Blockchain modularity has been the most significant development in the Web3 ecosystem in recent years. This shift has made blockchain solutions more flexible and specialized, enabling projects to choose configurations tailored to their unique needs rather than conforming to a one-size-fits-all model.
For instance, a project that prioritizes security might deploy directly on Ethereum, benefiting from its robust security model. Meanwhile, those requiring greater throughput can leverage various Layer 2 networks, which scale Ethereum by introducing a modular execution layer. Projects seeking even higher throughput might opt for a modular execution and data availability layer, as seen with solutions like Polygon zkEVM Validium. Additionally, the restaking model introduced by platforms like EigenLayer allows projects to access Ethereum-linked data availability at a lower cost while maintaining a significant level of security.
This approach fundamentally gives developers and projects the freedom to prioritize specific aspects of the blockchain stack—security, scalability, or cost efficiency—and pay accordingly. This modularity is crucial in a rapidly evolving landscape where applications have vastly different requirements.
The SKALE Network, the focus of this review, is an intriguing addition to this ecosystem. At first glance, SKALE may seem like another Ethereum scalability solution. However, it distinguishes itself with a unique mechanism that borrows Ethereum’s security guarantees while offering its distinct properties. Understanding these properties is crucial in grasping the value SKALE brings to the Ethereum ecosystem, and this review will break down those concepts in detail.
SKALE's modular architecture allows the creation of numerous independent blockchains, each customized to meet the needs of specific applications, whether in gaming, AI, DeFi, or beyond. This flexibility, combined with features like zero gas fees and full EVM compatibility, positions SKALE as a powerful tool for developers looking to build scalable, user-friendly blockchain applications.
This SKALE Network review will explore how its approach enhances scalability and contributes to a more seamless and efficient Web3 experience, laying the foundation for the next generation of decentralized applications.
What is the SKALE Network?
SKALE Network is an Ethereum-compatible multichain network supporting high-throughput, low latency, byzantine fault-tolerant application-specific sidechains.
 SKALE Homepage | Image via SKALE Network
SKALE Homepage | Image via SKALE NetworkTo grasp what this entails, let's break down these components:
Ethereum-compatible
- Seamless DApp Integration: All decentralized applications (DApps) developed for Ethereum can run on the SKALE Network without modifications.
- Developer-Friendly Tools: Developers can utilize Ethereum clients, tools, and libraries like Geth to build SKALE-native DApps, leveraging their existing knowledge and resources.
- Support for Solidity: SKALE supports Solidity, Ethereum's primary programming language for smart contracts.
Multichain Network
- Network of Multiple Chains: SKALE operates as a network comprising multiple chains rather than a single chain. Each application can run on its own dedicated chain within the network.
- Scalability and Customization: This architecture allows for greater scalability and enables applications to customize their sidechains according to specific needs.
High Throughput, Low Latency, Zero-Gas, Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant:
- High Throughput: SKALE can support between 400 to 700 transactions per second (TPS), according to its documentation. Each SKALE block has a gas limit of 280 million, compared to Ethereum's 30 million, allowing for more transactions per block.
- Low Latency: The network efficiently propagates block information across nodes, facilitating fast consensus and improving overall performance.
- Zero-Gas Transactions: SKALE operates on a subscription model where gas fees are prepaid by chain operators, resulting in zero gas costs for users when transacting on SKALE sidechains.
- Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant: SKALE maintains network security as long as more than two-thirds of validators are honest and active. Its asynchronous nature allows nodes to create and verify blocks simultaneously, enhancing efficiency.
Application-Specific Sidechains
- Dedicated Chains for Each Application: Each application on SKALE can run on its own sidechain, tailored to its specific requirements.
- Independent Consensus Mechanism: These sidechains do not rely on Ethereum's consensus. Instead, they utilize their own PoS network powered by the SKL token.
Actively Validated Services (AVS)
- Subscription-Based Validation: SKALE sidechains subscribe to the SKALE consensus layer by paying in SKL tokens, eliminating the need to bootstrap their own validator network.
- Validator Support: In return, SKALE validators run the sidechain execution in containerized environments and provide data availability and settlement through the SKL PoS consensus.
Expanded Description of the SKALE Network
The SKALE Network is an innovative Ethereum ecosystem solution designed to address scalability issues while maintaining compatibility. SKALE ensures that developers can seamlessly port their existing Ethereum DApps or build new ones using familiar tools. This compatibility lowers the barrier to entry and accelerates the development process.
 SKALE is a multichain network | Image via SKALE Blog
SKALE is a multichain network | Image via SKALE BlogThe application-specific sidechain design enhances scalability, prevents congestion, and allows for chain parameter customization to meet different applications' unique needs. By isolating applications on separate chains, SKALE ensures that high traffic on one chain doesn't adversely affect others.
 SKALE Gas Paid History | Image via SKALE Block Explorer
SKALE Gas Paid History | Image via SKALE Block ExplorerOne of the most user-friendly features of SKALE is its zero-gas transactions. By adopting a subscription model where chain operators prepay gas fees, SKALE eliminates transaction costs for end-users. This approach enhances the user experience and encourages more frequent micro-transactions, which are often discouraged on networks with high gas fees.
The asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant nature of SKALE's consensus mechanism ensures robust security and efficiency. Unlike synchronous systems where nodes must wait for each other, SKALE's asynchronous design allows nodes to process transactions and create blocks independently, provided that more than two-thirds of validators are honest and active. This improves network resilience and performance.
 SKALE is a Network of Sidechains | Image via SKALE Blog
SKALE is a Network of Sidechains | Image via SKALE BlogSKALE's use of application-specific sidechains means that each DApp can benefit from a blockchain environment tailored to its specific needs without the overhead of maintaining its own network infrastructure. These sidechains are secured by SKALE's PoS network, utilizing the SKL token, which streamlines operations and enhances security.
 SKALE Early Validators | Image via SKALE Blog
SKALE Early Validators | Image via SKALE BlogThrough Actively Validated Services (AVS), SKALE simplifies the validation and security process for sidechains. Instead of requiring each application to establish its own validator network, SKALE allows it to tap into its existing pool of validators by subscribing with SKL tokens. Validators then handle the execution environment, data availability, and settlement processes, enabling developers to focus on building their applications rather than managing network security.
The SKALE Network provides a highly scalable, efficient, and developer-friendly environment for building and running Ethereum-compatible DApps. By combining high throughput, low latency, zero-gas transactions, and robust security features within a multichain architecture, SKALE addresses many of the limitations faced by traditional blockchain networks. Its innovative approach allows projects to prioritize the features they need and pay for those specifically, moving away from a one-size-fits-all model and fostering a more flexible and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
SKALE Network Architecture
Examining its underlying architecture and unique components is essential to understand the SKALE Network's capabilities comprehensively.
The SKALE Network is designed with a modular framework that includes several key elements: the SKALE Manager, SKALE Chains, Validators, the Interchain Messaging Agent (IMA), Oracles, Hybrid Security mechanisms, Threshold Signature Schemes (TSS), and the SKL Token with its associated tokenomics.
 SKALE Architecture | Image via Messari
SKALE Architecture | Image via MessariEach component is vital in enabling the network's high throughput, low latency, zero-gas transactions, and robust security features.
SKALE Manager
At the core of the SKALE Network's architecture lies the SKALE Manager, a comprehensive set of over 35 smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum mainnet. The SKALE Manager is the primary entry point into the SKALE Network for both validators and developers, facilitating essential network operations and interactions.
For validators, the SKALE Manager handles the staking process. Validators stake SKL tokens through the SKALE Manager contracts to participate in the network's consensus mechanism. By staking, validators commit to securing the network and, in return, earn rewards for their services.
For developers, the SKALE Manager enables the creation of new SKALE Chains. Developers can pay a subscription fee, denominated in SKL tokens, to deploy their own application-specific sidechains within the SKALE Network. This subscription model allows developers to access the network's resources and benefits—such as high throughput, low latency, and zero-gas transactions—without the need to build and maintain their own infrastructure.
Beyond staking and chain creation, the SKALE Manager is responsible for several other critical functions:
- Node Selection and Rotation: The SKALE Manager orchestrates assigning validator nodes to SKALE Chains. It selects nodes from the validator pool and rotates them periodically to ensure fairness, security, and decentralization across the network.
- Token Bridging: It facilitates cross-chain token and smart contract interoperability with Ethereum and other SKALE Chains using the Interchain Messaging Agent (IMA) bridge.
- Governance and Slashing: The SKALE Manager includes mechanisms for network governance. While slashing (the penalization of validators for malicious behavior) is pending a future governance vote, the framework for such actions is integrated within the SKALE Manager contracts.
- Network Operations: As the operational backbone, the SKALE Manager oversees various network processes, including node monitoring and performance tracking, to maintain the overall health and efficiency of the SKALE Network.
By consolidating these functions into a robust set of smart contracts, the SKALE Manager simplifies interaction with the network. It abstracts the complexity of network operations, allowing validators and developers to engage with the SKALE Network through familiar Ethereum-based tools and interfaces.
SKALE Chains
SKALE Chains are a fundamental component of the SKALE Network's architecture, serving as EVM-compatible, application-specific sidechains connected to the Ethereum network. They are designed to provide developers with scalable and customizable blockchain environments while maintaining interoperability with Ethereum. Here's a closer look at how SKALE Chains function and their key features:
Application-Specific Sidechains
- EVM Compatibility: SKALE Chains are fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to deploy smart contracts written in Solidity without modifications. This ensures seamless integration with existing Ethereum tools and DApps.
- Customization: Each SKALE Chain is dedicated to a specific application or set of applications, enabling developers to tailor the chain's parameters—such as consensus protocols, virtual machine configurations, and security features—to meet their unique requirements.
Validator Support and Rotation
- Randomly Selected Validators: Each SKALE Chain is supported by a randomly selected group of validator nodes from the SKALE Network. This randomness enhances security by preventing collusion among validators.
- Node Rotation: Validator nodes assigned to a SKALE Chain are periodically swapped out. This rotation mechanism, managed by the SKALE Manager contracts on Ethereum, ensures fairness and further strengthens security by distributing validation responsibilities across the network.
Subscription Model and Zero-Gas Transactions
- Subscription-Based Access: SKALE Chains operate on a subscription model. Developers or chain operators pay a subscription fee in SKL tokens to connect their chain to the SKALE Network. This fee grants them access to the network's validator resources, leveraging their computing power and staked tokens for security, data availability (DA), and transaction finality.
- Zero-Cost Transactions for Users: One of the standout features of SKALE Chains is that transactions are zero-cost for end-users. Validators are compensated for processing transactions from the subscription fees collected, eliminating the need for users to pay gas fees when interacting with DApps on SKALE Chains.
- Chain Maintenance: The chain remains active within the network as long as the subscription fee is maintained. Anyone can top up the chain with additional SKL tokens to continue operations if the fee runs out.
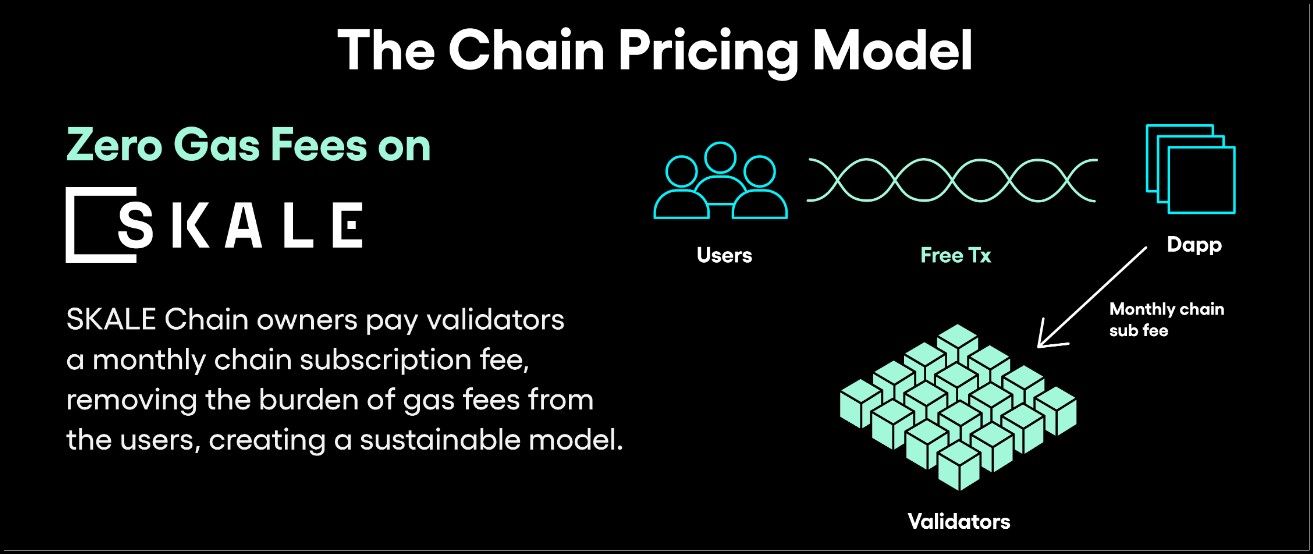 SKALE Chain Users Don’t Pay Gas | Image via SKALE Blog
SKALE Chain Users Don’t Pay Gas | Image via SKALE BlogNetwork Growth and Interoperability
- Active Chains: SKALE Network hosts multiple active SKALE Chains, each supporting different applications and use cases. There are 20 active chains in the network, which is expected to grow as more developers adopt the network for its scalability and efficiency.
- Interchain Communication: SKALE Chains can share token information and messages, including smart contract calls, with one another and with Ethereum via the Interchain Messaging Agent (IMA) bridge. This interoperability facilitates seamless interactions between different chains and the Ethereum mainnet.
sFUEL Tokens and Network Security
- Combating DDoS and Misuse: To prevent Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks and reckless use of zero-gas transactions, SKALE introduced sFUEL tokens. These tokens act as a form of gas on SKALE Chains but have no market value.
- Acquisition of sFUEL: Users can obtain sFUEL tokens from faucets and community channels like Discord. By requiring sFUEL to execute transactions, SKALE discourages spamming and ensures that only legitimate transactions consume network resources.
SKALE Chain Fee Model
The SKALE Network employs a dynamic fee model for SKALE Chains to align costs with resource usage and network demand. The pricing strategy targets an annual equivalent of $1 million in SKL tokens per chain at 70% network utilization, operating on a sliding scale based on network load.
Pricing Tiers
- Initial Cost: At 8% of the target rate, chains cost approximately $3,600 monthly. This lower entry point encourages new developers to adopt the network.
- Target Rate: At 50% network utilization, the cost rises to around $46,000 monthly. This reflects increased resource consumption as the network handles more transactions and applications.
- 70% Utilization: When the network reaches 70% utilization, chains cost about $84,000 per month. This pricing aligns with the target annual fee and accounts for the high demand for network resources.
Objectives of the Pricing Structure
The SKALE Chain fee model is thoughtfully designed to achieve several key objectives:
- Incentivize Validator Participation: By increasing fees as network demand grows, validators are incentivized to add more nodes to the network, enhancing its capacity and performance.
- Maintain Competitive Pricing: The sliding scale ensures chain costs remain competitive, making the SKALE Network an attractive option for developers compared to other scalability solutions.
- Support Profitable Validator Operations: The fee structure ensures validators can run profitable operations, encouraging them to continue contributing resources and securing the network.
- Adapt to Network Growth: As the network expands, the pricing model adapts to increased demand, ensuring sustainability and scalability over time.
- Align Costs with Resource Usage: By correlating fees with network utilization, costs are aligned with actual resource consumption, promoting efficient use of network resources.
In summary, SKALE Chains offer a scalable, efficient, and user-friendly environment for deploying decentralized applications. Their integration into the SKALE Network through a subscription model provides developers with dedicated resources and robust security features, all while maintaining interoperability with Ethereum. The innovative fee model and mechanisms like sFUEL tokens ensure that the network remains secure, efficient, and accessible as it grows and evolves.
SKALE Hubs
Within the SKALE Network, SKALE Hubs are community-operated SKALE Chains that function as specialized Web3 service layers, each dedicated to specific use cases. These hubs provide optimized environments for different sectors of the blockchain ecosystem, such as DeFi, NFTs, gaming, and AI. By segmenting services into dedicated hubs, SKALE enhances scalability, performance, and user experience for applications within these domains.
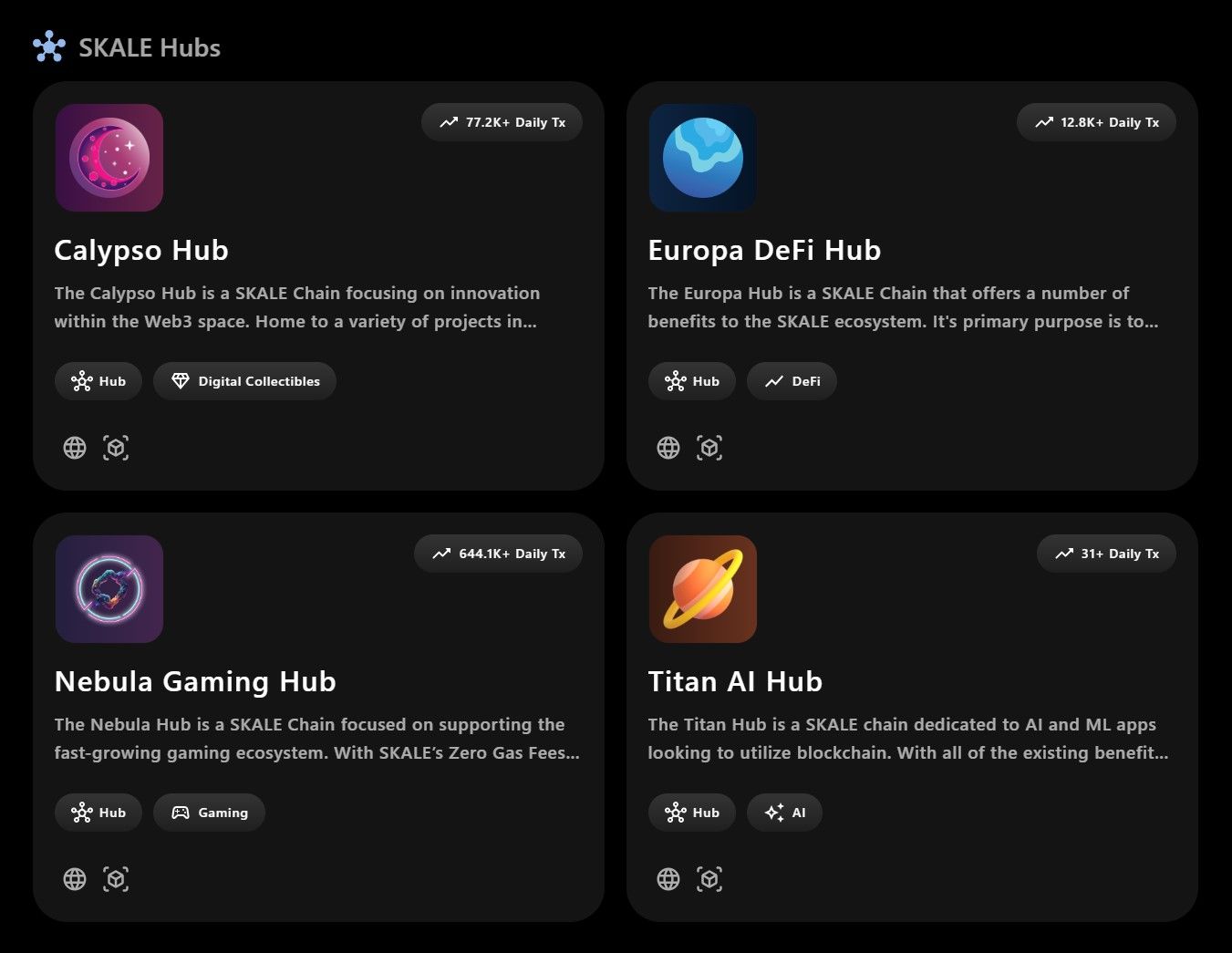 SKALE Hubs | Image via SKALE
SKALE Hubs | Image via SKALEThe four main SKALE Hubs are:
Europa - DeFi Hub
Europa is explicitly tailored for DeFi applications. It provides a high-performance environment for decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, stablecoins, and other financial instruments. By leveraging SKALE's high throughput and low latency, Europa enables fast transaction processing and seamless user interactions without the burden of high gas fees. This hub allows DeFi projects to operate efficiently, offering users a smooth and cost-effective experience.
Calypso - NFTs and Marketplaces Hub
Calypso is designed for NFT platforms and marketplaces, offering an optimized chain for minting, trading, and managing digital assets. This hub addresses the unique needs of NFT projects, such as handling high transaction volumes during drops and ensuring smooth interactions for buyers and sellers. By utilizing SKALE's zero-gas transactions and scalability, Calypso makes it economically feasible for users to engage with NFT platforms, fostering a vibrant digital art and collectibles ecosystem.
Nebula - Web3 Gaming Hub
Nebula serves as the hub for blockchain-based gaming applications. It provides a robust and scalable infrastructure to support complex game logic, real-time interactions, and asset ownership. Developers can build games that leverage blockchain features like true asset ownership, in-game economies, and interoperability while benefiting from SKALE's performance optimizations. Nebula enables gamers to experience seamless gameplay with the added benefits of blockchain technology.
Titan - AI Hub
Titan is dedicated to applications involving AI and machine learning within the blockchain context. This hub offers specialized resources to support AI computations, data processing, and integration with decentralized networks. Titan enables developers to build AI-powered decentralized applications (DApps) that leverage SKALE's capabilities for efficient and scalable operations by providing a tailored environment. This opens up possibilities for innovative solutions that combine AI with blockchain's transparency and security.
SKALE Validators
Validators are the backbone of the SKALE Network, responsible for securing the network, processing transactions, and maintaining consensus. Here's an in-depth look at how SKALE Validators function and their integral role within the network architecture:
Validator Participation and Network Composition
- Validator Organizations and Nodes: The SKALE Network comprises approximately 45 node service organizations that collectively provide over 150 individual nodes. These organizations contribute computational resources and expertise to support the network's decentralized infrastructure.
- Random Selection and Consensus Participation: From the pool of active nodes, 16 nodes are randomly selected to participate in the consensus process for each SKALE Chain. This random selection enhances security by minimizing the risk of collusion among validators and ensuring a fair distribution of validation duties.
Subnodes and Virtualization
- Subnode System: Each of the 16 selected nodes can be virtualized into 128 subnodes through a containerized architecture. This means that while multiple subnodes operate on the same physical hardware, they function as independent nodes within the network. This virtualization allows for efficient resource utilization and significant scalability.
- Individual Participation in Consensus: Each subnode participates separately in the consensus mechanism. By operating independently, subnodes contribute to increased network throughput and resilience, enabling parallel processing of transactions across the network.
Staking Requirements and Validator Commitment
- Staking SKL Tokens: Validators are required to stake 20 million SKL tokens to become a SKALE Validator. This substantial stake ensures validators have a significant financial commitment to the network's security and integrity.
- Security and Incentives: The staked tokens serve as collateral, incentivizing validators to act honestly and diligently. Validators earn rewards for their services but risk losing their stake if they engage in malicious activities or fail to meet performance standards, pending future governance decisions on slashing.
Flexible Resource Allocation for SKALE Chains
- Customized Resource Subscription: SKALE Chains can subscribe to resources dynamically based on their storage and throughput needs. They can choose between 1/128th of a node to a full node, allowing them to pay only for the required resources. This model promotes cost efficiency and scalability for developers.
- Node Core Management: The Node Core software assists validators in managing their subnodes. It handles tasks such as resource allocation, monitoring subnode performance, and facilitating communication with the SKALE Manager. This tool streamlines validator operations and ensures optimal performance of subnodes.
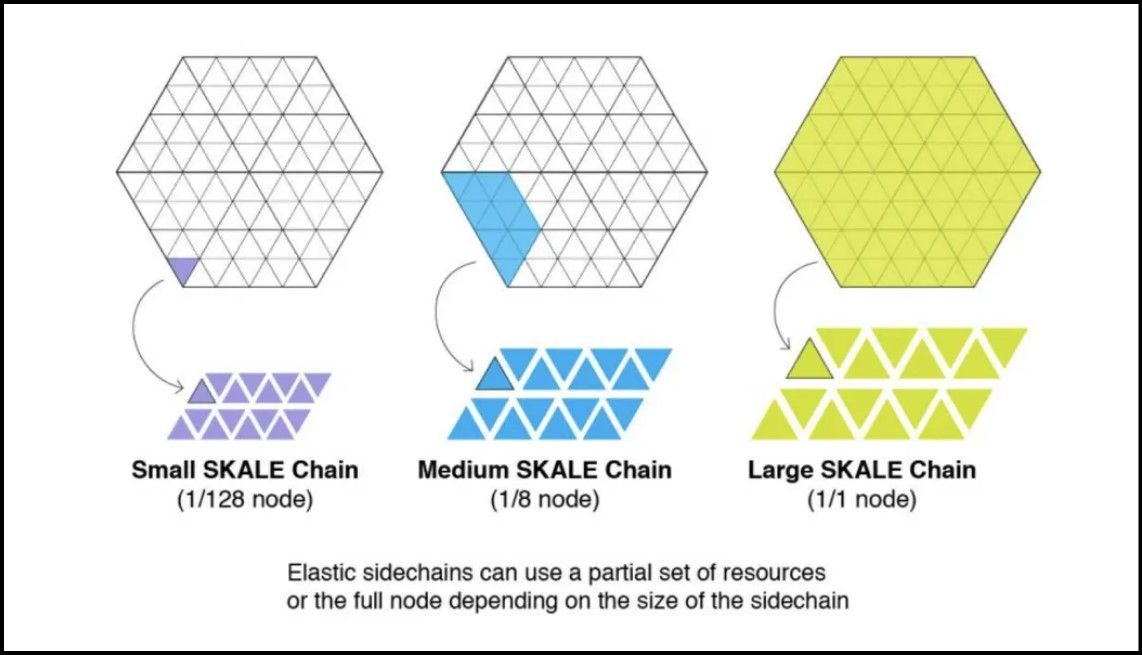 SKALE Nodes Can Containerize Into Subnodes | Image via SKALE Blog
SKALE Nodes Can Containerize Into Subnodes | Image via SKALE BlogConsensus Mechanism and Security
- Asynchronous Binary Byzantine Agreement (ABBA): SKALE employs an ABBA protocol for its consensus mechanism. This protocol enables the network to reach consensus efficiently, even in asynchronous environments where network delays or malicious actors may be present. ABBA enhances scalability by allowing nodes to process transactions and agree on their validity without synchronous communication.
- Role of the SKALE Manager: The SKALE Manager smart contracts on Ethereum are pivotal in validator management. They handle the staking process, node selection, and rotation, ensuring that validators are appropriately assigned to SKALE Chains and that the network remains decentralized and secure.
Validator Rotation and Network Integrity
- Periodic Rotation: Validators and their subnodes are periodically rotated among different SKALE Chains. This rotation reduces the likelihood of prolonged collusion or malicious behavior, as validators do not remain attached to a single chain indefinitely. It promotes fairness and distributes the validation workload evenly across the network.
- Node Monitoring: Validators must maintain high uptime and adhere to performance standards. The network employs monitoring systems to track validator activity and ensure compliance. While slashing for downtime or misconduct is pending a future governance vote, these measures encourage validators to act in the network's best interest.
Additional Considerations
- Scalability and Efficiency: The combination of virtualization into subnodes and the ABBA consensus protocol allows the SKALE Network to achieve high throughput and low latency. Validators contribute to this efficiency by providing the necessary computational resources and maintaining robust operations.
- Economic Alignment: By requiring a substantial stake and providing rewards for honest participation, the network aligns validators' economic incentives with its security and success. This alignment is crucial for maintaining trust and reliability within the decentralized ecosystem.
In summary, SKALE Validators are essential to the network's functionality and security. They provide the computational power and validation services that enable SKALE Chains to operate efficiently and securely. Through staking, participating in the consensus mechanism, and managing subnodes, validators support the network's scalability, decentralization, and interoperability goals with Ethereum. The coordination facilitated by the SKALE Manager ensures that validators are effectively managed, resources are optimally allocated, and the network maintains its integrity and performance as it continues to grow and evolve.
SKL Token
The SKALE Network's native token, SKL, is integral to the platform's functionality and economic model. It serves multiple purposes, including securing the network through validator staking, facilitating SKALE Chain subscription fees, and, in the future, enabling all SKL holders to participate in on-chain governance. The total supply of SKL tokens is fixed at 7 billion.
SKL Tokenomics
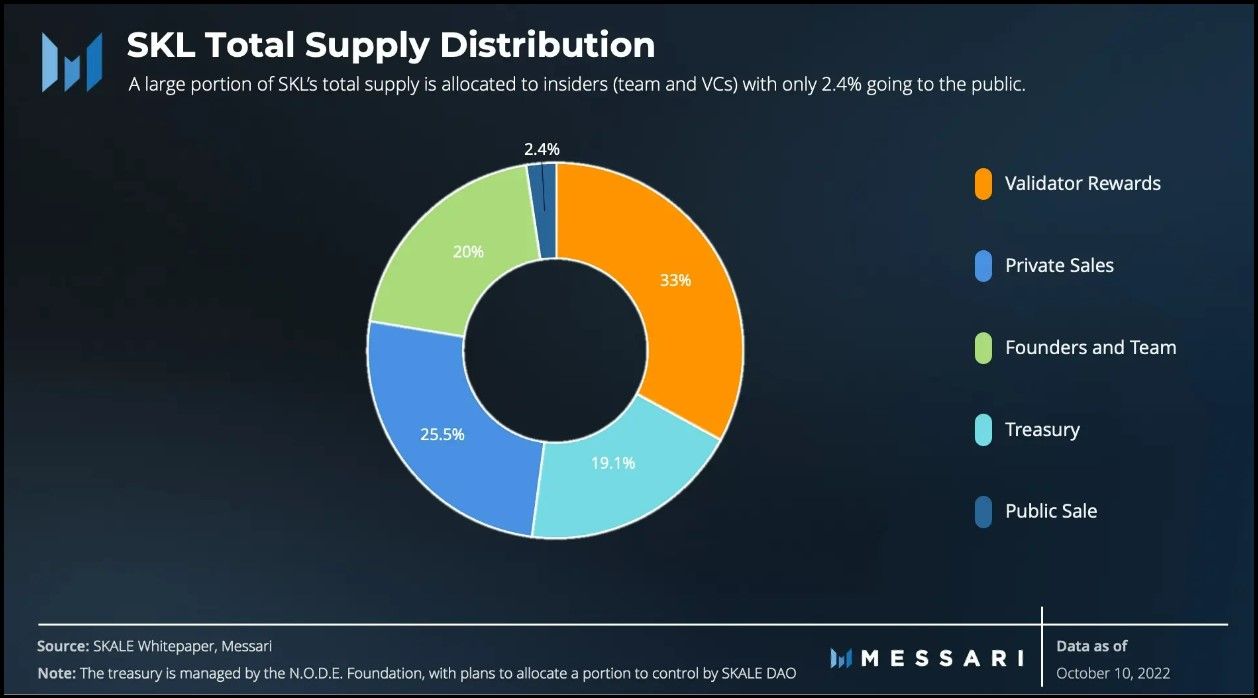 SKL Allocation | Image via Messari
SKL Allocation | Image via MessariThe allocation of SKL tokens is structured to support network security, incentivize participation, and fund ongoing development:
- Validator Rewards (33.3%): Approximately one-third of the total supply is allocated to validators as inflationary block rewards. This incentivizes validators to stake SKL tokens and actively participate in securing the network.
- Founders and Core Team (20%): A significant portion is allocated to the founders and core team. 10% of the total supply has already been distributed to them, with the remaining 10% set to unlock every three months over the next two years.
- Treasury Funds (18.9%): The treasury is allocated 18.9% of the total supply, divided among three funds managed by the NODE Foundation. These funds are intended for grants, network operations, and supporting the ecosystem's growth. So far, 11.9% has been distributed to the treasury, with the remaining 7% scheduled to be received over the next five years.
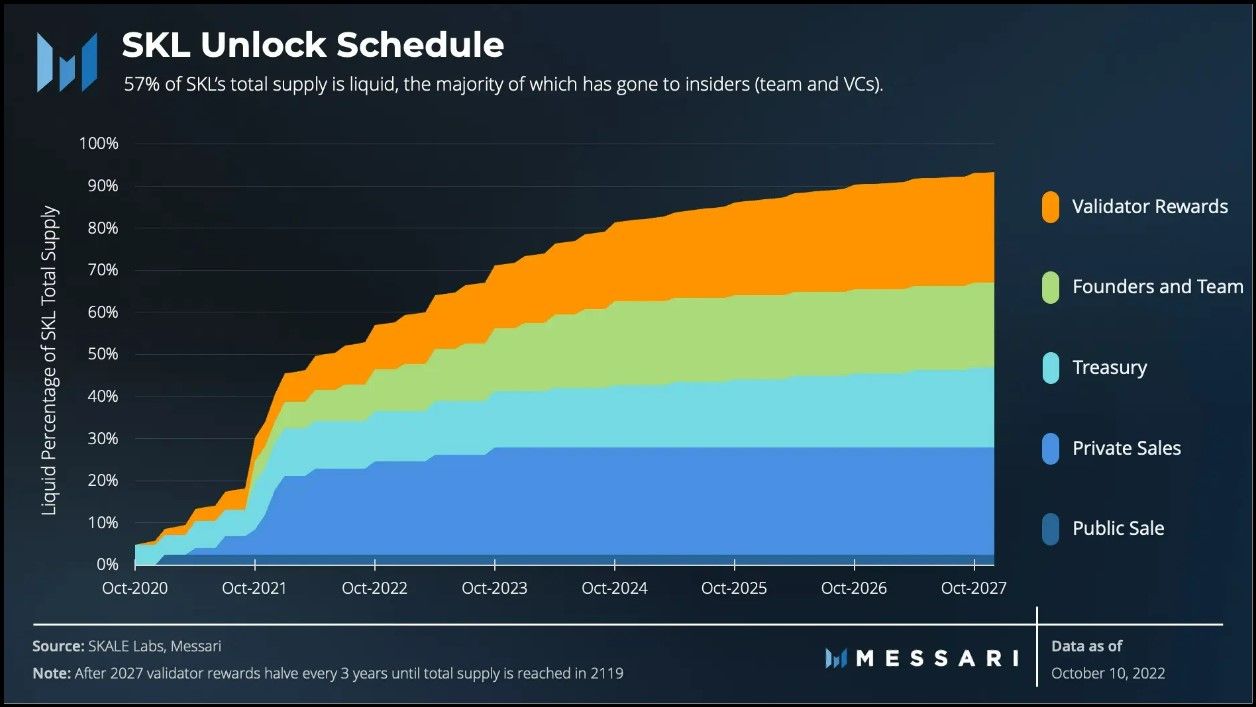 SKL Unlock Schedule | Image via Messari
SKL Unlock Schedule | Image via MessariEconomic Roles of SKL
- Security through Staking: Validators must stake SKL tokens to participate in the network's consensus mechanism. This staking secures the network and aligns validators' interests with its health and performance.
- Subscription Fees: Developers and chain operators use SKL tokens to pay subscription fees for deploying and maintaining SKALE Chains. This creates demand for SKL tokens and ensures efficient resource allocation within the network.
- Future Governance Participation: There are plans for SKL holders to engage in on-chain governance, allowing the community to influence the network's development and decision-making processes.
Treasury and the NODE Foundation
- Management of Funds: The treasury funds are managed by the NODE Foundation, which oversees three separate funds dedicated to grants, network operations, and ecosystem development.
- Transparency and Reporting: The Foundation is expected to release transparency reports on past token distributions every six months, starting in December. This commitment to transparency helps build trust within the community.
The tokenomics are strategically designed to incentivize validators, support developers, and encourage community participation while maintaining a balanced and transparent distribution of tokens over time. This approach aims to foster a sustainable and robust network that adapts and thrives as the blockchain landscape evolves.
Where to Buy SKL?
The SKL token can be bought on centralized exchanges, including:
Be sure to check out our article on the best crypto exchanges.
if you're looking to buy SKL via a decentralized exchange, your options are limited as there are only a few exchanges offering it, including Uniswap. While you're here, head over to our article on the best decentralized exchanges.
SKALE Ecosystem
The SKALE Network hosts a vibrant and expanding ecosystem of DApps and SKALE Chains, each leveraging the network's scalability, zero-gas transactions, and interoperability with Ethereum. Below are some of the top projects and SKALE Chains within the SKALE ecosystem:
Razor Network
 Razor Network is an Oracle | Image via Razor Network
Razor Network is an Oracle | Image via Razor NetworkRazor Network is a decentralized oracle platform that provides reliable and secure price-feed data to applications on the SKALE blockchain network. As a next-generation oracle system, Razor Network ensures that DApps on SKALE have access to accurate and timely external data, which is crucial for various decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
- Type: Dedicated SKALE Chain (SKALE sidechain)
- Total Value Locked (TVL): $1.12 million (as of October 2024)
SushiSwap V3
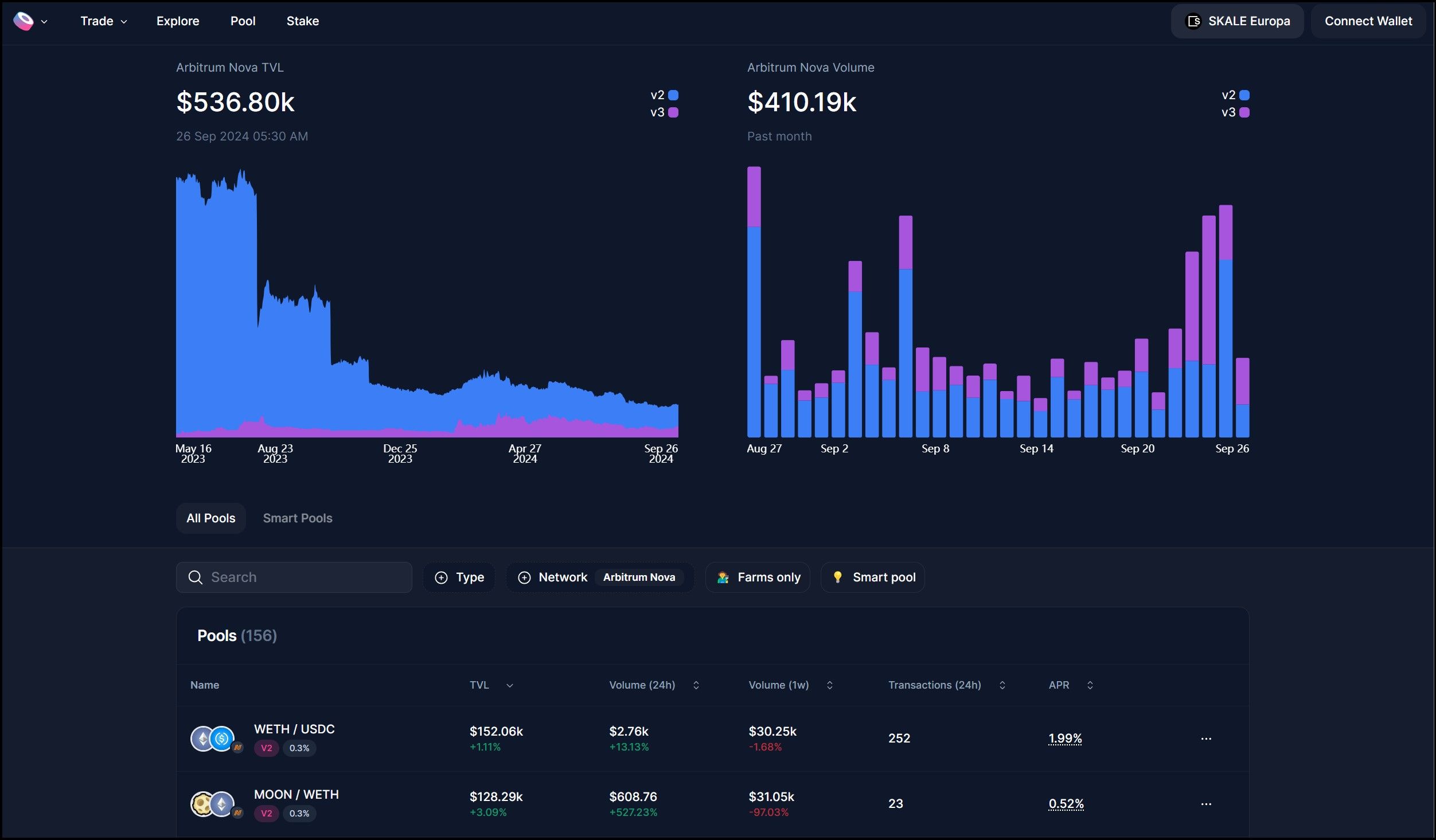 SushiSwap V3 Also Supports SKALE Europa | Image via SushiSwap
SushiSwap V3 Also Supports SKALE Europa | Image via SushiSwap SushiSwap, a well-known decentralized exchange (DEX), has deployed its V3 version on the Europa Hub of the SKALE Network. By leveraging SKALE's high throughput and zero-gas transactions, SushiSwap V3 on SKALE offers users faster and cost-effective trading experiences. This integration enhances liquidity and provides traders with seamless access to DeFi services.
- Type: Runs on the Europa Hub
- Total Value Locked (TVL): $360,000
Ruby Exchange
 Ruby Exchange is a DEX on Europa | Image via DappRadar
Ruby Exchange is a DEX on Europa | Image via DappRadarRuby Exchange is an NFT-enhanced automated market maker (AMM) built on the Europa SKALE Chain. It features a dual DEX model offering both traditional XY=K pools and a StableSwap 4Pool, including USDT, USDC, USDP, and DAI. By listing tokens against USDP as the default stablecoin, Ruby Exchange concentrates liquidity and minimizes slippage for traders. The platform also includes a fast, decentralized bridge that facilitates easy migration of assets from the Ethereum mainnet to SKALE.
- Type: Runs on the Europa Hub
- Total Value Locked (TVL): $113,140
Meson
 Meson Runs on Europa Hub | Image via DappRadar
Meson Runs on Europa Hub | Image via DappRadarMeson is a cross-chain swap platform that provides a stablecoin bridge connecting SKALE to more than 20 different chains. By enabling efficient and secure transfers of stablecoins across multiple blockchain networks, Meson enhances interoperability and liquidity within the DeFi ecosystem on SKALE. Users can perform cross-chain swaps with minimal fees and fast transaction times.
- Type: Runs on the Europa Hub
- Total Value Locked (TVL): $89,430
CryptoBlades
 CryptoBlasdes is a Play-to-Earn DApp | Image via DappRadar
CryptoBlasdes is a Play-to-Earn DApp | Image via DappRadarCryptoBlades is a play-to-earn NFT blockchain game available on eight different chains, including SKALE. Players engage in battles, earn rewards, and collect NFTs representing in-game assets. By utilizing SKALE's scalability and zero-gas transactions, CryptoBlades provides an enhanced gaming experience with faster transactions and lower costs, attracting a broader player base.
- Type: Dedicated Appchain on SKALE
These projects showcase the diverse applications and use cases that the SKALE Network supports, ranging from DeFi and NFTs to gaming. The ecosystem continues to grow as more developers and projects leverage SKALE's unique features to build innovative solutions.
Note: The Total Value Locked (TVL) figures are as provided as of October 2024, and sourced from DappRadar. For the most current metrics and updates on the SKALE ecosystem, please refer to official SKALE Network resources or reputable analytics platforms.
Closing Thoughts – What’s Next?
The SKALE Network has carved out a unique niche within the Ethereum ecosystem by providing an environment optimized for fast computation and high throughput, particularly suited for low-stakes interactions. This makes it an ideal platform for applications requiring rapid processing, sharing, and posting large amounts of on-chain data rather than focusing on high-value transactions. This specialization is evident in SKALE's current ecosystem, which is dominated by gaming and AI projects that benefit from the network's ability to handle micro-transactions and swift data exchanges.
Anticipated Upgrades
SKALE is set to enhance its capabilities with significant upcoming upgrades. One of the most notable is the introduction of Levitation and SKALE Ganymede (SKALE G), proposed in a SKALE Improvement Proposal in the second quarter of 2023. The Levitation protocol aims to enable ZK-rollups to connect seamlessly with the SKALE architecture, providing rollup connectivity to the Ethereum Mainnet. This advancement is expected to further bolster SKALE's scalability and interoperability, opening doors for more complex and high-performance applications to join the network.
Another anticipated upgrade is the implementation of Dynamic Chain Pricing for SKALE Chains. This feature will allow for more flexible and market-driven pricing models, making it more attractive for developers and businesses to deploy their applications on SKALE. By adjusting costs based on network demand and resource utilization, SKALE can provide a more economical and scalable solution for a broader range of projects.
SKALE's potential for expansion extends into other markets that require rapid data processing and high throughput. Sectors such as SocialFi, Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN), Internet of Things (IoT), decentralized storage, and digital identity are natural fits. These areas often involve processing and sharing large volumes of information quickly, and they stand to benefit significantly from SKALE's efficient and low-cost transaction environment.
Present Setbacks
A critical aspect of SKALE's growth strategy revolves around optimizing validator rewards. According to a report by Messari, a substantial portion of validator rewards currently comes from SKL token inflation—a model that is not ideal for long-term sustainability. The goal is to transition towards enabling validators to earn the majority of their revenue from SKALE Chain subscriptions. This shift would not only enhance the network's economic sustainability but also align validators' incentives with the network's growth and health.
To increase chain subscriptions and achieve this objective, SKALE can focus on two primary strategies:
- Integrate More Projects into the SKALE Ecosystem: By attracting a diverse array of applications and services, SKALE can enrich its ecosystem and provide more opportunities for validator participation. Marketing efforts should target projects and developers, highlighting SKALE's technical advantages, such as high throughput, zero gas fees, and EVM compatibility, to demonstrate how the network can meet their specific needs.
- Increase the Number of SKALE Users: Expanding the user base enhances the network's value proposition for both existing and potential projects. Marketing strategies should focus on end-users, emphasizing the benefits of interacting with applications on SKALE—such as seamless user experiences, fast transaction times, and cost savings from zero gas fees.
In conclusion, SKALE has established itself as a promising solution for addressing some of the most pressing challenges in blockchain scalability and efficiency. Its focus on facilitating rapid, low-cost interactions positions it well for supporting applications that demand high throughput and swift data processing. With strategic upgrades on the horizon and a clear pathway toward economic sustainability for validators, SKALE is poised to expand its ecosystem and play a significant role in the future of decentralized applications. By continuing to attract both developers and users, SKALE can drive increased adoption, enhance validator incentives, and solidify its position within the ever-evolving blockchain landscape.