Ethereum's layer-2 ecosystem is more crowded than ever. The surge in L2 networks is a direct result of Ethereum’s scalability-first approach, a shift in its roadmap that has encouraged developers to build on top of its secure settlement layer rather than competing with it. The outcome? A rapidly expanding landscape of rollups and scaling solutions, each taking a different approach to optimizing speed, cost, and usability.
At its core, a layer-2 chain is designed to handle smart contract execution and transactions while inheriting security and settlement from Ethereum. Initially, L2 networks built customized bridges and settlement mechanisms to interact with Ethereum, leading to fragmentation across rollup architectures. However, the emergence of "layer 3-like" rollup designs has introduced a new paradigm—one where L2 chains are no longer standalone entities but interconnected within a broader ecosystem.
We previously explored this shift in our piece on layer-3 blockchains and how projects like ZKsync's ZKChains are pioneering the next evolution of Ethereum scaling.
This review expands on that discussion by analyzing Abstract, a zero-knowledge rollup that builds on these ideas to create a high-performance L2 designed for consumer-facing blockchain applications. We'll explain how Abstract works, its key innovations, and what sets it apart in Ethereum's increasingly competitive scaling landscape.
Abstract Overview
Abstract is a Layer-2 network built on Ethereum, designed to provide low-cost, high-speed transactions while maintaining Ethereum’s security. As a ZK rollup, it uses zero-knowledge proofs to bundle transactions off-chain and verify them efficiently on Ethereum. This cryptographic approach allows Abstract to scale without compromising security or decentralization.
Unlike some L2s that create their own rollup infrastructure from scratch, Abstract is built using the ZK Stack, an open-source framework developed by ZKsync. Instead of deploying its own, Abstract leverages existing ZKsync infrastructure (like sequencers and provers), enabling faster deployment and smoother interoperability with other ZK Stack-based chains.
Another key feature of Abstract is its compatibility with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This ensures that most smart contracts built for Ethereum can be deployed on Abstract with minimal modifications, making it easy for developers to migrate their applications while benefiting from lower fees and improved transaction speeds.
Key Features of Abstract
- Abstract Global Wallet (AGW): A cross-application smart contract wallet designed for seamless user onboarding. Users sign up once using familiar login methods and can then interact with any application on Abstract without needing separate wallets for each DApp.
- Native Account Abstraction: Unlike Ethereum, which defaults to externally owned accounts (EOAs), Abstract natively implements account abstraction, meaning all accounts are smart contract wallets. This allows for recovery mechanisms, spending limits, and flexible gas payment options (including fee sponsorship via paymasters).
- Paymasters: Abstract supports gasless transactions via paymasters—smart contracts that cover gas fees on behalf of users, making DApps more accessible to a mainstream audience.
- ZK Stack Integration: Abstract is natively interoperable with other chains in the zkSync ecosystem by operating on ZK Stack, allowing atomic cross-chain transactions and shared liquidity across ZK-powered networks.
Abstract's Consumer Crypto Vision
Abstract’s approach to blockchain adoption is built around a focused, consumer-first strategy. Rather than positioning itself as a generic, all-purpose chain, Abstract is designed to be a "premier destination" for consumer-facing crypto applications. The team refers to this vision as "crypto’s digital amusement park"—a place where users can experience blockchain-based applications that are engaging, seamless, and fun.
 The Consumer Crypto Vision Values Hyper-Focusing on One Utility Over General-Purpose Approach | Image via Abstract Blog
The Consumer Crypto Vision Values Hyper-Focusing on One Utility Over General-Purpose Approach | Image via Abstract BlogThis perspective challenges the conventional wisdom of L2 scaling solutions, which often prioritize broad developer adoption over curated user experiences. Instead, Abstract is hyper-focused on cultivating "premier attractions" within its ecosystem, ensuring that the first wave of consumer apps delivers a polished, engaging experience. The idea is that by building a loyal user base around a well-defined niche, Abstract can later expand into adjacent markets organically.
By prioritizing ease of use, high-quality applications, and a "fun-first" approach, Abstract aims to become the most entertaining place on the internet, setting itself apart from traditional DeFi-heavy L2s.
Abstract Technical Overview
While Abstract functions as an independent layer-2 network, it does not operate in isolation. Instead, it builds on the ZK Stack, an open-source modular framework developed by ZKsync. This means that rather than creating its own rollup infrastructure—including sequencers, provers, and settlement mechanisms—Abstract leverages ZKsync’s existing infrastructure to streamline development and interoperability.
This approach comes with several advantages:
- Faster and cheaper transactions due to the efficiency of zero-knowledge proofs.
- Seamless interoperability with other ZK Stack-based chains.
- Shared security by using Ethereum as the final settlement layer.
- Developer-friendly environment, allowing DApps to integrate with Abstract while maintaining EVM compatibility.
At its core, Abstract is a ZK rollup, meaning that transactions are executed off-chain, batched together, and verified on Ethereum using zero-knowledge validity proofs. This ensures strong security guarantees without requiring every transaction to be individually re-executed on L1.
To better understand Abstract’s architecture, we will explore:
- ZK Stack Integration – How Abstract leverages ZKsync’s modular framework.
- Key ZKsync Components – The shared infrastructure Abstract utilizes.
- Transaction Life Cycle – The process of submitting and finalizing transactions.
- Native Account Abstraction – The benefits of smart contract-based accounts.
- Smart Contract Wallets & Paymasters – How Abstract enables gas sponsorship and seamless user interactions.
By the end of this section, you’ll understand how Abstract operates under the hood and what makes it distinct from other L2 solutions.
ZK Stack Integration
The ZK Stack is an open-source framework designed to simplify the creation of ZK rollups. Known as ZK Chains, layer-2 networks achieve scalability by using zero-knowledge proofs. Abstract is one such ZK rollup, leveraging the ZK Stack to reduce development complexity while ensuring high security, modularity, and interoperability with other ZK-powered chains.
Purpose of ZK Stack
The ZK Stack is a foundational framework that streamlines the development of scalable L2 chains. Instead of building a new rollup infrastructure, chains using the ZK Stack inherit core components from ZKsync, significantly reducing technical overhead while maintaining Ethereum’s security guarantees.
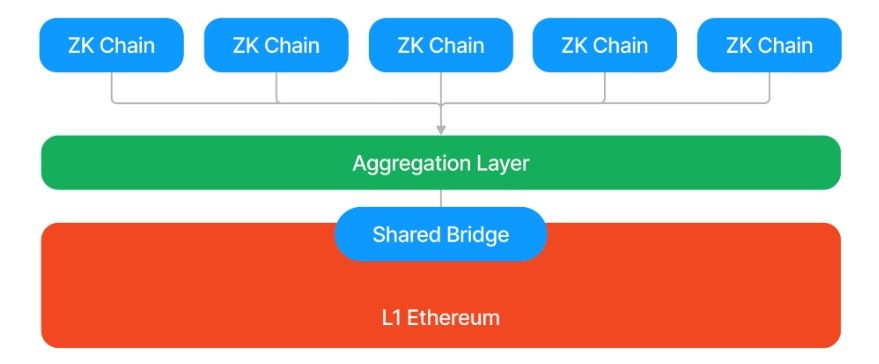 Abstract is a ZKsync’s Components For Interoperability And Settlement on Ethereum | Image via ZKsync
Abstract is a ZKsync’s Components For Interoperability And Settlement on Ethereum | Image via ZKsyncZK Chains & Interoperability
One of the standout features of the ZK Stack is the ability to create ZK Chains—independent yet interconnected and parallel instances of zkEVM rollups that achieve consensus and finality on Ethereum. These chains are linked via Hyperbridges, allowing for atomic interoperability between them. This means that transactions across ZK-powered chains can settle instantly without relying on traditional bridges that introduce security risks.
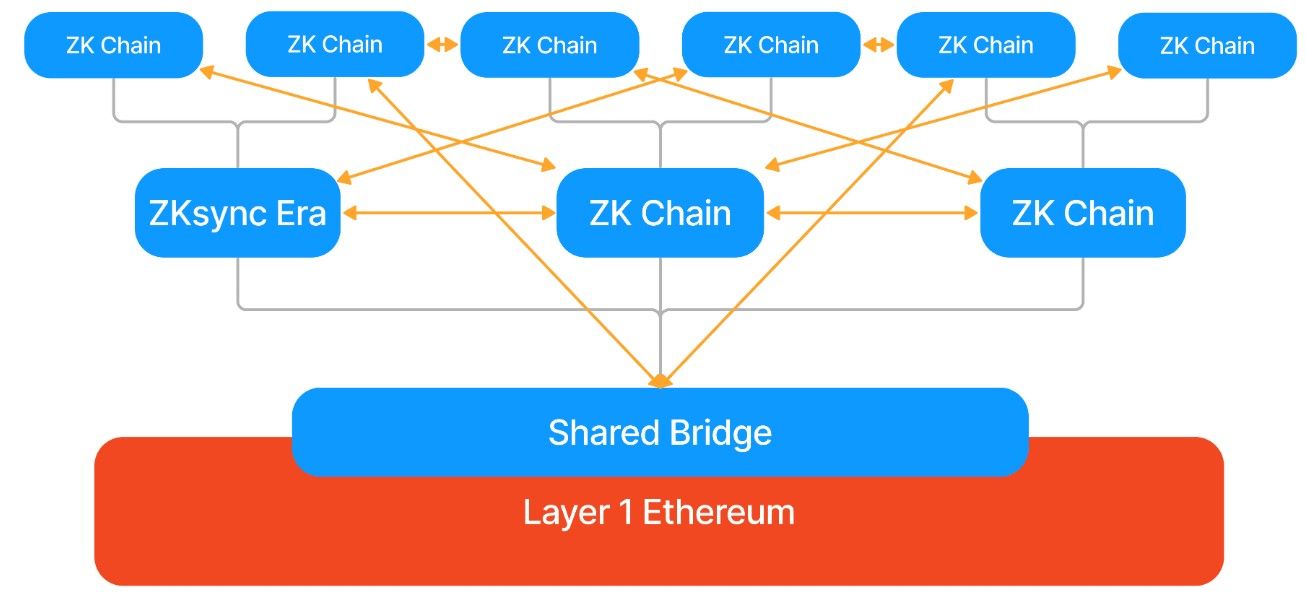 Hyperbridges Allow Seamless Interoperability Between ZK Chains (like Abstract) | Image via ZKsync
Hyperbridges Allow Seamless Interoperability Between ZK Chains (like Abstract) | Image via ZKsynczkEVM Engine: The Core of the ZK Stack
At the heart of the ZK Stack is the zkEVM (ZKsync Virtual Machine) engine, which ensures that all ZK Chains within the network execute transactions under shared security and compatibility standards. Any ZK Stack chain must utilize this zkEVM engine to be considered a fully interoperable and trust-minimized rollup. Abstract, being built with the ZK Stack, is an instance of zkEVM optimized for ZK proofs, ensuring seamless compatibility with ZKsync’s broader network.
Modularity & Customization
One of the defining attributes of the ZK Stack is its modularity. Developers can selectively integrate components from the stack while building custom solutions where necessary. However, the zkEVM engine is mandatory, as it serves as the fundamental execution environment that maintains compatibility and security across all ZK Chains.
Key ZK Stack Components Used by Abstract
Abstract utilizes several critical ZK Stack components, including:
- zkEVM – The execution environment that ensures full EVM compatibility while leveraging zero-knowledge proofs for scalability and security.
- Sequencer – Responsible for executing L2 transactions, constructing blocks, and batching them for submission to Ethereum.
- Prover – Generates zero-knowledge proofs off-chain, cryptographically validating batches of L2 transactions.
- Verifier – An on-chain component deployed on Ethereum that verifies the correctness of proofs submitted by the prover.
- Data Availability – While not explicitly named as a separate component, Abstract adheres to Ethereum’s data availability principles, publishing state diffs (L2 block state data) to Ethereum. This ensures trustless verification while aligning with Ethereum’s post-Pectra upgrade roadmap.
Why Abstract Uses the ZK Stack
By leveraging the ZK Stack, Abstract inherits Ethereum’s security while achieving scalability for consumer applications. The modular rollup design ensures flexibility, while zkEVM integration guarantees seamless interaction with Ethereum and other ZK Chains. Abstract is a part of an evolving network of interoperable ZK-powered ecosystems.
Abstract Transaction Life Cycle
The transaction life cycle on Abstract defines how transactions move through the Layer 2 network and are ultimately settled on Ethereum (L1). The process ensures fast execution on L2 while maintaining Ethereum’s security guarantees through zero-knowledge proofs.
The cycle consists of three main stages:
1. Processing on Abstract (L2 Execution)
- When a user submits a transaction to the Abstract network, it enters the transaction mempool, a waiting area, before processing.
- The sequencer picks up transactions, performs preliminary validity checks, and executes them if they are approved. The user receives a soft confirmation almost instantly.
- Once processed, the sequencer aggregates transactions into a block. Multiple blocks are then grouped into batches prepared for submission to Ethereum.
2. Sending to Ethereum (L1 Commitment & Data Availability)
- Instead of committing each batch separately, Abstract bundles multiple L2 batches into a single transaction on Ethereum to optimize efficiency and reduce costs.
- Following EIP-4844, these batches are submitted to Ethereum as blobs. This approach ensures data availability while lowering costs compared to traditional call data storage methods. To understand EIP-4844, consider reading the Ethereum Innovations article.
3. Validation and Finality (ZK Proof Verification on Ethereum)
- Once L2 batches are committed, a zero-knowledge proof (ZK-SNARK) is generated off-chain by the prover to validate all transactions within the batch.
- The L1 rollup contract on Ethereum receives this proof, where the on-chain verifier checks its validity.
- Since the ZK proof cryptographically guarantees correctness, Ethereum does not need to re-execute every transaction. This drastically reduces gas costs while ensuring security.
- Once the proof is verified, the Abstract L2 state is considered finalized, making the transactions irreversible and fully secured by Ethereum.
Abstract’s transaction flow combines the speed of L2 execution with Ethereum’s finality guarantees, making it a highly efficient and scalable rollup. By leveraging ZK proofs and EIP-4844 blobs, Abstract ensures that transactions remain both cost-effective and trustless, reinforcing its consumer-friendly vision while maintaining Ethereum’s core principles of security and decentralization.
Native Account Abstraction
In Ethereum’s original design, users interact with the network through Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs)—wallets controlled by private keys. EOAs, like MetaMask or Ledger wallets, allow users to sign transactions, but they come with limitations:
- No built-in recovery mechanisms—losing your private key means losing access to funds.
- Rigid transaction execution—EOAs must always pay gas fees in ETH, limiting flexibility.
- No programmable logic—EOAs cannot enforce spending rules or automated security measures.
To address these limitations, Ethereum introduced EIP-4337, which laid the foundation for account abstraction (AA). This proposal enables smart contract wallets—called smart accounts—to function like EOAs while allowing for custom transaction validation, flexible gas payments, and enhanced security mechanisms.
However, Ethereum still maintains a hybrid system in which EOAs and smart contract accounts coexist. Thus, not all wallets can leverage account abstraction features without additional setup.
Native Account Abstraction on Abstract
Unlike Ethereum, Abstract fully embraces account abstraction from the start. By default, every account on Abstract is a smart contract account, ensuring that all users—regardless of their wallet—benefit from the flexibility and security of account abstraction.
Abstract achieves this by implementing the IAccount interface, standardizing how accounts interact with the network. As a result:
- Every wallet functions as a smart contract wallet, whether originally created as an EOA-style wallet (e.g., MetaMask) or a dedicated smart contract wallet.
- Users interacting via traditional wallets (like MetaMask) are seamlessly connected to a smart contract account that follows the IAccount interface.
- All transactions undergo smart contract-based validation, allowing programmable spending rules, social recovery options, and multi-signature approvals at the account level.
By making account abstraction native, Abstract removes the friction users face on Ethereum when using smart contract wallets, creating a more intuitive and flexible blockchain experience.
Paymaster: Enabling Gas Sponsorship for Users
One of the most useful features enabled by account abstraction is Paymasters—smart contracts that allow one entity to sponsor gas fees for another address’s transactions.
On Ethereum, users must always hold ETH to pay for gas fees, creating a poor onboarding experience for new users. Abstract solves this by integrating native Paymaster support, allowing developers to build applications where:
- Gas fees can be covered by DApps or third parties, improving accessibility.
- Users can pay gas in ERC-20 tokens rather than ETH, making transactions more flexible.
- Subscription-based or freemium models can be implemented, where projects cover gas costs for new users or incentivized activities.
By embedding Paymaster functionality at the protocol level, Abstract enhances user experience and adoption, making it easier for non-crypto-native users to interact with Web3 applications.
Why This Feature Matters
Abstract provides a seamless and user-friendly alternative to Ethereum’s traditional account model by making account abstraction the default. Smart contract wallets, flexible gas payment options, and Paymasters work together to make transactions easier, removing many hurdles that slow down mass adoption.
With these features, Abstract aligns with its vision of creating a consumer-friendly blockchain experience that prioritizes usability without sacrificing security or decentralization.
Abstract Ecosystem
Abstract’s guiding ethos—Consumer Crypto—shapes its approach to blockchain development. Unlike general-purpose Layer-2s that attempt to be one-size-fits-all, Abstract focuses on creating a tailored experience for a specific audience. The idea is simple: consumer adoption in crypto won’t come from broad, generalized networks but curated ecosystems built around engaging and high-utility applications. Abstract envisions itself as the chain that delivers this experience by acting as a premier destination rather than just another infrastructure layer.
This philosophy drives Abstract’s ecosystem development, prioritizing gaming, social, entertainment, and trading. The network isn’t merely a platform for decentralized applications—it’s an ecosystem built to support sticky, consumer-facing products that incentivize continuous user interaction.
By leveraging its ZK rollup architecture, native account abstraction, and paymaster support, Abstract streamlines user onboarding, making blockchain interactions feel seamless. In practice, this means Web3-native games, gamified finance, digital collectibles, and interactive social hubs can all thrive within a cohesive framework designed for end users rather than just developers.
 Some Featured Abstract Applications | Image via Abstract
Some Featured Abstract Applications | Image via AbstractLet’s break down some of the most prominent applications shaping Abstract’s consumer-driven network, highlighting their role in making Abstract’s vision a reality.
Gaming Applications:
- Pudgy World: Pudgy World is the official gaming platform of the Pudgy Penguins NFT project. Players can create their own "forever Penguin," engage in mini-games, embark on quests, and explore various adventures within the game.
- Gigaverse: An epic on-chain RPG powered by Proof of Play, Gigaverse allows players to upgrade characters, participate in both PvE and PvP modes, and collect rare items.
- Onchain Heroes: Onchain Heroes is an idle RPG integrating on-chain financial mechanics, offering players a fully on-chain gaming experience.
Trading & Financial Applications:
- Magic Eden: A leading NFT marketplace, Magic Eden has expanded its presence to the Abstract network, allowing users to buy, sell, and discover Abstract NFTs from top creators.
- Pandora Swap: Serving as Abstract's decentralized finance (DeFi) suite, Pandora Swap offers decentralized swapping solutions, providing users with an advanced DeFi experience featuring low trading fees.
- Relay: Relay is a decentralized exchange (DEX) offering instant bridging features, enhancing interoperability within the blockchain ecosystem.
Social Applications:
- Gacha: Gacha is a consumer-focused platform that simplifies the crypto experience by abstracting its complexities through engaging on-chain activities.
- Alphabot: As a Web3 raffle hub, Alphabot enables users to discover new blockchain projects and participate in allocation giveaways, enhancing community involvement.
- Hueston: Hueston is a community rewards and launch platform that empowers creators and brands to engage with their audiences through on-chain interactions.
- Rey: As a decentralized attention portal, Rey allows brands and creators to interact directly on-chain, ensuring transparent and equitable attention metrics.
Abstract Global Wallet (AGW)
The Abstract Global Wallet (AGW) is the backbone of user interactions within the Abstract ecosystem. Designed as a cross-application smart contract wallet, AGW allows users to seamlessly engage with any application built on Abstract while benefiting from the network’s native account abstraction. Instead of juggling multiple wallets or worrying about complex onboarding, users can easily set up a single account and interact across the ecosystem.
Seamless Onboarding with Familiar Login Methods
One of AGW’s core strengths is its frictionless user onboarding. Unlike traditional crypto wallets that require seed phrases and manual private key management, AGW enables sign-ups using:
- Social accounts (Google, Twitter, etc.)
- Passkeys
- Existing wallets like MetaMask
Once set up, users retain a single account that grants them access to all applications on Abstract, eliminating the need for separate wallet setups across different DApps.
 Here’s an AGW I created with one click using a Metamask Address | Image via Abstract
Here’s an AGW I created with one click using a Metamask Address | Image via AbstractThe Mechanics of AGW: Smart Contract Wallets from the Start
AGW is built on native account abstraction, meaning all wallets within the Abstract ecosystem are smart contract wallets by default. This structure provides enhanced security and flexibility compared to externally owned accounts (EOAs).
The wallet creation process consists of two steps:
- EOA Creation: When a user signs up, an Externally Owned Account (EOA) is automatically created behind the scenes.
- Smart Contract Wallet Deployment: A smart contract wallet is generated, and the EOA is assigned as an approved signer. This structure allows for recovery mechanisms, spending limits, and flexible transaction approvals—features impossible with EOAs alone.
Interaction with Applications
Users don’t need to create an AGW on an Abstract website manually. Instead, any Abstract-integrated application can initiate wallet creation during the login process. Once connected, applications can request user approvals, and transactions are executed directly from the smart contract wallet.
Another key feature of AGW is support for Paymasters, which allows applications or third parties to sponsor gas fees. This feature removes one of the most significant onboarding barriers for new users, making gas-free transactions possible in certain use cases.
Why AGW Matters
The Abstract Global Wallet is more than just a wallet—it’s a user-centric innovation that enhances security, flexibility, and ease of use. By leveraging native account abstraction, AGW simplifies blockchain interactions, making Abstract’s ecosystem more accessible and consumer-friendly. Whether gaming, trading, or engaging in social applications, users can interact with DApps effortlessly without the typical complexities of Web3 wallets.
Final Thoughts - Abstract Future Prospects
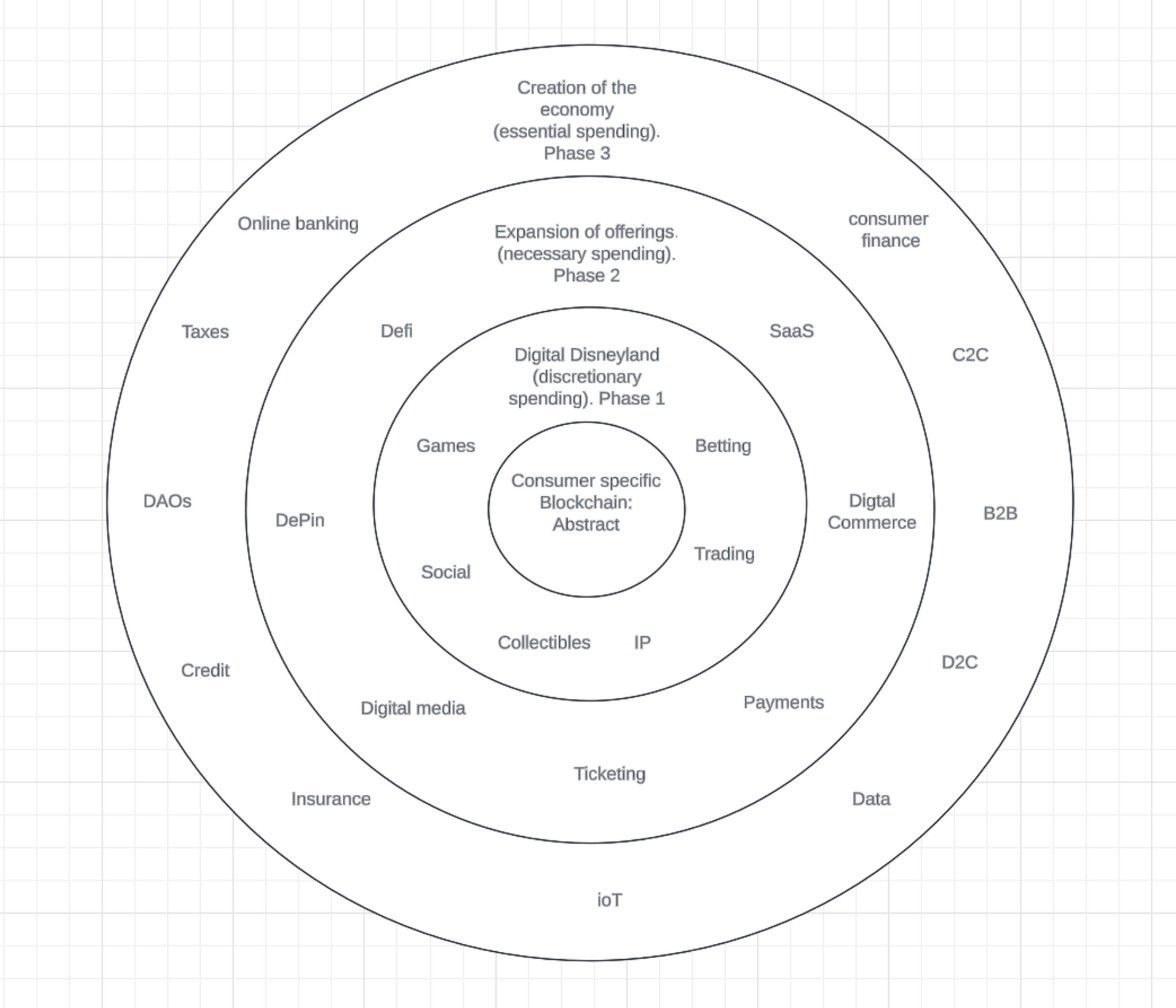
With the foundation of Abstract’s Consumer Crypto vision firmly in place, the network has successfully built an ecosystem of gaming, social, and trading applications—the first phase of its roadmap. The second phase, focused on expanding utility-driven offerings, has also seen significant progress, with DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, digital media applications, and commerce integrations flourishing. Now, the next stage of growth is poised to emerge from the outermost layers of the Abstract ecosystem, where essential financial and infrastructural services take shape.
Bridging into Consumer Finance & Economic Infrastructure
As Abstract evolves, the next wave of innovation will likely come from consumer finance and infrastructure-driven applications, supporting more traditional financial needs while maintaining its consumer-first approach. Key areas of development may include:
- On-Chain Credit & Lending – The abstracted finance model could extend to real-world borrowing and lending, where on-chain credit scoring enables trustless lending without traditional banking intermediaries.
- Insurance & Risk Management – Smart contract-based insurance solutions could become a significant part of Abstract’s ecosystem, allowing users to access decentralized protection services for their assets and activities.
- Banking & Payments – Seamlessly integrating on-chain banking features, including stablecoin-backed digital banking, direct merchant payments, and automated tax compliance, could push Abstract into mainstream financial adoption.
From Entertainment to Essential Services
The first wave of Abstract’s success stemmed from discretionary spending applications like gaming and collectibles. The next step is fostering an economy of essential services that cater to more sustainable, long-term user engagement.
- SaaS & Business Solutions – As Abstract continues to refine its account abstraction and payment flows, we could see B2B SaaS applications emerge, allowing Web3-native businesses to access subscription models, workflow automation, and data analytics services.
- IoT & Real-World Integrations – With the increasing role of DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks), Abstract could support applications integrating blockchain with IoT devices, enabling secure on-chain data management, automated micropayments for connected devices, and decentralized identity solutions.
- DAO-Governed Consumer Networks – Community-driven governance could play a larger role in Abstract’s future. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) manage consumer-driven economies for services like crowdfunding, peer-to-peer finance, and cooperative business models.
A Path Toward a Fully Digital Economy
Abstract’s success in building a sticky consumer ecosystem is a strong signal that it can transition into a broader economic network. The logical progression is moving from spending on entertainment and digital assets to fully integrating financial primitives, commerce, and governance structures. With its existing technical advantages—native account abstraction, ZK security, and seamless onboarding mechanisms—Abstract is well-positioned to scale into a blockchain-native digital economy.
Over the next few years, we may see Abstract cement itself as the consumer hub of Web3, providing both engaging digital experiences and essential financial services in a way that traditional blockchain networks have struggled to achieve.





