Stablecoins are the cornerstone of cryptocurrency investment. If you're active in the crypto space, chances are you own USD-backed stablecoins and use them for transactions on centralized or decentralized exchanges. These stablecoins, often considered Real-World Assets (RWAs), were among the first RWAs to emerge in the Web3 ecosystem, even before the term RWA became commonplace.
Many of us are relatively new to the blockchain industry, having spent less than half a decade navigating its complexities. This limited experience means we might have overlooked a significant, long-term value accrual instrument recently gaining traction: stablecoin yield.
Purpose of This Article
In a recent article on The Coin Bureau, we explored the concept of yield-bearing stablecoins and the various strategies they employ to generate yield. This piece builds on that foundation to explore how investors can leverage these yield sources to optimize their portfolios. While the immediate impact of stablecoin yields might not match the dramatic returns of a newly discovered altcoin you are waiting to 10x, the cumulative effect of these yields over time can be substantial. Diversifying stablecoin investments not only provides steady returns but also serves as a crucial hedging strategy that every savvy investor should understand.
By the end of this article, you'll understand how different yield-bearing stablecoins operate and how you can use them to create a balanced, diversified, and hedged portfolio. This piece will highlight the top yield-earing stablecoins and equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about integrating these stablecoins into your investment strategy.
Note: I am skipping the basics of yield-bearing stablecoins. We cover the concept extensively in a dedicated article. If you are unfamiliar with the concept, I urge you to refer to that piece before you advance to this article.
Understanding Stablecoin Yield Sources
Traditional fiat currencies earn passive yield from interest on fixed deposits or government debt. With yield-bearing stablecoins, investors get to choose from where their stablecoin sources its yield. It is perhaps the most groundbreaking innovation in stablecoins and is a testament to the programmability and flexibility of digital assets.
Before we explore stablecoin yield strategies, we must comprehensively understand the mechanics of yield sources and the different stablecoin projects that offer them. Here's a detailed explanation of each category and examples illustrating how they work.
DeFi Native Yield
DeFi Native Yield refers to the interest or returns generated through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms by leveraging the supply and demand of various crypto assets. DeFi operates on blockchain technology, unlike traditional financial systems, allowing for peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries like banks. This system democratizes access to financial services, allowing anyone with an internet connection to participate in lending, borrowing, and earning interest on their crypto holdings.
How Does It Work?
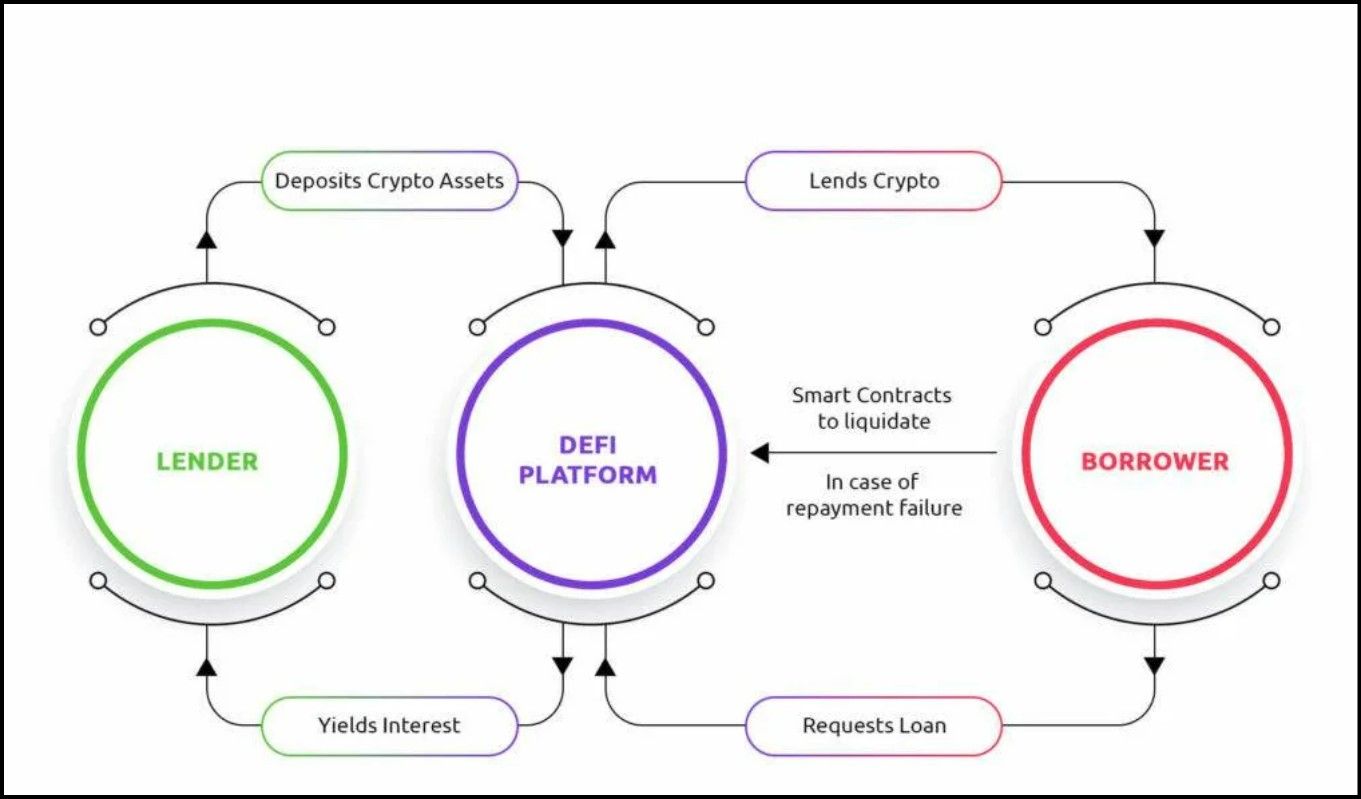 How DeFi Lending Works | Image via Reddit
How DeFi Lending Works | Image via Reddit- Lending and Borrowing Protocols:
- Lending: Users can deposit their crypto assets (e.g., DAI, Ethereum, Bitcoin) into DeFi platforms like MakerDAO, Aave, or Compound. These platforms pool the deposited assets and lend them to other users who need to borrow crypto.
- Borrowing: Borrowers provide collateral in crypto assets to secure a loan from the pool. They pay interest on the borrowed amount, which is typically higher than traditional bank loans due to the volatile nature of crypto assets.
- Interest Distribution: The interest paid by borrowers is distributed among the lenders based on the amount they have deposited. This interest constitutes the DeFi native yield.
- Automated Market Makers (AMMs): AMMs like Uniswap and SushiSwap facilitate decentralized trading by allowing users to provide liquidity to trading pairs (e.g., ETH/USDT). In return, liquidity providers earn a share of the trading fees generated on the platform, adding another layer of yield generation.
Advantages of DeFi Native Yield
- High Returns: DeFi platforms often offer higher returns than traditional savings accounts due to the competitive and dynamic nature of the crypto market.
- Decentralization: Eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing transparency.
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection and crypto assets can participate, democratizing access to financial services.
Risks to Consider
- Volatility: Crypto assets are known for their price volatility, which can impact the collateral's value and the yield's stability.
- Smart Contract Risk: DeFi platforms rely on smart contracts, which are susceptible to bugs and exploits. A flaw in the code can lead to significant financial losses.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for DeFi is still evolving, and future regulations could impact the operation and profitability of DeFi platforms.
MakerDAO's sDAI
 MKR, MakerDAO's Governance Token
MKR, MakerDAO's Governance TokenMakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that governs the Maker Protocol, one of the pioneering DeFi platforms. The Maker Protocol allows users to generate the DAI stablecoin, an over-collateralized asset backed by cryptocurrencies like Ethereum (ETH), USDC, and others. Users can mint DAI by purchasing it on the market or by depositing approved cryptocurrencies into the protocol as collateral.
Introduction to the Dai Savings Rate (DSR)
The Dai Savings Rate (DSR) is a feature of the Maker Protocol that allows DAI holders to earn a variable interest rate on their holdings. Users can lock their DAI in the DSR smart contract to earn savings, with the rate of accrual determined by MKR token holders through governance. This mechanism enables DAI holders to earn passive income on their stablecoin investments.
How DSR Works:
- Deposit DAI: Users deposit their DAI into the DSR contract.
- Earn Interest: The deposited DAI accrues interest at a variable rate, set by MKR holders.
- Withdraw Anytime: Users can withdraw their DAI along with the accumulated interest at any time, without any lock-up period.
What is the Spark Protocol?
Launched on May 9, 2023, the Spark Protocol is a new addition to the Maker ecosystem, serving as a front-end protocol for lending and borrowing assets. It also introduces the sDAI Yield Bearing Stablecoin, leveraging the DSR to create an ERC-4626 vault token called sDAI.
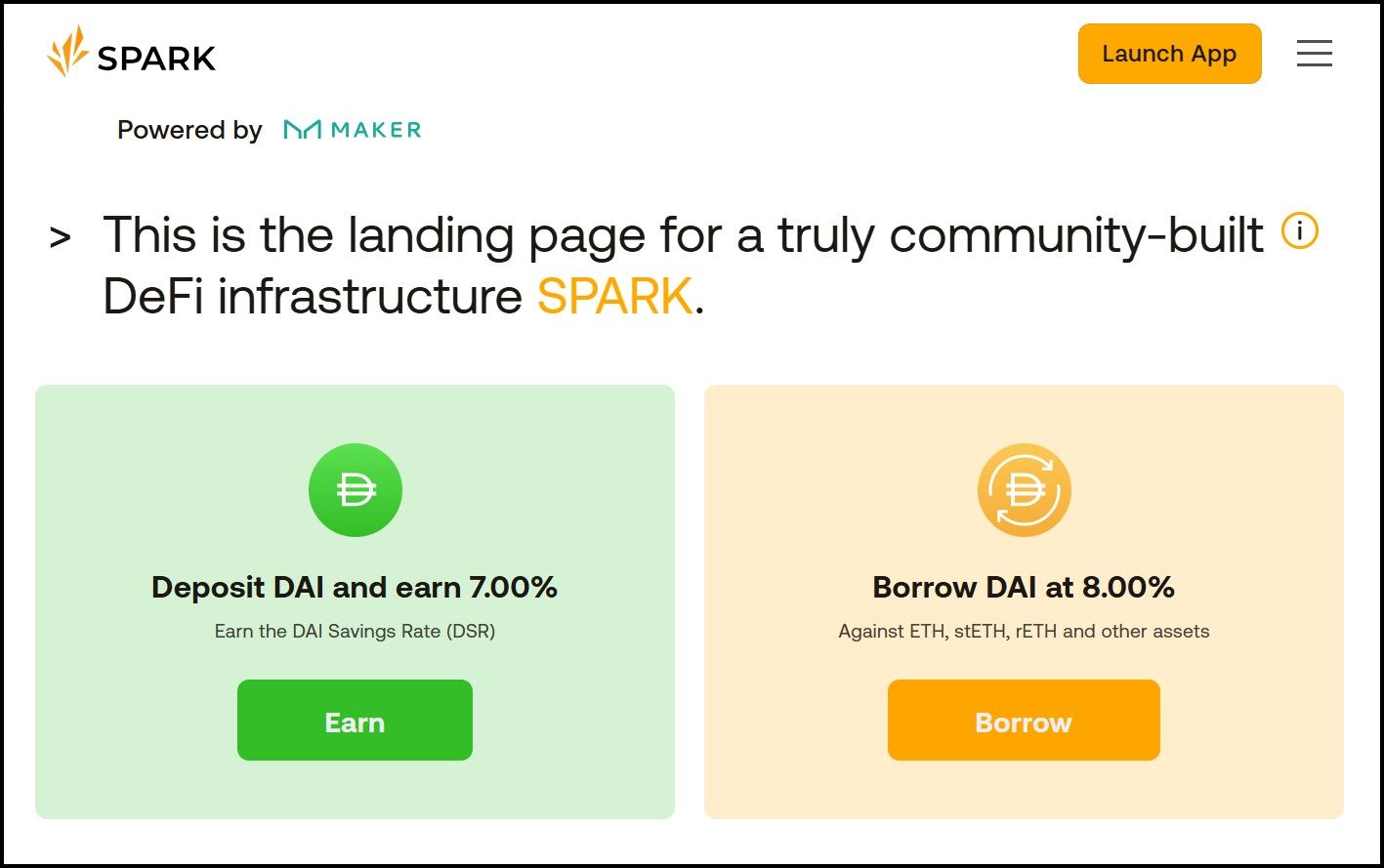 Spark Offers Impressive Yield On sDAI | Image via Spark
Spark Offers Impressive Yield On sDAI | Image via SparkHow sDAI Works:
- Deposit Mechanism: Users deposit DAI into the Spark Protocol, which is then deposited into the DSR contract.
- Minting sDAI: In return, users receive sDAI tokens representing their position in the DSR contract.
- Yield Accrual: The sDAI token accrues interest from the DSR, increasing in value over time.
Key Features and Benefits of sDAI
- Yield Accumulation: Unlike traditional stablecoins, sDAI continuously increases in value due to the interest accrued from the DSR.
- Flexibility: Users can trade, stake, lend, or borrow with sDAI just like any other stablecoin. There are no restrictions on its use, providing liquidity and versatility.
- Immediate Redemption: sDAI can be redeemed for DAI at any time, ensuring users have access to their funds without lock-up periods.
- Non-Rebasing Token: sDAI is an accumulating token, meaning it increases in value instead of issuing new tokens to represent earned interest.
Risks of sDAI
1. Protocol Risks:
- Project Continuity Risk: The continuity of the Maker Protocol is a concern due to recent developer departures and changes in governance.
- Counterparty Risk: Counterparty risk is low as the strategy directly interacts with the DSR through sDAI, minimizing reliance on third-party providers.
- Liquidity Risk: Funds in the DSR contract are redeemable at any time, making the liquidity risk low.
2. Strategy Risks:
- Complexity: The strategy involves a straightforward process of depositing DAI into the DSR via the Spark Protocol, with minimal complexity.
- Scalability: The strategy is highly scalable, with the DSR's APY dynamically adjusted to optimize staking incentives. Scalability risk is low.
- Sustainability: The yield from the DSR is funded by MakerDAO revenues, but there is a potential misalignment of incentives between MKR and DAI holders. This sustainability risk is high.
- Yield Risk: The APY of the DSR is subject to governance votes, leading to potential volatility. Yield risk is high.
3. Regulatory Risks:
- MakerDAO operates in a legally grey area as a DeFi protocol. Regulatory gaps and compliance challenges could pose risks, especially with the protocol's shift towards greater reliance on RWAs.
Conclusion
The sDAI Yield Bearing Stablecoin from MakerDAO offers an innovative way for DAI holders to earn interest while maintaining the flexibility and liquidity of their assets. By leveraging the DSR through the Spark Protocol, users can benefit from a stable and predictable increase in value. However, potential investors should be aware of the associated risks, including protocol continuity, regulatory challenges, and the dynamic nature of the yield. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about integrating sDAI into their investment strategies.
Yields From On-Chain Derivative Tokens
Crypto derivative yield refers to the returns generated from financial instruments whose value is derived from underlying crypto assets. These derivatives can take various forms, such as options, futures, or liquid staking tokens, and they allow investors to earn yield by participating in complex financial strategies without directly holding the underlying assets.
Liquid Staking: An Overview
Liquid staking is a process that allows users to stake their cryptocurrency assets (such as Ethereum) in a blockchain network to support its operations (like transaction validation and security) while still maintaining liquidity. Traditionally, staking involves locking up assets for a specific period, during which they cannot be used or traded. Liquid staking, however, overcomes this limitation by issuing liquid staking tokens that represent the staked assets.
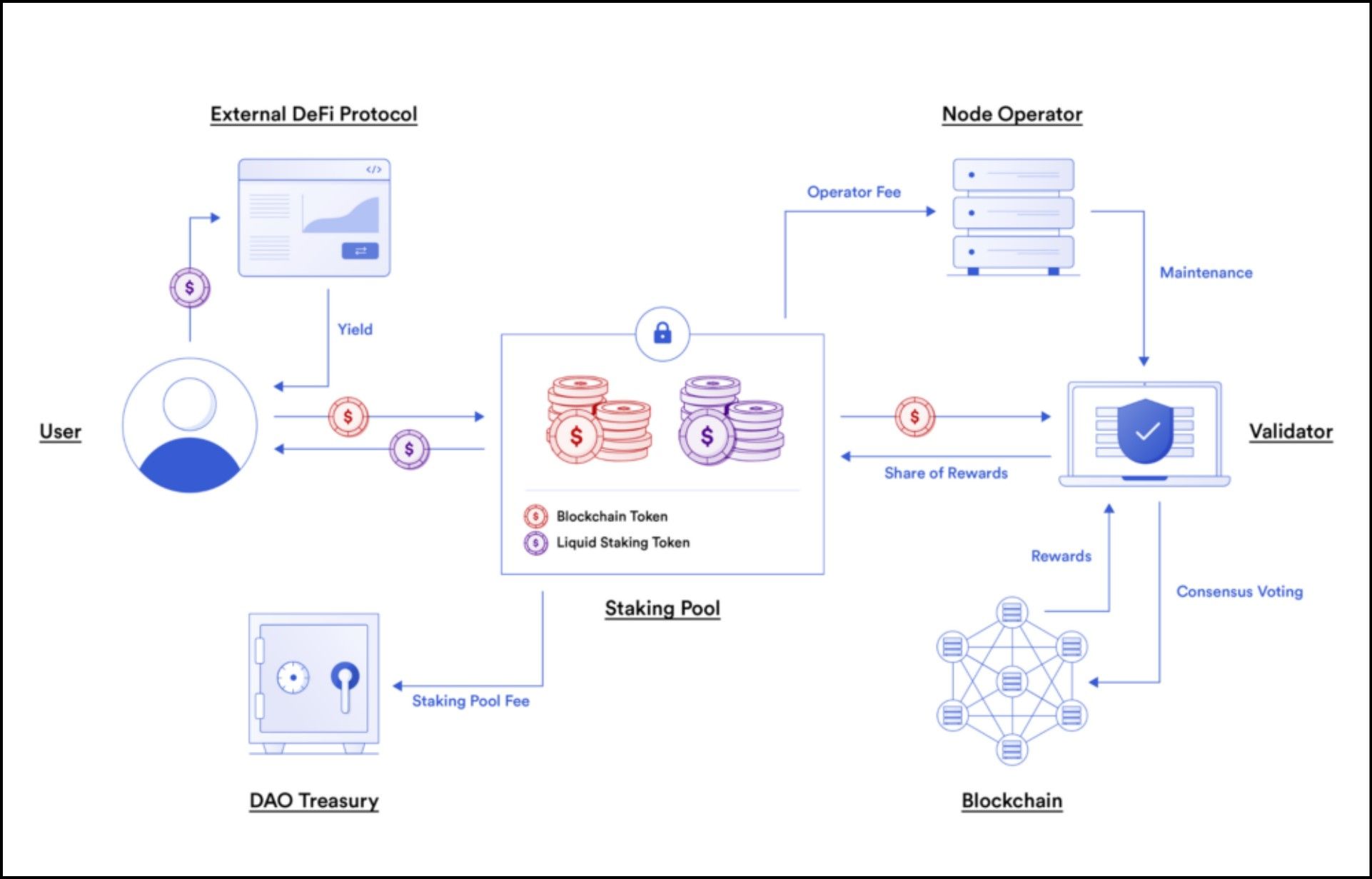 How Liquid Staking Works | Image via Chainlink
How Liquid Staking Works | Image via ChainlinkHow Liquid Staking Works:
- Staking Assets: Users deposit their cryptocurrency into a liquid staking protocol, which stakes the assets on their behalf.
- Issuance of Liquid Staking Tokens: In return, the protocol issues the user liquid staking tokens (e.g., stETH for staked Ethereum). These tokens represent the user's stake in the network and can be freely traded or used in other DeFi applications.
- Earning Rewards: The staked assets earn staking rewards, which are reflected in the value or quantity of the liquid staking tokens.
Dual Purpose of Liquid Staking Tokens
Liquid staking tokens serve two primary purposes: as a source of yield and as a mechanism for stablecoin stability.
1. Source of Yield:
- Earning Staking Rewards: The primary purpose of liquid staking tokens is to earn staking rewards. As the underlying staked assets generate rewards, the value of the liquid staking tokens increases. This increase allows users to earn yield without losing access to their assets.
- Additional DeFi Opportunities: Liquid staking tokens can be used in various DeFi applications such as lending, borrowing, and trading. It enables users to earn additional yield on top of the staking rewards. For example, users can provide liquidity in a decentralized exchange (DEX) or lend their liquid staking tokens on a lending platform, further enhancing their yield.
2. Stablecoin Stability:
- Backing Stablecoins: Some protocols use liquid staking tokens as collateral to back stablecoins. It ensures that the stablecoin is supported by an asset continuously earning yield, contributing to its stability.
- Reducing Volatility: Stablecoins can maintain a more stable value by using liquid staking tokens, which are typically less volatile than other crypto assets due to their staking rewards. The yield generated from the staking rewards helps absorb market fluctuations, thereby enhancing the stablecoin's stability.
Here are some Yield Bearing Stablecoins using liquid staking tokens:
Ethena Finance
 Ethena Finance Homepage
Ethena Finance HomepageEthena markets itself as a synthetic dollar protocol. It offers a stablecoin solution that is not reliant on banking institutions storing reserves of fiat currencies and equivalent assets to maintain price stability. Instead, Ethena utilizes the 'Internet Bond,' an Ethereum-based financial instrument, to generate yield and maintain price stability.
Ethena offers USDe, an yield-bearing stablecoin pegged to the dollar by delta-hedging staked Ethereum and Bitcoin. Here is how USD works:
What is Delta-Hedging?
"Delta" is a measure of how much the value of a derivative changes in response to a change in the underlying asset's price. For instance, if you have a derivative contract linked to Ethereum (ETH), the delta indicates how sensitive the value of this contract is to changes in ETH's price.
- Positive Delta: If a derivative has a positive delta of 1, it means that for every $1 increase in the price of ETH, the derivative's value also increases by $1.
- Negative Delta: Conversely, if the delta is negative, the derivative's value decreases as the price of ETH increases.
Delta-Neutral Stability
A portfolio is said to be "delta-neutral" when its overall delta is zero. This means that the portfolio is unaffected by underlying asset price changes. In other words, the portfolio's value remains stable regardless of market fluctuations in the price of ETH.
Example:
- Imagine Ethena issues a stablecoin called USDe, backed by 1 ETH. Initially, the delta is 1, meaning the value of USDe changes with the price of ETH.
- To achieve delta-neutrality, Ethena takes a short position in a perpetual contract equivalent to 1 ETH. The short position's delta is -1.
- The positive delta (+1) from holding ETH and the negative delta (-1) from the short position cancel each other out, resulting in a net delta of 0.
When the portfolio is delta-neutral, the USD value of USDe remains constant, regardless of whether ETH's price triples or drops by 90%. Profits from the ETH price increase are offset by losses from the short position and vice versa.
Minting USDe
- User Action: A whitelisted user provides stETH to the Ethena protocol.
- Minting Process:
- In return for the stETH, the user receives approximately the same number of newly minted USDe. This process is carried out atomically, meaning it happens in a single, seamless transaction.
- The amount of USDe received is net of gas and execution costs required to perform the hedge.
- Fee Management: Any slippage and execution fees are included in the price during the minting process. This ensures that the user is aware of all costs upfront.
- Hedging:
- The protocol opens a corresponding short perpetual position on a derivatives exchange to maintain a delta-neutral position.
- The notional dollar value of this short position is approximately the same as the value of the stETH provided by the user.
- Settlement and Custody: The backing assets (stETH) are transferred directly to an "Off Exchange Settlement" solution. This solution ensures that the assets remain on-chain and are custody by off-exchange service providers to minimize counterparty risk.
- Custody and Delegation: Ethena delegates the backing assets to derivatives exchanges to margin the short perpetual hedging positions. However, Ethena never transfers custody of these assets, maintaining control and security over the backing assets.
Yield Sources
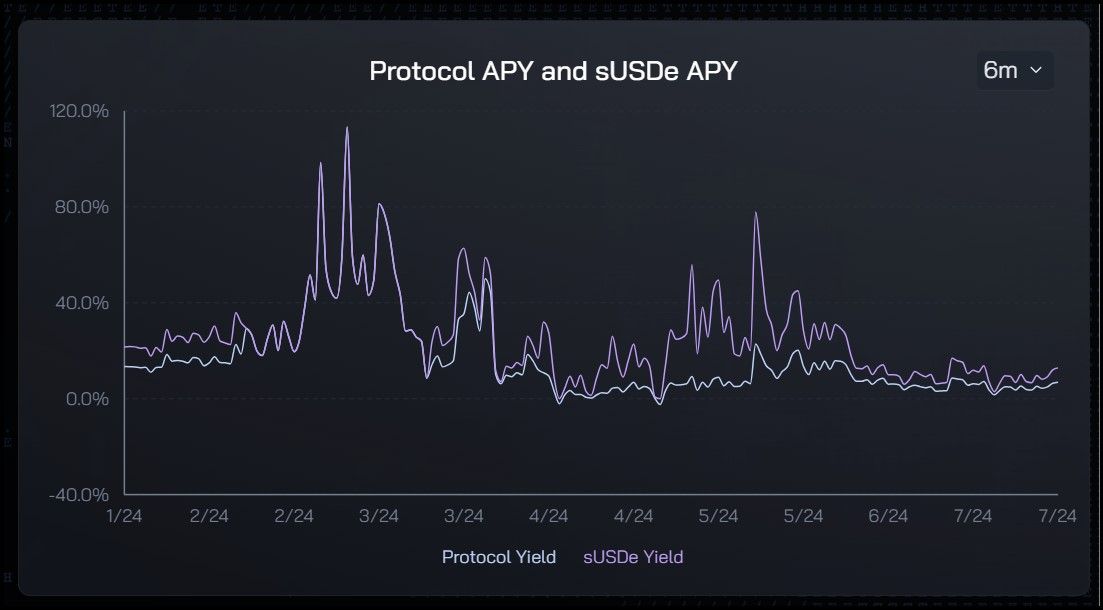 USDe Six Month USDe Yield. Image via Ethena
USDe Six Month USDe Yield. Image via EthenaUSDe, the stablecoin issued by Ethena, derives its yield from two primary sources:
1. Staked ETH Assets Receiving Consensus and Execution Layer Rewards
Consensus Layer Rewards:
- Staking Rewards: When ETH is staked in the Ethereum network, it participates in its consensus mechanism (proof-of-stake). Stakers help validate transactions and secure the network, earning rewards in return.
- Consensus Layer Yield: These rewards come from both the newly issued ETH as block rewards and transaction fees paid by users of the Ethereum network. It contributes to the yield for staked ETH assets.
Execution Layer Rewards:
- MEV (Maximal Extractable Value): Stakers can also earn additional rewards through opportunities such as Maximal Extractable Value (MEV). MEV refers to the potential profits that can be made by reordering, including, or excluding transactions within a block.
- Execution Layer Yield: By capturing these execution layer rewards, staked ETH can generate additional income, further boosting the yield derived from the staking process.
2. The Funding and Basis Spread from Delta Hedging Derivatives Positions
Funding Spread:
- Perpetual Contracts: The protocol uses short perpetual contracts to hedge the ETH backing the USDe stablecoin. Perpetual contracts often have funding payments exchanged between long and short positions.
- Funding Rate Yield: Depending on market conditions, these funding payments can result in a net positive yield for the protocol. If the funding rate is positive for short positions, Ethena earns yield from these payments.
Risks of USDe
1. Liquid Staking Token (stETH) Related Risks Associated with the Lido Protocol
- Smart Contract Risks: The stETH tokens are issued by the Lido Protocol, which relies on smart contracts. These contracts can be susceptible to bugs, vulnerabilities, or exploits that could lead to loss of funds.
- Validator Risks: stETH depends on the performance of the validators in the Ethereum network. Poor performance, malicious behavior, or penalties imposed on these validators can affect the rewards and the overall value of stETH.
- Liquidity Risks: While stETH is designed to be liquid, market conditions or issues within the Lido Protocol could impact the ability to quickly convert stETH back to ETH or other assets without significant price slippage.
2. Centralized Counterparty Risks
- Custodial Risks: USDe's backing assets are custodied by off-exchange service providers. If these centralized custodians face operational issues, insolvency, or malicious activities, the backing assets could be lost.
- Dependency on Centralized Platforms: The stability and functionality of USDe partly rely on the centralized platforms managing these custodial services. Any failure, regulatory intervention, or service disruption in these platforms can pose significant risks to USDe.
3. Negative Funding Rate Risks
- Market Conditions: The funding rate in perpetual contracts can turn negative, meaning that short positions (used for delta-hedging) may need to pay funding to long positions. This can reduce the yield generated from the hedging strategy.
- Sustained Negative Rates: If the market conditions lead to a prolonged period of negative funding rates, it could result in consistent losses for the hedging positions, impacting the overall yield and potentially the stability of USDe.
- Volatility: High market volatility can lead to rapid changes in funding rates, adding another layer of risk and uncertainty to the yield derived from these positions.
Summary
Delta-hedging and maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio ensure the stability of USDe in volatile markets by offsetting positive and negative deltas. This approach provides a reliable and predictable asset, protecting against price volatility and aligning with institutional financial strategies.
USDe generates yield from staking ETH (consensus and execution layer rewards) and financial strategies involving funding and basis spreads from delta hedging derivatives positions. These yield sources maintain USDe's stability while providing steady returns for holders.
USDe carries risks related to the Lido Protocol's liquid staking tokens (stETH), centralized custodial counterparty risks, and potential negative funding rates in its delta-hedging strategy. Investors should be aware of these risks when using USDe in their portfolios.
TradFi and RWA-Backed Stablecoins
Yield-bearing stablecoins that derive their yield from traditional financial instruments represent a bridge between decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional finance (TradFi). These stablecoins invest in assets such as short-term US Treasuries and bank demand deposits to generate returns. By doing so, they offer their holders a stable and low-risk yield source.
Traditional Financial Instruments Involved:
- Short-term US Treasuries:
- Nature: US Treasuries are government debt securities with a one-year or less maturity. They are considered one of the safest investments because the full faith and credit of the US government backs them.
- Yield Generation: The interest earned from these short-term bonds provides a stable and predictable yield.
- Bank Demand Deposits:
- Nature: These funds are held in bank accounts that can be withdrawn on demand without notice. Banks often offer interest on these deposits as a way to attract and retain customers.
- Yield Generation: The interest banks pay on these deposits contributes to the overall yield for the stablecoin.
Promoting the RWA Narrative
These stablecoins invest in RWAs, such as government bonds and bank deposits, integrating traditional financial assets into the blockchain ecosystem. It promotes the RWA narrative by demonstrating how blockchain technology can be used to manage and distribute traditional financial instruments.
Returns:
- Safety and Stability: By investing in secure and well-established financial instruments, these stablecoins offer a low-risk return. It is often referred to as a "risk-free" return because the underlying assets (like US Treasuries) have very low default risk.
- Predictable Yields: The returns from these investments are stable and predictable.
Permissionless and Censorship-Resistant:
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can invest in these stablecoins, without going through traditional financial institutions. It opens up investment opportunities to a global audience, including those who might not have access to traditional banking services.
- Censorship Resistance: Transactions and holdings on the blockchain are resistant to censorship. It ensures that all users, regardless of location or status, can participate in the financial system without fear of interference.
Equitable Environment for Investors:
- Inclusivity: By leveraging blockchain technology, these stablecoins create a more inclusive financial system where anyone can earn investment returns, democratizing access to financial instruments traditionally available only to institutional investors or individuals with significant capital.
- Transparency: Blockchain provides transparency in how the stablecoins are managed and yields are generated, building trust among investors.
Therefore, yield-bearing stablecoins that derive yield from traditional financial instruments like short-term US Treasuries and bank demand deposits offer a secure and predictable return.
Ondo Finance
Ondo Finance is a DeFi platform that bridges the gap between DeFi and TradFi by offering on-chain access to real-world assets (RWAs) like U.S. Treasury bonds. The platform is designed to integrate various parties and compliance components, making institutional-grade financial products accessible on the blockchain.
Ondo focuses on providing investment opportunities for both crypto-natives and risk-averse investors, emphasizing regulatory and tax compliance. Users must complete KYC to access these services, ensuring adherence to relevant laws and regulations.
Ondo Finance OUSG Fund
 The OUSG Fund APY. Image via Ondo
The OUSG Fund APY. Image via OndoThe OUSG Fund provides tokenized on-chain ownership of BlackRock's iShares Short Treasury Bond ETF. This product offers liquid exposure to short-term U.S. Treasuries, which are considered low-risk investments. The process involves users depositing USDC or USD, which is then used to purchase the underlying assets. The fund has attracts a 0.15% management fee from Ondo, alongside intermediary and BlackRock fees. However, due to SEC regulations, access is restricted to accredited investors and qualified purchasers, making it less accessible to the average DeFi participant.
Ondo USDY Stablecoin
 The USDY Stablecoin APY. Image via Ondo
The USDY Stablecoin APY. Image via OndoUSDY is an interest-bearing stablecoin that provides access to yields from short-term U.S. Treasuries and bank demand deposits. This stablecoin is designed to pass most of the yield to its holders, with Ondo charging only a small fee for operational expenses and redemptions. USDY offers daily redemptions and can be transferred freely to users on a secondary allowlist after a holding period, promoting greater accessibility to institutional-grade yields.
USDY Eligibility
USDY is designed to provide institutional-grade yields to a global audience while adhering to strict regulatory requirements. To access USDY, individuals and organizations must meet specific eligibility criteria:
- Geographical Restrictions:
- Ineligible Countries: Individuals or organizations cannot be located, organized, or residents of the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Crimea, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Syria, Albania, Barbados, Belarus, Cambodia, Colombia, Haiti, Jamaica, Japan, Myanmar, Nicaragua, Russia, Ukraine, Vanuatu, Venezuela, Yemen, any African country except Mauritius and South Africa, or any countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States (ex-Soviet states).
- Sanctioned Regions: Entities in any country, territory, or geographical region under comprehensive sanctions are also ineligible.
- Citizenship Restrictions: Citizens of the above countries are ineligible regardless of their residence, except those from the United States and the United Kingdom, who can participate if they live outside these countries.
- Secondary Market Access:
- Transferability: USDY can be transferred to users on a secondary allowlist based on geographical criteria 40-50 days after purchase. It helps in expanding access to users globally while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Key Points
- High Accessibility: The target market includes Europe, Latin America, Southeast Asia, and US or UK expats living in these regions.
- Low Investment Barrier: The minimum investment and redemption amount is set at $500, with plans to reduce this further over time, making it accessible to a broader audience compared to other institutional-grade products.
Ondo Finance's innovative approach to integrating TradFi and DeFi, its focus on regulatory compliance, and its partnership with top-tier institutional players position it as a significant player in the growing RWA space. However, potential investors should carefully consider the risks of RWAs and their eligibility for accessing these products.
Market Conditions Analysis for Yield Bearing Stablecoins
Here, we will explore the risk and return profiles of different yield-bearing stablecoins.
sDAI (MakerDAO)
Risk and Return Profiles:
- Potential Misalignment of Incentives: The incentives of DSR (Dai Savings Rate) and MKR (MakerDAO governance token) holders can conflict. Higher interest rates paid to DSR decrease the profits from MKR Burn, potentially creating instability in the yield for sDAI holders.
- Revenue Stability: Data shows that revenue from DSR has been erratic in the short term but stable around 7% in the long run.
Optimal Market Conditions:
- Stable Interest Rates: sDAI performs well when the DSR is consistently managed, providing predictable yields. Periods of stable interest rates benefit sDAI by ensuring steady returns.
- Regulatory Clarity: When regulatory conditions favor DeFi platforms and their operations are not threatened, sDAI can attract more deposits, enhancing its stability and returns.
Market Scenarios:
- Bull Markets: Moderate to high demand for decentralized finance services leads to increased use of MakerDAO, boosting DSR revenue.
- Stable Economic Conditions: Stable economic conditions with predictable regulatory environments support the consistent yield for sDAI.
USDe (Ethena Finance)
Risk and Return Profiles:
- Yield from Delta-Neutrality: Ethena generates yield through delta-neutral strategies, leveraging market conditions to earn positive funding rates and basis spreads.
- Volatility and Leverage: Ethena benefits from market conditions where there is a high demand for leverage and stable or moderate volatility.
Optimal Market Conditions:
- High Leverage Demand: In bull markets where investors are optimistic and seek leveraged long positions, USDe benefits from higher funding rates paid by these positions.
- Stable or Moderate Volatility: Consistent demand for leveraged positions and moderate volatility increases the funding rates, enhancing the returns from short positions.
- High Staking Returns: High staking returns on stETH contribute to overall yield, benefiting USDe holders.
Market Scenarios:
- Bull Markets: Optimistic trading behavior leads to increased leverage, boosting funding rates and yields for USDe.
- Periods of High Staking Returns: Times when staking rewards on Ethereum are high, combined with favorable funding rates, maximize the yield for USDe holders.
USDY (Ondo Finance)
Risk and Return Profiles:
- Yield from Traditional Financial Instruments: USDY derives its yield from short-term US Treasuries and bank demand deposits. The yields are closely tied to the interest rates set by the Federal Reserve.
- Regulatory Compliance: USDY operates under strict regulatory compliance, ensuring a stable and legally sound investment option.
Optimal Market Conditions:
- High Interest Rates: When the Federal Reserve maintains high interest rates, USDY can offer attractive yields, drawing in more investors.
- Stable Macro Environment: A stable macroeconomic environment with predictable interest rate policies supports consistent returns for USDY.
Market Scenarios:
- High Interest Rate Environment: During periods when the Federal Reserve sets high interest rates (e.g., the current environment with rates around 5%), USDY provides competitive yields.
- Economic Uncertainty: In times of economic uncertainty, investors might prefer the stability of government-backed yields, increasing the attractiveness of USDY.
Summary
- sDAI performs best in stable economic conditions with consistent interest rates and favorable regulatory environments. It benefits from the stable management of DSR and increased demand for DeFi services.
- USDe excels in bullish markets with high demand for leverage, moderate volatility, and high staking returns on Ethereum. It leverages delta-neutral strategies to maximize funding rates and basis spreads.
- USDY thrives in high interest rate environments set by the Federal Reserve, providing risk-averse investors with stable yields from traditional financial instruments. It benefits from a stable macroeconomic environment and regulatory compliance.
Each stablecoin has distinct market conditions where it performs optimally, providing diverse opportunities for investors to diversify and hedge their portfolios based on prevailing economic and market scenarios.
Top Yield-Bearing Stablecoins: Final Thoughts
In summary, sDAI, USDe, and USDY each offer unique opportunities for yield-bearing stablecoins under different market conditions.
sDAI thrives in stable economic environments with consistent interest rates, leveraging MakerDAO's DSR for returns. USDe excels during bull markets with high-leverage demand and moderate volatility, utilizing delta-neutral strategies to benefit from positive funding rates and basis spreads.USDY shines in high-interest rate environments set by the Federal Reserve, offering stable yields from traditional financial instruments like U.S. Treasuries and bank deposits.
Each stablecoin presents distinct risk profiles and benefits, making them suitable for various investment strategies. By understanding these dynamics, investors can optimize their portfolios, diversifying and hedging effectively to leverage the strengths of each stablecoin based on prevailing market conditions. This approach ensures a balanced exposure to both DeFi and TradFi yields, catering to different risk appetites and investment goals.





