It’s hard to imagine a time before decentralised exchanges (DEXs) existed, despite the relatively recent introduction only eight years ago.
In 2016, the world was introduced to the first-ever decentralised exchange: EtherDelta. Admittedly, the new decentralised model was extremely basic but was an absolute game-changer, as you can imagine. EtherDelta created the first platform where crypto traders could swap tokens anonymously, offering something that traditional financial systems never could.
And though the SEC would shut down the platform just two years later, it paved the way for an important host of platforms we depend on today. Our article explores the humble beginnings of decentralised exchanges, diving into their benefits, challenges, and limitations, as well as looking ahead to future trends and innovations.
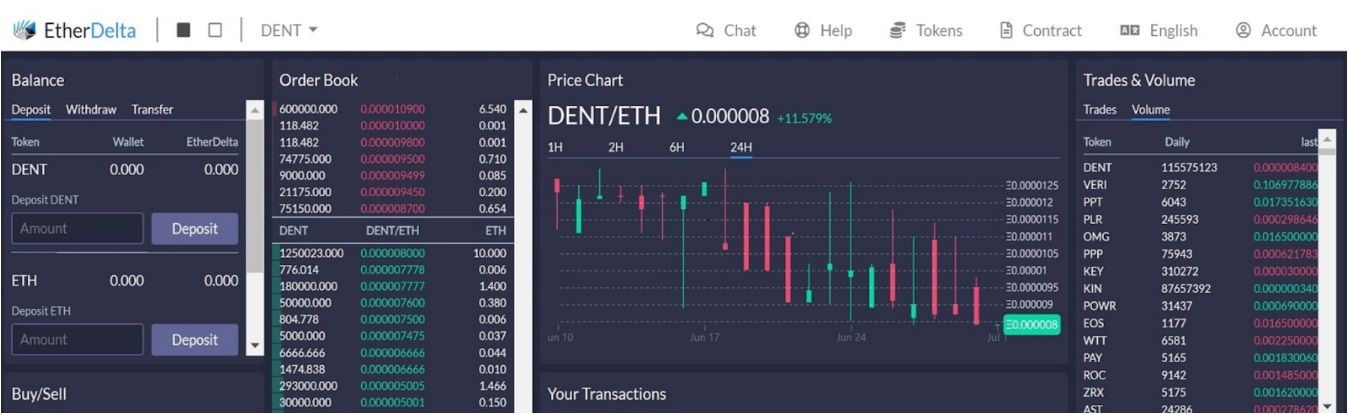 EtherDelta Was Shut Down by The SEC Two Years After its Launch
EtherDelta Was Shut Down by The SEC Two Years After its LaunchWhat is a DEX?
DEXs are essentially platforms that act as a direct middleman between two participants wanting to exchange a cryptocurrency. As simple as that sounds, it directly challenged the traditional way we used to trade our cryptocurrencies on centralised exchanges (CEXs). CEXs were already around for a few years prior, and are still around today, some notable ones being Bybit, Binance, Coinbase and Kraken.
With this new option, we became the custodian of our own funds. DEXs use automated protocols so that transactions can be sent directly between users in a peer-to-peer trading environment. There were no meddling hands getting in the way anymore.
In addition, the switch from the previous model to this one created more security and privacy which is something crypto enthusiasts certainly appreciated. The decision also embraces what blockchain tech has always preached — openness, inclusivity, and user sovereignty. Bitcoin was a bold “middle finger” to centralization, kicking off the march toward decentralised systems. It only made sense then to continue exploring further down this decentralised path. DEXs help us accomplish that goal.
They offer more privacy than traditional markets whose power is typically centralised in a few individuals. The driving force behind DEXs doesn’t require human interaction at all. Algorithms take care of everything. In these types of systems, it’s like an invisible hand runs things so everyone can trade with each other at the best price possible. Automated market makers (AMMs), as they’re called, aren’t driven by people haggling over prices but instead by formula-driven protocols. Users deposit their own money into a liquidity pool which is then used to make trades happen. Unlike typical order book models that need buyers and sellers lined up for every transaction, AMMs will always get someone to trade with you.
This way of running things makes trading cheaper and easier while adding an extra layer of transparency and security digital systems desperately need in today’s world where hacking has become commonplace.
Check out our top picks for the best decentralized exchanges.
Prominent DEX Platforms
Here are some of the famous DEXs today.
Uniswap
Uniswap's DEX is one of the most widely recognized names in the space. It was the first to implement an AMM system that enabled trading without traditional order books. Instead, liquidity is provided by users who pool their funds and gain fees as a reward for doing so. This setup simplifies and speeds up trading while offering better privacy and security than centralised exchanges.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockMany other DEXs, including PancakeSwap and SushiSwap have since copied this approach. However, Uniswap continues to push boundaries and is currently working on v4 to give even more power to users, by allowing them to make trade-off decisions through "hooks." These hooks are contracts that can be activated at different stages and help the pool action lifecycle. This means that not only will v4 let pools mirror what v3 did, but they’ll also allow developers to add new things completely. For example: dynamic fees or on-chain limit orders.
Aside from these customization options, Uniswap v4 has made more changes. It also aims for better cost-efficiency with a new contract design called "singleton.” This will put all of its pools into one contract. With this structure and its flexibility of hooks, Uniswap hopes to offer an even sturdier platform. It will allow developers quick customization access that is safe for transaction routing across multiple pools. Doing this will boost the advancement of fast, innovative AMM capabilities in one ecosystem.
All of these innovations underline how focused Uniswap's developers are on refining its architecture so that it can support more efficient and scalable DeFi interactions.
We have a detailed Uniswap review for those who want to learn more about the world's leading DEX.
Pancakeswap
PancakeSwap is unique in that it functions like any other DeFi exchange or AMM DEX, but comes with a few tricks up its sleeve. It operates on the Binance Smart Chain and has focused on being deflationary since its inception. The supply of CAKE, PancakeSwap’s native token, is regularly reduced, which increases its value over time (theoretically). The exchange also rewards folks who stake their CAKE through a revenue-sharing program. The more users that help grow the platform, the more money they make. Staking also gives access to yield farming, staking, and participation in prediction markets and lotteries.
 Image via Shutterstock.
Image via Shutterstock.You can read our full PancakeSwap review here.
Sushiswap
SushiSwap started off as a clone of Uniswap but quickly set itself apart with the introduction of the Kashi lending platform, MISO token launchpad, and other projects that aim to make Sushiswap a fully-fledged DeFi ecosystem.
However, it is important to note that this DEX is in the process of moving further away from decentralisation. After a preliminary vote, more than 62% of the SushiSwap community voted for a less decentralised business structure called the “Labs model.” This will allow for better ecosystem management but has created some friction between members. The proposed Sushi Labs will hold 25 million tokens worth almost $39 million and have exclusive rights to future airdrops. Understandably, some members are worried about money management and vote manipulation.
This raises an interesting question: Will DEXs be forced into positions where they must pivot just to survive? Back in March 2023, SushiSwap CEO Jared Grey expressed feeling “uninspired” due to regulatory challenges. Now, with the SEC ramping up its regulatory actions against Uniswap, this might hint at a potential trend for the future of decentralised exchanges. We'll touch on this later in the article.
We also have a review on SushiSwap.
NEAR Protocol, Solana and Cosmos Ecosystems
In this section, we'll touch on DEXs in these three ecosystems.
Orderly Network on NEAR Protocol
Operating on the NEAR Protocol, Orderly Network has made a name for itself in the DEX world by focusing on permissionless spot and future order book trading. The platform prides itself on its smart contracts that enable peer-to-peer trading, robust risk management, and shared asset pools designed to boost user security and operational efficiency.
In December 2023, Orderly Network unveiled an industry-first Omnichain SDK aimed at developers who want to create and deploy perpetual DEXs with built-in liquidity. By prioritising efficiency and creativity in the EVM community, this tool allows users to make their concepts a reality quickly. Moreover, it broadens Orderly’s appeal across multiple blockchain ecosystems — laying the foundations for a more interconnected DeFi landscape.
Raydium on Solana
Raydium operates on the Solana blockchain and provides unmatched speed and cost-effectiveness, allowing users to trade at low cost and in a highly liquid market. Raydium’s compatibility with Serum DEX makes it even more appealing, increasing its liquidity and creating a dynamic trading environment across the Solana ecosystem. In addition, its cross-chain capability widens its scope and improves its use case as a multi-purpose decentralised trading platform and liquidity provider.
Raydium recently released its beta version for V3, where the backend infrastructure was completely rebuilt to sustain the current load and future traffic. V3 has been optimised for mobile users because of increasing demand, ensuring a smooth experience and seamless integration with wallet apps. All types of pools, including CLMMs Standard AMMs, have been consolidated under their new liquidity page. Notably, they’ve added a new portfolio page where users can manage all their liquidity positions.
In the new version, token lists are now editable and have been improved to make searches easier. This feature also automatically populates metadata for any searched mint address, enabling tokens to be added directly to the user’s local list to eliminate confusion. The swap now has charts for mobile and desktop with an easy toggle on/off option for any tradable Raydium token pair. The routing engine has been upgraded to support baseIn and baseOut swaps so that in the “Swap To” field, users can specify exactly how much of a given token they want removed from their balance when swapping hence enhancing the precision/flexibility of trading.
Jupiter Exchange on Solana
Jupiter is fascinating because it is a DEX aggregator, so it ensures that users get the best price for their token swaps. It searches for the best trade paths between any token pair using resources from leading DEXs such as Raydium, Serum, Orca, Saber, Penguin Mercurial, and Supernova, essentially blending several DEXs and AMMs for the most extensive liquidity options. This integration also guarantees access to a broad range of tokens by traders and the most favourable conditions for conducting trades to simplify trading and provide an improved user experience.
Being on Solana, the speed of transactions and low transaction costs make it preferable for people willing to maximise their chances without being overwhelmed by hefty fees or delays. It has been designed to provide a frictionless trading environment that bridges the gap between complicated trading dynamics and easy-to-use operations, especially for new entrants.
Osmosis DEX on Cosmos
Osmosis is a DEX specifically built for the Cosmos ecosystem. Launched in 2021, Osmosis is a multi-chain automated market maker (AMM) designed to enhance interoperability among blockchains. It uses the Inter-blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC) and Axelar within the Cosmos network, allowing for smooth token and data transfers across different chains.
 Image via Osmosis Zone
Image via Osmosis ZoneAdditionally, the Gravity DEX, initially part of Osmosis, has been rebranded to Crescent and transitioned to its own network. Crescent aims to introduce innovative features such as an order book exchange model and cross-chain lending capabilities.
In terms of competition and growth, Osmosis, which now includes Crescent, wants to establish itself as a leading DeFi destination within the Cosmos ecosystem. Osmosis sets itself apart by focusing on interchain communication and scalability. This strategy puts Osmosis in a great position to connect blockchains, provide liquidity, and drive DeFi growth within the Cosmos network.
Benefits of DEXs
DEXs have been increasingly recognized for their significant advantages in digital asset trading. The most praised benefits include their non-custodial nature, which guarantees users' control of private keys. This feature mitigates risks such as fund mismanagement, asset freezing, or insolvency issues commonly faced on centralised exchanges. Trading can be done anytime without downtime, which affects CEXs during high traffic or maintenance.
Privacy and accessibility are also significant advantages of DEXs. They operate on a permissionless basis, allowing anyone to use them without submitting personal information, unlike CEXs, which comply with regulations that request these details. This quality makes DEXs especially attractive in regions with limited traditional banking access. Additionally, most new tokens debut on DEXs, allowing early adopters to buy them at lower prices before they're listed on CEXs and rise in value.
However, DEXs also have drawbacks.
They often come with higher levels of risk and complexity — placing greater responsibility on the user to secure their funds properly — one simple mistake like a wrong address could cause irreversible losses. Furthermore, transaction fees can be considerably higher than usual values depending on the network used, such as Ethereum, where gas fees tend to fluctuate significantly during network congestion.
So, while DEXs offer improved security measures, privacy, and early access to new tokens, they require a higher level of responsibility from the user and may entail further costs.
Challenges and Limitations
Although the popularity of DEXs has been increasing, they aren’t really widely accepted due to several impediments such as regulatory challenges, technical issues, insufficient trading assets, and security concerns.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockFrom a regulatory standpoint, DEXs operate in a somewhat unregulated space. This freedom allows new ideas to flourish without immediate regulatory interference. However, this laissez-faire approach also exposes users to fraud and money laundering risks. For instance, the SEC sent a Wells Notice to Uniswap, underscoring the need for DEXs to navigate complex legalities while maintaining their core decentralisation.
Technically, DEXs often present usability challenges, especially for newcomers to the crypto space. The interfaces can be complex and intimidating, pushing less tech-savvy traders towards more user-friendly centralised exchanges. Additionally, technologies used by many DEXs, such as automated market maker systems, face issues including impermanent loss and price slippage, primarily in pools with low liquidity.
Liquidity and slippage issues are also significant challenges. Generally, DEXs' liquidity is lower than CEXs, particularly for less popularly traded tokens. This can lead to increased price volatility and slippage, making executing large orders difficult. Further, the reliance on liquidity providers, who may withdraw their funds anytime, adds to the instability.
Scalability is another major concern. A DEX's performance is limited by its underlying blockchain technology. Notably, DEXs built on Ethereum may suffer from slow transaction times and high gas fees during congestion, resulting in a poor user experience and increased operational costs.
Security remains a pressing issue as well; although DEXs allow users to control their private keys, they are still vulnerable to risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities. Hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities, and as DEXs grow, the potential impact of security breaches also increases.
To thrive and grow sustainably, DEXs must overcome these obstacles. Future improvements will likely focus on enhancing technology and user interfaces while ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks necessary for broader acceptance by various stakeholders.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockCase Studies and Real-World Impact
Undoubtedly, DEXs have significantly influenced the broader financial landscape by introducing DeFi innovations that challenge traditional models of financial services. Here are some key case studies and examples:
1. Lowering Transaction Costs and Increasing Accessibility: DEXs and DeFi platforms lower transaction costs by eliminating intermediaries such as banks and financial institutions that often charge fees for transactions, account maintenance, or currency conversion. This is important for frequent or international transactors as it makes financial transactions cost-effective. Additionally, DeFi platforms enhance financial inclusion by giving access to financial services to the unbanked populations of people who live in areas that lack banking facilities, thereby bridging accessibility gaps typically seen with traditional finance systems.
2. Impact on Traditional Financial Services: By-passing traditional middlemen like banks, Ethereum-based DeFi protocols provide decentralised alternatives for popular conventional financial services like lending and borrowing. This change gives users more control over their finances and introduces automated market-making systems and decentralised lending that compete with traditional financial products. Blockchain technology brings transparency and efficiency in lowering the costs of accessing financial services, making it an attractive alternative to traditional finance systems.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via Shutterstock3. Regulatory and Security Challenges: Integrating traditional finance with DeFi presents challenges. DeFi's largely unregulated status exposes it to risks like fraudulence or money laundering without consumer protections typical of conventional finance frameworks. Furthermore, applying blockchain technology to regular financial mechanisms requires tackling a complex regulatory framework and ensuring compliance with existing laws and regulations.
4. Innovation in Financial Products: The innovation brought about by Defi has led to the creation of new types of monetary devices that could potentially revolutionise the sector. These include yield farming methods, which were not possible before within the traditional ecosystem that affects finances. Only smarter traders would benefit from such innovations. Thus, such innovations make financial markets more efficient while providing more flexibility to users and enhancing the chances of higher returns.
As a result, integrating DEXs into DeFi has shifted how financial services are delivered and experienced by users globally. It holds the potential for improved effectiveness, decreased charges, and expanded availability; however, as we can see, some challenges require well-thought-out approaches as the industry grows.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of DEX technology may well rely on developments in layer-2 solutions, cross-chain interoperability, and the broader evolution of blockchain technologies — anything to significantly improve the scalability, efficiency, and usability of DEXs. Let’s take a look at a few to get a better understanding of where some of the focus has been aimed:
- Layer-2 Solutions: This is especially important for improving the scalability of blockchain networks like Ethereum, which underlies many DEXs. Optimism and Arbitrum are some examples of Layer-2 solutions that use Optimistic Rollups to fast-track the execution of transactions away from the main Ethereum chain, thereby leading to increased transaction throughput at lower cost. Similarly, Zero-Knowledge Rollups batch many transactions into a single one, thus maintaining network security while enhancing performance.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: The growth of the blockchain ecosystem has emphasised the need for interaction across different networks. Chainlink developed protocols like the Cross Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) to allow secure communication and asset transfer across various blockchains. This increases fluidity in asset movements within the DeFi ecosystem while expanding DEXs' capabilities, like multi-chain trading strategies or wider availability of assets.
- Continued Blockchain Evolution: Integrating blockchain technologies into DEX platforms continues to evolve, with developments focusing on enhancing security, user experience, and platform performance. For instance, Chainlink’s innovation has led to the creation of automation tools for layer 2 networks that enable more complicated and dependable smart contract operations, thereby expanding DEXs’ potential use cases in areas such as gaming and finance.
These technologies pave the way toward a more dynamic DeFi world where different DEXs can operate better with high efficiency, ease of reach, and increased functionality. This development is important if we want the adoption of decentralised exchanges not only among cryptocurrency enthusiasts but also among conventional financial institutions looking for decentralised and efficient solutions against outdated systems. With time, these transitions could redefine how financial services are done, leading to a fairer, more transparent, and more efficient market.
Conclusion
As we dive deeper into the digital age, DEXs will likely continue reshaping traditional finance. Built on the pillars of blockchain technology — security and transparency — they facilitate direct peer-to-peer transactions without relying on traditional financial intermediaries. This shift challenges the long-established dominance of CEXs and aligns closely with the foundational principles of blockchain: decentralisation, anonymity, and user empowerment. Such transformations are steering us towards more open financial markets, where users have greater control over managing their assets and can interact more freely.
As we continue to transition, DEXs will become increasingly important, given the development of the DeFi ecosystem. In addition to facilitating simple swaps, these platforms have already gone beyond that point by venturing into complicated areas such as yield farming and on-chain asset management, thus pushing forward development. Further, as we progress in these aspects, projects will continue to push through regulatory scrutiny, scalability concerns, and security improvements.
The future direction of DEX technology indicates even more integration with layer two solutions, cross-chain interoperability for a wider asset range, and further advancements in blockchain infrastructure to support sophisticated financial products. These groundbreaking developments are laying the groundwork for a globally interconnected and efficient financial system.
So, while moving through this changing digital landscape, we must recognize that DEXs form a basis for a broader shift towards a decentralised democratised global finance sector. They demonstrate how powerful blockchain can be in changing our thinking about monetary operations or even power relations globally.





