The holy grail for crypto isn't the technology itself — it's the integration of that technology into everyday life.
Let's face it: the reality is that the vast majority of people aren’t interested in how a blockchain works — they care about how it impacts their lives. For instance, most people don’t understand the inner workings of the Internet, but that hasn't stopped you and me from using it for everything from shopping to communicating and banking. We aren’t concerned with how data packets travel across networks or the complexities of web protocols — we just want to be able to order groceries with a few taps on our phones or stay connected with loved ones instantly.
In that same vein, people won't adopt blockchain because it's innovative; they'll adopt it because it makes their lives easier. Whether it's enabling fast, low-cost international money transfers or providing access to financial services in regions without a reliable banking infrastructure, people care about the benefits, not the mechanics.
In this article, we’ll explore the multifaceted aspects of cryptocurrency adoption, focusing on how blockchain technology is transitioning from a niche innovation to a mainstream tool. Additionally, we’ll touch on solutions aimed at making blockchain invisible to users, and feature expert insights on the challenges and opportunities shaping crypto's future.
What is Crypto Adoption?
Adoption is one of the most talked-about topics in the cryptosphere, yet it remains somewhat elusive. Simply put, crypto adoption is the process through which digital currencies, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, move from niche assets to mainstream tools of value exchange, investment and utility.
The concept of crypto adoption is tied to the question of why and how these assets are used.
Individuals
For individuals, crypto adoption can take many forms. Some start by buying small amounts of cryptocurrency, perhaps as a curiosity or a speculative investment, hoping to benefit from potential price increases. But for many people, this interest develops into deeper engagement as they explore other uses, like using crypto for peer-to-peer transactions, paying for goods and services or even engaging with decentralized applications. Each of these activities indicates a level of adoption that goes beyond mere investment.
On a deeper level, individual adoption of crypto often stems from a desire for financial independence. Cryptocurrencies are free from the constraints of traditional financial systems. A prime example are credit scores, which often limit access to loans and financial services. In decentralized finance (DeFi), for example, users can borrow funds by using crypto assets as collateral, regardless of their credit history.
Additionally, crypto provides a sense of ownership and control. In traditional banking, individuals are dependent on institutions, with funds subject to oversight and potential restrictions. With crypto, individuals hold private keys, which grant them direct ownership over their assets. This control over one's own funds represents a significant shift from traditional finance.
Businesses
For businesses, blockchain technology presents operational efficiencies and competitive advantages. However, the journey toward widespread adoption involves overcoming hurdles like regulatory uncertainty, technological limitations and cybersecurity risks.
The Current State of Crypto Adoption
In its 2024 Geography of Cryptocurrency Report, Chainalysis reveals that Central and Southern Asia and Oceania (CSAO) are leading global crypto adoption, with India, Indonesia, and the Philippines ranking highly.
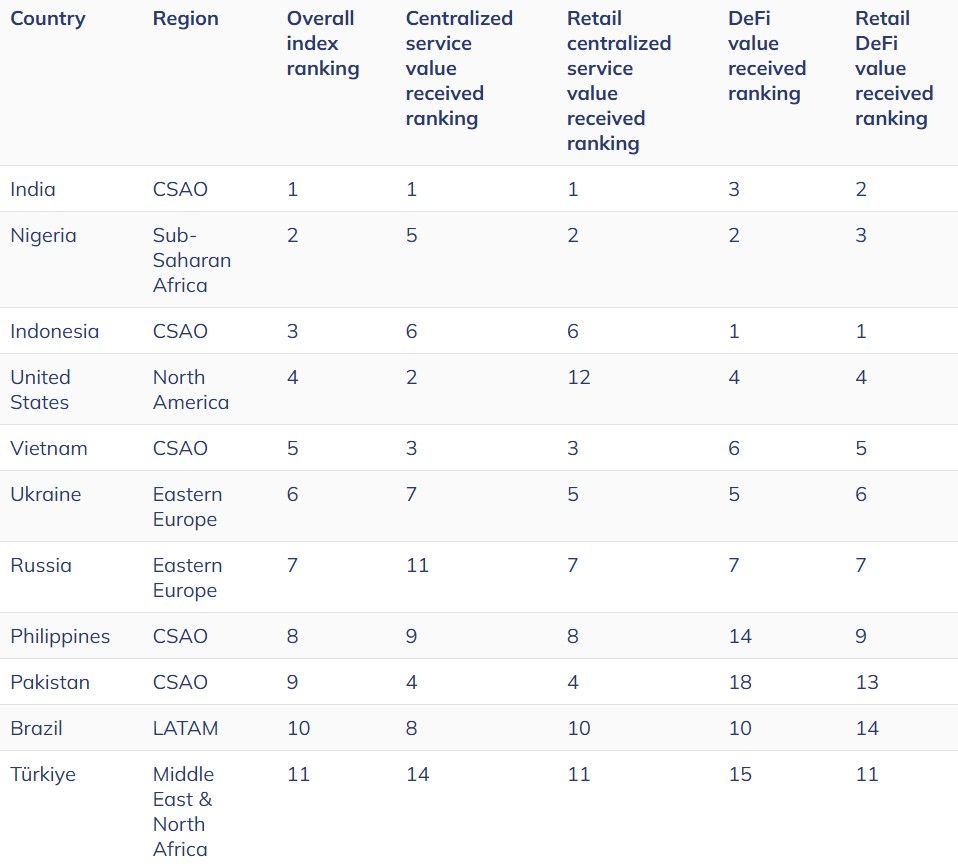 Central and Southern Asia and Oceania are Leading Global Crypto Adoption. Image via Chainalysis
Central and Southern Asia and Oceania are Leading Global Crypto Adoption. Image via ChainalysisThe report's findings, based on transaction data and web traffic across 151 countries, highlight the rise in adoption across various income levels, with significant growth observed in emerging markets and middle-income countries. DeFi activity and retail crypto usage, especially in regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, and Eastern Europe, are surging, reflecting broader trends toward practical, real-world applications like remittances and small investments.
The report indicates that while North America and Western Europe have seen institutional adoption grow — especially after the U.S. Bitcoin ETF launch — retail adoption remains more robust in developing regions.
Meanwhile, a study by Security.org revealed significant growth in cryptocurrency ownership and enthusiasm in the U.S. As of early 2024, crypto ownership among Americans reached 40%, up from 30% in 2023, with over 93 million adults reportedly owning digital assets. Interest in Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin, and Cardano dominated. Note: This survey of over 1,500 Americans was conducted before the SEC's approval of the Bitcoin ETF.
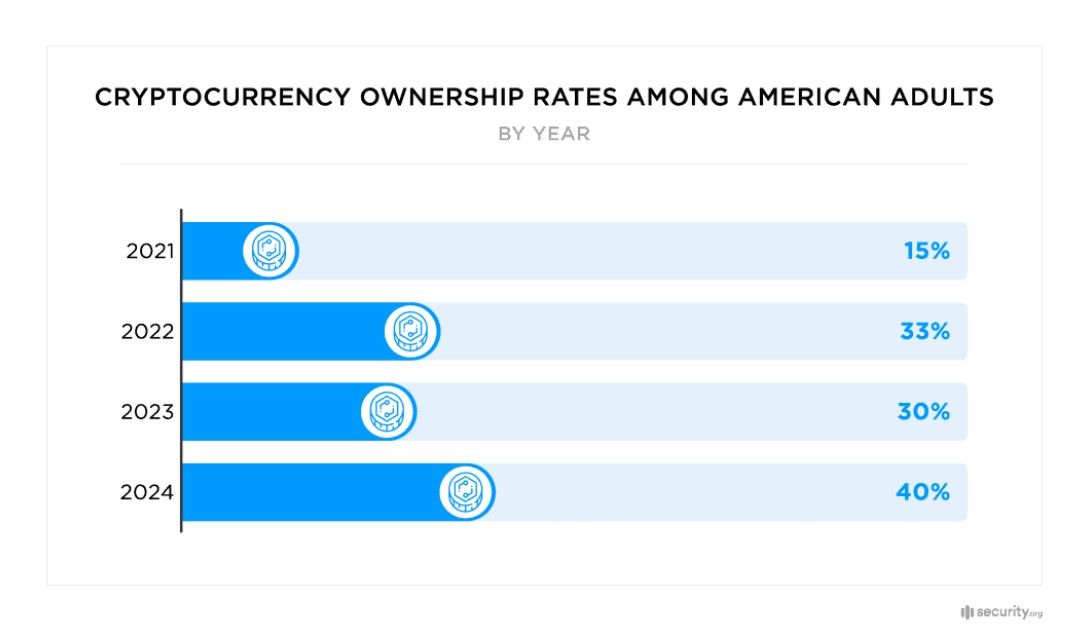 A Survey Revealed Significant Growth in Cryptocurrency Ownership and Enthusiasm in the US. Image via Security.org
A Survey Revealed Significant Growth in Cryptocurrency Ownership and Enthusiasm in the US. Image via Security.orgWomen's crypto ownership notably surged from 18% to 29%, attributed to prominent figures like crypto journalist Laura Shin and Ark Invest CEO Cathie Wood, who advocate for blockchain investment.
According to Triple A, a crypto payments company, adoption is steadily growing worldwide, with an estimated 6.8% global ownership as of 2024 — that's over 560 million people. Demographic data shows 61% of crypto owners are male, and 34% are aged 25 to 34. Additionally, 65% of users are interested in making payments with cryptocurrency, highlighting its potential for further integration into everyday transactions.
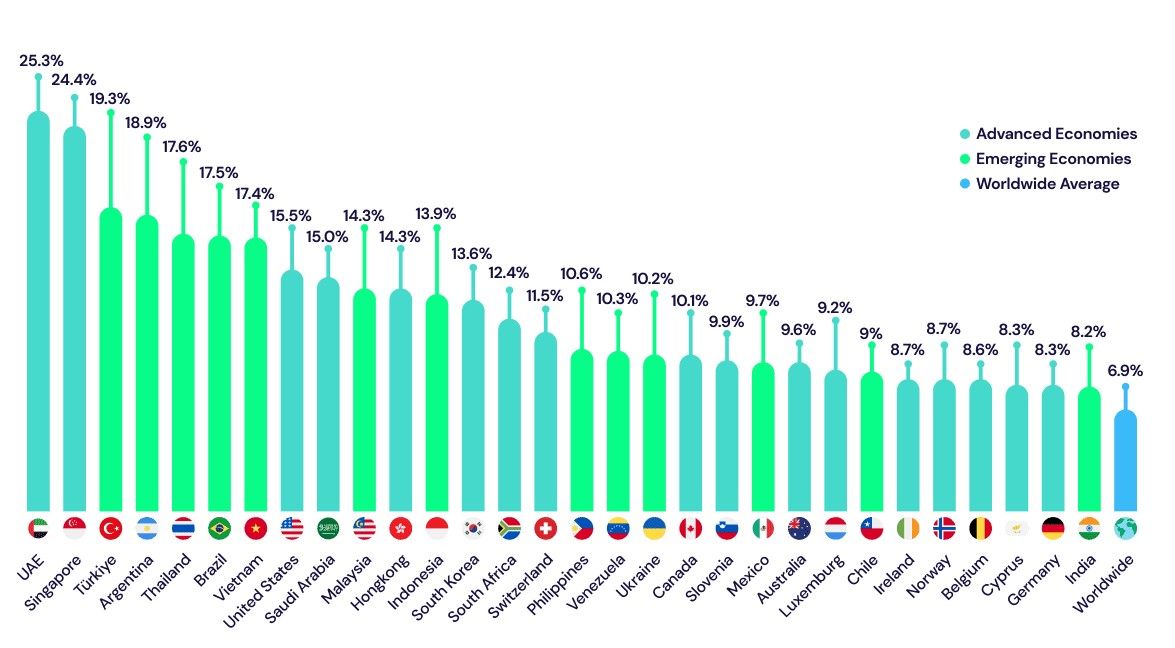 Global Crypto Adoption Stood At 6.8% as of 2024. Image via Triple A
Global Crypto Adoption Stood At 6.8% as of 2024. Image via Triple ACountry-specific data reveals varying adoption rates, with Vietnam leading at 21.19%, followed by the U.S. at 15.56%. The rapid growth of crypto ownership has a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 99%, outpacing traditional payment methods, which grew by 8% between 2018 and 2023, Triple A said.
Conclusion
It's clear: The global adoption of cryptocurrency is accelerating at an unprecedented rate, driven by diverse factors across regions and demographics.
Emerging markets in Central and Southern Asia, Oceania, and regions like Latin America and Sub-Saharan Africa are leading in retail crypto usage, showing the practical role of digital assets in remittances and micro-investments. Meanwhile, institutional interest in North America and Europe has grown, particularly following the U.S. Bitcoin ETF launch, indicating rising mainstream acceptance. The significant increase in U.S. ownership, with notable growth among women, further highlights crypto’s expanding appeal.
Overall, with global ownership now at 6.8% and growth outpacing traditional payment methods, cryptocurrency is becoming more integrated into daily life and investment portfolios worldwide.
The Importance of Use Cases
As we've seen with other technologies, it’s not the complexity or novelty that captures public interest but rather the tangible ways it can solve problems and create value.
Take smartphones, for instance. Early mobile phones were remarkable for making wireless calls, yet they didn't become universally adopted until smartphones brought together multiple functions in one device, from browsing the internet to photography and GPS navigation. People embraced them not for the tech, but for the real-world convenience they offered.
Real-World Applications: Successful Use Cases Driving Adoption
Let's explore the real-world use cases of blockchain technology:
Banking and Finance
In the banking and finance sector, blockchain is being adopted in two main ways: by traditional financial institutions and through Web3-native decentralized finance (DeFi) services.
Traditional Financial Institutions Adopting Blockchain: Many banks are leveraging blockchain technology to improve operational efficiency and ensure secure transactions. A prime example is JPMorgan's creation of JPM Coin, which facilitates instantaneous payment transfers. Similarly, HSBC has utilized blockchain to streamline trade finance, cutting down the time required for document processing. In a groundbreaking move in 2023, JPMorgan executed the first live blockchain-based collateral settlement involving BlackRock and Barclays Bank. Such applications underline how blockchain can enhance operational workflows, mitigate fraud, and lower costs in traditional banking systems.
Web3-Native DeFi Banking and Finance Services: Platforms such as MakerDAO and Compound provide decentralized lending and borrowing solutions without the need for intermediaries. Users can earn interest, secure loans, and trade assets within a trustless framework. By employing smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum, these DeFi applications offer an accessible and flexible alternative to conventional finance.
Healthcare
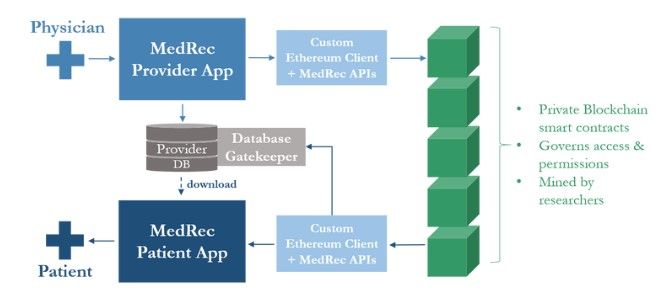 MedRed Leveraged Ethereum Private Smart Contracts to Share Medical Data. Image via Viral Communications
MedRed Leveraged Ethereum Private Smart Contracts to Share Medical Data. Image via Viral CommunicationsBlockchain technology is redefining the healthcare industry through its core characteristics of security, immutability, and decentralization.
- Adoption by Traditional Healthcare Institutions: Traditional healthcare providers are increasingly turning to blockchain to bolster data security, safeguard patient privacy, and enhance process efficiencies. For instance, Estonia has adopted blockchain technology to secure and manage patient health records, ensuring that any alterations are transparent and verifiable. This use of an immutable ledger significantly improves data integrity and curbs fraud.
- Web3-Native Healthcare Services: In the realm of Web3, decentralized platforms like MedRec are emerging to manage medical records, empowering patients with control over their own health information. This facilitates secure and efficient sharing between patients and providers, enhancing care coordination and patient empowerment.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain sector is undergoing a transformation, thanks to blockchain technology's capabilities in enhancing transparency, traceability, and security.
- Improving Transparency and Traceability: With blockchain’s transparent ledger, all participants in the supply chain can access transaction histories, which is crucial for tracing products from their source to the final customer. For example, Walmart employs blockchain to trace food products' origins, drastically reducing the time taken to track produce from farms to stores, thus ensuring enhanced food safety.
- Strengthening Security and Immutability: The unchangeable nature of blockchain records enhances the security of supply chain data, making it resistant to tampering and fraud. De Beers, the renowned diamond company, uses blockchain to trace the journey of diamonds from mines to retailers, guaranteeing that they are sourced ethically.
- Boosting Efficiency: By minimizing reliance on paper-based processes, blockchain streamlines supply chain operations, making them more cost-effective. Maersk has collaborated with IBM to optimize its shipping processes using blockchain, reducing paperwork and improving efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence
 Use of Blockchain in AI | Image via SingularityNET
Use of Blockchain in AI | Image via SingularityNETThe intersection of blockchain technology and artificial intelligence (AI) is fostering new solutions in both traditional sectors and Web3 initiatives.
- Traditional Adoption of Blockchain in AI: Many organizations are combining AI with blockchain to enhance data integrity and security. For instance, healthcare providers utilize AI for patient diagnosis while employing blockchain to secure patient data management, ensuring privacy and reliability in AI analyses. In the finance sector, banks leverage AI for risk assessments and predictive analytics, using blockchain to secure transaction data.
- Web3-Native AI Initiatives: Within the Web3 ecosystem, decentralized AI projects like SingularityNET are emerging. These platforms use blockchain to democratize access to data and AI models, allowing users to create, share, and monetize AI services.
Also, check out our top picks for the best crypto AI projects.
Personal Identity Security
Blockchain technology is proving instrumental in enhancing personal identity security through its decentralization, immutability and encryption features.
- Decentralization and User Control: By decentralizing identity management, blockchain empowers individuals to control their personal data, contrasting with traditional systems that store identity information in centralized locations susceptible to breaches.
- Immutability and Trustworthiness: The unchangeable nature of blockchain records establishes a reliable identity verification process, crucial for various applications such as voting and benefits distribution.
Practical Implementations:
- Soulbound Tokens: These non-transferable tokens represent personal credentials and achievements, providing a reliable measure of identity.
- Proof of Personhood: A blockchain-based system that offers unique and verifiable digital identities, preventing multiple identities for one individual.
- Polygon ID: A self-sovereign identity solution built on the Polygon blockchain, enabling users to manage and control their identity data.
Real Estate
 You Can Buy Vitual Land in The Sandbox. Image via Cointribune
You Can Buy Vitual Land in The Sandbox. Image via CointribuneThe real estate sector is increasingly adopting blockchain technology, with both traditional and Web3-native projects leveraging its advantages.
- Blockchain in Traditional Real Estate: Conventional real estate markets are using blockchain to facilitate smoother transactions and improve record-keeping. Tokenizing property titles ensures secure, transparent records and reduces fraud. For instance, Propy enables global real estate transactions through a blockchain platform, minimizing paperwork and enhancing efficiency.
- Innovations in Web3 Real Estate: Beyond improving traditional transactions, blockchain is creating new opportunities in the realm of virtual real estate. Platforms such as Decentraland and The Sandbox allow users to buy, sell, and develop virtual land, opening up new avenues for digital experiences and assets.
Digital Media and Entertainment
Blockchain technology is significantly reshaping the digital media and entertainment industries, with both traditional and Web3-native players harnessing its capabilities.
- Usage by Traditional Media Companies: Traditional media firms are exploring blockchain to enhance content monetization and rights management. This technology creates immutable records for copyrights, ensuring that creators are compensated fairly. For example, KodakOne provides a platform to manage image rights for photographers, facilitating transparent revenue distribution.
- Emerging Web3 Entertainment Platforms: Decentralized platforms enable creators to monetize their work directly, bypassing intermediaries. Audius, for instance, offers a decentralized music streaming service, allowing artists greater control over their distribution and direct engagement with fans. Additionally, blockchain-based games like Axie Infinity have introduced economic models where players can earn cryptocurrency and trade in-game assets as NFTs.
Tokenization of Real-World Assets
The tokenization of real-world assets (RWAs) through blockchain technology is gaining traction, capitalizing on features like immutability, transparency, and fractional ownership.
- Immutability and Transparency Benefits: Public blockchains guarantee that once an asset is tokenized, its ownership and transaction records remain immutable and easily verifiable. This transparency enhances trust and reduces the likelihood of fraud.
- Facilitating Fractional Ownership: Tokenization allows for fractional ownership of assets, making investments more accessible to a wider range of investors. This significantly lowers entry barriers for assets such as real estate and art.
Illustrative Examples:
- Real Estate Tokenization: Platforms like RealT and Propy allow investors to purchase fractional ownership of properties, democratizing access to real estate investments.
- Art and Collectibles: Platforms like Maecenas enable the tokenization of artworks and collectibles, allowing investors to hold shares of valuable pieces.
- Commodities: Companies like Paxos are tokenizing commodities like gold, providing a digital representation that can be traded on blockchain networks.
Interested to know more? Our best RWA projects article covers how these companies are setting new standards for financial security, efficiency and inclusivity.
Making Sense of Blockchain: Account and Chain Abstraction
The complexity of crypto and blockchain keeps many would-be users at bay. As a result, the industry is actively trying to devise ways of making the blockchain aspect invisible to the Average Joe. Chain and account abstraction are two solutions in that direction.
Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction is a concept that enhances interactions between different blockchain networks through cross-chain tools and protocols. It emphasizes that users engage with applications rather than specific blockchains, allowing them to use their accounts flexibly without worrying about the underlying network.
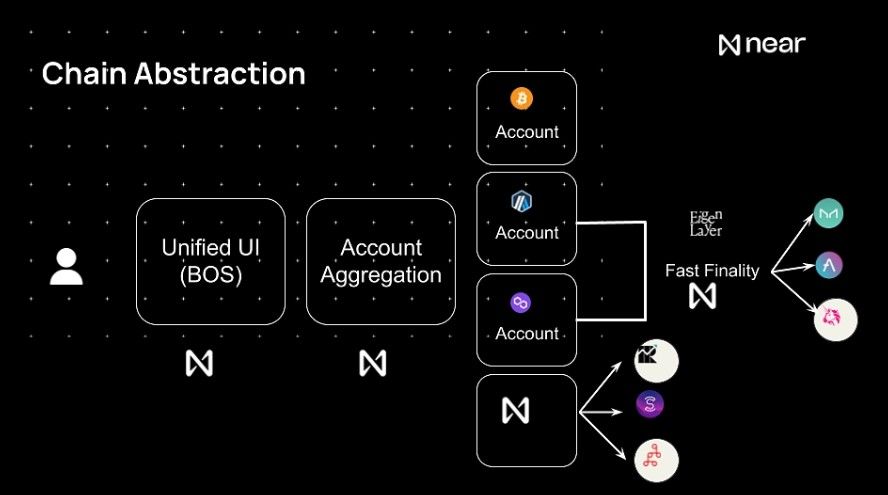 Chain Abstraction Enhances Interactions Between Blockchain Networks. Image via Medium
Chain Abstraction Enhances Interactions Between Blockchain Networks. Image via MediumKey components of chain abstraction include:
- Interoperability: Facilitates seamless interaction between blockchains without needing unique protocols for each.
- Simplified Development: Developers can build applications using a unified interface, simplifying the process.
- Cross-Chain Communication: Enables the transfer of data and value across different blockchain networks, essential for complex decentralized applications.
- Standardization: Establishes standards or protocols that reduce the differences between blockchains, standardizing transactions, smart contracts, and data access.
- Enhanced User Experience: Provides a cohesive interface for users to interact with multiple blockchains without understanding their technical details.
- Layer 2 Solutions and Sidechains: Integrates these technologies to improve scalability and efficiency, making interactions easier.
NEAR Protocol is one project working on chain abstraction. According to The Rollup, there are over 80 such projects.
 Chain Abstraction Market Map. Image via X
Chain Abstraction Market Map. Image via XAccount Abstraction
Account abstraction is a concept aimed at simplifying user interactions with blockchain systems by decoupling account ownership from traditional key-based cryptography. Traditionally, accounts were divided into Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs), controlled by private keys, and contract accounts, which operated under predefined functionalities but lacked ownership. This structure imposed cumbersome transaction processes, requiring users to sign every action individually.
The ethos of account abstraction seeks to enhance user experience and accessibility by allowing arbitrary verification logic to define account control. This shift addresses key barriers to crypto adoption, such as complex user experiences, steep learning curves, and the challenges of self-custody.
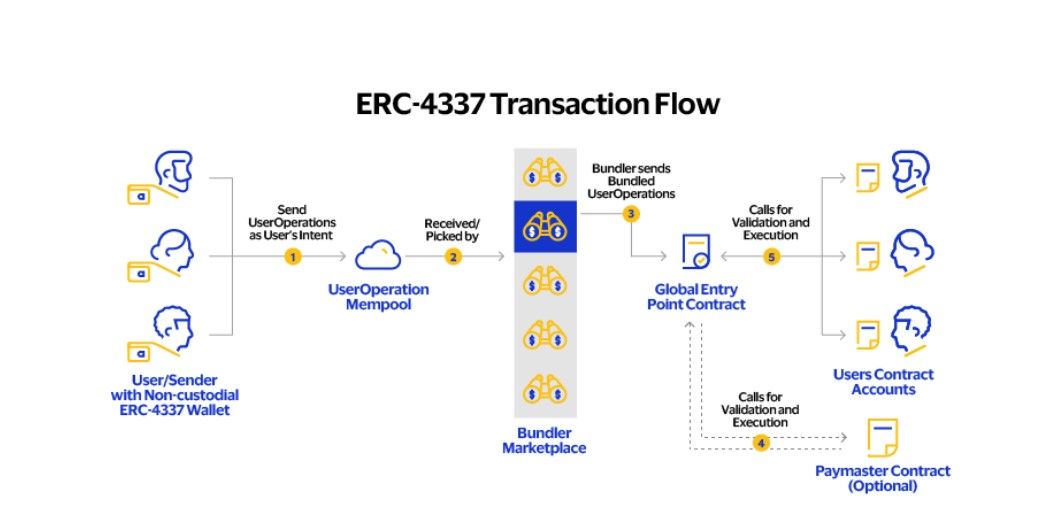 Account Abstraction Aims to Simplify User Interactions With Blockchain Systems. Image via Visa
Account Abstraction Aims to Simplify User Interactions With Blockchain Systems. Image via VisaThe key features of ERC-4337 are:
- Simplified User Experience: Users can authorize transactions using multiple methods, such as biometric verification or digital identities, reducing the reliance on private keys.
- Social Recovery: Users can designate trusted individuals as guardians who can assist in recovering access to accounts, providing a safety net against key loss or theft.
- Gas Abstraction: Users can pay transaction fees using various tokens instead of needing to maintain a specific cryptocurrency balance for gas fees.
- Programmable Security: Smart wallets can implement multi-factor authentication and other advanced security measures, enhancing the protection of user assets.
- Custom Signature Schemes: Users can opt for alternative signature methods, potentially increasing security against emerging threats like quantum computing.
- Batch Transactions: Smart contract wallets can execute multiple operations in a single transaction, streamlining complex actions that would typically require multiple steps.
Account abstraction serves a number of use cases:
- Gas Abstraction with Paymasters: Enables users to pay transaction fees with any ERC-20 token instead of requiring a balance in a specific cryptocurrency, such as ETH. Paymasters can sponsor these fees, enhancing accessibility.
- Social Recovery: Allows users to appoint trusted guardians who can help recover access to their wallet if keys are lost, protecting against theft and user error.
- Dead Man’s Switch: Functions like a digital will, enabling automatic transfer of wallet ownership to a designated account upon specific conditions, such as user inactivity or death.
- Programmable Security: Integrates features like two-factor authentication (2FA) and real-world identity verification, providing customizable security enhancements for wallets.
- Custom Signature Schemes: Supports alternative, potentially quantum-resistant signature schemes, which increases security and future-proofs wallets against emerging threats.
- Batch Transactions: Allows users to execute multiple actions in a single transaction, streamlining complex operations and saving time by automating sequences of actions.
What the Experts Think
As cryptocurrencies gain traction, industry observers see real-world applications and financial innovations as pivotal to the future of crypto adoption.
Al Alof, founder and CEO of the crypto and currency exchange platform ChicksX, and Ethan Keller, president of Dominion, a network of global legal and financial consultants, shared insights with The Coin Bureau on the key drivers and barriers to crypto’s mainstream potential. Both see tremendous promise in crypto’s role in improving financial access and transforming traditional asset ownership.
Real-World Applications Fueling Adoption
Alof identifies the rise of practical crypto applications in areas with limited financial infrastructure as one of the primary drivers of adoption, particularly through stablecoins. He notes their growing popularity in low- and lower-middle-income regions, including Sub-Saharan Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia, where stablecoins offer “an accessible means of transferring value” without the volatility associated with other cryptocurrencies. According to Alof, stablecoins like USDC and USDT have made a measurable impact in these areas, now accounting for approximately 30% of global remittances, as reported by Circle.
DeFi is another significant trend that Alof sees as instrumental in expanding financial access globally. DeFi platforms, which include decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending protocols, allow users to borrow, lend, and trade assets without intermediaries. These platforms are growing in prominence, with some traditional banks and government institutions beginning to support or partner with DeFi initiatives. This, he believes, shows DeFi’s potential as “a viable alternative to traditional financial systems” as more established institutions acknowledge its value.
Tokenization and NFTs: New Frontiers in Asset Ownership
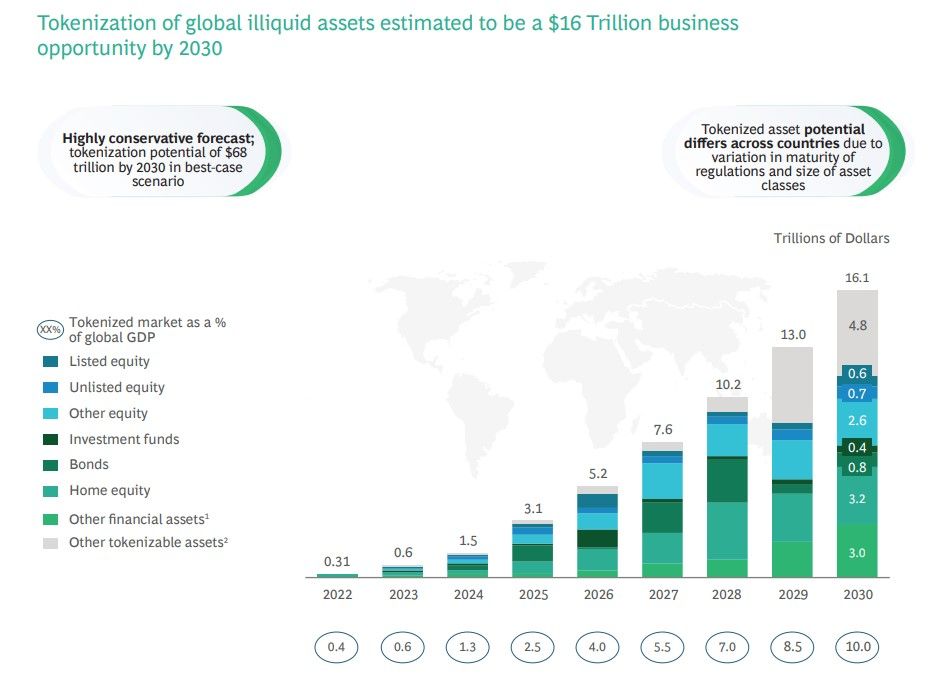 Tokenization of Illiquid Assets Is Estimated to Be a $16 Trillion Business Opportunity by 2030. Image via Boston Consulting Group
Tokenization of Illiquid Assets Is Estimated to Be a $16 Trillion Business Opportunity by 2030. Image via Boston Consulting GroupKeller envisions a powerful role for tokenization in reshaping finance over the next decade. By 2030, tokenizing traditionally illiquid assets could develop into a $16 trillion industry, particularly through applications like securitized mortgages and asset-backed securities. Tokenization offers “immense potential across finance,” he explained, enabling a shift from illiquid to liquid assets, which could bring new efficiencies and accessibility to the financial sector. He also sees tokenization as especially promising for the metaverse and for digital ticketing, areas where it could "revolutionize asset ownership and accessibility."
Keller also points to the growing corporate interest in NFTs and digital asset technologies, noting that “nearly three-quarters of business respondents will explore crypto and digital assets like NFTs or stablecoins” in the coming years. This optimism stems from the positive experiences of early adopters who have integrated digital assets into their operations. “Most CEOs trust crypto,” Keller said, adding that those with hands-on experience tend to be “the most optimistic,” demonstrating the current and future potential of crypto to add value at the corporate level.
Overcoming Perceived Barriers to Adoption
While some, myself included, argue that blockchain’s technical complexity hinders adoption, Alof disagrees, seeing it as a misconception. While blockchain is intricate, Alof asserts that it remains accessible due to “a wide array of user-friendly software” built around open-source blockchain projects. Platforms like Bitcoin are “precisely and intricately designed” but still allow for straightforward interactions. Usability, he believes, is more critical than technical innovation alone, as shown by the dominance of well-established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Learning from the fintech sector, Alof also emphasizes the importance of “navigating the waters of regulatory compliance” while maintaining trust and security, both of which are essential for user confidence. Reflecting on past fintech failures, such as Clinkle’s demise, Alof suggests that crypto must “innovate and be technologically relevant” to stay competitive.
Addressing Challenges: Regulation, Security, and Accessibility
To move forward, Alof identifies regulation, security, and accessibility as key challenges. Different regulatory approaches worldwide have created a complex landscape, and some restrictions limit users’ ability to engage with crypto. He stresses the need for regulatory frameworks that support innovation rather than stifle it, noting that overly restrictive laws “limit users’ ability to transact in crypto.”
Security issues, such as pump-and-dump schemes, NFT scams, and exchange collapses, continue to affect public perception. Incidents like the FTX collapse have “compounded a sense of negativity” around crypto, making it essential to address security concerns to foster greater trust. Finally, accessibility remains a challenge, as crypto’s irreversible transactions and privacy complexities can be intimidating. Simplifying the transaction process while maintaining robust security, Alof argued, is essential for wider adoption.
Closing Thoughts
While the technology behind cryptocurrencies is indeed revolutionary, its adoption will not hinge on technical sophistication but on the practical, real-world solutions it provides. Just as the internet became ubiquitous not because of its underlying architecture but because of the conveniences it brought to daily life, blockchain’s true potential lies in how seamlessly it integrates into our everyday activities.
From improving financial access in underserved regions to reshaping industries like real estate, healthcare, and digital identity, blockchain has already begun to demonstrate its capacity to solve real-world problems. The future of crypto adoption will be driven by use cases that enhance convenience, security, and inclusivity, making the technology an invisible part of our lives.





