Crypto cyber security is a critical aspect that every crypto user should be on top of in the fast-evolving world of cryptocurrencies. As the crypto community continues to grow, so do the challenges associated with safeguarding digital assets.
The decentralized and pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies presents both opportunities and risks. To mitigate these risks, the development and implementation of decentralised security protocols are crucial, offering robust protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
In this article, we explore the rising concerns surrounding ransomware and cybercrime within the crypto space, shedding light on the importance of robust security measures and staying in the know so you can remain up to speed on active threats in our beloved crypto space.

In today's interconnected digital landscape, the potential impact of ransomware attacks and cybercrime targeting cryptocurrencies cannot be ignored. These threats pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and even the stability of the entire crypto ecosystem. As the value and popularity of cryptocurrencies surge, they become lucrative targets for malicious actors seeking financial gain.
The disruptive consequences of such attacks can result in not only substantial financial losses but also erode public trust in the crypto industry, hindering adoption and the recognition of digital assets as being a legitimate and useful asset class. This is where blockchain forensics comes into play, offering a method to trace illicit activities and recover assets in the aftermath of cybercrimes
To mitigate these risks and ensure the safe and secure utilization of cryptocurrencies, proactive measures and awareness are paramount. By understanding the evolving landscape of ransomware and cybercrime within the crypto space, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves and their digital assets.
In the following sections, we will delve into common cryptocurrency security concerns, exploring common vulnerabilities, best practices for safeguarding crypto assets, and the efforts being made to combat these threats. By staying informed and adopting robust security practices, we can navigate the crypto space with confidence and mitigate the potential risks associated with ransomware and cybercrime.
Understanding Malware, Ransomware & Cybersecurity Risks
Instead of trying to waffle my way through trying to define and explain Malware, I figured I would let the cybersecurity experts do the explaining. The definition of Malware according to Forcepoint is:
“The collective name for a number of malicious software variants, including viruses, ransomware and spyware. Shorthand for malicious software, malware typically consists of code developed by cyberattackers, designed to cause extensive damage to data and systems or to gain unauthorized access to a network. Malware is typically delivered in the form of a link or file over email and requires the user to click on the link or open the file to execute the malware”. (Source: Forcepoint.com/cyber-edu)
Since the emergence of the Creeper virus in the early 1970s, malware has posed a continuous threat to both individuals and organizations. Over the years, countless malware variations have targeted the world, aiming to inflict maximum disruption and harm. One of the most well-known results of malware is ransomware being injected into a computer system.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockOther examples of Malware include:
- Trojan horse: A type of malware disguised as legitimate software, allowing unauthorized access or causing harm to a computer system.
- Ransomware: Malware that encrypts files or locks users out of their systems, demanding a ransom in exchange for restoring access.
- Spyware: Software that covertly gathers user information or monitors activities without consent.
- Adware: Software that displays unwanted advertisements or redirects users to malicious websites.
- Botnets: Networks of infected computers controlled by a central server, typically used for malicious activities such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
As a response to the rising cyber threats in the crypto space, many companies are now considering cyber insurance to protect against potential financial losses due to hacks and breaches.
Let’s focus on Ransomware. According to the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency, National Cybersecurity and Communications Center (NCCIC), the definition of Ransomware is as follows:
“Ransomware is a type of malware that infects a computer and restricts a user’s access to the infected computer. This type of malware, which has now been observed for several years, attempts to extort money from victims by displaying an on-screen alert. These alerts often state that their computer has been locked or that all of their files have been encrypted, and demand that a ransom is paid to restore access. This ransom is typically in the range of $100–$300 dollars and is sometimes demanded in virtual currency, such as Bitcoin”. (Source: Cisa.gov)
Phishing emails containing malicious attachments and drive-by downloading are the typical means by which ransomware spreads. Drive-by downloading occurs when an individual unintentionally visits an infected website, resulting in the automatic download and installation of malware without their awareness. Crypto ransomware, a variation that encrypts files, is commonly propagated through similar methods, including Web-based instant messaging applications.
Why Ransomware Is So Successful
The creators of ransomware instil a sense of fear and panic in their victims, compelling them to either click on a provided link or make a ransom payment. They employ messages resembling the following:
- "Your computer has been infected with a virus. Click here to resolve the issue."
- "Your computer was utilized to access websites containing illegal content. To regain control of your computer, you must remit a $100 fine."
- “All the files on your computer have been encrypted. To regain access to your data, you must make the ransom payment within 72 hours.”
While this threat used to be an annoyance and some users chose to pay the fines, with the introduction of cryptocurrencies, the stakes are higher than ever as many crypto users risk exposure of their investments to bad actors as many software wallets rely on files and encryption on their personal computing device that could become infected.
There is a big difference between paying a demand to regain access to your favourite downloaded cat memes and photos, and a whole different ballgame when we are talking about regaining access to your digital assets that could be worth 6 figures or more. That is why most crypto experts, including us here at the Coin Bureau, preach the importance of using a good hardware wallet to eliminate this risk.
Recent incidents and emerging threats serve as stark reminders of the vulnerabilities within the crypto space. From the emergence of new malware to targeted attacks on crypto wallets and exchanges, the need for robust security measures has never been more critical. Staying informed about cryptocurrency security issues is crucial for ensuring crypto safety in this dynamic environment.
Examples of Malware in Crypto
Bad Rabbit Malware
One notable malware that caused havoc was the so-called "Bad Rabbit," which saw its largest impact on users in Germany, Ukraine, and Russia. Though there have been no recent cases of this particular type of malware, it is still good to know about. This malware encrypts users' files, demanding a ransom in Bitcoin for the decryption key. While not directly targeting crypto users, the potential loss of data, including valuable crypto investments, highlights the importance of secure storage, such as hardware wallets.
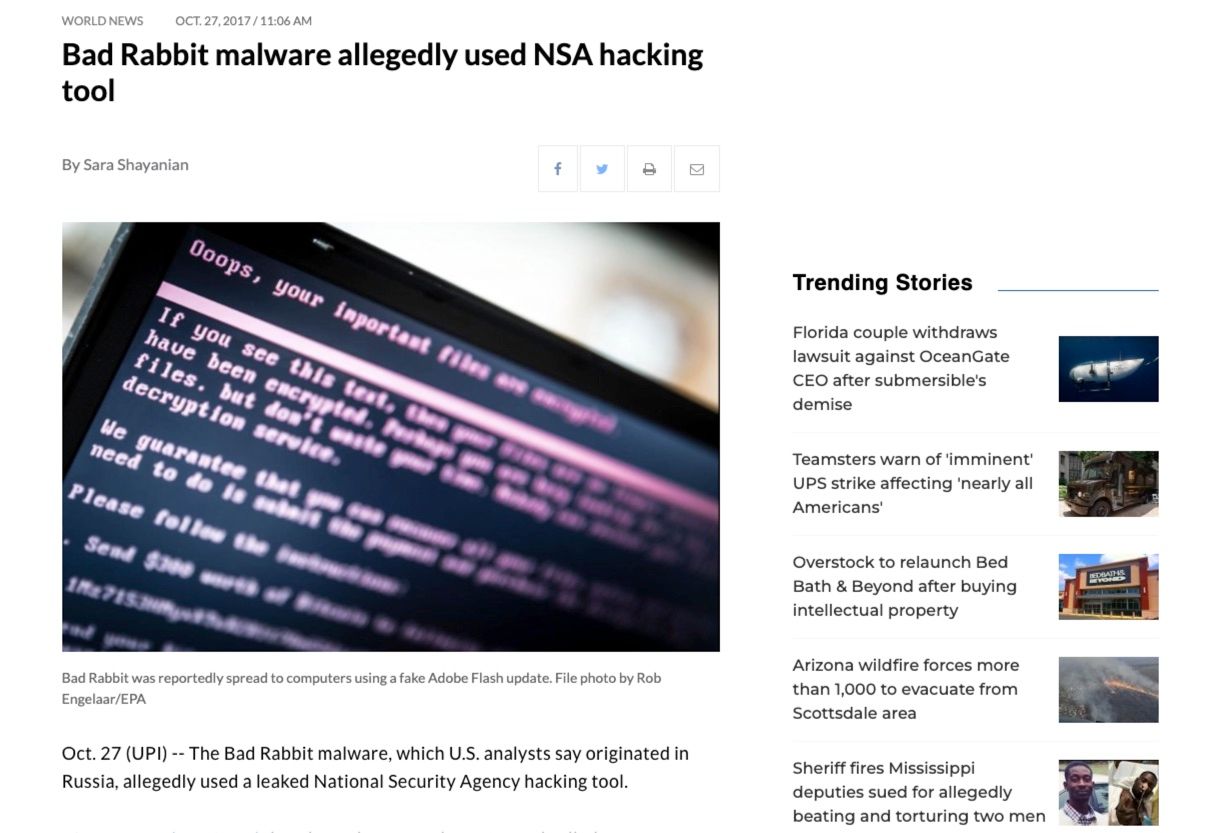 Image via upi.com
Image via upi.comThis was an interesting case as it was believed that stolen NSA (National Security Agency) tools were repurposed by the malicious actors.
ICO Phishing
Another alarming trend is the rise in ICO phishing scams. As the popularity of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) remains prevalent, cybercriminals work tirelessly to deceive unsuspecting investors. Clicking on a malicious link can lead to the draining of crypto wallets in mere seconds. The case of Kori Williams, CEO of a social media company, falling victim to a phishing scam through a Slack chat serves as a stark reminder of the risks faced by both novices and experienced investors.
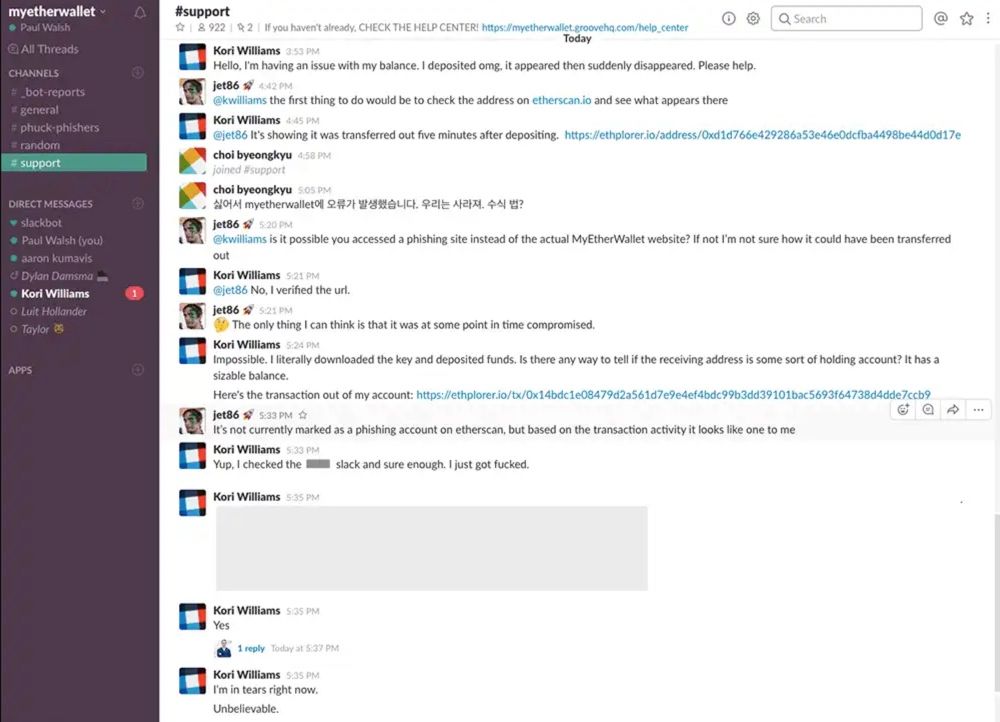 Image Source
Image SourceThere have been hundreds of millions of dollars stolen through these types of ICO scams over the past few years.
Crypto Exchange Hacks
Crypto exchange attacks have had some of the most significant impacts on the markets, and there aren’t many exchanges that have survived multiple years unscathed. Asian exchanges, in particular have been targeted, with suspicions pointing to North Korean involvement and the infamous Lazarus Group.
South Korea's largest exchange, Bithumb, experienced a high-profile hack in 2019 and has had repeat hacks resulting in millions worth of lost customer funds.
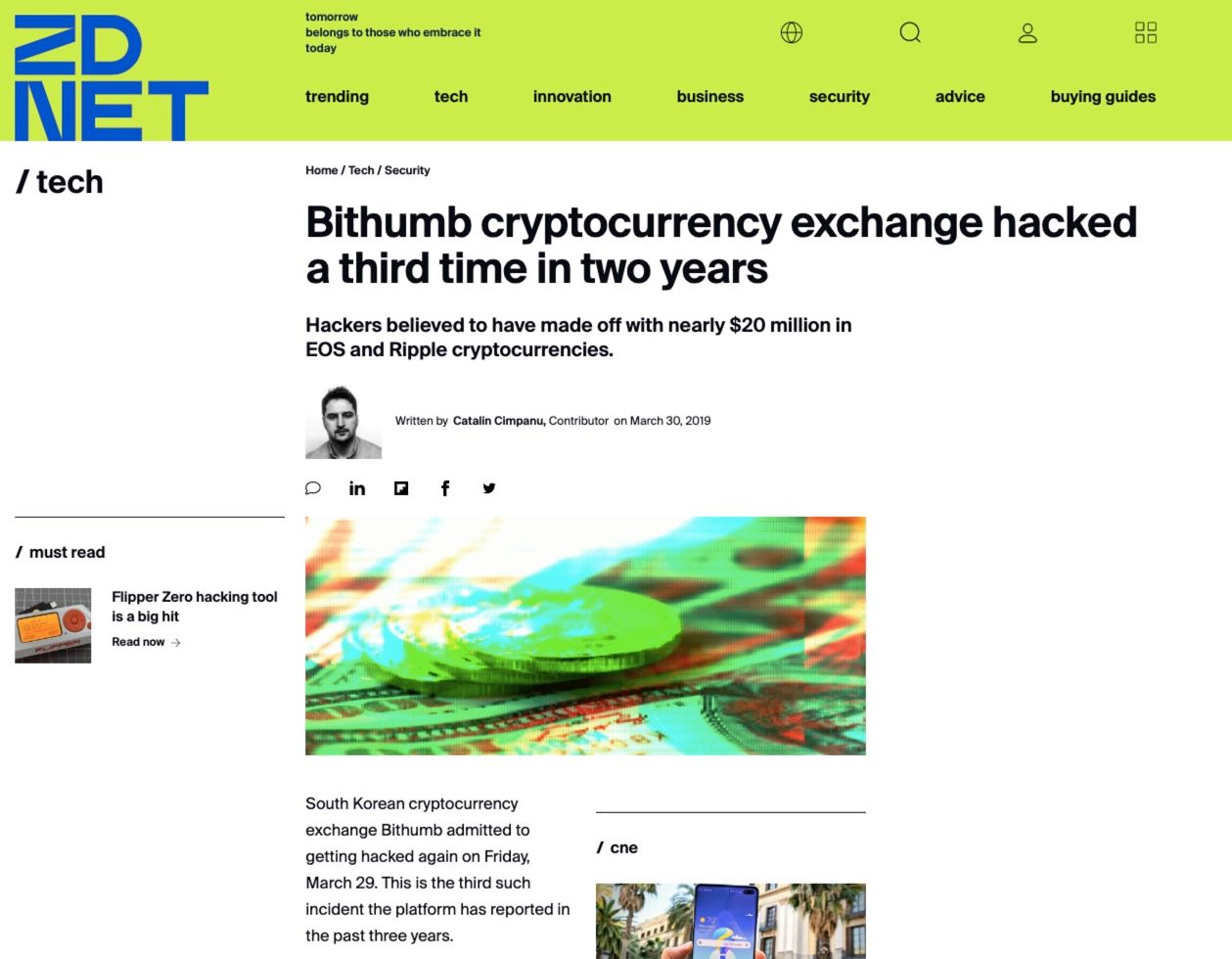 Three Hacks in Two Years. Ouch. Image Source: ZDNET.com
Three Hacks in Two Years. Ouch. Image Source: ZDNET.comKuCoin and Binance have also experienced security breaches resulting in stolen customer assets, and even Coinbase has had its share of cyber attacks that exposed customer data and was hacked in 2021, seeing thousands of customer assets stolen.
This is where I need to tip my hat to the Kraken exchange, they are the only “OG” crypto exchange that has been around since the early days, always as a top 5 exchange, that has never experienced a hack. Other notable exchanges that take their security to the next level are SwissBorg and Crypto.com.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking refers to the unauthorized use of a person's computing resources to mine cryptocurrencies without their consent. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in websites, apps, or devices to inject malicious scripts that run in the background, using the victim's processing power. This can result in decreased device performance, increased electricity bills, and potential damage to hardware. In 2017, the Coinhive cryptojacking script was widely used, infecting numerous websites and affecting millions of users.
Supply Chain Attacks
Supply chain attacks involve compromising the software or hardware supply chain to inject malicious code or backdoors into legitimate products. In the crypto industry, attackers may target hardware wallets or other software used for cryptocurrency transactions. This is why you will hear many crypto experts, including us here at the Bureau harp on about only buying your hardware wallets from reputable vendors and never second-hand, as there is a good chance the original owner has a copy of the private keys someplace.
 Checking Both the Box and Device to Ensure Security Tape Isn’t Broken and Devices Haven’t Been Tampered With During Transit. Image via Trezor
Checking Both the Box and Device to Ensure Security Tape Isn’t Broken and Devices Haven’t Been Tampered With During Transit. Image via TrezorYou also need to verify that the security tape isn’t broken upon arrival, as shown above with Trezor devices. You can learn more about this concern in our Trezor Hardware Wallet Review.
Sim Swapping
SIM swapping, also known as SIM hijacking, involves fraudulently transferring a victim's phone number to a new SIM card controlled by the attacker. By gaining control of the victim's phone number, the attacker can bypass two-factor authentication (2FA) measures and gain access to the victim's cryptocurrency accounts. This type of attack has resulted in significant financial losses for individuals and even high-profile targets.
This is why many security professionals never recommend using SMS as a form of two-factor authentication and instead consider a free service like Google Authenticator or a YubiKey device.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks involve tricking users into revealing their sensitive information, such as login credentials, recovery phrases or private keys, by posing as a legitimate entity. In the crypto industry, phishing attacks often target cryptocurrency exchange users or holders of digital wallets. Attackers may send fraudulent emails, create fake websites, or use social engineering techniques to deceive victims. For example, in 2018, the MyEtherWallet phishing attack targeted users by redirecting them to a malicious website that resembled the legitimate MyEtherWallet interface.
 Image via Shutterstock
Image via ShutterstockPro Tip: I have personally witnessed this more times than I care to count. When reaching out for help or asking questions in communities like Reddit, Telegram, or Discord, beware of direct messages from people reaching out pretending to work for the support team of the product or platform you are inquiring about. A VERY common scam is for people to pretend to work for customer support. They will tell you they need information like passwords, private keys, or recovery phrases to help you out. This will be a scam 100% of the time, never give that information away. I provide more examples of this in our article on Crypto Safety.
Pump and Dump Schemes
Okay, so technically this one doesn’t really constitute as malware and some might not even consider this cybercrime, but it is still worth knowing about so you can watch out for it.
Pump and dump schemes involve artificially inflating the price of a cryptocurrency through misleading information or coordinated trading. The attackers typically accumulate a low-value cryptocurrency, spread positive rumors or news, and then sell their holdings when the price reaches a peak. This causes unsuspecting investors to suffer significant losses. While not technically a cybercrime, pump-and-dump schemes often rely on online platforms and social media manipulation to deceive investors. We cover these schemes and what to look out for in more detail in our dedicated Pump-and-Dump Article.
ICO Scams
ICO scams involve fraudulent projects that raise funds through an initial coin offering, promising investors high returns or innovative products that never materialize. These scams often lure investors with enticing whitepapers, fake teams, and misleading marketing tactics. In 2017, the infamous Centra Tech ICO scam defrauded investors of over $25 million by fabricating partnerships and promoting a non-existent debit card.
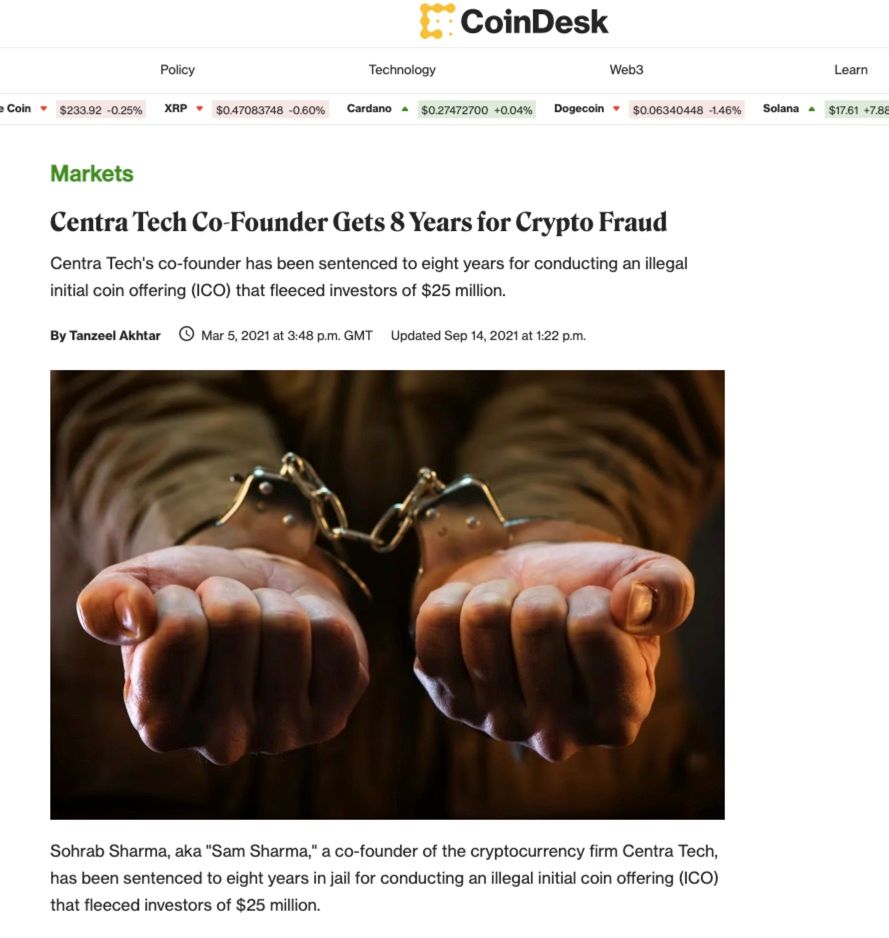 Image via CoinDesk
Image via CoinDeskSmart Contract Exploits
Smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements on blockchain platforms, can be vulnerable to coding flaws or vulnerabilities that allow attackers to exploit them. These exploits can result in the loss or theft of cryptocurrency funds locked within the smart contract. The largest smart contract exploit to date was the infamous Ronin Bridge hack built for the Axie Infinity Play to Earn Game.
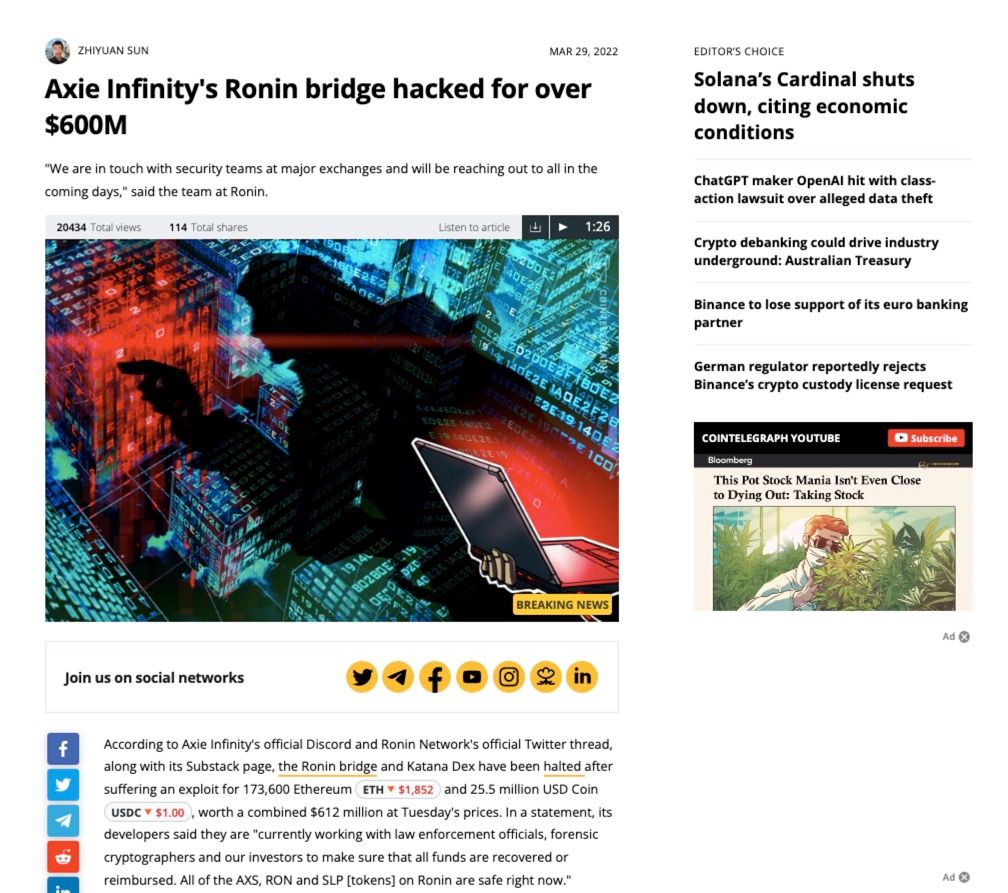 Image via CoinTelegraph
Image via CoinTelegraphOn March 23, 2022, the crypto community witnessed the biggest breach in crypto history involving the exploitation of the Ronin bridge, resulting in a staggering sum of approximately $612 million. This amount included 173,600 ETH and 25.5 million USD Coin (USDC).
Ronin serves as an Ethereum sidechain specifically designed for Axie Infinity, a popular nonfungible token (NFT) game centered around play-to-earn mechanics. The developers of Axie Infinity, known as Sky Mavis, revealed that the hackers managed to gain unauthorized access to private keys, compromise validator nodes, and execute approved transactions that ultimately siphoned off funds from the bridge.
Insider Attacks
Insider threats refer to attacks or data breaches caused by individuals within an organization who have authorized access to sensitive information or systems. Within the crypto industry, insider threats can occur in cryptocurrency exchanges or crypto wallet providers where employees abuse their access privileges or collude with external actors to steal funds or compromise user data. While specific publicized scenarios are limited, insider threats remain a concern due to the potential for significant financial losses and reputational damage.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks involve overwhelming a target system with a flood of requests or traffic, rendering it unavailable to users. Attackers often use a network of compromised computers (botnets) to execute these attacks. In September 2021, the Solana network experienced an incident where it fell victim to a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack. This malicious act targeted the Solana blockchain, resulting in network congestion and causing transactions to be unsuccessful.
Then in April 2022, a noteworthy distributed denial of service attack took place on a prominent cryptocurrency platform, standing out as one of the largest ever recorded. Bad actors inundated the platform with a staggering 15.3 million requests, severely disrupting its operations. That would not have been a good day for traders on the platform, that’s for sure.
 Image via Wired
Image via WiredEmail Spoofing
You know when you get an email from someone you think you know, but it turns out to be a scammer? That's email spoofing, and it's used for all kinds of bad stuff. That is why many crypto companies will now include an anti-phishing code in emails to verify authenticity and why they say you should never click links in emails, but rather navigate to the website to access your account the normal way. There are also tools you can use to scan a link before clicking it.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks (MitM)
Intercepting communication between two parties to eavesdrop, manipulate, or steal information. Let's say you're using a public Wi-Fi network in a coffee shop. A hacker who is also connected to the same network can secretly intercept your communication with the intended website or service. They can then capture your login credentials or other sensitive information by posing as a legitimate website or service, effectively gaining unauthorized access to your accounts or data. A way to protect yourself from this is to avoid personal websites on public networks and use a VPN.
SQL Injection and Zero-Day Exploits
SQL injection is a type of cyber attack where an attacker inserts malicious SQL code into a vulnerable application's database query. This allows the attacker to manipulate or retrieve unauthorized data, modify database content, or even execute arbitrary commands on the database server.
Zero-Day Exploits refer to vulnerabilities in software or systems that are unknown to the vendor or have not yet been patched. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to launch attacks before they can be identified or fixed, making them highly effective and difficult to defend against.
Keylogging & Clipboard Hijacking
❗This is a big one, so listen up❗
In a previous life, I worked as a support engineer for a major crypto company, investigating lost and stolen funds. I could not believe how many crypto users fell victim to Clipboard Hijacking. This subtle attack could happen to any of us if we aren’t careful.
A clipboard hijacker is a type of malware that intercepts and modifies the contents of a user's clipboard on their computer, typically in order to replace copied information with malicious or fraudulent data. By tampering with the clipboard, the hijacker aims to deceive users into pasting sensitive information, such as passwords or cryptocurrency addresses to unintended destinations controlled by the attacker.
The main way I have seen this used is that every time a customer copies and pastes a crypto-receiving address, the clipboard hijacker will replace the address with the attacker’s address, so you think you may be sending Bitcoin to your exchange or wallet as you copied your own address, but the hijacking software replaced your address with the hacker’s address. Sneaky stuff!
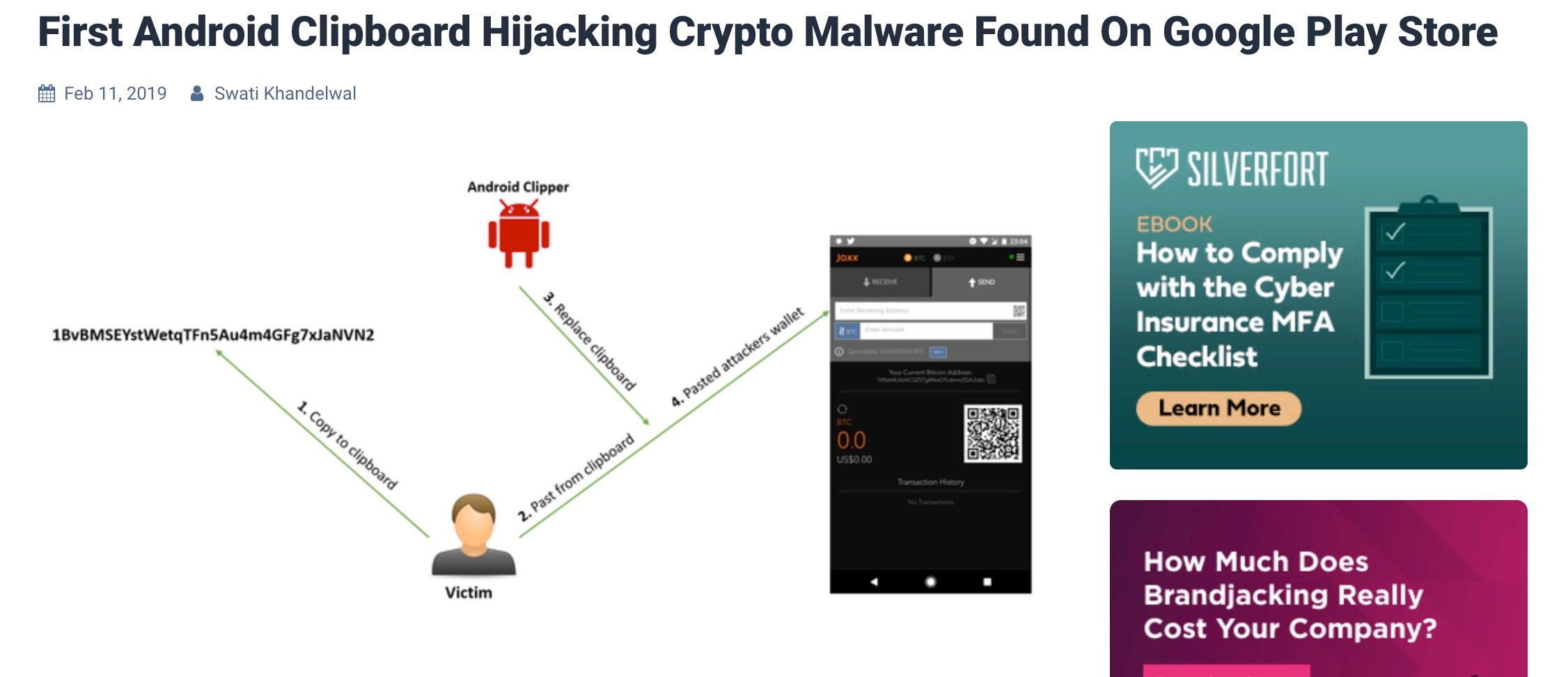 A Look At How Clipboard Hijackers Work. Image via Hackernews
A Look At How Clipboard Hijackers Work. Image via HackernewsKeylogging is a type of spyware that can record keystrokes on a compromised device to capture sensitive information such as passwords, recovery phrases, and credit card details.
This is why in our Crypto Safety article, we say that copy and paste should ALWAYS be used when sending crypto to ensure there are no typos, and even when copy/pasting ALWAYS double check the pasted address to ensure it is the right one. And in the same line of thought, a keylogger cannot read your recovery phrase if you never type it, which is why security experts will harp on never storing your recovery phrase in any digital format for a plethora of reasons.
The more you know… 🤓
Zero Value Transfers Scam
This one is frustrating as it mingles with users' personal wallet transactions. If hackers want to exploit a centralized platform I choose to trust, that’s one thing, but please have the decency to leave our self-custodial wallets alone! This is the digital equivalent of someone trying to rob the bank you use vs them breaking into your home and robbing you, making you feel personally victimised.
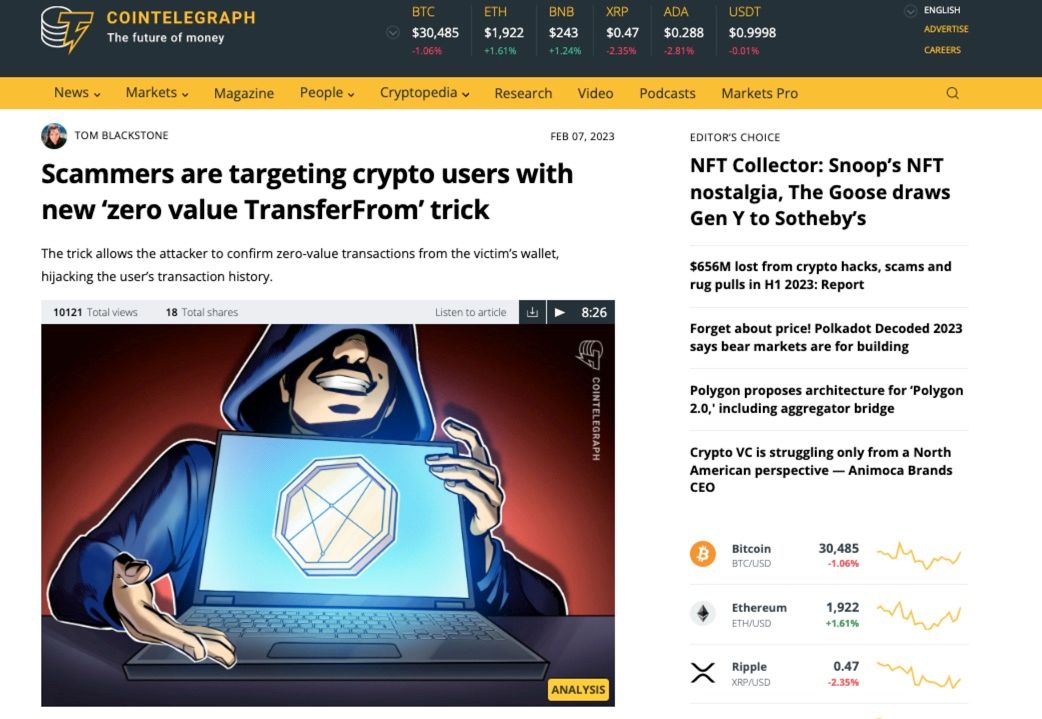 Image via CoinTelegraph
Image via CoinTelegraphCrypto scammers have unleashed a cunning new trick dubbed the "zero-value TransferFrom" to ensnare users and lure their tokens into the clutches of attackers. This is made possible by a loophole within specific token contracts, granting the malefactors the ability to execute transactions from any wallet without the need for a private key or the owner's green light.
By dispatching zero-value transactions to addresses strikingly similar to those previously used by victims, these swindlers lure the token sender with addresses that appear correct.
The crypto community has acted quickly on these attacks with countermeasures being deployed to curtail the menace. SafePal and Etherscan have implemented protective measures, while Trezor is set to flag dubious zero-value transactions in an upcoming software update, and Etherscan grays out unapproved zero-value token transactions and informs users through alerts.
You can do your part to protect yourself through the utilization of whitelist functionalities in wallets/exchanges and copy/pasting your address from the source, not transfer history, and of course, still double-checking them!
Wallet Woes
Even the security of crypto wallets, considered a stronghold for protecting investments, have been compromised. The Jaxx wallet experienced a security flaw in 2017 that allowed hackers to gain unauthorized access to user accounts, resulting in significant financial losses. In 2023, we also had the tragic Atomic Wallet hack, where users lost funds.
These stories are perhaps the most tragic of all as users believe they are taking the most important steps in crypto security by taking self-custody of their assets, and still getting burned. This would be like choosing to hide a gold bar in your home with a state-of-the-art security system in a hidden vault and coming home to find it empty. That is why it is critically important to use only the best crypto hardware wallets on the market.
These incidents underscore the constant vigilance required to stay one step ahead of hackers and reinforce the need for robust security practices.
To finish up the section with all the depressing information I have provided, and to depress you further, you may find the following sites interesting. This isn’t meant to turn you away, but education is key, and we need to learn from history to prevent repeating previous mistakes.
Here is an extensive timeline of exchange hacks: https://chainsec.io/exchange-hacks/
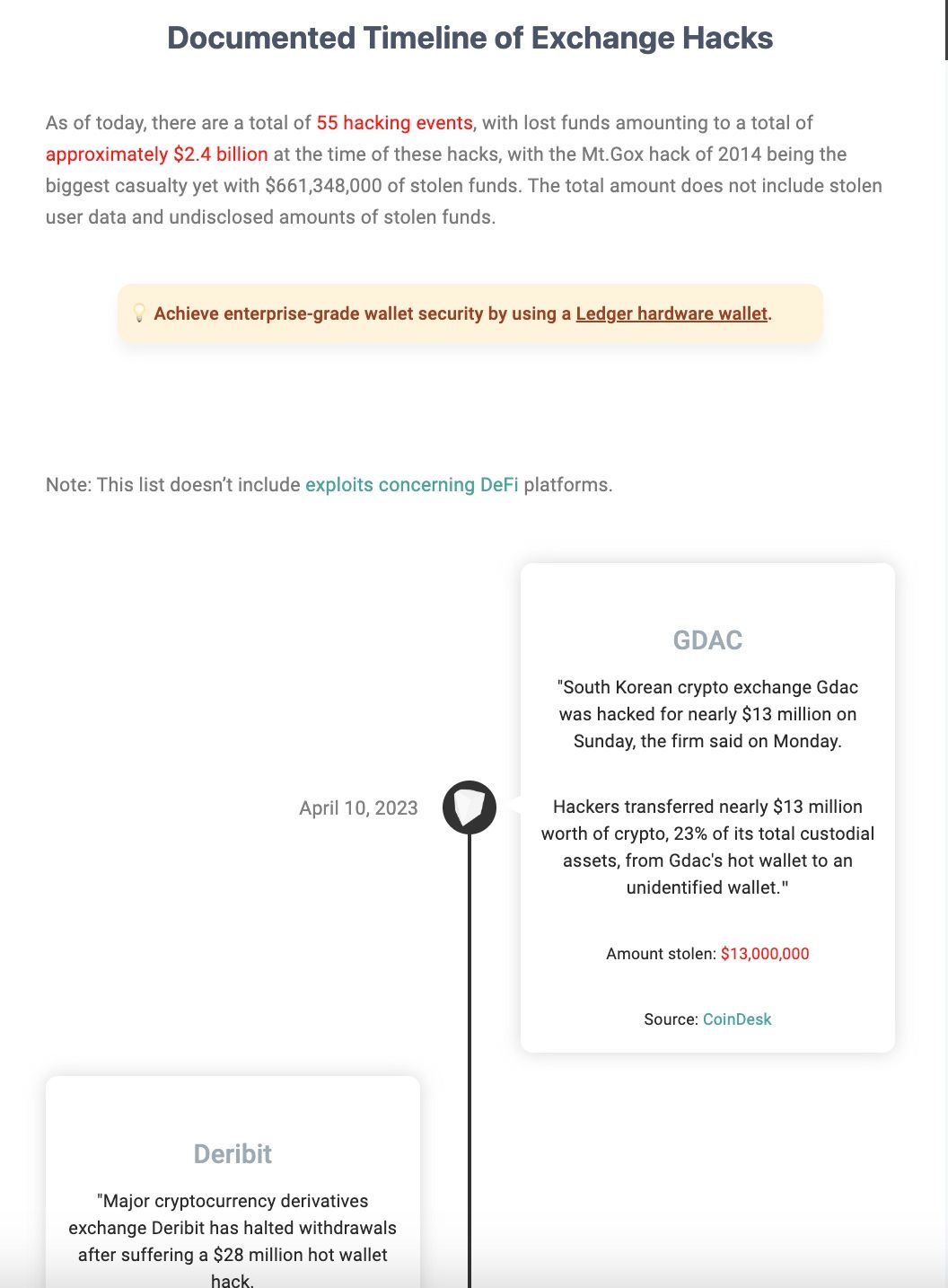 A Look at the Exchange Hacks Timeline. Image via Chainsec
A Look at the Exchange Hacks Timeline. Image via ChainsecAnd if you have a spare few hours to mindlessly scroll and want to see something even more unfortunate, here’s a timeline of DeFi hacks… The list goes on and on: https://chainsec.io/defi-hacks/
Effect on the Crypto Industry
Unfortunately, these incidents have damaged the reputation of our industry, leading to skepticism and reduced adoption among institutions, governments, and individuals.
Impact on Reputation and Trust
The concerns around cryptocurrency safety and reliability have prompted regulatory bodies like the Federal Reserve System and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency to issue warnings about the risks associated with crypto-assets and their sector participants. The cybersecurity dangers associated with cryptocurrencies make it challenging for institutions to assess the safety, financial stability, and consumer protection implications of crypto-related activities. The lack of regulation in the crypto market leaves investors with limited protections, making them vulnerable to cybercriminals targeting the rising values of cryptocurrencies. Therefore, ensuring regulatory compliance becomes essential for crypto platforms to enhance security measures and build trust among users.
Unfortunately, in light of all the hacks, scams, exploits, and bad actors in the crypto space, many institutions and agencies are hesitant to consider crypto assets as a legitimate investment or asset, and even lead to instances such as Elizabeth Warren’s Anti-Crypto army campaign, insults being slung at crypto investors from the likes of Warren Buffet and Peter Schiff, occurrences like Chokepoint 2.0, and even sophisticated investors being ridiculed as being “crypto bros.”
Impact on Adoption
The cybersecurity risks associated with cryptocurrency have posed challenges for institutions in evaluating the safety, financial stability, and implications for consumer protection in crypto-related activities. The lack of trust and clear regulation in the crypto market has left investors with limited safeguards.
These happenings have not only led to institutions and agencies not being on board but have also scared the common person away from adopting and exploring the multitude of benefits that cryptocurrency offers as trust is chipped away more and more as there seems to be another crypto exploit every other week.
Impact on Investors
All these different forms of blunders have had major negative impacts on investors, with many cases resulting in the loss of hundreds of millions of dollars in the cases of FTX and Celsius. Then there are DeFi hacks and attacks such as the Poly Network and Ronin that made mainstream headline news.
And hacks are only a portion of the cause behind the turbulence, there are also events such as death spirals, rug pulls, liquidity pump and dumps, impermanent loss and more that have resulted in investors losing considerable sums of money.
Regulatory Measures Addressing Crypto Security Concerns
The following are just some of the steps that are being taken by different industry participants to address security concerns. I am not advocating for or against the following, just highlighting some of the steps being taken.
Increased Scrutiny: Regulatory bodies across the globe have recognized the importance of addressing security concerns in the crypto industry. They have ramped up their efforts to monitor and regulate crypto-related activities to safeguard users' interests and maintain market integrity.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations: To mitigate the risks associated with illicit activities and money laundering, many jurisdictions have implemented KYC and AML regulations. These measures require crypto exchanges and other service providers to verify the identity of their customers and report suspicious transactions.
Data Protection and Privacy Regulations: Governments are focusing on strengthening data protection and privacy regulations to safeguard personal information and prevent data breaches. Compliance with these regulations helps in maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of user data in the crypto space.
Information Sharing and Collaboration: Industry players, including crypto exchanges, wallet providers, and cybersecurity firms, are increasingly collaborating to share information and insights on emerging threats. These collaborations enable proactive measures to be taken in countering cyber attacks and enhancing overall security.
Best Practice Standards: Various industry bodies and associations are developing best practice standards for crypto security, including things like publishing Proof of Reserves, undergoing regular audits, cutting off wallets attached to known exploiters, enhancing encryption protocols, secure key management, secure coding practices, and more.
Security Audits and Certifications: Crypto businesses are recognizing the importance of third-party security audits and certifications to demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high security standards. Independent audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry-accepted security practices.
Technology Advancements: The crypto industry is witnessing advancements in security technologies such as multi-signature wallets, hardware security modules, and secure enclave processors. These technological innovations aim to provide enhanced protection against hacking attempts and unauthorized access.

How to Stay Safe in Crypto
After everything discussed in this article, you may be thinking to yourself, “I don’t know, this crypto thing seems too risky.” And while I’m not going to say the risks are minimal, do remember that there are tens of millions of users who navigate crypto without any issues every day. Awareness of cryptocurrency security issues plays a vital role in enhancing overall crypto safety.
As long as you practice both good crypto and internet security hygiene, you can mitigate the majority of the risks. I won’t go into detail about the different ways to stay safe in crypto here, as we outline that in our robust Crypto Security Guide.
Along with best practices, you can further protect yourself by staying informed and remaining vigilant. Stay connected with the crypto community and keep an eye out for security alerts, news, and updates. Subscribe to reputable security blogs, follow industry experts on social media, and join relevant forums to stay informed about the latest security practices and potential threats. Being proactive and vigilant will help you adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of crypto security. Here are a couple of resources that can help you with that:
BleepingComputer: BleepingComputer is a well-known cybersecurity news and resource website, definitely one of my favourites. And look at that, even at the time of writing this, I just grabbed their link and see there are stories about ongoing ransomware attacks. 🙄
While they cover a broad range of cybersecurity topics, they also report on crypto-related exploits and attacks.
Cyware: Cyware is a cybersecurity platform that offers real-time threat intelligence and analysis. They cover a variety of cyber threats, including those targeting the crypto industry. Their platform offers free and paid tools that can provide updates on the latest cyber attacks, data breaches, and ransomware incidents.
De.Fi: Then finally, one of my favourite tools and a must-have for anyone into DeFi is the appropriately named De.Fi application. This is one of the most powerful free tools I’ve come across, being branded as a “Web3 Super App & Antivirus”. This tool allows users to assess the risk exposure of their crypto wallet/portfolio and scan tokens, DeFi protocols, Smart-Contracts, peruse security audits, and more.
 Image via De.Fi
Image via De.FiThe platform features the largest database of blockchain security audits and offers a shield plus scanner function where you can enter any token or smart contract address and it will scan the token based on over 30 metrics and give you a breakdown of the legitimacy and safety of the token. Personally, I don’t interact with a new token or DeFi protocol without running it through De.Fi first.
Closing Thoughts
As the crypto space continues to evolve and attract more participants, the importance of security becomes ever more important. The rising concerns about ransomware and cybercrime highlight the need for proactive measures to safeguard cryptocurrencies and protect not only users' investments but the very trust, reputation and credibility of our entire industry. Addressing cryptocurrency security issues is fundamental to ensuring the safety and resilience of the crypto space. By adopting robust security practices and staying informed, users can navigate the crypto world more securely
I am not naive enough to suggest that we will fully overcome and eliminate bad actors in the space. Every aspect of our lives have been targeted by bad actors with malicious intent since the beginning of time, from being intentionally overcharged by the cafe down the street and our local car mechanic to slimy salespeople and bribery in politics. Not to mention that the very internet itself to this day is rife with scams and cybercrime. So no, I am afraid we will likely never eliminate cybercrime in crypto, in the same way that we will never eradicate real-world crime. Just as it is in real life, crime vs protection/justice is always a game of cat and mouse.
But what we do need in crypto is to mitigate the frequency and severity of these attacks. Fortunately, there is real progress being made in the space, but if we ever want to see crypto reach mainstream adoption and fulfil its full potential, we need to remain one close step behind the attackers (as we will never get a step ahead, criminals will always find ways to strike first) but we need to catch up as we are not currently a close step behind, but I would say miles back...But we are gaining ground and catching up, fast.





