Uniswap is no longer something most users “discover.” It sits quietly underneath a large share of on-chain trading. If you swap tokens on Ethereum or its major Layer 2 networks, there’s a good chance Uniswap liquidity touches your trade, whether you interact with the interface or not. Aggregators route through it, other DEXs measure themselves against it, and many markets still find their first reliable prices there.
What’s changed is the context. Decentralized trading has matured. Gas costs are less of a defining constraint than they once were. Interface fees now matter. Layer 2s have reset expectations around speed and cost. Uniswap continues to offer deep, non-custodial liquidity at scale. That remains its core strength.
This review looks at Uniswap as it actually functions in 2026. Not as an idea, but as a tool. When does it still make sense to use, and when are the risks or costs no longer worth it?
Read: Our top picks for the best decentralized exchanges
Quick Verdict and Rating
Key trade-offs: You get self-custody + best liquidity, but you accept gas/fees variability + user-side risk (phishing, bad approvals, scam tokens, MEV).
Best For
- Self-custody users who want the most dependable spot execution for major pairs
- Traders using L2s (Arbitrum/Optimism/Base/Polygon) to keep gas low
- Anyone comparing routes and slippage, and verifying token contracts before swapping
- DeFi power users who value composability (Uniswap liquidity under countless apps)
Who Should Skip
- Beginners who want an “undo button,” password recovery, or human support
- Users who click links from search/social instead of using a bookmarked interface
- Small mainnet swappers where gas can dwarf the trade
- Anyone unwilling to manage approvals, slippage, and basic on-chain hygiene
- Decentralization & Security: Core execution is on-chain and battle-tested; real-world risk is usually phishing and approval mistakes.
- Fees: Pool fees are predictable, but gas and route-dependent costs swing wildly, especially on Ethereum mainnet.
- Ease of Use: Clean swap flow, yet concepts like slippage, approvals, and MEV still punish inattentive users.
- Liquidity: Consistently among the deepest venues for majors, anchoring price discovery across DeFi.
- Features: Strong routing plus UniswapX and V4 hooks expand flexibility and execution styles over time.
- Mobile: Works well in mobile browsers, but wallet UX and network switching can add friction.
- Support: No account-level support or reversals; help is mostly docs/community, which is fine until something goes wrong.
Uniswap 2025 Updates
Several developments meaningfully shape how Uniswap operates and how you should evaluate it in 2026.
Uniswap V4 introduced “hooks” and a new contract architecture that reduces deployment costs and allows customized pool behavior, as documented by Uniswap Support. These changes primarily affect developers, but they expand the range of pools that can exist and improve efficiency over time, which eventually benefits traders.
Uniswap Labs also applied an interface fee on certain swaps executed through its official front end. This policy shift was first reported by DL News. The protocol itself does not enforce this fee, which makes it critical to distinguish between protocol costs and interface costs when estimating what you actually pay.
In 2024, Uniswap Labs disclosed receipt of a Wells Notice from the US Securities and Exchange Commission. That disclosure raised concerns about enforcement risk around DeFi interfaces. In early 2025, Uniswap announced that the investigation had closed without an enforcement action. This outcome reduced immediate legal uncertainty but did not eliminate long-term regulatory risk.
Finally, UniswapX expanded intent-based and gasless swaps, explained by Uniswap Labs. This feature changed how some trades execute and introduced new trade-offs around pricing transparency, eligibility, and execution guarantees.
How We Tested and Reviewed Uniswap
This section explains how the review was conducted and where its limits are, so you can judge how closely it reflects real-world usage.
Testing Methodology
We tested Uniswap using real swaps, not simulations, across the Ethereum mainnet and several major Layer 2 networks, focusing on two to three widely used L2s where most retail trading now occurs. Swaps were small, everyday trades to observe how execution quality, fees, and slippage changed with size.
Testing focused on swap execution only. All testing was performed using both desktop and mobile browsers to reflect how most users interact with Uniswap in practice.
What We Didn’t Test
We did not test long-term LP performance or attempt to model returns across market cycles. We also excluded exotic or extremely illiquid pairs, as well as high-frequency or automated trading strategies.
Those scenarios involve different tooling, risks, and assumptions than typical Uniswap usage. Excluding them keeps the review focused on realistic, everyday behavior, rather than edge cases.
At a Glance: What Uniswap Is and What It Isn’t
This section sets expectations clearly by defining what Uniswap actually provides and where its responsibilities end.
 Uniswap V4 Introduced Hooks and a New Contract Architecture. Image Via Uniswap
Uniswap V4 Introduced Hooks and a New Contract Architecture. Image Via UniswapWhat Uniswap Actually Does
Uniswap lets you trade tokens straight from your own wallet using smart contracts on public blockchains. There’s no need to sign up for an account, move funds into a custodial wallet, or wait for a middleman to approve your trades, and you stay in control the whole time. Every transaction requires your wallet signature, and the protocol executes swaps automatically based on rules encoded in smart contracts.
The separation between the Uniswap protocol and the Uniswap Labs interface matters. The protocol consists of immutable contracts deployed on-chain. The interface is a web application that helps you interact with them. This distinction is central to understanding risk, censorship resistance and regulatory exposure.
Uniswap is a protocol, not a service provider.
What Uniswap Does NOT Do
Uniswap does not provide a bank account or native fiat balance. You must rely on third-party services to move money between traditional finance and crypto. There’s also no customer support that can undo mistakes or recover accounts. If you approve a malicious contract, interact with a fake interface, or send assets to the wrong address, the protocol will simply carry out your instructions. Put simply, there’s no undo button.
How Uniswap Works
Here’s how Uniswap functions at a practical level, first conceptually and then mechanically.
DEX vs CEX (Why People Use Uniswap)
You use Uniswap to stay in full control of your assets. Your private keys never leave your wallet, and there is no centralized exchange that can freeze withdrawals, restrict access, or take custody of your funds. You also do not have to go through mandatory identity checks. The protocol is permissionless by design, and access is determined by code, not approval.
These properties—self-custody, permissionless access, composability, and resistance to discretionary censorship—are the core reasons users choose a decentralized exchange over centralized exchanges.
Uniswap enables composability by acting as a shared liquidity layer for the broader DeFi ecosystem. Lending platforms, yield strategies, and aggregators integrate directly with its pools rather than operating in isolation. The trade-off is responsibility. There is no intermediary to absorb losses caused by user error, poor judgment, or unsafe interactions.
Advanced users also favor Uniswap for execution neutrality. On a centralized exchange, trades occur inside a proprietary system that controls matching logic, order visibility, and internal routing. On Uniswap, execution happens on-chain according to transparent, predefined rules. This does not eliminate adverse outcomes, but it removes discretionary interference.
That distinction matters most during periods of market stress. Centralized platforms can halt withdrawals, throttle trading, or change rules mid-session. Uniswap cannot do that. If the network is live and your transaction is valid, it executes. That predictability is often undervalued until it becomes essential.
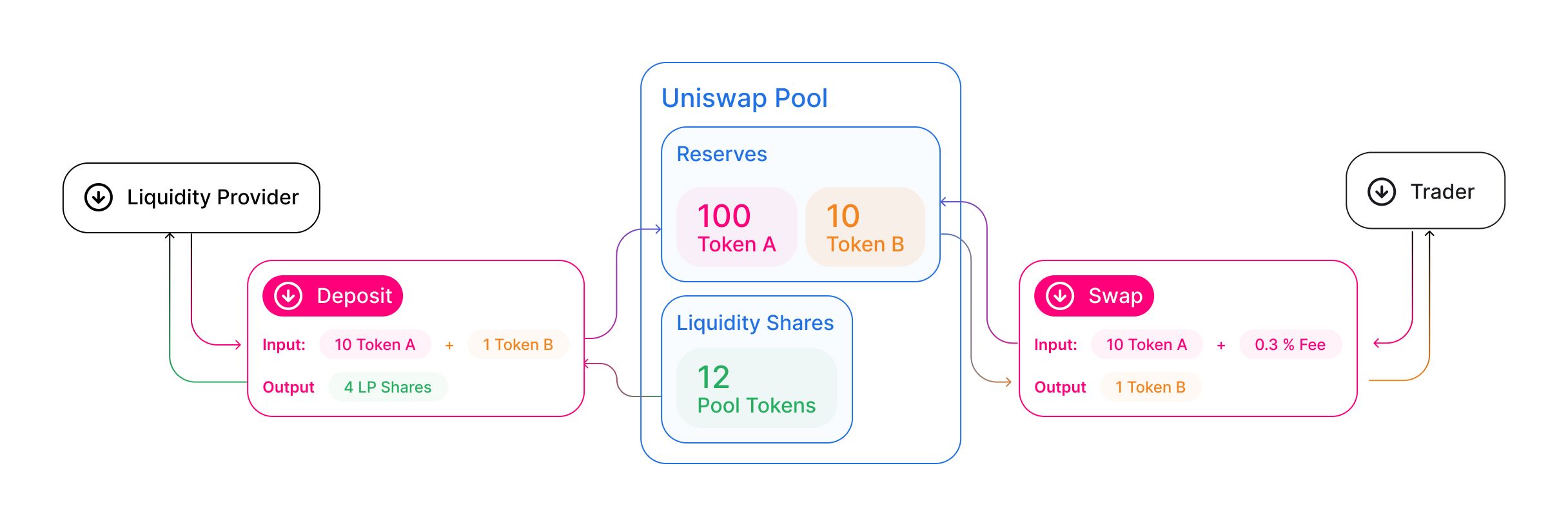
AMMs and Liquidity Pools
Uniswap replaces order books with automated market makers (AMM). Liquidity providers deposit two assets into a pool, and traders swap against that pool. Prices adjust automatically based on the pool’s balances. Large trades relative to pool size create greater price impact, while thin liquidity increases slippage. Deep liquidity reduces both.
This model guarantees continuous liquidity, but it requires you to think carefully about trade size and pool depth before executing swaps.
Liquidity pools also change how you think about market depth. On an order-book exchange, liquidity appears and disappears as orders are placed or canceled. On Uniswap, liquidity is locked into pools and visible on-chain. This makes price impact more predictable, especially for larger trades.
However, this visibility cuts both ways. Because liquidity is transparent, sophisticated traders and bots can anticipate how your trade will move the price. That is one reason slippage settings and trade sizing matter more on AMMs than many first-time users expect.
Constant Product Formula
Uniswap pools follow a constant product formula, commonly written as x × y = k, where x and y represent the balances of the two tokens in the pool and k remains constant. When you trade, you change the ratio between tokens while the product stays the same, which moves the price. Price impact increases nonlinearly as trade size grows, which explains why liquidity depth matters more than headline fees for larger trades.
One practical implication of the constant product formula is that slippage accelerates rapidly once your trade size approaches pool depth. Doubling trade size does not double the price impact. It increases faster than linearly. This is why breaking large trades into smaller chunks or using aggregators can materially improve outcomes.
This behavior also explains why Uniswap’s deepest pools dominate price discovery. Liquidity concentration smooths price movement and reduces the advantage of aggressive arbitrage.
Uniswap Protocol Architecture
This section explains where execution happens, where risk lives, and how trades are routed behind the scenes.
Interface vs Smart Contracts (where risk really lives)
Protocol risk lives in the smart contracts. These contracts are open source, widely audited, and have operated under real market stress for years. Interface risk lives in the front end. Phishing sites copy Uniswap branding and layout, and losses may occur because users interact with fake interfaces rather than because the protocol fails. Bookmarking the correct site remains one of the most effective safety practices.
Routing and Liquidity Sources
Uniswap routes trades across multiple pools to optimize execution. The router can split trades across paths if doing so reduces slippage, and this happens automatically. Aggregators frequently source liquidity from Uniswap pools, which means Uniswap often sits underneath competing interfaces when execution quality is compared.
Uniswap’s router does more than select a single pool. It evaluates multiple possible paths, including multi-hop routes, to minimize slippage. For example, a token may have poor direct liquidity against ETH but strong liquidity against USDC. The router can split the trade across hops to achieve a better effective price.
This routing intelligence is one reason Uniswap execution often outperforms simpler DEX interfaces, even when headline fees appear similar.
 Uniswap Has Evolved Significantly Over Time. Image Via Uniswap
Uniswap Has Evolved Significantly Over Time. Image Via UniswapUniswap Versions Explained: V2 vs V3 vs V4
Uniswap has evolved significantly over time, and each version changes how liquidity and fees behave. This section will take a look at the three models and how they are different from each other.
Uniswap V2 (Legacy, still relevant sometimes)
Uniswap V2 introduced the automated market maker model that defined early DeFi, using simple token-to-token liquidity pools with no price ranges or dynamic fee structures. Liquidity was spread evenly across all possible prices, which made the system easy to understand and passive for liquidity providers, but inherently capital-inefficient compared to newer designs.
While some long-tail assets and legacy pairs still rely on V2 pools, most meaningful liquidity has migrated to more advanced versions of the protocol that offer better capital efficiency and execution for active markets.
Uniswap V3 (Current “standard” LP design)
Uniswap V3 introduced concentrated liquidity, a structural change that allows liquidity providers to deploy capital within custom price ranges rather than evenly across the entire price curve. Liquidity is only active while the market price remains inside the selected range. When the price moves outside it, that liquidity stops earning fees. This design dramatically improves capital efficiency by concentrating liquidity near the current market price, which reduces slippage for traders while allowing LPs to take more active positions. The mechanism is implemented through discrete price “ticks,” which define where liquidity becomes active or inactive, rather than continuous pricing.
V3 also introduced multiple fixed fee tiers, allowing liquidity providers to price volatility risk more precisely. Pools can be deployed with one of four fee levels: 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.30%, or 1.00%. Lower tiers are intended for stable or highly correlated pairs, while higher tiers compensate LPs for greater volatility or tail risk. Unlike earlier versions, fee selection is tied to the pool itself, not dynamically adjusted, which creates clearer market segmentation and more efficient liquidity placement.
Uniswap V4 (What it adds in practice)
Uniswap V4 introduced hooks that allow developers to customize pool behavior without deploying separate contracts. It also lowered deployment costs by consolidating pools into a single architecture. Traders tend to notice efficiency improvements over time, while developers gain far more flexibility.
From a user perspective, the most important aspect of V4 is not hooks themselves, but what they enable. Hooks allow pool creators to embed logic such as dynamic fees, custom incentives, or conditional behavior directly into pools. Over time, this leads to more specialized liquidity rather than one-size-fits-all pools.
Users notice this indirectly through better pricing, lower slippage, or pools that behave differently under stress. Developers notice it immediately because it reduces deployment overhead and expands design space. This difference explains why V4 discussions often sound developer-focused even though the long-term impact is user-facing.
UniswapX and Gasless Swaps
UniswapX introduces a different execution model that affects pricing, gas costs, and exposure to MEV.
What is UniswapX?
UniswapX is an intent-based trading system. Instead of executing a transaction directly, you submit a request to swap tokens. Off-chain fillers compete to fulfill that request at the best available price. This model can reduce exposure to front-running and improve execution under certain conditions, a topic discussed extensively in public repositories such as GitHub. UniswapX also changes how MEV interacts with user trades. In a traditional on-chain swap, your transaction sits in the public mempool, where searchers can attempt to front-run or sandwich it. With UniswapX, the intent is matched off-chain by fillers, reducing mempool exposure in some cases.
This does not eliminate MEV entirely, but it can reduce the most aggressive forms of extraction, especially for smaller trades.
 UniswapX is an Intent-Based Trading System. Image via Uniswap
UniswapX is an Intent-Based Trading System. Image via UniswapHow Gasless Swaps Work on Uniswap Apps
When eligible, the Uniswap interface routes your trade through UniswapX. A filler pays the gas fee on your behalf, and you receive tokens without paying gas upfront. The cost of this service is embedded in the execution price, which means gasless does not mean free.
When to Use UniswapX vs Regular Swaps
UniswapX works best for smaller trades and during periods of network congestion. Regular swaps offer more predictable execution for large trades or when price certainty matters. You should always review the execution route and quoted output before confirming.
Eligibility matters. Not all tokens, networks, or trade sizes qualify for UniswapX routing. Execution timing can also vary because fillers compete to complete the trade. This means UniswapX is best treated as an optimization, not a guarantee.
For large or time-sensitive trades, direct swaps often provide more predictable outcomes.
Fees and Real Trading Costs
This section breaks down what you actually pay when trading on Uniswap, and why total costs can vary meaningfully depending on pool selection, network choice, and interface.
Protocol Fees vs Interface Fees
On Uniswap, it is important to distinguish between protocol fees, which are enforced on-chain by smart contracts, and interface fees, which are controlled by the application used to access the protocol.
Protocol fees are defined at the pool level. In Uniswap V3, pools are deployed with predefined swap fee tiers of 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.30%, or 1.00%, selected based on the expected volatility of the trading pair. These swap fees are applied automatically during execution and cannot be bypassed by using a different interface. In pools where protocol fees are enabled, the total swap fee can be split between liquidity providers and the protocol itself, rather than flowing entirely to LPs. The exact split is configurable at the protocol level and may differ by pool and fee tier.
Meanwhile, v4 introduces flexible fees that can range from 0% to 100%, offering more customization options for pools.
Interface fees are separate from protocol fees, and they are controlled by the interface operator rather than the protocol. However, according to Uniswap’s official documentation, Uniswap Labs does not currently charge any interface fees on trades executed through its web interface. Users interacting with Uniswap via the official interface pay only the underlying protocol fee and network gas costs.
Gas Fees and Why L2s Change Everything
Ethereum mainnet gas fees remain volatile, and during periods of congestion, they can easily exceed the value of small trades. A simple swap can cost tens of dollars, discouraging frequent rebalancing, approval management, or experimentation.
Layer 2 networks such as Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, and Polygon reduce those costs by batching transactions off-chain and settling them on Ethereum. In typical conditions, swaps on Layer 2s cost cents rather than dollars, fundamentally changing what is economical to do on-chain.
Lower fees also change behavior. On the mainnet, users avoid small adjustments because every action is expensive. On Layer 2s, users rebalance LP positions, fine-tune slippage, and manage approvals more actively because doing so is cheap. That flexibility improves execution quality and risk control.
If you take one takeaway: default to a Layer 2 unless you explicitly need Ethereum mainnet liquidity. For a while now, L2s have been the standard for cost-efficient Uniswap trading.
Example Cost Scenarios
The table below shows how total trading costs typically behave at different swap sizes, comparing the Ethereum mainnet with major Layer 2 networks.
| Swap Size | Ethereum Mainnet | Layer 2 Networks |
|---|---|---|
| $200 | Gas fees often exceed or rival the value of the swap due to base layer execution costs, making small trades inefficient on mainnet | Rollups batch transactions and amortize gas costs, keeping fees low even for small trades, as described by Optimism Docs and Arbitrum Docs |
| $1,000 | Gas becomes a smaller percentage of the trade but still materially affects efficiency during congestion, consistent with Ethereum’s execution fee structure | Gas impact remains minimal because execution occurs offchain and settles in batches, which L2 networks document in their cost models at Base Docs |
| $10,000 | Gas is largely diluted by trade size, and execution quality depends more on liquidity depth and price impact than on fees, a dynamic inherent to AMM design | Low, predictable gas costs persist even for large trades, allowing liquidity depth and routing efficiency to dominate total execution cost |
Rule of thumb: On the Ethereum mainnet, gas dominates small trades and becomes less relevant as trade size increases. On Layer 2s, gas remains consistently low, so liquidity depth and price impact are the primary drivers of total cost.
Is Uniswap Safe?
Here’s what Uniswap’s security track record shows, and where user behavior still creates risk.
Protocol Security
Uniswap V4 has been built under heavy security scrutiny. The core contracts have gone through multiple independent audits, with several reviews finalized and others published as drafts while remediation continues. Completed and draft assessments are maintained in the core repository’s audits directory on GitHub and include reviews by OpenZeppelin (July 17, 2024), Certora (July 2024, draft), Trail of Bits (Sept. 5, 2024), Spearbit (Sept. 5, 2024, draft), and ABDK Consulting (Sept. 5, 2024, draft).
The V4 periphery contracts have been audited separately, with reports available in the periphery repository’s audits directory. These include a completed review by OpenZeppelin (Sept. 5, 2024) alongside draft reports from Spearbit and ABDK Consulting dated the same day.
Beyond audits, Uniswap Labs has backed V4 with a substantial economic incentive for disclosure. In November 2024, Uniswap announced a $15.5 million bug bounty covering the V4 contracts, hosted on Cantina, reinforcing an ongoing, public-first approach to protocol security.
The Real Risks
Most losses on Uniswap do not come from protocol exploits; they come from user-side mistakes.
The most common risks:
- Scam tokens and fake contract addresses
Malicious or misleading tokens are still widespread, especially around trending narratives. - Phishing and fake front-ends
Cloned interfaces and malicious links can trick users into signing harmful transactions. - Wrong-address irreversibility
On-chain transactions cannot be reversed. Sending funds to the wrong address or network is permanent. - MEV and front-running
Public transaction visibility allows searchers to reorder or sandwich trades, degrading execution. - Unlimited token approvals
Broad approvals persist indefinitely. If a contract is later compromised, funds can be drained without further interaction.
Regularly reviewing and revoking unused approvals is one of the simplest ways to reduce long-term exposure.
Safety Checklist
Self-custody means mistakes are final. A few basic checks dramatically reduce the risk of avoidable losses, especially when trading unfamiliar tokens or meaningful size.
Before every swap:
- Verify the token contract address to avoid scams or fake assets
- Check price impact and slippage before confirming execution
- Use a bookmarked, trusted interface rather than links from search or social
- Use a hardware wallet for meaningful size
- Revoke unused or unlimited approvals periodically
These steps are not optional hygiene. They are the cost of self-custody.
Liquidity Providing on Uniswap
Providing liquidity can generate fees, but it comes with trade-offs that are often misunderstood.
How LPing Works (V2 vs V3 positions)
Liquidity providers earn a share of trading fees based on the pool’s fee tier and their relative liquidity. On Uniswap V2, all pools charge a fixed 0.30% swap fee, which is fully paid to LPs and passively compounded into the pool. On Uniswap V3, LPs choose from fee tiers of 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.30%, or 1.00%, but earn fees only when their liquidity is within the active price range, and fees are collected separately rather than auto-compounded.
V3’s concentrated liquidity model can be up to 4,000× more capital-efficient than V2 when liquidity is placed near the market price, allowing LPs to earn more fees with less capital. The trade-off is management. As prices move, ranges must be adjusted or liquidity goes inactive and earns nothing.
Impermanent Loss
If one asset in a pair moves sharply, the pool rebalances automatically, and you may withdraw with less value than if you held the assets. Volatile pairs increase this risk, while stable or correlated pairs reduce it. Fees can offset impermanent loss, but they do not eliminate it.
For example, depositing $1,000 into an ETH/USDC pool and seeing ETH double in price might leave your LP position worth ~$1,414, versus $1,500 if you had held. Volatile pairs amplify this effect, while stable or correlated pairs reduce it. Trading fees can offset impermanent loss, but they rarely eliminate it.
Impermanent loss is not a flaw. It is the cost of providing liquidity to a rebalancing system. You earn fees in exchange for giving up some upside exposure. Whether that trade makes sense depends on volatility, fee volume, and time horizon.
Practical LP Playbooks
- Conservative
This approach is about minimizing surprises. Conservative LPs stick to stable or tightly correlated pairs and set wide ranges so positions stay active even when prices drift. Returns are usually modest, but impermanent loss is low and positions don’t need constant babysitting. It’s not exciting, but it’s predictable, which is the point. - Balanced
Balanced strategies usually pair ETH with a stablecoin and use moderate ranges around the current price. You get meaningful fee income during normal market conditions without the position constantly flipping in and out of range. There’s some impermanent loss risk, but it’s manageable, and you only need to rebalance occasionally. - Aggressive
Aggressive LPing is about squeezing maximum fees out of volatile pairs by using tight ranges. When it works, capital efficiency can look great. When it doesn’t, liquidity goes out of range quickly and earns nothing. This style requires frequent rebalancing, comfort with volatility, and a willingness to actively manage positions. It’s closer to trading than passive investing.
There’s no “best” playbook. Each profile trades effort for risk and potential return. The right choice depends on how much time you want to spend managing positions and how much volatility you’re willing to live with.
Uniswap vs Competitors
Uniswap does not exist in isolation, so this section compares it to other major DEXs and aggregators.
Quick Comparison Table (Uniswap vs PancakeSwap vs SushiSwap vs Curve vs dYdX vs 1inch)
| Platform | Chains (DeFiLlama) | Fees (official) | Core Strength | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uniswap | 38 chains | 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.3%, or 1.0% fee tiers on most pools, chosen per pair and paid to LPs; dynamic possible in V4. See fee tiers | Deepest onchain liquidity and price discovery | Large trades, best execution, self-custody users |
| PancakeSwap | 11 chains | 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.25%, or 1.0% fee tiers on V3 pools; V2 default is 0.25% per swap. See PancakeSwap protocol docs | Low-cost swaps with fast confirmation | Small trades, BNB Chain-native users |
| Sushi (combined) | 26 chains | 0.30% standard swap fee; V2 LPs receive 0.25% and 0.05% goes to token holders; V3 offers optional fee tiers (0.01%, 0.05%, 0.3%, 1%). See SushiSwap fee FAQ | Broad chain support and modular DeFi features | Users operating across many networks |
| Curve | 30 chains | ~0.04% typical stable swap fee, shared with liquidity providers. Curve pools are low-fee by design for stable/like-asset trades. Fee structure reflected in ecosystem data. (Zealynx Security) | Minimal slippage for stable and correlated assets | Stablecoin swaps, low-volatility strategies |
| dYdX | dYdX, Ethereum | Maker/Taker model with default ranges roughly 0.01%–0.05% depending on volume tier. See trading fee docs dYdX | High-liquidity perpetual futures | Leverage and derivatives trading |
| 1inch | Ethereum, BSC | No separate protocol fee by 1inch; underlying DEX fees vary (often 0.01%–1.0% depending on source). Gas and routing built into price. See fee explanation 1inch fees | Smart routing across multiple DEXs | Best-price sourcing across fragmented liquidity |
Which DEX Should You Choose?
Uniswap
The general-purpose default.
- Deepest liquidity for most major pairs
- Predictable on-chain execution and broad ecosystem support
- Best used on Layer 2s to keep gas costs low
PancakeSwap
The BNB Chain native.
- Optimized for BNB Chain users and assets
- Lower gas fees, faster execution
- Less depth for Ethereum-native or institutional flows
SushiSwap
Multi-chain and community-driven.
- Available across many chains and L2s
- Flexible feature set beyond simple swaps
- Liquidity depth is inconsistent compared to Uniswap
Curve
Purpose-built for stability.
- Best-in-class execution for stablecoin and correlated pairs
- Extremely low slippage on large stable trades
- Not designed for volatile or long-tail assets
dYdX
For derivatives, not swaps.
- Optimized for perpetual futures trading
- Deep liquidity for leveraged positions
- Not a spot DEX replacement
1inch
Execution optimizer.
- Routes trades across multiple DEXs
- Often finds better prices when liquidity is fragmented
- Adds complexity and relies on external routing logic
For most users, the simplest compromise is Uniswap on a Layer 2. You get deep liquidity, transparent execution, and low fees without over-optimizing. Other DEXs shine in specific niches, but Uniswap via L2 remains the most reliable all-around choice.
If You Only Care About Best Execution
- Uniswap tends to deliver the best execution when liquidity is deep and concentrated. For major pairs, its pools often anchor price discovery, resulting in lower price impact and more predictable fills, especially for larger trades.
- Aggregators like 1inch perform better when liquidity is fragmented across venues. By sourcing prices from multiple DEXs and splitting orders, they can sometimes achieve better blended execution for long-tail or thinly traded pairs.
Deep liquidity favors Uniswap. Fragmented liquidity favors aggregators.
Regulatory Status
This section separates protocol reality from interface risk and explains what recent regulatory developments mean.
The Uniswap/SEC case
In April 2024, Uniswap Labs disclosed that the SEC had issued a Wells Notice. In plain English, it meant the regulator was looking into the company and deciding whether to take action. Nothing had been charged yet; it was more of a “we’re reviewing this” moment.
At the time, the SEC was looking at whether Uniswap Labs should be treated like a traditional financial company. Specifically, whether it was acting as an unregistered exchange or broker under U.S. securities laws. Uniswap Labs pushed back hard on that idea. Their argument was pretty straightforward: the Uniswap protocol is decentralized, non-custodial, and runs on smart contracts. It doesn’t hold user funds, approve trades, or operate like a middleman the way a normal exchange does. The company laid out this position publicly in a response posted on its own blog.
Then, in February 2025, the SEC closed the investigation without filing any charges. The decision removed the immediate regulatory overhang surrounding Uniswap Labs and the primary Uniswap interface.
What could still change
The closure of the investigation materially reduced near-term regulatory risk, but it did not redefine how DeFi is treated under U.S. law. The key distinction remains intact: the Uniswap protocol itself is a set of permissionless smart contracts. It cannot be shut down, modified, or selectively restricted by a company or regulator once deployed.
Regulatory pressure, where it does exist, tends to focus on identifiable legal entities rather than autonomous code. That means discussions around compliance are more likely to involve how companies communicate, build tooling, or provide ancillary services around a protocol, not the protocol’s core mechanics. Importantly, this is not the same dynamic as centralized exchanges, which custody assets, approve listings, and can directly block user access.
For users, the takeaway is structural rather than tactical. Uniswap works because the protocol is independent of any single interface or operator. As long as the underlying smart contracts exist on-chain, the protocol remains usable. Understanding that separation between the protocol and any given front end is what gives DeFi its resilience, and why Uniswap’s legal outcome mattered far beyond a single investigation.
How to Use Uniswap
Here’s a practical walkthrough of how a typical swap works and where users most often make mistakes.
Before You Start
You need a compatible wallet, funds for the swap, extra funds for gas, and the correct network selected, preferably a Layer 2.
Step-by-step Swap Walkthrough
- Step 1: Connect wallet
First, open the Uniswap web app in your browser. Next, connect your wallet when the prompt pops up. Once you land on the swap screen, the token selector will be ready, letting you start building your trade right away.
 Image via Uniswap
Image via Uniswap- Step 2: Choose network (L2 recommended)
Before you pick tokens, pick the right network. For most everyday swaps, you should default to a major L2 because it usually cuts network costs while keeping execution quality high. In the Uniswap web app, you choose the network from the network dropdown, then proceed on that network.
 Image via Uniswap
Image via Uniswap- Step 3: Select tokens + verify contract address
Pick the token you want to swap from, then the token you want to receive. When you trade anything outside the obvious majors, you should verify the token’s contract address from the project’s official site or a reputable explorer page, then paste that address into the Uniswap token search so you select the correct contract, not a lookalike.
 Image via Uniswap
Image via Uniswap- Step 4: Set slippage + deadline
Open swap settings and set your max slippage. Uniswap supports auto slippage, but you can switch to custom when the pair is volatile, liquidity is thin, or the trade fails due to slippage limits. Also, check your transaction deadline setting. Uniswap’s interface uses a default deadline to prevent execution after meaningful price movement, and it can be extended in advanced settings if you understand the trade-off.
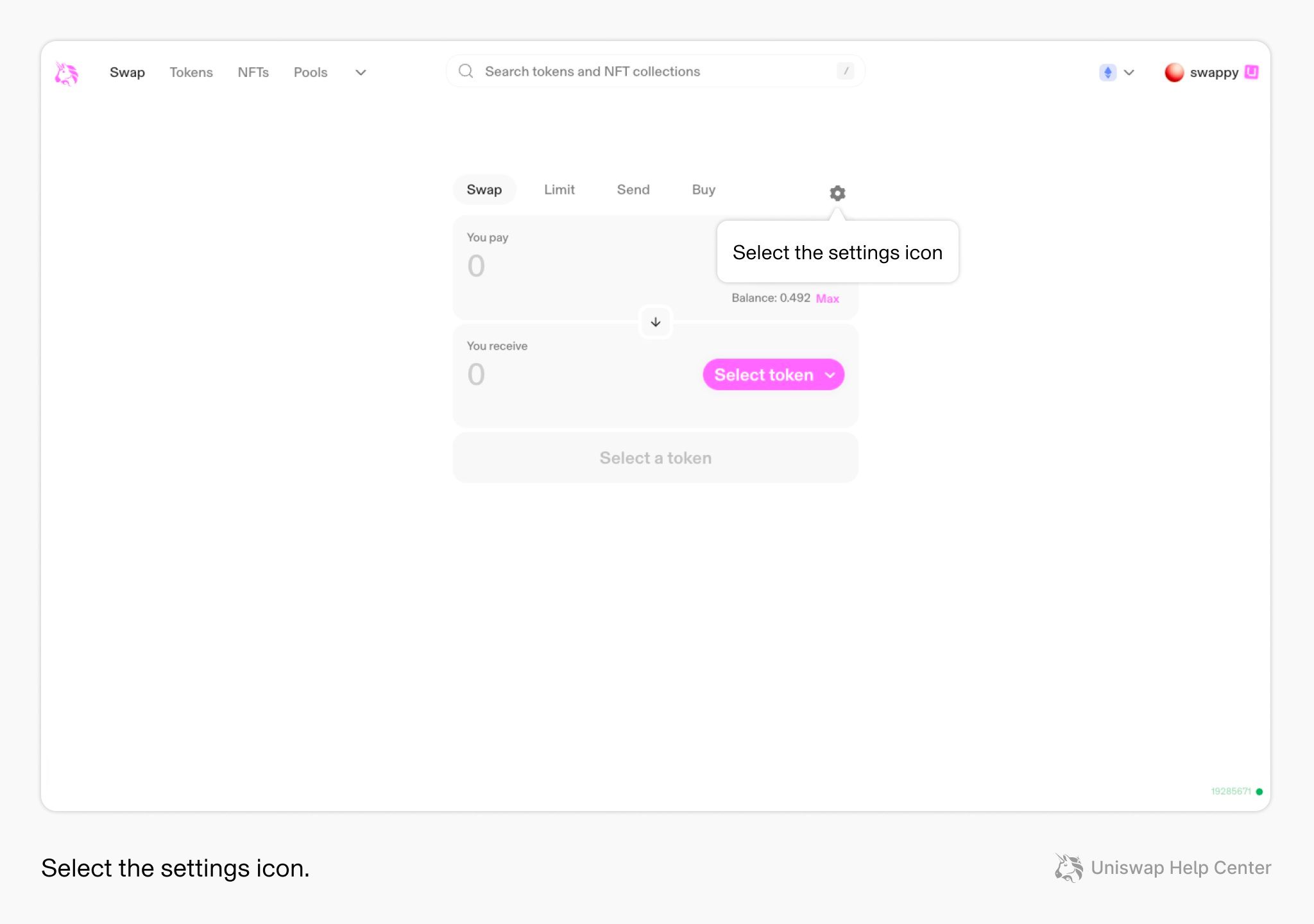 Image via Uniswap
Image via Uniswap- Step 5: Approve token (explain why approvals exist)
If you are swapping an ERC-20 token for the first time, you need to approve the Uniswap router to spend that token on your behalf. This approval is separate from the swap itself. It exists because token contracts require explicit permission before another contract can move your tokens. Approvals cost gas because they are on-chain transactions.
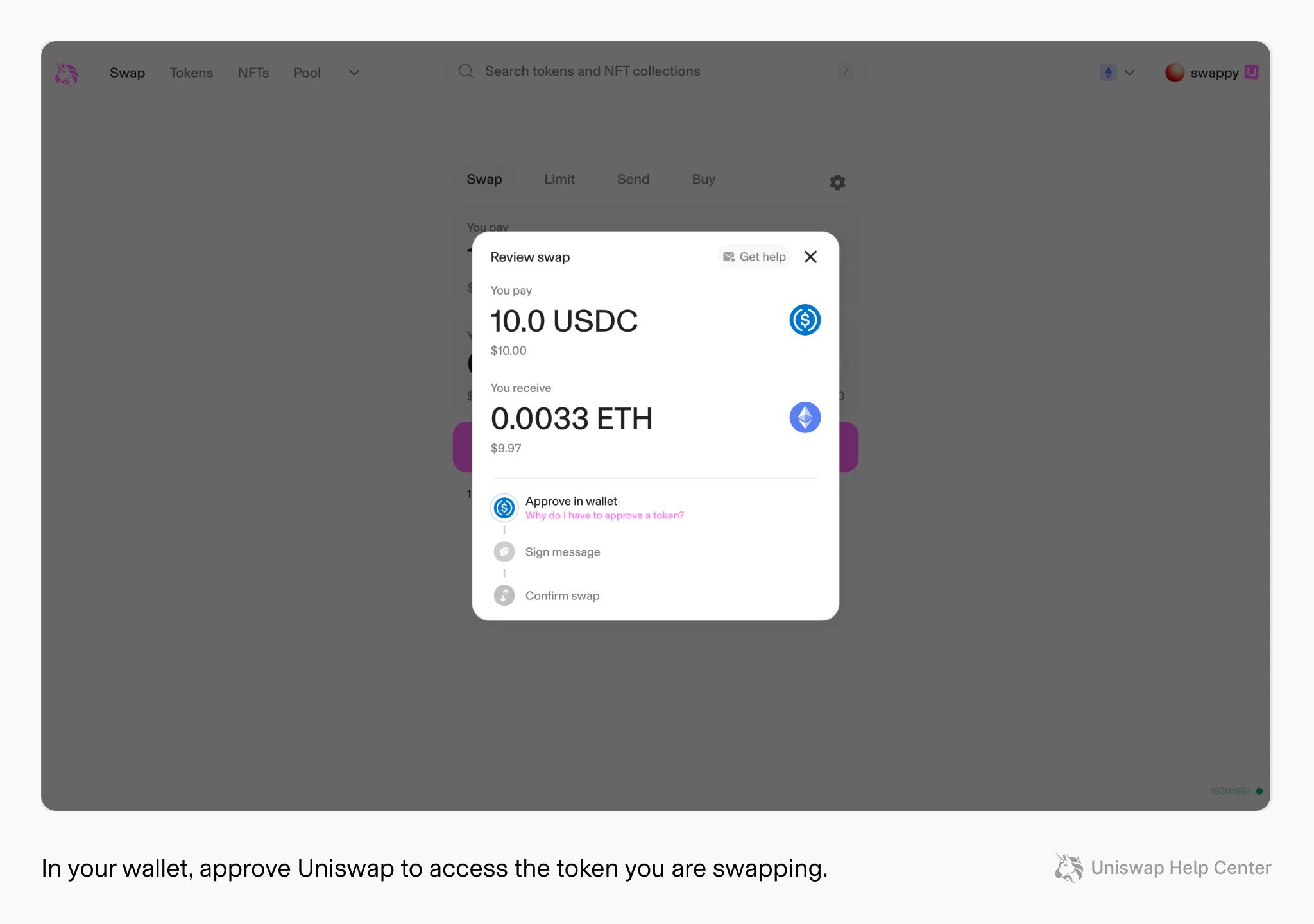 Image via Uniswap
Image via Uniswap- Step 6: Execute swap + verify receipt
Review the swap details, then execute the swap. Your wallet will ask you to confirm the final transaction. After submission, verify the result by checking the success state in the app and opening the transaction in a block explorer to confirm the status, token amounts, and destination address.
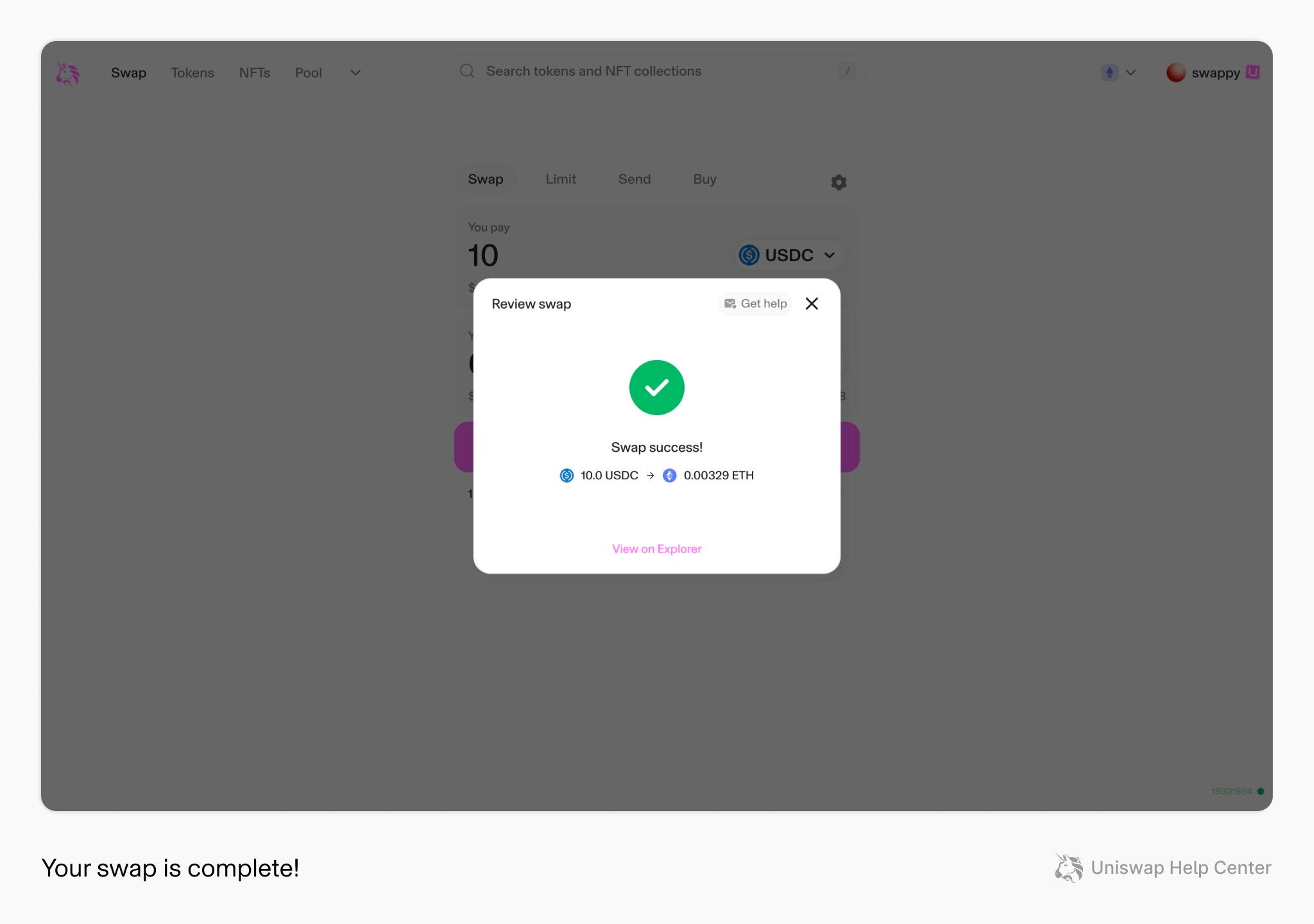 Image via Uniswap
Image via UniswapCommon Errors and Fixes
- Insufficient gas or balance for fees
This usually happens when your wallet does not hold enough of the network’s native token to cover gas. Even if you have enough tokens to swap, the transaction will fail if you cannot pay the network fee. The fix is simple. Keep a small buffer of ETH or the relevant L2 gas token in your wallet before you trade. - High price impact warning
A high price impact means your trade is large relative to the pool’s liquidity. This often happens with low-liquidity tokens or when trading outside peak hours. If you see this warning, consider reducing trade size, breaking the swap into smaller parts, or checking whether a different route or network offers deeper liquidity. - Transaction failed but gas was still charged
On-chain transactions consume gas whether they succeed or fail. Common causes include slippage set too low, sudden price movement, or network congestion. To reduce repeat failures, increase slippage slightly for volatile pairs, avoid peak congestion, and double-check that the pool has enough liquidity for your trade size. - The token does not appear in your wallet after the swap
This does not usually mean the swap failed. Many wallets do not automatically display new tokens. The fix is to add the token manually using its contract address or refresh your wallet’s token list. Always verify the contract address before adding it to avoid fake assets. - Approval issues or stuck approvals
If an approval transaction fails or remains pending, the swap cannot proceed. This often happens during congestion or when the gas is set too low. Speeding up or replacing the approval transaction in your wallet usually resolves the issue. - Wrong network selected
Swaps only work on the network where the liquidity exists. If you attempt a swap while connected to the wrong network, the interface may fail or show missing balances. Always confirm the selected network before approving any transaction.
These issues are common, predictable and usually fixable. The key is to slow down, read the warnings the interface provides, and understand that on-chain trading requires a bit more attention than centralized exchanges.
UNI Token and Governance
UNI plays a governance role rather than a revenue role, and that distinction matters because it defines what the token does and what it does not do. UNI exists to coordinate decisions around how the Uniswap protocol evolves, not to function as an ownership claim or a cash-flow asset.
What UNI Does Today
UNI is Uniswap’s governance token. Holding UNI lets you propose changes and vote on how the protocol is run. This can include things like upgrades to the system, how the treasury is used, incentive programs, or tweaking parameters like fees or new deployments. Voting power depends on the amount of UNI held or delegated, which means influence can concentrate unless tokens are actively delegated across the community.
Holding UNI does not entitle you to a share of trading fees or protocol revenue. Its utility today comes from governance participation and long-term protocol relevance, not from yield.
Value Accrual Debate
The fee switch is a recurring topic in Uniswap governance discussions. In simple terms, it refers to a mechanism that could redirect a portion of protocol fees from liquidity providers to UNI holders. The mechanism exists in theory and has been discussed in past proposals, but it remains inactive.
Whether it ever activates depends entirely on governance decisions and broader regulatory considerations. Until that changes, UNI should be viewed strictly as a governance token, not a revenue-generating asset, and any value accrual beyond governance remains speculative.
Final Verdict
Uniswap is still the go-to decentralized exchange. It offers top-notch liquidity, reliable trades, and full self-custody, but it also asks a lot from its users—you need to know what you’re doing and pay attention. If you value control and understand the trade-offs, Uniswap is hard to beat. But if you want built-in safety nets, it’s probably not for you.





