendle for yield optimization | Image via Pendle
Here are ways you can use Pendle for yield optimization | Image via PendlePendle AMM
The Pendle AMM provides liquidity pools that allow users to trade these PT and YT tokens in a decentralized manner. This is essential because it creates a marketplace where users can easily buy or sell their future yield or principal holdings based on their strategy.
Benefits of Trading PT and YT on Pendle AMM:
- Yield Flexibility: Users can sell their future yield (YT) for immediate returns or buy YT to speculate on higher future yields.
- Capital Efficiency: Traders can unlock liquidity by selling YT, freeing up capital that would otherwise be locked in yield-bearing assets.
- Risk Management: The ability to trade PT and YT allows users to hedge against potential yield fluctuations by locking in fixed returns.
- Speculation Opportunities: Traders can take long or short positions on future yield rates, enabling them to speculate on market trends.
Having a platform like Pendle AMM enables users to seamlessly interact with these tokenized yield components, providing more flexibility, liquidity, and control over yield-bearing assets in DeFi.
The PENDLE Token
The PENDLE token is the backbone of the Pendle Finance protocol, providing utility and governance functions within the ecosystem. As a yield-trading platform, Pendle allows users to split yield-bearing assets into principal and yield tokens, and the PENDLE token enables users to interact with this system meaningfully.
Tokenomics of PENDLE
- Supply Emissions: As of September 2024, PENDLE emissions stand at 216,076 tokens per week, with a scheduled 1.1% reduction in emissions each week until April 2026. After this point, the protocol will implement a terminal inflation rate of 2% per annum to maintain incentives within the system.
- Vesting: By September 2024, all team and investor tokens have fully vested, meaning that future supply increases will primarily come from incentives and ecosystem-building efforts.
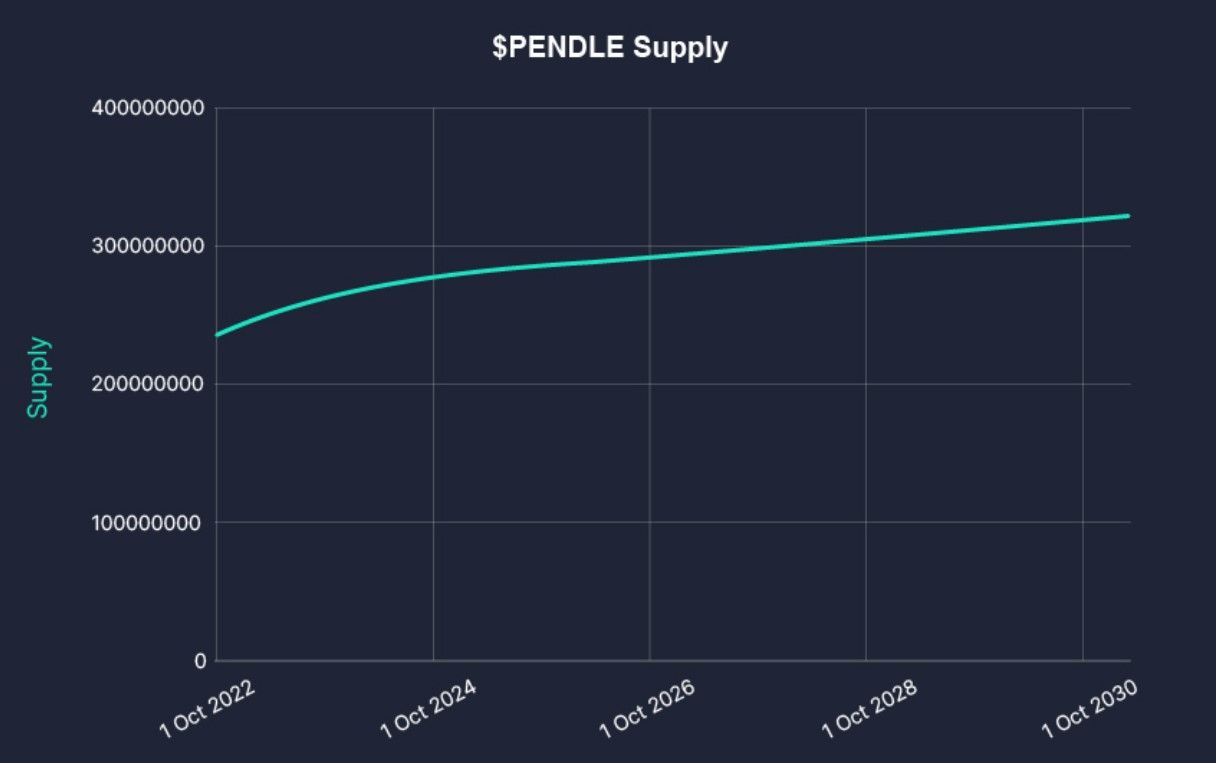 PENDLE Supply Schedule | Chart via Pendle Docs
PENDLE Supply Schedule | Chart via Pendle DocsvePENDLE (Vote-Escrowed PENDLE)
The vePENDLE system is inspired by the "vote-escrow" model (similar to Curve's veCRV). Users can lock their PENDLE tokens to receive vePENDLE, which decays over time. Holding vePENDLE gives several benefits:
- Governance Voting: vePENDLE holders participate in the governance of the protocol by voting on key decisions such as the distribution of PENDLE incentives to specific liquidity pools.
- Revenue Share: vePENDLE holders receive 80% of the swap fees collected from the pools they vote for. Additionally, a portion of the yield from unredeemed principal tokens (PTs) is distributed to vePENDLE holders.
- Boosting Liquidity Rewards: vePENDLE holders can boost their liquidity provider (LP) rewards by up to 250%, depending on the amount of vePENDLE they hold relative to their share of the liquidity pool.
- Incentive Channelling: By locking PENDLE, users can direct incentives to certain liquidity pools, increasing the liquidity and trading activity in the pools they support.
The vePENDLE system introduces a dual-purpose mechanism that aligns both governance participation and reward maximization, creating a virtuous cycle for long-term ecosystem engagement. By locking PENDLE tokens, users reduce the circulating supply, thus contributing to the token's stability while enjoying various benefits tied to their governance and staking activities.
Where to Buy PENDLE?
You can buy PENDLE on:
Pendle Finance Risks and Mitigation Strategies
1. Smart Contract Risks
- Risk: Potential vulnerabilities could lead to loss of funds.
- Mitigation:
- Audits: Pendle provides regular audits from multiple auditing firms to ensure protocol robustness.
- Formal Verification: Ensures contract logic is sound.
2. Market Risks
- Risk: Volatility in underlying asset prices and yield rates.
- Mitigation:
- Diversification: Users should diversify holdings.
- Stay Informed: Yield from Pendle’s products is depends greatly on the yield of underlying assets, staying informed about them is essential.
3. Liquidity Risks
- Risk: Low liquidity can result in high slippage or inability to exit positions.
- Mitigation:
- Incentives: Pendle provides rewards to encourage liquidity provision.
- Education: Inform users about liquidity pool participation.
4. Regulatory Risks
- Risk: Changes in legal frameworks could affect operations.
- Mitigation: Decentralized governance to reduce centralized points of failure.
Pendle Finance Review: Closing Thoughts
Pendle Finance represents a significant advancement in the DeFi landscape by enabling future yield trading. Its innovative approach to yield tokenization allows users to unlock liquidity, manage risk, and engage in new speculative opportunities. By addressing key limitations in yield management and introducing flexible, user-centric solutions, Pendle is well-positioned to contribute to the ongoing evolution of decentralized finance.
As the DeFi ecosystem continues to mature, protocols like Pendle will play a crucial role in providing sophisticated financial instruments that mirror traditional finance while leveraging the transparency, accessibility, and composability of blockchain technology.